Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ultrasound
Ultrasound
Uploaded by
Bichoy OssamaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ultrasound
Ultrasound
Uploaded by
Bichoy OssamaCopyright:
Available Formats
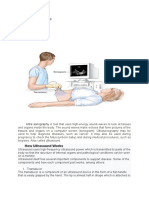
Ultrasound is a form of sound wave that has frequencies above the audible range for
humans. It is commonly used in various industries for its ability to penetrate solid
objects and detect internal features.
In the medical field, ultrasound technology has been widely used for diagnostic
purposes. It allows medical professionals to visualize internal organs and tissues,
monitor fetal development, and detect abnormalities. The ultrasound machine works by
emitting high-frequency sound waves, which then bounce back off the internal
structures and are detected by the machine. The data is then processed and displayed
on a screen, allowing doctors to see inside the body without the need for invasive
procedures.
Ultrasonic testing is also used in the industrial sector for flaw detection and quality
control. The method involves using an ultrasonic transducer to send high-frequency
sound waves into a material. The waves travel through the material and are reflected
back by any internal features, such as cracks or voids. By analyzing the reflected waves,
technicians can detect the presence and location of defects. This method is commonly
used in the aerospace, automotive, and construction industries.
In addition to its practical applications, ultrasound technology has also been used in
research fields such as materials science, chemistry, and biology. It can be used to study
the physical properties of materials and the behavior of molecules.
Despite its numerous applications, ultrasound technology also has limitations. It can
only penetrate certain materials, and the accuracy of the results can be affected by
factors such as surface roughness and the material’s composition. However, with
ongoing research and advancements in technology, ultrasound continues to be a
valuable tool in various fields.
You might also like
- Scope of Diagnostic Imaging in Veterinary PracticeDocument9 pagesScope of Diagnostic Imaging in Veterinary PracticeAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Physics ResearchDocument2 pagesPhysics Researchlailo tototNo ratings yet
- UltrasoundDocument19 pagesUltrasoundAli AliNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonography Report PDFDocument3 pagesUltrasonography Report PDFKruthi M LNo ratings yet
- Medical Physics Course Notes (Greg Pitt)Document92 pagesMedical Physics Course Notes (Greg Pitt)Mel ClancyNo ratings yet
- Nama: Saifullah Ali NPM: 720621444 Kelas: 2B: How Ultrasound WorksDocument3 pagesNama: Saifullah Ali NPM: 720621444 Kelas: 2B: How Ultrasound WorksSaifullah AliNo ratings yet
- BAB IIRadiology Is A Specialty That Uses Medical Imaging To Diagnose and Treat Diseases Seen Within The BodyDocument7 pagesBAB IIRadiology Is A Specialty That Uses Medical Imaging To Diagnose and Treat Diseases Seen Within The BodySupian Ats-tsauriNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Imaging System: Hardik Tiwari (20SCE1010441) Aman Mittal (20SCSE1010518)Document10 pagesUltrasonic Imaging System: Hardik Tiwari (20SCE1010441) Aman Mittal (20SCSE1010518)Aman AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Thesis UltrasonicDocument6 pagesThesis Ultrasonicrachelphillipsbillings100% (2)
- Gas Dynamics Sound Applications: Name: Mohamed Mostafa Elsaid Salem Sec: 10Document8 pagesGas Dynamics Sound Applications: Name: Mohamed Mostafa Elsaid Salem Sec: 10mohamed352No ratings yet
- Ultrasound: Asst - Lec. Sura Mohammed Saeed AhmedDocument17 pagesUltrasound: Asst - Lec. Sura Mohammed Saeed AhmedOsama HayderNo ratings yet
- General UltrasoundDocument114 pagesGeneral Ultrasoundgilbert centerNo ratings yet
- Obstacle Detection Using Ut LT A Sonic SensorDocument39 pagesObstacle Detection Using Ut LT A Sonic Sensor2020pie417No ratings yet
- Medical ImagingDocument7 pagesMedical ImagingAlejandra AlfaroNo ratings yet
- ULTRASONICS Lecture Notes EbookDocument4 pagesULTRASONICS Lecture Notes EbookVikram KailashNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Application of Radiation in Medical Diagnosis and TherapyDocument3 pagesOverview of The Application of Radiation in Medical Diagnosis and TherapyJeya Plays YTNo ratings yet
- X-RaysDocument8 pagesX-RaysannoyonamusNo ratings yet
- Radiology Techniques - 1Document10 pagesRadiology Techniques - 1IraqiNo ratings yet
- المستندDocument11 pagesالمستندNoor S NajemNo ratings yet
- Biology For Engineers Module 3Document40 pagesBiology For Engineers Module 3moaaz ahmedNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Ultrasound:: ACR-accredited Facilities DatabaseDocument2 pagesBenefits of Ultrasound:: ACR-accredited Facilities DatabaseFelix KylieNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonograph yDocument2 pagesUltrasonograph yAdrin Ma'rufNo ratings yet
- Obstacle Detection Using Utltasonic Sensor: November 2020Document39 pagesObstacle Detection Using Utltasonic Sensor: November 2020vishwasNo ratings yet
