Professional Documents
Culture Documents
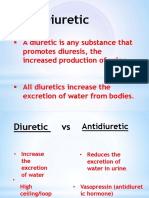
Diuretics
Diuretics
Uploaded by
Ma Cristina Miranda0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageDiuretics are a class of drugs that stimulate water excretion from the body. They are used to treat hypertension, edema, and reduce intracranial pressure. There are several classes of diuretics that act on different parts of the nephron including loop diuretics, thiazide diuretics, potassium-sparing diuretics, and osmotic diuretics. All diuretics can cause electrolyte imbalances like hypokalemia and hyponatremia as adverse effects.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDiuretics are a class of drugs that stimulate water excretion from the body. They are used to treat hypertension, edema, and reduce intracranial pressure. There are several classes of diuretics that act on different parts of the nephron including loop diuretics, thiazide diuretics, potassium-sparing diuretics, and osmotic diuretics. All diuretics can cause electrolyte imbalances like hypokalemia and hyponatremia as adverse effects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageDiuretics
Diuretics
Uploaded by
Ma Cristina MirandaDiuretics are a class of drugs that stimulate water excretion from the body. They are used to treat hypertension, edema, and reduce intracranial pressure. There are several classes of diuretics that act on different parts of the nephron including loop diuretics, thiazide diuretics, potassium-sparing diuretics, and osmotic diuretics. All diuretics can cause electrolyte imbalances like hypokalemia and hyponatremia as adverse effects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
PHARMACOLOGY-FINALS
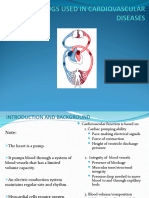
Diuretics Considered as a weak diuretic but also has
What are diuretics? vasodilatory effects (FIRST CHOICE IN
These are classes of drugs that stimulate excretion of HYPERTENSION)
water from the body. Adverse Effects
Uses Electrolyte imbalances
Management of hypertension Hyponatremia
Treatment of fluid retention aka edema Hypokalemia
Reduction of intracranial pressure Hypercalcemia
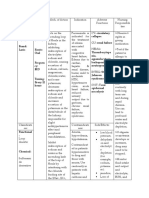
Classifications of diuretics Hyperuricemia → Gout
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors Hyperglycemia
Loop diuretics Hyperlipidemia
Thiazide diuretics d) Potassium-Sparing Diuretics
K-Sparing diuretics This type of diuretic doesn’t excrete the potassium in the
Osmotic diuretics body, and it blocks the aldosterone receptors, which are
responsible for fluid retention; blocking them will not
retain the fluid in the body, hence we’ll urinate it.
Amiloride, Triamterene, Spironolactone
Acts on Aldosterone Receptors in the collecting
duct
Considered as a weak diuretic; often used as an
add-on to other diuretics.
Rarely used alone (ex: Thiazide + K-sparring diuretic).
Adverse Effects
Electrolyte imbalances
Hyperkalemia→cardiac arrest
Potassium should not be given as an IV bolus; instead, it
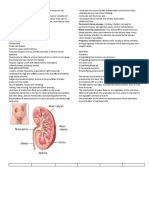
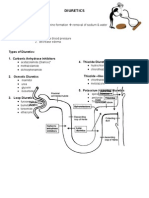
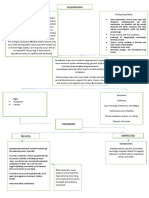
The illustration above shows the nephron, and it indicates
should be given as an IV drip because giving it to the
where the different diuretics act:
circulatory system too quickly may result in cardiac
Carbonic anhydrase inhinitors→proximal convuluted
arrest.
tubule
Loop diuretics→ascending loop of henle Menstrual irregularities in females
Thiazide diuretics→distal convuluted tubule Gynecomastia in males
K-sparring diuretics→collecting duct e) Osmotic Diuretics
Osmotic diuretics- doesn’t act particularly in nephron. Mannitol
a) Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Directly stimulates excretion of water rather than
Acetazolamide excretion of sodium.
Acts on the Proximal Convoluted Tubule It is the only diuretic that excretes only water because the
Has very weak diuretic effect other diuretics excrete sodium and water ("where sodium
Therefore it is preferred for other uses such as goes, water follows").
treatment of glaucoma
Adverse Effects Mainly used for
Malaise DOC for reduction of intracranial pressure.
