Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sugestão Formulario MAP 1 - Aeroelasticidade
Sugestão Formulario MAP 1 - Aeroelasticidade
Uploaded by
MartimAlentejoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sugestão Formulario MAP 1 - Aeroelasticidade
Sugestão Formulario MAP 1 - Aeroelasticidade
Uploaded by
MartimAlentejoCopyright:
Available Formats
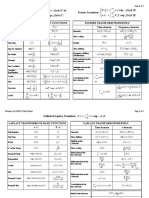
Formula Sheet - Aeroelasticity - Assessment 1
Euler-Lagrange Energy Equations Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Dissipation Work
d ∂T ∂T ∂F ∂U ∂(𝛿W) 1 1 1 ∂(𝛿W)
- + + = T= mv 2 + I𝜔 2 U= k𝛥x 2 + K𝛥𝜃 2 F = c𝛥␒x 2 =f
dt ∂x␒ i ∂xi ∂x␒ i ∂xi ∂(𝛿xi ) 2 2 2 ∂(𝛿x)
SDoF Systems ⟹ mx␒␒ + cx␒ + kx = f(t)
Free Vibration f=0
x(t) = Xe 𝜆t 𝜆1,2 = - 𝜉𝜔n ± i𝜔d c
⟹ -𝜉𝜔 t wn = k/m wd = 𝜔n 1 - 𝜉2 𝜉=
mx␒␒ + cx␒ + kx = 0 x(t) = Ae n sin(𝜔d t + 𝜓) 2m𝜔n
Forced Vibration f = F sin(𝜔t) (harmonic excitation case) (𝜉 = 1 : critical )
x(t) = X sin(𝜔t - 𝜙), 𝜙 ≡ phase lag
i𝜔t i(𝜔t-𝜙) i𝜔t
mx␒␒ + cx␒ + kx = f(t) ⇔ -𝜔 2 m + i𝜔c + k Xe i𝜔t = Fe i𝜔t
f(t) = Fe , x(t) = Xe = Xe
X k Vel. FRF
F HD (𝜔) = ⇔ HD = HV = i𝜔HD
𝜔c F 𝜔 2 𝜔
X= 𝜙 = tan 1- + i · 2𝜉
𝜔n 𝜔n Acc. FRF
k - 𝜔2m
2
+ (𝜔c) 2 k - 𝜔2m
kHD ≡ dynamic magnification HA = - 𝜔HD
Hysteric Damping: k * = k(1 + ig) g ≡ structural damping / loss factor gk g 𝜔n 1
ceq = 𝜉eq = HD =
mx␒␒ + k(1 + ig)x = f(t) Single frequency: mx␒␒ + ceq x␒ + kx = f(t) 𝜔 2 𝜔 k - 𝜔2m
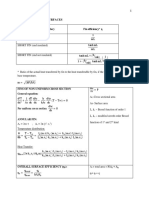
*
(Step Response Function - SRF) (Impulse Response Function - IRF)
-𝜉𝜔n t F
F e 𝜔d 1 - 𝜉2 x(t) = e -𝜉𝜔n t sin(𝜔d t)
x(t) = ⋅ 1- sin(𝜔d t + 𝜓) tan 𝜓 = = ⇔ cos 𝜓 = 𝜉 m𝜔d
k 1 - 𝜉2 𝜉𝜔n 𝜉
Amplitude Decrement Peak Time Max.Response (SRF)
Ai 𝜋 𝜉𝜋
1 |x(t)| 2𝜋 𝛿 tp = xk
-
𝛿 = ln = e𝛿 ⟹ 𝛿 = ⟹𝜉= = 1+e 1 - 𝜉2
n Ai+n |x(t + T)| 2 2 2 𝜔n 1 - 𝜉2
1-𝜉 𝛿 + 4𝜋 F
nDoF Systems ⟹ Mx␒␒ + Cx␒ + Kx = f(t)
Free Vibration f = 0
Normal Modes Series Parallel
{ x }(t) = { X }sin(𝜔t) Undamped Natural Freq.
