Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 viewsRC Phase Shift Oscillator
RC Phase Shift Oscillator
Uploaded by
Sakshi GosaviThis document describes an experiment to build and test an RC phase shift oscillator circuit using a JFET. The circuit uses a CE amplifier followed by three RC networks to provide the necessary 180 degree phase shift for oscillation. The experiment aims to observe the sinusoidal output waveform on an oscilloscope. Key components include a power supply, JFET, resistors, capacitors, breadboard, and oscilloscope. Calculations are provided to determine the theoretical oscillation frequency based on the RC component values. Measurements of output voltage, period and frequency will be recorded and plotted on a graph.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
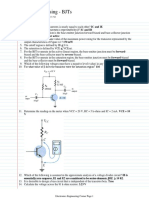
- Electronic Principles and Circuits Lab Manual - BEC303 - 18-11-2023Document69 pagesElectronic Principles and Circuits Lab Manual - BEC303 - 18-11-2023Maithira H0% (1)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab NewDocument86 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits Lab NewleevasusanNo ratings yet
- BR93Lxx-W: Microwire BUS EEPROM (3-Wire)Document39 pagesBR93Lxx-W: Microwire BUS EEPROM (3-Wire)Wee Chuan PoonNo ratings yet
- Common Emitter UnbypassedDocument38 pagesCommon Emitter Unbypassedaliffuden 123No ratings yet
- Open Ended 1Document12 pagesOpen Ended 1AneeshaNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Directional CouplerDocument10 pagesLab 4 Directional Couplernurin runNo ratings yet
- MCQ in DC Biasing - BJTsDocument6 pagesMCQ in DC Biasing - BJTsPaolo PerezNo ratings yet
- Scan 10 RulesDocument42 pagesScan 10 RulesSivaramakrishna Anumolu67% (3)
- NV 2001-07 Op-Amp Cookbook Parts 1-4Document29 pagesNV 2001-07 Op-Amp Cookbook Parts 1-4Dylan Komichek100% (1)
- Wein Bridge OscillatorDocument3 pagesWein Bridge OscillatorSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Expt 4 RC Phase Shift Oscillator (2020)Document4 pagesExpt 4 RC Phase Shift Oscillator (2020)samarthNo ratings yet
- Edc 2 Mumbai University Lab ManualDocument32 pagesEdc 2 Mumbai University Lab ManualXavier50% (4)
- ECA ManualDocument50 pagesECA ManualkrajenderreddyNo ratings yet
- Eca Lab-Min PDFDocument87 pagesEca Lab-Min PDFAkashita SharmaNo ratings yet
- PDC Lab ManualDocument68 pagesPDC Lab Manualnama varapuNo ratings yet
- 566 LIC Expt 2Document22 pages566 LIC Expt 2Hrivu Dasmunshi (RA1911004010566)No ratings yet
- Expt 5 - Wein Bridge Oscillator (2020)Document3 pagesExpt 5 - Wein Bridge Oscillator (2020)samarthNo ratings yet
- AE Manual GECR PDFDocument105 pagesAE Manual GECR PDFhimadrimandal2006No ratings yet
- Analog Circuits Lab manual18ECL48Document29 pagesAnalog Circuits Lab manual18ECL48Dintle PhofuNo ratings yet
- ECLDocument65 pagesECLAnonymous eWMnRr70qNo ratings yet
- JFET AmplifierDocument4 pagesJFET AmplifierSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- BEEE 2353 - 2354 - Lab 4 Wein-Bridge OscillatorDocument5 pagesBEEE 2353 - 2354 - Lab 4 Wein-Bridge OscillatorAina BalqisNo ratings yet
- Colpitts OscillatorDocument3 pagesColpitts OscillatorSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- EDC Manual PDFDocument83 pagesEDC Manual PDFMrinal MitraNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits I Lab ManualDocument44 pagesElectronic Circuits I Lab Manualkunaraj100% (7)
- 15EE209L Analog and Digital Circuits Lab2017 18Document91 pages15EE209L Analog and Digital Circuits Lab2017 18THIRUNEELAKANDANNo ratings yet
- 17eel38 El Lab ManualDocument65 pages17eel38 El Lab Manuallakshay madaanNo ratings yet
- Rr-10205-Edc Apr 2003Document8 pagesRr-10205-Edc Apr 2003mpssassygirlNo ratings yet
- Pulse & Digital Circuits Lab Manual PDFDocument61 pagesPulse & Digital Circuits Lab Manual PDFKarunakar Reddy MNo ratings yet
- Pulse & Digital Circuits Lab Manual 3Document61 pagesPulse & Digital Circuits Lab Manual 3Suda KrishnarjunaraoNo ratings yet
- Bec3l1 - Edc Lab NewDocument55 pagesBec3l1 - Edc Lab NewAhyen TambongNo ratings yet
- Ed ManualDocument66 pagesEd ManualshilpaNo ratings yet
- Ex #7 (TWO STAGE)Document6 pagesEx #7 (TWO STAGE)manishNo ratings yet
- LIC Lab ManualDocument94 pagesLIC Lab Manualmamathasuvarna1121No ratings yet