Anorexia Urination of toxic substances
Fatigue Urine production in patients with acute kidney
Restlessness failure
b) Loop Diuretics Acute kidney failure can cause urinary retention, so an
Furosemide, Ethacrynic Acid osmotic diuretic can be used to produce urine.
Acts on the Thick Ascending Loop of Henle =
Considered as the strongest diuretic Adverse Effects
Adverse Effects Dehydration
Rapid reduction in blood volume aka
hypovolemia (low blood volume)
May lead to hypotension, shock, cardiac
arrhythmias
Electrolyte imbalances
Hyponatremia
Hypokalemia
Hypocalcemia
Ototoxicity
Hyperuricemia → Gout
c) Thiazide Diuretics
Hydrochlorothiazide, Chlorothiazide
Ends in Acts on the Distal Convoluted Tubule
-thiazide
QUELUSTINA
1
You might also like
- Orthodontic Case PresentationDocument21 pagesOrthodontic Case PresentationEman Nazzal100% (1)
- CM FrancisDocument229 pagesCM FrancisDrHassan Ahmed Shaikh50% (2)
- Document About Medical RecordsDocument1 pageDocument About Medical RecordsPitchfork News100% (1)
- Essay 1Document1 pageEssay 1coachcrossley1785No ratings yet
- Mannitol Furosemide - Less Potent, Longer Bumetanide-More Potent, Shorter Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) ChlorthalidoneDocument1 pageMannitol Furosemide - Less Potent, Longer Bumetanide-More Potent, Shorter Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) ChlorthalidoneKarinaNo ratings yet
- PHS CVSDocument25 pagesPHS CVStewogbadeomobuwajo005No ratings yet
- Phys Block 2Document63 pagesPhys Block 2drunkenwukongNo ratings yet
- Renal Drugs - Dr. UretaDocument4 pagesRenal Drugs - Dr. UretaAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: BY-DR. Saurabh Kansal Dept. of Pharmacology Msy Medical College MeerutDocument33 pagesDiuretics: BY-DR. Saurabh Kansal Dept. of Pharmacology Msy Medical College MeerutPrakhar GoelNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: DR Mozna TalpurDocument33 pagesDiuretics: DR Mozna TalpurShahid HameedNo ratings yet
- MS1 DRUG CARDSDocument22 pagesMS1 DRUG CARDStheresefrancotuNo ratings yet
- Diuretics and Anti Diuretics: Year Iii Pharm.D Dr. V. ChitraDocument49 pagesDiuretics and Anti Diuretics: Year Iii Pharm.D Dr. V. ChitranikithaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Generic and Brand NamesDocument22 pagesDiuretics: Generic and Brand NamesKish GabrielNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument3 pagesDiureticsarshu98172No ratings yet
- Unit 04: Drugs Acting On The Renal System Diuretic Agents: Thiazide and Thiazide-Like DiureticsDocument8 pagesUnit 04: Drugs Acting On The Renal System Diuretic Agents: Thiazide and Thiazide-Like DiureticsDental LecturesMMQNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Basic Pharmacology Block Pdnt/Pmed - PMSC/PPHR - 213Document19 pagesDiuretics: Basic Pharmacology Block Pdnt/Pmed - PMSC/PPHR - 213JedoNo ratings yet
- Summary of DiureticsDocument3 pagesSummary of DiureticsHaris SaeedNo ratings yet
- Diuretic Drugs: Prof - Dr.M.Aydın BarlasDocument10 pagesDiuretic Drugs: Prof - Dr.M.Aydın Barlasnasan shehadaNo ratings yet
- Pharma 7 To 13Document212 pagesPharma 7 To 13Loai Mohammed IssaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Final TermDocument19 pagesPharmacology Final TermDWIGHT LESTER O. MANGILANo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument4 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseImnot YouNo ratings yet
- The Heart and Circulatory System and The Kidney 2Document28 pagesThe Heart and Circulatory System and The Kidney 2Izzuddin AhmadNo ratings yet
- Zalameda - Thiazides Loop Diuretics Osmotic Diuretics Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Potassium SparingDocument16 pagesZalameda - Thiazides Loop Diuretics Osmotic Diuretics Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Potassium SparingNicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Name: DR Iqra RasoolDocument65 pagesName: DR Iqra RasoolFaryalBalochNo ratings yet
