Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Differential and Linear Cryptanalysis
Differential and Linear Cryptanalysis
Uploaded by
santhosh kumar B J100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
124 views3 pagesDifferential cryptanalysis is a general form of cryptanalysis applicable to block ciphers, stream ciphers, and cryptographic hash functions. It studies how small differences in input can affect larger differences in output. Differential cryptanalysis analyzes how differences propagate through the cipher to gain information about the secret key. It is one of the most common attacks against block ciphers, along with linear cryptanalysis.
Original Description:
Original Title
Differential and linear cryptanalysis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDifferential cryptanalysis is a general form of cryptanalysis applicable to block ciphers, stream ciphers, and cryptographic hash functions. It studies how small differences in input can affect larger differences in output. Differential cryptanalysis analyzes how differences propagate through the cipher to gain information about the secret key. It is one of the most common attacks against block ciphers, along with linear cryptanalysis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
124 views3 pagesDifferential and Linear Cryptanalysis
Differential and Linear Cryptanalysis
Uploaded by
santhosh kumar B JDifferential cryptanalysis is a general form of cryptanalysis applicable to block ciphers, stream ciphers, and cryptographic hash functions. It studies how small differences in input can affect larger differences in output. Differential cryptanalysis analyzes how differences propagate through the cipher to gain information about the secret key. It is one of the most common attacks against block ciphers, along with linear cryptanalysis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Differential cryptanalysis is
a general form of cryptanalysis
applicable primarily to block ciphers, but also to stream
ciphers and cryptographic hash functions. In the broadest
sense, it is the study of how differences in information input
can affect the resultant difference at the output.
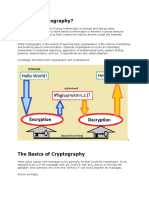
Cryptanalysis is the process of transforming or decoding communications
from non-readable to readable format without having access to the real key.
OR we may say it is the technique of retrieving the plain text of the
communication without having access to the key. Cryptoanalysis is the art,
science, or practice of decrypting encrypted messages. The secret key used
for encryption and decoding is considered to be unknown to the
cryptologists, mathematicians, and other scientists participating in the
process. In contrast to a brute force attack, this form of analysis seeks
vulnerabilities in a cryptosystem.
Cryptanalysis frequently comprises a direct evaluation of the cryptosystem in
use, which is essentially an advanced concentrated mathematical attempt at
decryption utilizing knowledge about the encryption scheme that is already
available. They can employ intercepted encrypted messages (ciphertext),
intercepted complete, partial, likely, or similar original messages (plaintext),
or information (encrypted or original) that is known to be used adaptively in
subsequent trials.
Process of cryptanalysis
Different Forms of Cryptanalysis:
Cryptanalysis basically has two forms:
1. Linear Cryptanalysis:
Linear cryptanalysis is a general type of cryptanalysis based on discovering
affine approximations to a cipher’s action in cryptography. Block and stream
ciphers have both been subjected to attacks. Linear cryptanalysis is one of
the two most common attacks against block ciphers, with differential
cryptanalysis being the other.
2. Differential Cryptanalysis:
Differential cryptanalysis is a sort of cryptanalysis that may be used to
decrypt both block and stream ciphers, as well as cryptographic hash
functions. In the widest sense, it is the study of how alterations in information
intake might impact the following difference at the output. In the context of a
block cipher, it refers to a collection of strategies for tracking differences
across a network of transformations, finding where the cipher displays non-
random behaviour, and using such attributes to recover the secret key
(cryptography key)
Difference between Linear Cryptanalysis and Differential Cryptanalysis
S.
No. Linear Cryptanalysis Differential Cryptanalysis
Linear cryptanalysis was basically Differential cryptanalysis was first
invented by Matsui and Yamagishi in defined in the year 1990 by Eli Biham
1. the year 1992. and Adi Shamir.
Linear cryptanalysis always works on Differential cryptanalysis can work on
2. a single bit (one bit at a time). multiple bits at a time.
In the case of Linear cryptanalysis, In the case of differential cryptanalysis
ciphertext attack is a very big plain text attack is a very big
3. disadvantage. disadvantage.
The use of linear cryptanalysis is to
figure out what is the linear The use of differential cryptanalysis is
relationship present between some to get clues about some critical bits,
plaintext bits, ciphertext bits, and reducing the need for an extensive
4. unknown key bits very easily. search.
S.
No. Linear Cryptanalysis Differential Cryptanalysis
The underlying structure of each
individual input is unimportant in this
Subsets of input attributes refer to the case since the input attributes are
5. internal structures of a single input. differential.