- Commnication-Lab Manual EceDocument46 pagesCommnication-Lab Manual EceSudeepa BgspNo ratings yet
- LIC Lab ManualDocument89 pagesLIC Lab ManualTAMILAN XEROX VtmNo ratings yet
- Nis Cie 2Document5 pagesNis Cie 2Manju BhuvanNo ratings yet
- Ecad Lab ManualDocument48 pagesEcad Lab Manualsivapc3105No ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument66 pagesLab ManualcommunicationridersNo ratings yet
- Commn Systems Lab ManualDocument37 pagesCommn Systems Lab Manualnidheeshlal10No ratings yet
- Lab 4: Design and Analysis of BJT Biasing and Amplifier CircuitDocument7 pagesLab 4: Design and Analysis of BJT Biasing and Amplifier CircuitSatyam SatyaprakashNo ratings yet
- Ec8461 Cd&si LabDocument86 pagesEc8461 Cd&si LabReena RajNo ratings yet
- Linear Wave Shaping: Name of The Component/Equipment Specifications QuantityDocument61 pagesLinear Wave Shaping: Name of The Component/Equipment Specifications QuantitySainadh YerrapragadaNo ratings yet
- Lab BJTDocument10 pagesLab BJTStella PinkNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuits Lab Manual: Atria Institute of TechnologyDocument60 pagesAnalog Circuits Lab Manual: Atria Institute of TechnologyTháHäKâduvàyîLzNo ratings yet
- Analog System Design ExperimentsDocument27 pagesAnalog System Design ExperimentsAnsh BhaganiaNo ratings yet
- BJT WCCDocument11 pagesBJT WCCPavan ParameshwarNo ratings yet
- EC6311 ADC Regulation 2013Document29 pagesEC6311 ADC Regulation 2013Umamaheswari RajeshNo ratings yet
- ECA Lab ManualDocument63 pagesECA Lab ManualsivadanamsNo ratings yet
- RC Phase Shift Oscillator 230510 - 195846Document32 pagesRC Phase Shift Oscillator 230510 - 195846Pranav msNo ratings yet
- PH 411 Physics Laboratory I (Electronics) : Instruction Manual IndexDocument28 pagesPH 411 Physics Laboratory I (Electronics) : Instruction Manual IndexReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- LIC+COM Lab Manual - 17ECL48Document58 pagesLIC+COM Lab Manual - 17ECL48Surendra K V100% (4)
- Expt 7 - Hartley Oscillator (2020)Document4 pagesExpt 7 - Hartley Oscillator (2020)samarthNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics LAB ManualDocument52 pagesAnalog Electronics LAB ManualPrahlad ReddyNo ratings yet
- 3.transient Analysis of Series RL, RC CircuitsDocument11 pages3.transient Analysis of Series RL, RC CircuitsshubhamNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Heterojunction Bipolar Transistors for Circuit Design: Microwave Modeling and Parameter ExtractionFrom EverandHeterojunction Bipolar Transistors for Circuit Design: Microwave Modeling and Parameter ExtractionNo ratings yet
- Organic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyFrom EverandOrganic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- A Presentation ON File Transfer ProtocolDocument8 pagesA Presentation ON File Transfer ProtocolSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Internship PPT ON Iot Based ProjectDocument10 pagesInternship PPT ON Iot Based ProjectSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Traffic Control System Using Ultrasonic SensorsDocument9 pagesTraffic Control System Using Ultrasonic SensorsSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Tenses 6 KDocument17 pagesTenses 6 KSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- REPORTDocument34 pagesREPORTSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Monostable MultivibratorDocument4 pagesMonostable MultivibratorSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- JFET AmplifierDocument4 pagesJFET AmplifierSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Barrier DetectionDocument25 pagesBarrier DetectionSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Report ProjectDocument20 pagesReport ProjectSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Wein Bridge OscillatorDocument3 pagesWein Bridge OscillatorSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Smart Medicine BoxDocument15 pagesSmart Medicine BoxSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- HTMLDocument3 pagesHTMLSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Colpitts OscillatorDocument3 pagesColpitts OscillatorSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Smart Home Automation SystemDocument30 pagesSmart Home Automation SystemSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Water MeterDocument9 pagesWater MeterSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Lead CompensatorDocument9 pagesLead CompensatorSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Tenses FormulaDocument8 pagesTenses FormulaSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- TRAFFICDocument9 pagesTRAFFICSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Soluciones 9Document4 pagesSoluciones 9manuNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project UpdatedDocument18 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Updatedjohhnysins1978No ratings yet