- General UltrasoundDocument9 pagesGeneral UltrasoundblucienNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - BIOLOGYDocument36 pagesModule 4 - BIOLOGYPunith PuniNo ratings yet
- .Prepare Patient For Abdominal Ultrasonography? . Preparing A Patient For Abdominal Ultrasonography Involves Several Steps ToDocument21 pages.Prepare Patient For Abdominal Ultrasonography? . Preparing A Patient For Abdominal Ultrasonography Involves Several Steps Toss solutionsNo ratings yet
- SP 4f - Ultrasound (Notes)Document2 pagesSP 4f - Ultrasound (Notes)nisalielisha rodrigoNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonics Sound OccurrenceDocument2 pagesUltrasonics Sound OccurrenceAllison PerezNo ratings yet
- Sound Frequency Hearing Range: Ultrasound Is An OscillatingDocument1 pageSound Frequency Hearing Range: Ultrasound Is An OscillatingShanmuga NavaneethanNo ratings yet
- FOL Unit 5Document4 pagesFOL Unit 5Sudhar SanNo ratings yet
- XRAYSDocument10 pagesXRAYSkeeratkbediNo ratings yet
- Multiple Reflection of Sound and Applications of UltrasoundDocument9 pagesMultiple Reflection of Sound and Applications of UltrasoundEkashmanNo ratings yet
- Time Imaging .: Ultrasonography Machine For Veterinary ApplicationDocument22 pagesTime Imaging .: Ultrasonography Machine For Veterinary ApplicationKanhaiyalal RamNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound - Pelvis: What Is Pelvic Ultrasound Imaging?Document8 pagesUltrasound - Pelvis: What Is Pelvic Ultrasound Imaging?Trandafir LacramioaraNo ratings yet
- Radiologic ScienceDocument1 pageRadiologic ScienceMichael MaligsaNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic SensorDocument17 pagesUltrasonic Sensorjitenderthakur490No ratings yet
- Nama: Putu Deva Prihananta NIM: 18081001 Prodi: Teknik ElektromedikDocument3 pagesNama: Putu Deva Prihananta NIM: 18081001 Prodi: Teknik ElektromedikDeva PrihanantaNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Corrosion MonitoringDocument2 pagesUltrasonic Corrosion MonitoringMohamed AoudiNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic TestingDocument29 pagesUltrasonic TestingMeryL Ang100% (1)
- GroupA Working ManuscriptDocument9 pagesGroupA Working Manuscriptshopeemark88No ratings yet
- Prince Jorlan ADocument2 pagesPrince Jorlan ARemy BedañaNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Fact Sheet 508Document2 pagesUltrasound Fact Sheet 508CuuzonNo ratings yet
- Introduction Hafizh Cahya Aryansyah 20711034Document1 pageIntroduction Hafizh Cahya Aryansyah 20711034HAFIZH CAHYA ARYANSYAHNo ratings yet
- Instrumentasi Dan Teknologi KedokteranDocument51 pagesInstrumentasi Dan Teknologi KedokteranalfianhasbiNo ratings yet
- What Is General Ultrasound ImagingDocument12 pagesWhat Is General Ultrasound Imagingfatah.ozilNo ratings yet
- Rezonanta MagneticaDocument2 pagesRezonanta MagneticaIancu JianuNo ratings yet
- 2011 Catalog PIC Parte34Document1 page2011 Catalog PIC Parte34Paolo RossiNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Ultrasound: What Is Obstetrical Ultrasound Imaging?Document6 pagesObstetric Ultrasound: What Is Obstetrical Ultrasound Imaging?Activity ManagerNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Monitoring (A New Method For Condition Monitoring)Document4 pagesUltrasonic Monitoring (A New Method For Condition Monitoring)Ankur KumarNo ratings yet
- Uses of Ultrasound Waves - PhysicsDocument7 pagesUses of Ultrasound Waves - PhysicsKatherineNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound ApksDocument2 pagesUltrasound ApksgnjuezNo ratings yet
- Presentation 5Document30 pagesPresentation 5shannpalao06No ratings yet
- Proiect Parodontologie RACAVCIUC ANDREI EngDocument13 pagesProiect Parodontologie RACAVCIUC ANDREI EngRacavciuc AndreiNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing: Department of Mechanical Engineering, SJCITDocument22 pagesUltrasonic Testing: Department of Mechanical Engineering, SJCITgabrielNo ratings yet
- NDT IntroDocument2 pagesNDT IntrojomsedNo ratings yet
- Biology For Engineers, Unit-IVDocument33 pagesBiology For Engineers, Unit-IVtharunn6364No ratings yet
- Topic 1 Technologies in SurgeryDocument29 pagesTopic 1 Technologies in Surgeryzynna.abadiNo ratings yet
- LoopogramDocument4 pagesLoopogram15- RGIT-bsc Roja.RNo ratings yet
- Member:: Bibliographic StudyDocument6 pagesMember:: Bibliographic StudyArifNo ratings yet
- Ureteroscopy: A Comprehensive Contemporary GuideFrom EverandUreteroscopy: A Comprehensive Contemporary GuideBradley F. SchwartzNo ratings yet
- NonDocument2 pagesNonBichoy OssamaNo ratings yet
- Thermography Is A NonDocument1 pageThermography Is A NonBichoy OssamaNo ratings yet
- Non 1Document1 pageNon 1Bichoy OssamaNo ratings yet
- ThermographyDocument1 pageThermographyBichoy OssamaNo ratings yet
- NDTDocument1 pageNDTBichoy OssamaNo ratings yet
- Non Destructive TechnicsDocument1 pageNon Destructive TechnicsBichoy OssamaNo ratings yet
- MagnetoscopieDocument1 pageMagnetoscopieBichoy OssamaNo ratings yet