The cryptanalyst decrypts each After several encryption rounds,
ciphertext using all available subkeys Cryptanalyst analyses the changes in
and analyses the resultant the intermediate ciphertext obtained.
intermediate ciphertext to determine The practice of combining assaults is
the random outcome for one known as differential linear
6. encryption cycle. cryptanalysis.
Any random plaintext is selected in Plaintext is Carefully chosen in
7. Linear Cryptanalysis. Differential Cryptanalysis.
Plaintext is used one by one in linear Plaintext is used in pairs in Differential
8. Cryptanalysis. Cryptanalysis.
Complexity of attack is low in linear Complexity of attack is High in
9. Cryptanalysis. Differential Cryptanalysis
Mathematical relation between
plaintexts used has Linear Mathematical relation between
approximation (such as a series of plaintexts used has Specific
10. XOR operations). differences (such as XOR).
Goal of the attack is to identify the
linear relation between some bits of
the plaintext, some bits of the cipher
text and some bits of the unknown Goal of the attack is to Identify some
11. key. bits of the unknown key.
You might also like
- Ins510 Group Project ReportDocument17 pagesIns510 Group Project Reportradia amalin99No ratings yet
- Hiradc Merentang KabelDocument3 pagesHiradc Merentang KabeladelenaNo ratings yet
- CryptanalysisDocument13 pagesCryptanalysisRahmatullah MehrabiNo ratings yet
- Is PTSSSS: AxssanboyDocument3 pagesIs PTSSSS: AxssanboyCabdi Fitaax KulmiyeNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Stream Ciphers and RC4Document19 pagesLecture Notes On Stream Ciphers and RC4my storiesNo ratings yet
- Computer Security AsDocument4 pagesComputer Security AsHagos gebreslasieNo ratings yet
- Cryptanalysis and Types of AttacksDocument3 pagesCryptanalysis and Types of AttacksSourav DebnathNo ratings yet
- Cryptanalysis of Mono-Alphabetic Substitution Ciphers Using Genetic Algorithms and Simulated AnnealingDocument5 pagesCryptanalysis of Mono-Alphabetic Substitution Ciphers Using Genetic Algorithms and Simulated AnnealingTân HoàngNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document47 pagesUnit 3Andualem BegunoNo ratings yet
- CB3491-CCS 2marksDocument12 pagesCB3491-CCS 2markssmitcse2021No ratings yet
- Symmetric Ciphers: Data Encryption & Security (CEN-451) Spring 2020, BUKCDocument26 pagesSymmetric Ciphers: Data Encryption & Security (CEN-451) Spring 2020, BUKCMuhammad RehanNo ratings yet
- 4 Cry PaDocument28 pages4 Cry PaVenkata AppajiNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Shibani Sarangi IT Branch, Regd No. 1001289324 Guided By: Prof. XDocument22 pagesPresented By: Shibani Sarangi IT Branch, Regd No. 1001289324 Guided By: Prof. XChandra ShekarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CryptographyDocument20 pagesIntroduction To CryptographyAkshay GautamNo ratings yet
- CS8792-CNS - 2marksDocument13 pagesCS8792-CNS - 2markssmitcse2021No ratings yet
- What Is Cryptography?: Cryptography Is The Science of Using Mathematics To Encrypt and Decrypt DataDocument10 pagesWhat Is Cryptography?: Cryptography Is The Science of Using Mathematics To Encrypt and Decrypt Datadivya6990No ratings yet
- Tut 4Document3 pagesTut 4Bibek ShresthaNo ratings yet
- CryptographyDocument23 pagesCryptographyAnubhav KumarNo ratings yet
- Military College of Signals, NUSTDocument75 pagesMilitary College of Signals, NUSTWaqas KhanNo ratings yet
- Classical Encryption CipherDocument164 pagesClassical Encryption CipherShahriarNo ratings yet
- 02 Symmetric CiphersDocument73 pages02 Symmetric CiphersGeorgeStenNo ratings yet
- Seminar SkiDocument11 pagesSeminar SkiSarabitrovicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document91 pagesChapter 2Destaye Sole WonideNo ratings yet
- Cryptography Course WorkDocument27 pagesCryptography Course WorkSovan PalNo ratings yet
- IAS Chapter TwoDocument80 pagesIAS Chapter TwodigafeeyuelNo ratings yet
- 2 CryptographyDocument71 pages2 CryptographyDhairya ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Network Security Two Marks Unit-1 Network Security 1. Specify The Four Categories of Security Threads?Document11 pagesCryptography and Network Security Two Marks Unit-1 Network Security 1. Specify The Four Categories of Security Threads?PiriyangaNo ratings yet