- Digital IC Tester (DIT24)Document6 pagesDigital IC Tester (DIT24)Abvolt IndiaNo ratings yet
- EL2043 L09 Rangkaian LogikaDocument103 pagesEL2043 L09 Rangkaian LogikaDian Asfriany NurfalahNo ratings yet
- LM555 DatasheetDocument21 pagesLM555 DatasheetBram Ba BambNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4: Circuit Theorems: 4.0 Intended Learning OutcomesDocument29 pagesUNIT 4: Circuit Theorems: 4.0 Intended Learning OutcomesMark BerioNo ratings yet
- ENGG2310A/ESTR2300 (Fall 2018) Problem Set #3Document6 pagesENGG2310A/ESTR2300 (Fall 2018) Problem Set #3Tsz Wing YipNo ratings yet
- Swru295e-Sub-1 GHZ RF TransceiversTransmitterDocument111 pagesSwru295e-Sub-1 GHZ RF TransceiversTransmitterjrnelsonNo ratings yet
- NJM13403 Single Supply Quad Operational Amplifier: General Description Package OutlineDocument6 pagesNJM13403 Single Supply Quad Operational Amplifier: General Description Package OutlineMokh TarNo ratings yet
- Sanch PLC Price List: Standard TypeDocument1 pageSanch PLC Price List: Standard TypeAhmed AbdelrazekNo ratings yet
- Tut - Digital IntegratedDocument32 pagesTut - Digital IntegratedqawaNo ratings yet
- 10-Becker Co-Simulation CDS PDFDocument33 pages10-Becker Co-Simulation CDS PDFDebidas KunduNo ratings yet
- Insights of An InverterDocument4 pagesInsights of An InverterSowmya BarliNo ratings yet
- Wien Bridge OscillatorDocument16 pagesWien Bridge Oscillatorahmed omarNo ratings yet
- MX29F800Document42 pagesMX29F800Gudda BhaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document85 pagesChapter 8edward solomonNo ratings yet
- Notes 1Document4 pagesNotes 1MohanNo ratings yet
- Cap4. Digital Systems - Combinational Logic CircuitsDocument11 pagesCap4. Digital Systems - Combinational Logic CircuitsMiguelNo ratings yet
- Handout of MEL-G-632Document2 pagesHandout of MEL-G-632Bijayshree AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Latch Up: Causes and Prevention: ELEC 353 - Electronics II Instructor: Prof. C. SaavedraDocument20 pagesLatch Up: Causes and Prevention: ELEC 353 - Electronics II Instructor: Prof. C. SaavedraSandesh Kumar B VNo ratings yet
- K2638 FujiElectricDocument2 pagesK2638 FujiElectricRoiser DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Freescale ADC and QADC Modules With ColdFire MicrocontrollersDocument24 pagesFreescale ADC and QADC Modules With ColdFire MicrocontrollersJim GunterNo ratings yet
- Lab Nand TaskDocument5 pagesLab Nand TaskMuzammil AliNo ratings yet
- BLG IRFB4227 MOSFET Datasheet PDF - Equivalent. Cross Reference SearchDocument5 pagesBLG IRFB4227 MOSFET Datasheet PDF - Equivalent. Cross Reference Searchsisay bitewNo ratings yet
- Cse Lab Manual OnlyDocument52 pagesCse Lab Manual OnlyR ChandrasekharNo ratings yet
- ME4812/ME4812-G: N-Channel 30-V (D-S) MOSFET, ESD ProtectionDocument5 pagesME4812/ME4812-G: N-Channel 30-V (D-S) MOSFET, ESD ProtectionMaikol DominguezNo ratings yet
RC Phase Shift Oscillator
RC Phase Shift Oscillator
Uploaded by
Sakshi Gosavi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesThis document describes an experiment to build and test an RC phase shift oscillator circuit using a JFET. The circuit uses a CE amplifier followed by three RC networks to provide the necessary 180 degree phase shift for oscillation. The experiment aims to observe the sinusoidal output waveform on an oscilloscope. Key components include a power supply, JFET, resistors, capacitors, breadboard, and oscilloscope. Calculations are provided to determine the theoretical oscillation frequency based on the RC component values. Measurements of output voltage, period and frequency will be recorded and plotted on a graph.