-1 keq = k1 + k2
keq = (1 / k1 + 1 / k2 )
Mx␒␒ + Cx␒ + Kx = 0 det K - 𝜔 2 M =0 K - 𝜔j2 M { Xj } = 0
ceq = c1 + c2 ceq = (1 / c1 + 1 / c2 ) -1
(Proportional Dampening ⟹ 𝜔j equal to undamped natural frequency)
Forced Vibration f = F sin(𝜔t) (harmonic excitation case)
Modal Matrix Modal Coordinates FRF
T T -1
Φ = { X1 } | ... | { X2 } Mq = Φ M Φ fq = Φ f H(𝜔) = K + i𝜔 C - 𝜔 2 M
{x} = Φ {q} Kq = Φ T K Φ Cq = Φ T C Φ
-1 -1
Modal Coord. { q } = -𝜔 2 M q + i𝜔C q + K q Φ T f e i𝜔t Physical Coord. { x } = -𝜔 2 M + i𝜔C + K f e i𝜔t
(Mq and Kq diagonal. If damping is proportional: Cq diagonal and ⟹ m␒␒qj + cq␒ j + kqj = fqj (t) )
(SDoF expressions can be used to compute responses in modal coordinates - the equations are uncoupled)
Rayleigh-Ritz Method (Assumed Shapes)
One-Dimensional Systems z(y, t) = ∑ 𝜓j (y)qj (t) , 𝜓j ≡ j th assumed shape, qj ≡ j th generalized coordinate
Two-Dimensional Systems Either a function of two dim. or the product of functions of coordinates (x) & (y)
2 2
1 s 2 1 s 1 ∂ 2 zSC 1 ∂𝜃
Kinetic Energy: T = ∫ 𝜇z␒ CM dy + ∫ 𝜒𝜃␒ 2 dy Potential Energy: U = ∫EI 2
dy + ∫GJ dy
2 0 2 0 2 ∂y 2 ∂y
You might also like
- 13 - 2D Model Monoatomic Lattice N-N-NDocument39 pages13 - 2D Model Monoatomic Lattice N-N-Narslan virkNo ratings yet
- Awp Lab 2Document13 pagesAwp Lab 2Bisma pari MemonNo ratings yet
- EE 261 The Fourier Transform and Its Applications Fall 2006 Midterm Exam SolutionsDocument12 pagesEE 261 The Fourier Transform and Its Applications Fall 2006 Midterm Exam SolutionsManas ChetryNo ratings yet
- Homework #18 (Phy 112) SolutionsDocument20 pagesHomework #18 (Phy 112) SolutionsKvn4N6No ratings yet
- Lec13 PDFDocument7 pagesLec13 PDFanilNo ratings yet
- Lect 7Document29 pagesLect 7Hermain KarimNo ratings yet
- Single-Degree-of-Freedom (Single DOF) Linear SystemDocument14 pagesSingle-Degree-of-Freedom (Single DOF) Linear SystemWintWintKhineNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 TPDEDocument62 pagesUnit 4 TPDEanirudh3369No ratings yet
- Lect 9Document25 pagesLect 9Hermain KarimNo ratings yet
- HW3 SolutionDocument4 pagesHW3 SolutionThienPhuc TranNo ratings yet
- Midterm Review PDFDocument16 pagesMidterm Review PDFMt RushNo ratings yet
- Formulas (EXAM)Document3 pagesFormulas (EXAM)Thanh Dat NguyenNo ratings yet
- Boddeker's PHY132 Lecture14Document4 pagesBoddeker's PHY132 Lecture14bitconcepts9781No ratings yet
- Module 1 - DC PrintDocument21 pagesModule 1 - DC Printunknown MeNo ratings yet
- Applictions of FT by RajuDocument3 pagesApplictions of FT by Rajuputta rajesh007No ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing L03 FourierDocument59 pagesDigital Signal Processing L03 FouriertortomatoNo ratings yet
- Digital Communications: Chapter 2: Deterministic and Random Signal AnalysisDocument106 pagesDigital Communications: Chapter 2: Deterministic and Random Signal AnalysisMUCKRAKERNo ratings yet
- Homework 10Document5 pagesHomework 10Khalil UllahNo ratings yet
- Formulas (QUIZ)Document2 pagesFormulas (QUIZ)Thanh Dat NguyenNo ratings yet
- ELEN3012 - 2020 Part 2Document7 pagesELEN3012 - 2020 Part 2Bongani MofokengNo ratings yet
- Vibrations and WavesDocument125 pagesVibrations and WavesGika NurdianaNo ratings yet
- °1996 by Andrew E. YagleDocument26 pages°1996 by Andrew E. Yaglesiva123456987No ratings yet
- Slides STFTMoodleDocument7 pagesSlides STFTMoodleRui RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Cs3491 - Aiml - Unit III - Gradient DescentDocument12 pagesCs3491 - Aiml - Unit III - Gradient DescentSobanNo ratings yet