- Ph'cology of Diuretics (RZH)Document48 pagesPh'cology of Diuretics (RZH)beby febyola siagianNo ratings yet
- Farmakoterapi Sistem RenalDocument89 pagesFarmakoterapi Sistem RenalNhovieNhowaaNo ratings yet
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFurosemide Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- DIURETICS LECTURE ZebDocument52 pagesDIURETICS LECTURE ZebPROF DR SHAHMURAD100% (2)
- Lecture15-Diuretics and AntidiureticsDocument36 pagesLecture15-Diuretics and Antidiureticsharis.18No ratings yet
- De Methaq L2 HyponatreamiaDocument11 pagesDe Methaq L2 Hyponatreamiaزين العابدين محمد عويش مشريNo ratings yet
- Diuretic Theraphy and Drugs For Renal FailureDocument2 pagesDiuretic Theraphy and Drugs For Renal Failurerenz bartolomeNo ratings yet
- The Most Commonly Ordered (Chemistry) Laboratory InvestigationsDocument94 pagesThe Most Commonly Ordered (Chemistry) Laboratory InvestigationsZEESHAN YOUSUFNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Renal SystemDocument44 pagesDrugs Affecting Renal SystemRwapembe StephenNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument5 pagesDiureticsapi-3739910100% (1)
- Diuretic Drugs: Thiazides Sites of ActionDocument52 pagesDiuretic Drugs: Thiazides Sites of Actionuzzal ahmedNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Renal System I. Diuretics II. Parenteral Fluids (Video) III. Electrolytes (Video)Document44 pagesDrugs Affecting The Renal System I. Diuretics II. Parenteral Fluids (Video) III. Electrolytes (Video)Juliene Hannah FloresNo ratings yet
- Diuretics 1Document34 pagesDiuretics 1ياسمين مجديNo ratings yet
- Diuretics MergedDocument727 pagesDiuretics MergedRinkiNo ratings yet
- Diuretics 171130131557Document31 pagesDiuretics 171130131557Lety AgistiniaNo ratings yet
- Vidconf Diuretic Antidiuretic 2014Document51 pagesVidconf Diuretic Antidiuretic 2014naltrisilvianNo ratings yet
- Yuktiana Kharisma Bagian Farmakologi FK UNISBA 2017Document55 pagesYuktiana Kharisma Bagian Farmakologi FK UNISBA 2017Nurul PertiwiNo ratings yet
- Diuretic: A Diuretic Is Any Substance ThatDocument17 pagesDiuretic: A Diuretic Is Any Substance ThatAnalizaNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument61 pagesDiureticsJoyce WacukaNo ratings yet
- Felixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 3Document3 pagesFelixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 3Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Diuretics (Part 2)Document21 pagesDiuretics (Part 2)Aryaman MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular For PharmacologDocument134 pagesCardiovascular For Pharmacologephremtigabie7No ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument15 pagesDiureticsGAURI CHATURVEDINo ratings yet
- Drugs Mechanism Side Effect DiureticDocument3 pagesDrugs Mechanism Side Effect DiureticRebecca MarshallNo ratings yet
- DR Yosra Diuretics 2023Document46 pagesDR Yosra Diuretics 2023gntawfeqNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drugs: HCTZ Increases Urinary Hydrochlorothiazide IsDocument3 pagesAntihypertensive Drugs: HCTZ Increases Urinary Hydrochlorothiazide IsJesse ViolaNo ratings yet
- PHARMA-5Document27 pagesPHARMA-5yuson.joan001No ratings yet
- Hyponatremia: Presenter: DR Arun Karmakar Moderator: Prof. N. SharatkumarDocument50 pagesHyponatremia: Presenter: DR Arun Karmakar Moderator: Prof. N. SharatkumarLyra FebriandaNo ratings yet
- Hyponatremia Algorhythm Concept MapDocument2 pagesHyponatremia Algorhythm Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Potassium (Hyperkalaemia and Hypokalaemia) - Armando HasudunganDocument4 pagesPotassium (Hyperkalaemia and Hypokalaemia) - Armando HasudunganDr.Snehal100% (1)
- Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument1 pageElectrolyte ImbalanceJulia HermoginoNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Sumolly Anak DavidDocument29 pagesDiuretics: Sumolly Anak Davidfarmasi_hmNo ratings yet
- Diuretics PCMDocument8 pagesDiuretics PCMAnuj panditNo ratings yet
- Topic - Diuretics: Submitted By, Group - 07Document28 pagesTopic - Diuretics: Submitted By, Group - 07Arvi KhanNo ratings yet
- Renal SystemDocument39 pagesRenal SystemJhennie Rose PalaganasNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Agents 2ndDocument40 pagesAntihypertensive Agents 2ndalikhan52612No ratings yet
- HYPONATREMIA Final HandoutsDocument2 pagesHYPONATREMIA Final HandoutsSahata BOHARINo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- So Juni 2023Document5 pagesSo Juni 2023Aida H.djamhuriNo ratings yet
- BibliografieDocument3 pagesBibliografieAnonymous Kv663lNo ratings yet
- Acne ScarsDocument8 pagesAcne Scarsjp516No ratings yet
- Malaria: Michelle Carandang-Cuvin, M.D. FPPS, Fpidsp Pediatric Infectious Disease ConsultantDocument77 pagesMalaria: Michelle Carandang-Cuvin, M.D. FPPS, Fpidsp Pediatric Infectious Disease ConsultantHanako AranillaNo ratings yet
- AntidotesDocument5 pagesAntidotesUtkarshNo ratings yet
- Reconnective Healing: Beyond IntentionDocument2 pagesReconnective Healing: Beyond IntentionBentiv50% (2)
- II. Vital Statistics Iii. Fhsis Iv. Copar V. Health EducationDocument18 pagesII. Vital Statistics Iii. Fhsis Iv. Copar V. Health EducationJUANJOSEFOXNo ratings yet
- Presentation For InaugurationDocument35 pagesPresentation For InaugurationPing KyNo ratings yet
- Free Modafinil at ModafinilXLDocument11 pagesFree Modafinil at ModafinilXLMark AndersonNo ratings yet
- Medical Claim Sheet RajuDocument2 pagesMedical Claim Sheet RajurajusgowdarNo ratings yet
- Patologi RishaDocument11 pagesPatologi RisharishaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 151 - Cellulitis and ErysipelasDocument8 pagesChapter 151 - Cellulitis and ErysipelasDorothy BullecerNo ratings yet
- Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Nonketotic Syndrome (HHNS)Document8 pagesHyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Nonketotic Syndrome (HHNS)amiraNo ratings yet
- Medical PG BrochureDocument52 pagesMedical PG BrochurepstindiaNo ratings yet
- Keeping Left Ventricular Assist Device Acceleration On TrackDocument11 pagesKeeping Left Ventricular Assist Device Acceleration On TrackVashish RamrechaNo ratings yet
- Designer Babies ProjectDocument19 pagesDesigner Babies Projectapi-394843034No ratings yet
- Reference Regulatory AuthoritiesDocument2 pagesReference Regulatory AuthoritiesziadddNo ratings yet
- Spanish Flu HistoryDocument3 pagesSpanish Flu Historyrichlion50% (6)
- Fluidar 100Document4 pagesFluidar 100Jurgen SchirmacherNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Lymphatic SystemDocument153 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Lymphatic SystemNellie Grace Montes Aba-aNo ratings yet
- Exercise For Sciatic Pain From Piriformis SyndromeDocument3 pagesExercise For Sciatic Pain From Piriformis SyndromeFaizul Haque100% (1)
- Business LettersDocument39 pagesBusiness Lettersjdvroxas100% (1)
- Kinesthetic and Organic SensationDocument16 pagesKinesthetic and Organic SensationNicole Jenne TanNo ratings yet
- Scrub Typhus GuidelinesDocument40 pagesScrub Typhus GuidelinesnarasimhahanNo ratings yet
- GENESIS II Surgical Technique DCFDocument46 pagesGENESIS II Surgical Technique DCFMazilo VictorNo ratings yet
- Naturopathy: Naturopathy or Naturopathic Medicine Is A Form of AlternativeDocument20 pagesNaturopathy: Naturopathy or Naturopathic Medicine Is A Form of AlternativeAK KJNo ratings yet