Original Description:
Original Title
RC phase shift oscillator
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document describes an experiment to build and test an RC phase shift oscillator circuit using a JFET. The circuit uses a CE amplifier followed by three RC networks to provide the necessary 180 degree phase shift for oscillation. The experiment aims to observe the sinusoidal output waveform on an oscilloscope. Key components include a power supply, JFET, resistors, capacitors, breadboard, and oscilloscope. Calculations are provided to determine the theoretical oscillation frequency based on the RC component values. Measurements of output voltage, period and frequency will be recorded and plotted on a graph.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesRC Phase Shift Oscillator
RC Phase Shift Oscillator
Uploaded by
Sakshi GosaviThis document describes an experiment to build and test an RC phase shift oscillator circuit using a JFET. The circuit uses a CE amplifier followed by three RC networks to provide the necessary 180 degree phase shift for oscillation. The experiment aims to observe the sinusoidal output waveform on an oscilloscope. Key components include a power supply, JFET, resistors, capacitors, breadboard, and oscilloscope. Calculations are provided to determine the theoretical oscillation frequency based on the RC component values. Measurements of output voltage, period and frequency will be recorded and plotted on a graph.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Dr.
Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University Lonere, Raigad, Maharashtra
2017
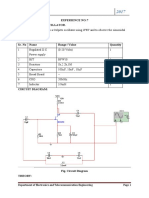
EXPERIENCE NO:5
TITLE: RC PHASE SHIFT OSCILLATOR
AIM: To design and set up an RC phase shift oscillator using JFET and to observe the
sinusoidal output waveform
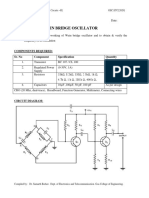
APPARATUS:
Sr. No Name Range / Value Quantity
1 Regulated D.C (0-20 Volts) 1
Power supply
2 BJT BFW10 1
3 Resistors 47kΩ, 10kΩ, 2.2kΩ, 680Ω ,4.7KΩ 1
4 Capacitors 1μF,22μF Each 1
5 Bread Board and -- 1 Set
connecting wires
6 CRO 20MHz 1
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
Fig. Circuit Diagram
THEORY:
Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering Page 1
Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University Lonere, Raigad, Maharashtra
2017
An oscillator is an electronic circuit for generating an AC signal voltage with a DC supply as
the only input requirement. The frequency of the generated signal is decided by the circuit
elements used. An oscillator requires an amplifier, a frequency selective network and a
positive feedback from the output to the input.
The Barkhausen criterion for sustained oscillation is Aβ = 1 where A is the gain of the
amplifier and β is the feedback factor (gain). The unity gain means signal is in phase. ( If the
signal is 1800 out of phase and gain will be -1). RC-Phase shift Oscillator has a CE amplifier
followed by three sections of RC phase shift feed-back Networks. The output of the last stage
is return to the input of the amplifier. The values of R and C are chosen such that the phase
shift of each RC section is 60º.Thus The RC ladder network produces a total phase shift of
180º between its input and output voltage for the given frequency. Since CE Amplifier
produces 180 º phases shift. The total phase shift from the base of the transistor around the
circuit and back to the base will be exactly 360º or 0º. This satisfies the Barkhausen condition
for sustaining oscillations and total loop gain of this circuit is greater than or equal to 1, this
condition used to generate the sinusoidal oscillations.
MODEL GRAPH:
PROCEDURE:
Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering Page 2
Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University Lonere, Raigad, Maharashtra
2017
1. Identify the pin details of BC107 Transistor (or equivalent silicon Transistor such as
BC108/547) and test it using a millimeter. Set up the circuit on breadboard as shown in
figure.