- QB PDFDocument16 pagesQB PDFsadhana mmNo ratings yet
- Lec4 Software SecurityDocument9 pagesLec4 Software SecuritySemsem SameerNo ratings yet
- Tokareva NDocument54 pagesTokareva NveeramNo ratings yet
- Lecture Number 1Document20 pagesLecture Number 1AnAs FFNo ratings yet
- CryptographyDocument7 pagesCryptographyHaile MelakuNo ratings yet
- Symmetric Cipher ModelDocument17 pagesSymmetric Cipher ModelAsif KoujaganurNo ratings yet
- New Security Lectures FinallyDocument87 pagesNew Security Lectures Finallyطيبه محمد احمد حمد هندسة تقنيات الحاسوبNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two - Fundamentals of CryptographyDocument107 pagesChapter Two - Fundamentals of CryptographyJONAS J JONASNo ratings yet
- Crypto IntroductionDocument26 pagesCrypto Introductionunknown studentNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document33 pagesLecture 2Jasleen VirdiNo ratings yet
- Cryptography & Network SecurityDocument25 pagesCryptography & Network Securityrrs_1988No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 IAS)Document41 pagesChapter 2 IAS)Abduu MizaabNo ratings yet
- CryptographyDocument37 pagesCryptographySamir JhaNo ratings yet
- CRYPTO Mod1@AzDOCUMENTS - inDocument24 pagesCRYPTO Mod1@AzDOCUMENTS - insasindhur rNo ratings yet
- Course 2.1Document2 pagesCourse 2.1Thailand EliteVisaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 CryptanalysisDocument14 pagesUnit 3 Cryptanalysisvladsado-ipt25No ratings yet
- Q. Applications of All Ciphers Studied Till NowDocument3 pagesQ. Applications of All Ciphers Studied Till NowAnkita PatilNo ratings yet
- Part ADocument14 pagesPart AHANISHA SAALIHNo ratings yet
- CNS ImpDocument9 pagesCNS Impwhen.urja.writesNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Highlights - Cryptographic ToolsDocument5 pagesTopic 2 Highlights - Cryptographic ToolsOlivia RadaNo ratings yet
- Modul1-Cryptanalysis, Classical Encryp TechDocument15 pagesModul1-Cryptanalysis, Classical Encryp TechAtharv DarekarNo ratings yet
- DR Waseem PaperDocument21 pagesDR Waseem PaperAsadullah Tariq TariqNo ratings yet
- 3 - Block Ciphers and The Data Encryption StandardDocument32 pages3 - Block Ciphers and The Data Encryption StandardDaneil RadcliffeNo ratings yet
- Computer Security Chapter 2-3-4-1Document72 pagesComputer Security Chapter 2-3-4-1guta lamessaNo ratings yet
- Network Design and Security ManagementDocument52 pagesNetwork Design and Security ManagementmehraDpaNo ratings yet
- EncryptionDocument115 pagesEncryptionrajashekarpula100% (4)
- U21CS601 CT Unit 123 Part B QADocument13 pagesU21CS601 CT Unit 123 Part B QASanthosh kannaNo ratings yet
- Csci 360 Exam 1 Review PDFDocument1 pageCsci 360 Exam 1 Review PDF2fz4np5b5xNo ratings yet
- Cryptography Using Automata TheoryDocument8 pagesCryptography Using Automata TheoryAbdullah AlahdalNo ratings yet
- Vol1. No2Document133 pagesVol1. No2IJCNSNo ratings yet
- The Stone Cipher-192 (SC-192) : A Metamorphic Cipher: Magdy SaebDocument7 pagesThe Stone Cipher-192 (SC-192) : A Metamorphic Cipher: Magdy Saebzios1977No ratings yet
- DNS PP Short QuestionDocument13 pagesDNS PP Short Question13 Samia farnazNo ratings yet
- 2 Mark Questions Answers PDFDocument12 pages2 Mark Questions Answers PDFdurai muruganNo ratings yet
- Cryptography And Computer Science: Design Manual For Algorithms, Codes And CiphersFrom EverandCryptography And Computer Science: Design Manual For Algorithms, Codes And CiphersNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument16 pagesSyllabussanthosh kumar B JNo ratings yet
- What Is IndexingDocument4 pagesWhat Is Indexingsanthosh kumar B JNo ratings yet
- Selectors in CSS ID ClassDocument2 pagesSelectors in CSS ID Classsanthosh kumar B JNo ratings yet
- Noframes Audio Video TagDocument1 pageNoframes Audio Video Tagsanthosh kumar B JNo ratings yet
- Noisy and Noiseless ChannelDocument1 pageNoisy and Noiseless Channelsanthosh kumar B JNo ratings yet