- Applications and Review of Fourier Transform/Series: Solving Linear Partial Differential Equations (PDE's)Document9 pagesApplications and Review of Fourier Transform/Series: Solving Linear Partial Differential Equations (PDE's)Mohit NehraNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer FormulasDocument14 pagesHeat Transfer FormulasOrient nursery and primary school kovilpattiNo ratings yet
- Frequency Domain Analysis of Dynamic Systems: Jos E C. GeromelDocument43 pagesFrequency Domain Analysis of Dynamic Systems: Jos E C. Geromelblister_xbladeNo ratings yet
- Communication EngineeringDocument58 pagesCommunication EngineeringMadhavan SamNo ratings yet
- ELEN3012 - 2020 Part 1Document6 pagesELEN3012 - 2020 Part 1Bongani MofokengNo ratings yet
- .1 Fourier Analysis For CT Signals and SystemsDocument2 pages.1 Fourier Analysis For CT Signals and SystemsYassine DjillaliNo ratings yet
- PowerSpectralDensity KISA PDFDocument9 pagesPowerSpectralDensity KISA PDFOmer EmhanNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii-1Document24 pagesUnit Ii-1dr.omprakash.itNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing - Sampling TheoryDocument56 pagesDigital Image Processing - Sampling TheoryLong Đặng HoàngNo ratings yet
- HW 5Document2 pagesHW 5Kuann CNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 - Convex FunctionDocument32 pagesChapter - 2 - Convex FunctionHong KimmengNo ratings yet
- Principles of Communication Systems-I - Unit 2 - Basic Tools For Communication, Fourier Series - Transform, Properties, Parsevals RelationDocument4 pagesPrinciples of Communication Systems-I - Unit 2 - Basic Tools For Communication, Fourier Series - Transform, Properties, Parsevals RelationbnatarajNo ratings yet
- 2019.04.10 L14 S&S Fourier Transform Convergence, PropertiesDocument18 pages2019.04.10 L14 S&S Fourier Transform Convergence, PropertiesbilalNo ratings yet
- Ee4501f18 HW 8Document4 pagesEe4501f18 HW 8al-muntheral-mairikiNo ratings yet
- DC11 Minimum Distance Sequence ReceiverDocument8 pagesDC11 Minimum Distance Sequence ReceiverMalkurthi SreekarNo ratings yet
- 04 ARIMA ModelsDocument45 pages04 ARIMA ModelsCristian MoretaNo ratings yet
- CF NotesDocument7 pagesCF NotesHồ Nghĩa PhươngNo ratings yet
- Transformada FourierDocument60 pagesTransformada FourierAlisson FigueiredoNo ratings yet
- Lattice DiagramDocument19 pagesLattice DiagramDDragos GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform, in 1D and in 2DDocument110 pagesFourier Transform, in 1D and in 2DMaram ShbairNo ratings yet
- T R F R T R: To Seismology Exercise 2Document1 pageT R F R T R: To Seismology Exercise 2UdhamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Fourier Optics: D D y X J F y X F FDocument14 pagesChapter 4 Fourier Optics: D D y X J F y X F FansarixxxNo ratings yet
- Appendix FourierDocument5 pagesAppendix FourierSupriya DuttaNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesFourier Transform Cheat Sheetalbert60467% (3)
- Probability Theory Notes Chapter 2 VaradhanDocument20 pagesProbability Theory Notes Chapter 2 VaradhanJimmyNo ratings yet
- Best Ignored: Force Constant "K"Document3 pagesBest Ignored: Force Constant "K"Tuan TranNo ratings yet
- Lect 8Document26 pagesLect 8Hermain KarimNo ratings yet
- Balke Ma 1990Document10 pagesBalke Ma 1990Btari ArsytaNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument18 pagesReportKiran RavyNo ratings yet
- Slides Ch2 2Document30 pagesSlides Ch2 2rsmyrsmy14No ratings yet
- MIT2 71S14 Lec13 NotesDocument5 pagesMIT2 71S14 Lec13 Noteslolopopo28No ratings yet
- MIT2 71S14 Lec13 NotesDocument5 pagesMIT2 71S14 Lec13 Noteslolopopo28No ratings yet