2. A 12V Supply Voltage is given by using Regulated power supply and output is taken from
collector of the Transistor.
3. By using CRO the output time period and voltage are noted.
4. Plot all the readings curves on a single graph sheet.
CALCULATIONS:
1
f=
2 πRC √ 6
TABULAR FORM:
Sr.No FREQ.(Theoretically) FREQ.(practically)
CONCLUSION:
QUESTION:
Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering Page 3
You might also like
- Electronic Principles and Circuits Lab Manual - BEC303 - 18-11-2023Document69 pagesElectronic Principles and Circuits Lab Manual - BEC303 - 18-11-2023Maithira H0% (1)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab NewDocument86 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits Lab NewleevasusanNo ratings yet
- BR93Lxx-W: Microwire BUS EEPROM (3-Wire)Document39 pagesBR93Lxx-W: Microwire BUS EEPROM (3-Wire)Wee Chuan PoonNo ratings yet
- Common Emitter UnbypassedDocument38 pagesCommon Emitter Unbypassedaliffuden 123No ratings yet
- Open Ended 1Document12 pagesOpen Ended 1AneeshaNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Directional CouplerDocument10 pagesLab 4 Directional Couplernurin runNo ratings yet
- MCQ in DC Biasing - BJTsDocument6 pagesMCQ in DC Biasing - BJTsPaolo PerezNo ratings yet
- Scan 10 RulesDocument42 pagesScan 10 RulesSivaramakrishna Anumolu67% (3)
- NV 2001-07 Op-Amp Cookbook Parts 1-4Document29 pagesNV 2001-07 Op-Amp Cookbook Parts 1-4Dylan Komichek100% (1)
- Wein Bridge OscillatorDocument3 pagesWein Bridge OscillatorSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Expt 4 RC Phase Shift Oscillator (2020)Document4 pagesExpt 4 RC Phase Shift Oscillator (2020)samarthNo ratings yet
- Edc 2 Mumbai University Lab ManualDocument32 pagesEdc 2 Mumbai University Lab ManualXavier50% (4)
- ECA ManualDocument50 pagesECA ManualkrajenderreddyNo ratings yet
- Eca Lab-Min PDFDocument87 pagesEca Lab-Min PDFAkashita SharmaNo ratings yet
- PDC Lab ManualDocument68 pagesPDC Lab Manualnama varapuNo ratings yet
- 566 LIC Expt 2Document22 pages566 LIC Expt 2Hrivu Dasmunshi (RA1911004010566)No ratings yet
- Expt 5 - Wein Bridge Oscillator (2020)Document3 pagesExpt 5 - Wein Bridge Oscillator (2020)samarthNo ratings yet
- AE Manual GECR PDFDocument105 pagesAE Manual GECR PDFhimadrimandal2006No ratings yet
- Analog Circuits Lab manual18ECL48Document29 pagesAnalog Circuits Lab manual18ECL48Dintle PhofuNo ratings yet
- ECLDocument65 pagesECLAnonymous eWMnRr70qNo ratings yet
- JFET AmplifierDocument4 pagesJFET AmplifierSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- BEEE 2353 - 2354 - Lab 4 Wein-Bridge OscillatorDocument5 pagesBEEE 2353 - 2354 - Lab 4 Wein-Bridge OscillatorAina BalqisNo ratings yet
- Colpitts OscillatorDocument3 pagesColpitts OscillatorSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- EDC Manual PDFDocument83 pagesEDC Manual PDFMrinal MitraNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits I Lab ManualDocument44 pagesElectronic Circuits I Lab Manualkunaraj100% (7)
- 15EE209L Analog and Digital Circuits Lab2017 18Document91 pages15EE209L Analog and Digital Circuits Lab2017 18THIRUNEELAKANDANNo ratings yet
- 17eel38 El Lab ManualDocument65 pages17eel38 El Lab Manuallakshay madaanNo ratings yet
- Rr-10205-Edc Apr 2003Document8 pagesRr-10205-Edc Apr 2003mpssassygirlNo ratings yet
- Pulse & Digital Circuits Lab Manual PDFDocument61 pagesPulse & Digital Circuits Lab Manual PDFKarunakar Reddy MNo ratings yet
- Pulse & Digital Circuits Lab Manual 3Document61 pagesPulse & Digital Circuits Lab Manual 3Suda KrishnarjunaraoNo ratings yet
- Bec3l1 - Edc Lab NewDocument55 pagesBec3l1 - Edc Lab NewAhyen TambongNo ratings yet
- Ed ManualDocument66 pagesEd ManualshilpaNo ratings yet
- Ex #7 (TWO STAGE)Document6 pagesEx #7 (TWO STAGE)manishNo ratings yet
- LIC Lab ManualDocument94 pagesLIC Lab Manualmamathasuvarna1121No ratings yet