- Linux System Administration Question Bank Tyit Linux System Administration Question Bank Unit 1Document4 pagesLinux System Administration Question Bank Tyit Linux System Administration Question Bank Unit 1santhosh kumar B JNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Literature Review: Parts of A Research PaperDocument7 pagesHow To Write A Literature Review: Parts of A Research Papersanthosh kumar B JNo ratings yet
- 2 (V.v.imp) Security Goals or Key Principles of SecurityDocument18 pages2 (V.v.imp) Security Goals or Key Principles of Securityckoparkar123No ratings yet
- fm3 09Document272 pagesfm3 09Mark Cheney100% (1)
- 03 Data Breach PreventionDocument3 pages03 Data Breach PreventionambonulanNo ratings yet
- NIS IMP QuestionsDocument4 pagesNIS IMP QuestionsAbhijit chavanNo ratings yet
- QP16 Network SecurityDocument2 pagesQP16 Network SecurityreshmapdscemailboxNo ratings yet
- A Study On Challenges of Indian Hospitality Industry and Remedies For Sustainability in The Ever Changing Market ScenarioDocument16 pagesA Study On Challenges of Indian Hospitality Industry and Remedies For Sustainability in The Ever Changing Market Scenariodinu_eshu100% (1)
- Vloluntary Principles On Security Human RightsDocument12 pagesVloluntary Principles On Security Human RightsUrvashi JhaNo ratings yet
- CBP SecurityHandbookDocument1,280 pagesCBP SecurityHandbookAshley Winchester100% (2)
- Mercado Livre Brasil Scorecard 1Document1 pageMercado Livre Brasil Scorecard 1DanielNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Cryptography: Encryption and DecryptionDocument5 pagesThe Basics of Cryptography: Encryption and DecryptionAngelyn BlanquiscoNo ratings yet
- ISO27k Controls Cross Check 2013Document11 pagesISO27k Controls Cross Check 2013kblocatNo ratings yet
- CH4 CNSDocument29 pagesCH4 CNSSARDAR PATELNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document75 pagesChapter 6Ahmed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Dudley Et Al. - 2016 - Natural Solutions For Water Management of The Future Freshwater Protected Areas at The 6th World Parks CongressDocument12 pagesDudley Et Al. - 2016 - Natural Solutions For Water Management of The Future Freshwater Protected Areas at The 6th World Parks CongressImanol O'ConnorNo ratings yet
- Wiley - Information Security - Principles and Practice, 2nd Edition - 978-0-470-62639-9Document3 pagesWiley - Information Security - Principles and Practice, 2nd Edition - 978-0-470-62639-9PrithviRaj GadgiNo ratings yet
- The ProtonMail Guide To IT SecurityDocument59 pagesThe ProtonMail Guide To IT SecurityNaing WinNo ratings yet
- 25 Great But Little-Known Cybersecurity FrameworksDocument2 pages25 Great But Little-Known Cybersecurity Frameworkssecurity.researcherNo ratings yet
- Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP)Document5 pagesDisaster Recovery Plan (DRP)Md Ali AbbasNo ratings yet
- 4 Security Maturity Monitoring: A. PurposeDocument4 pages4 Security Maturity Monitoring: A. PurposeRakesh Ricki RadharamanNo ratings yet
- Animated Scrolling Dashboard PPT by Gemo EditsDocument15 pagesAnimated Scrolling Dashboard PPT by Gemo Editsnsikakabasi OkonNo ratings yet
- Strategic Planning-IsoDocument11 pagesStrategic Planning-Isobitature timothyNo ratings yet
- Leidos Inc. Nuclear Weapons Work For US Military and DOEDocument5 pagesLeidos Inc. Nuclear Weapons Work For US Military and DOEdarwinbondgrahamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document97 pagesChapter 12Ayrton WidiutomoNo ratings yet
- 2021 Registered Insurance Agents As at 15th February 2021 CompressedDocument164 pages2021 Registered Insurance Agents As at 15th February 2021 CompressedericmNo ratings yet
- 4 September 1445 - Sharuddin Bin Mohd Noor - Malaysian CBRN Detect & DeconDocument35 pages4 September 1445 - Sharuddin Bin Mohd Noor - Malaysian CBRN Detect & DeconMohd Zulhairi Mohd NoorNo ratings yet
- Latihan HiradcDocument17 pagesLatihan HiradcArya Fahrul tamaNo ratings yet
- Soviet Military Order of Battle MD: Talent KeyholeDocument8 pagesSoviet Military Order of Battle MD: Talent KeyholeНикитаNo ratings yet
- Network Security: Solutions To Review Questions and ExercisesDocument8 pagesNetwork Security: Solutions To Review Questions and ExercisesXafran KhanNo ratings yet