- MIT2 71S14 Lec13 NotesDocument5 pagesMIT2 71S14 Lec13 Noteslolopopo28No ratings yet
- MIT2 71S14 Lec13 NotesDocument5 pagesMIT2 71S14 Lec13 Noteslolopopo28No ratings yet
- Wavelet Basics: Hennie Ter MorscheDocument26 pagesWavelet Basics: Hennie Ter MorscheNitasha SharmaNo ratings yet
- A Tutorial of The Wavelet Transform: Chun-Lin, Liu February 23, 2010Document72 pagesA Tutorial of The Wavelet Transform: Chun-Lin, Liu February 23, 2010Husam Al-AmeenNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- AcousticsDocument86 pagesAcousticsHemchandh RavellaNo ratings yet
- Lect4 Optical WaveguidesDocument93 pagesLect4 Optical WaveguidespratiharmukeshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Radio Propagation Large Scale EffectsDocument59 pagesChapter 3 Radio Propagation Large Scale EffectsAdisu WagawNo ratings yet
- Mec404 TH 226 2Document6 pagesMec404 TH 226 2commander91gamingNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibrations Lab ManualDocument22 pagesMechanical Vibrations Lab ManualTahir Hasan100% (1)
- g482 Mod 4 2 4 4 Stationary WavesDocument9 pagesg482 Mod 4 2 4 4 Stationary Wavesapi-236179294No ratings yet
- Syllabus - Engineering ElectromagneticsDocument1 pageSyllabus - Engineering ElectromagneticssrihariNo ratings yet
- MOSH-Chapter 10 Occupational VibrationDocument13 pagesMOSH-Chapter 10 Occupational Vibrationsiti zubaidahNo ratings yet
- Behaviour of Nonlinear SystemsDocument11 pagesBehaviour of Nonlinear SystemsCheenu SinghNo ratings yet
- Ports and Harbour 1Document2 pagesPorts and Harbour 1Hanz SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum: By: Nigmt FoundationDocument17 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum: By: Nigmt FoundationKhushi YadavNo ratings yet
- Combustion Characteristics and Flame Stability at The Microscale A CFD Study of Premixed Methane or Air MixturesDocument12 pagesCombustion Characteristics and Flame Stability at The Microscale A CFD Study of Premixed Methane or Air MixturesHERDI SUTANTONo ratings yet
- Q4 STEM General Physics 2 Week 6Document4 pagesQ4 STEM General Physics 2 Week 6Renz PerlasNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes Ch10 For Class 10thDocument14 pagesPhysics Notes Ch10 For Class 10thSafdar AliNo ratings yet
- Mechanism For Start of Oscillation and Stabilization of Amplitude - ClassleDocument2 pagesMechanism For Start of Oscillation and Stabilization of Amplitude - ClassleJoseph JohnNo ratings yet
- Assignment4 SolutionsDocument12 pagesAssignment4 SolutionsabaalharthiNo ratings yet
- Pptu-5 Oscillation 1Document19 pagesPptu-5 Oscillation 1Abraham DamtewNo ratings yet
- Waves NOTESDocument7 pagesWaves NOTESJames SergeantNo ratings yet
- Ppsb-Class X - Physics-Sound MCQDocument7 pagesPpsb-Class X - Physics-Sound MCQKrishna Agarwal [PRIMUS]No ratings yet
- Wave PropertiesDocument122 pagesWave PropertiesschlemielzNo ratings yet
- Chap01 Science Answer KeyDocument34 pagesChap01 Science Answer Keydearonalmeida12100% (4)
- Branislav Kisa Canin Eric K. Zhang Draft Version: 2011-2018 Solutions ManualDocument16 pagesBranislav Kisa Canin Eric K. Zhang Draft Version: 2011-2018 Solutions Manualbus9No ratings yet
- Unit Test Study Guide Waves Light and Sound2Document4 pagesUnit Test Study Guide Waves Light and Sound2JohnnyNo ratings yet
- 7E Lesson PlanDocument2 pages7E Lesson PlanMarie VicNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 OscillatorsDocument20 pagesUnit 3 Oscillatorsvimalaspl7831No ratings yet
- Wave FinalDocument22 pagesWave FinalDewan Olin Chotepadae0% (1)
- LAB 15 ThermometerDocument2 pagesLAB 15 ThermometerroseNo ratings yet