- Commnication-Lab Manual EceDocument46 pagesCommnication-Lab Manual EceSudeepa BgspNo ratings yet
- LIC Lab ManualDocument89 pagesLIC Lab ManualTAMILAN XEROX VtmNo ratings yet
- Nis Cie 2Document5 pagesNis Cie 2Manju BhuvanNo ratings yet
- Ecad Lab ManualDocument48 pagesEcad Lab Manualsivapc3105No ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument66 pagesLab ManualcommunicationridersNo ratings yet
- Commn Systems Lab ManualDocument37 pagesCommn Systems Lab Manualnidheeshlal10No ratings yet
- Lab 4: Design and Analysis of BJT Biasing and Amplifier CircuitDocument7 pagesLab 4: Design and Analysis of BJT Biasing and Amplifier CircuitSatyam SatyaprakashNo ratings yet
- Ec8461 Cd&si LabDocument86 pagesEc8461 Cd&si LabReena RajNo ratings yet
- Linear Wave Shaping: Name of The Component/Equipment Specifications QuantityDocument61 pagesLinear Wave Shaping: Name of The Component/Equipment Specifications QuantitySainadh YerrapragadaNo ratings yet
- Lab BJTDocument10 pagesLab BJTStella PinkNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuits Lab Manual: Atria Institute of TechnologyDocument60 pagesAnalog Circuits Lab Manual: Atria Institute of TechnologyTháHäKâduvàyîLzNo ratings yet
- Analog System Design ExperimentsDocument27 pagesAnalog System Design ExperimentsAnsh BhaganiaNo ratings yet
- BJT WCCDocument11 pagesBJT WCCPavan ParameshwarNo ratings yet
- EC6311 ADC Regulation 2013Document29 pagesEC6311 ADC Regulation 2013Umamaheswari RajeshNo ratings yet
- ECA Lab ManualDocument63 pagesECA Lab ManualsivadanamsNo ratings yet
- RC Phase Shift Oscillator 230510 - 195846Document32 pagesRC Phase Shift Oscillator 230510 - 195846Pranav msNo ratings yet
- PH 411 Physics Laboratory I (Electronics) : Instruction Manual IndexDocument28 pagesPH 411 Physics Laboratory I (Electronics) : Instruction Manual IndexReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- LIC+COM Lab Manual - 17ECL48Document58 pagesLIC+COM Lab Manual - 17ECL48Surendra K V100% (4)
- Expt 7 - Hartley Oscillator (2020)Document4 pagesExpt 7 - Hartley Oscillator (2020)samarthNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics LAB ManualDocument52 pagesAnalog Electronics LAB ManualPrahlad ReddyNo ratings yet
- 3.transient Analysis of Series RL, RC CircuitsDocument11 pages3.transient Analysis of Series RL, RC CircuitsshubhamNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Heterojunction Bipolar Transistors for Circuit Design: Microwave Modeling and Parameter ExtractionFrom EverandHeterojunction Bipolar Transistors for Circuit Design: Microwave Modeling and Parameter ExtractionNo ratings yet
- Organic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyFrom EverandOrganic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- A Presentation ON File Transfer ProtocolDocument8 pagesA Presentation ON File Transfer ProtocolSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Internship PPT ON Iot Based ProjectDocument10 pagesInternship PPT ON Iot Based ProjectSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Traffic Control System Using Ultrasonic SensorsDocument9 pagesTraffic Control System Using Ultrasonic SensorsSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Tenses 6 KDocument17 pagesTenses 6 KSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- REPORTDocument34 pagesREPORTSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Monostable MultivibratorDocument4 pagesMonostable MultivibratorSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- JFET AmplifierDocument4 pagesJFET AmplifierSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Barrier DetectionDocument25 pagesBarrier DetectionSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Report ProjectDocument20 pagesReport ProjectSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Wein Bridge OscillatorDocument3 pagesWein Bridge OscillatorSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Smart Medicine BoxDocument15 pagesSmart Medicine BoxSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- HTMLDocument3 pagesHTMLSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Colpitts OscillatorDocument3 pagesColpitts OscillatorSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Smart Home Automation SystemDocument30 pagesSmart Home Automation SystemSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Water MeterDocument9 pagesWater MeterSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Lead CompensatorDocument9 pagesLead CompensatorSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Tenses FormulaDocument8 pagesTenses FormulaSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- TRAFFICDocument9 pagesTRAFFICSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Soluciones 9Document4 pagesSoluciones 9manuNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project UpdatedDocument18 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Updatedjohhnysins1978No ratings yet
- Digital IC Tester (DIT24)Document6 pagesDigital IC Tester (DIT24)Abvolt IndiaNo ratings yet
- EL2043 L09 Rangkaian LogikaDocument103 pagesEL2043 L09 Rangkaian LogikaDian Asfriany NurfalahNo ratings yet
- LM555 DatasheetDocument21 pagesLM555 DatasheetBram Ba BambNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4: Circuit Theorems: 4.0 Intended Learning OutcomesDocument29 pagesUNIT 4: Circuit Theorems: 4.0 Intended Learning OutcomesMark BerioNo ratings yet
- ENGG2310A/ESTR2300 (Fall 2018) Problem Set #3Document6 pagesENGG2310A/ESTR2300 (Fall 2018) Problem Set #3Tsz Wing YipNo ratings yet
- Swru295e-Sub-1 GHZ RF TransceiversTransmitterDocument111 pagesSwru295e-Sub-1 GHZ RF TransceiversTransmitterjrnelsonNo ratings yet
- NJM13403 Single Supply Quad Operational Amplifier: General Description Package OutlineDocument6 pagesNJM13403 Single Supply Quad Operational Amplifier: General Description Package OutlineMokh TarNo ratings yet
- Sanch PLC Price List: Standard TypeDocument1 pageSanch PLC Price List: Standard TypeAhmed AbdelrazekNo ratings yet
- Tut - Digital IntegratedDocument32 pagesTut - Digital IntegratedqawaNo ratings yet
- 10-Becker Co-Simulation CDS PDFDocument33 pages10-Becker Co-Simulation CDS PDFDebidas KunduNo ratings yet
- Insights of An InverterDocument4 pagesInsights of An InverterSowmya BarliNo ratings yet
- Wien Bridge OscillatorDocument16 pagesWien Bridge Oscillatorahmed omarNo ratings yet
- MX29F800Document42 pagesMX29F800Gudda BhaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document85 pagesChapter 8edward solomonNo ratings yet
- Notes 1Document4 pagesNotes 1MohanNo ratings yet
- Cap4. Digital Systems - Combinational Logic CircuitsDocument11 pagesCap4. Digital Systems - Combinational Logic CircuitsMiguelNo ratings yet
- Handout of MEL-G-632Document2 pagesHandout of MEL-G-632Bijayshree AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Latch Up: Causes and Prevention: ELEC 353 - Electronics II Instructor: Prof. C. SaavedraDocument20 pagesLatch Up: Causes and Prevention: ELEC 353 - Electronics II Instructor: Prof. C. SaavedraSandesh Kumar B VNo ratings yet
- K2638 FujiElectricDocument2 pagesK2638 FujiElectricRoiser DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Freescale ADC and QADC Modules With ColdFire MicrocontrollersDocument24 pagesFreescale ADC and QADC Modules With ColdFire MicrocontrollersJim GunterNo ratings yet
- Lab Nand TaskDocument5 pagesLab Nand TaskMuzammil AliNo ratings yet
- BLG IRFB4227 MOSFET Datasheet PDF - Equivalent. Cross Reference SearchDocument5 pagesBLG IRFB4227 MOSFET Datasheet PDF - Equivalent. Cross Reference Searchsisay bitewNo ratings yet
- Cse Lab Manual OnlyDocument52 pagesCse Lab Manual OnlyR ChandrasekharNo ratings yet
- ME4812/ME4812-G: N-Channel 30-V (D-S) MOSFET, ESD ProtectionDocument5 pagesME4812/ME4812-G: N-Channel 30-V (D-S) MOSFET, ESD ProtectionMaikol DominguezNo ratings yet