Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1st Year Chem
1st Year Chem
Uploaded by
Education0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageThis document contains a chemistry exam with two parts - an objective multiple choice section and a short answer subjective section. The objective section contains 10 multiple choice questions testing concepts like rate of reaction, order of reaction, radioactive decay rates, and enzyme catalysis. The subjective section contains 10 short answer questions asking about topics such as homogeneous vs heterogeneous catalysis, fast vs rate determining steps, auto-catalysis, catalytic poisoning, and characteristics of 1st order reactions and enzyme catalysis.
Original Description:
Original Title
1st year chem
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains a chemistry exam with two parts - an objective multiple choice section and a short answer subjective section. The objective section contains 10 multiple choice questions testing concepts like rate of reaction, order of reaction, radioactive decay rates, and enzyme catalysis. The subjective section contains 10 short answer questions asking about topics such as homogeneous vs heterogeneous catalysis, fast vs rate determining steps, auto-catalysis, catalytic poisoning, and characteristics of 1st order reactions and enzyme catalysis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 page1st Year Chem
1st Year Chem
Uploaded by
EducationThis document contains a chemistry exam with two parts - an objective multiple choice section and a short answer subjective section. The objective section contains 10 multiple choice questions testing concepts like rate of reaction, order of reaction, radioactive decay rates, and enzyme catalysis. The subjective section contains 10 short answer questions asking about topics such as homogeneous vs heterogeneous catalysis, fast vs rate determining steps, auto-catalysis, catalytic poisoning, and characteristics of 1st order reactions and enzyme catalysis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
CENTRAL COLLEGE MULTAN
Subject: Chemistry Max Marks: 30 Time: 1 Hour
Class:1st year Name: Roll No.
Objective Part-I
Q.No.1: You have FOUR choices for each objective type question as A, B, C and D. Choose the
option you think right. 1x10=10
i. The rate of reaction determined at any given time is called:
(A) Average rate (B) Instantaneous rate (C) Spontaneous rate (D) Overall rate
ii The rate of reaction __ as the reaction proceeds.
(A) Increases (B) Decreases (C) Remains the same (D) May decrease or Increase
iii Unit of Rate Constant is the same as that of the rate of reaction in:
(A) 0 Order Reaction (B) 1st Order Reaction (C) 2nd Order Reaction (D) 3rd Order Reaction
iv The order of decomposition of Nitrogen Pent oxide 2N2O5 ⟶ 2N2O4 + O2 is:
(A) First-order (B) Second-order (C) Third-order (D) Zero order
v All radioactive disintegration nuclear reactions are of:
(A) First-order (B) Second-order (C) Third-order (D) Zero order
vi Half-life period for U92 235is:
(A) 710 million years (B) 720 million years (C) 810 million year (D) 820 million years
vii Glucose can be converted into ethanol by an enzyme:
(A) Lipase (B) Zymase (C) Sucrose (D) Urease
viii The unit of rate constant is the same as that of the rate of reaction is:
(A) First order (B) Second order (C) Zero-order (D) Third order
ix If the rate equation of a reaction 2A + B → products is, rate =k[A] 2 [B], and A is present in
large excess, then order of reaction is
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) none of these
x With increase in 10 0C temperature, the rate of reaction doubles. This increase in rate of
reaction is due to:
(A) Decrease in activation energy of reaction
(B) Decrease in the number of collisions between reactant molecules
(C) Increase in activation energy of reactants (D) Increase in number of effective collisions
Subjective Part-II (Short Questions)
QNO#2: Give short answers of following 8x2=16
i. Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis.
ii. Differentiate between Fast step and the rate determining step.
iii. The radioactive decay is always a first order reaction, justify.
iv. Define Auto-catalysis, give example.
v. Define Catalytic poisoning.
vi. Briefly describe the following with examples that change of physical state of a
catalyst at the end of reaction.
vii. Rate of chemical reaction is an ever-changing parameter under the given
conditions, justify.
viii. What are instantaneous and average rates?
ix. Define 1st order reaction. Give example.
x. Mention the characteristics of enzyme catalysis.
You might also like
- Chapter 6 Test BankDocument80 pagesChapter 6 Test BankPam Garcia90% (10)
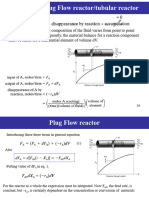
- Chemical Engineering Kinetics by J M SmithDocument626 pagesChemical Engineering Kinetics by J M SmithMahita Reddy77% (30)
- 8 PDFDocument84 pages8 PDFElijah Punzalan100% (1)
- Kinetics Ans Key Master FileDocument10 pagesKinetics Ans Key Master FileJOANA RHEA SAGPAEYNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Kinetics Lecture Notes Second Edition: July 2017Document19 pagesEnzyme Kinetics Lecture Notes Second Edition: July 2017Rao WasimNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8 Kinetics of Hydrolysis of Ethyl AcetateDocument6 pagesExercise 8 Kinetics of Hydrolysis of Ethyl AcetatePalak BansalNo ratings yet
- 1032 1st Exam 1040325 A PDFDocument8 pages1032 1st Exam 1040325 A PDFTrung TranNo ratings yet
- 3 - QP - Chemical KineticsDocument5 pages3 - QP - Chemical Kineticsssheeladevi84No ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Question BankDocument5 pagesChemical Kinetics Question BankShivam kumarNo ratings yet
- Quiz 12Document5 pagesQuiz 12Hằng ThanhNo ratings yet
- Class XII Chemical KineticsDocument6 pagesClass XII Chemical KineticsvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- (Section A) - Answer The Following For 1 Mark.Document6 pages(Section A) - Answer The Following For 1 Mark.vivek daveNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics FinalDocument7 pagesChemical Kinetics Finalaxiliya6No ratings yet
- 3 QP Chemical KineticsDocument4 pages3 QP Chemical KineticsSnehit RajNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - C18 PS1aDocument6 pagesMicrosoft Word - C18 PS1aabcdelololNo ratings yet
- CH-4 Kinetics MaterialDocument18 pagesCH-4 Kinetics MaterialBishal MishraNo ratings yet
- 2012EC 2 Semester 3 Quarter Chemistry Worksheet For Grade 11. I. Choose The Best Answer From The Given AlternativesDocument5 pages2012EC 2 Semester 3 Quarter Chemistry Worksheet For Grade 11. I. Choose The Best Answer From The Given AlternativesPatrix ParkerNo ratings yet
- Test ReviewDocument3 pagesTest ReviewgraceNo ratings yet
- PracticeMCQ D23 Mar 2024Document10 pagesPracticeMCQ D23 Mar 2024comedianyourNo ratings yet
- Option (Iii) Is The Answer.: NCERT Exemplar Solutions of Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical KineticsDocument15 pagesOption (Iii) Is The Answer.: NCERT Exemplar Solutions of Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Kineticspriyaranjan singhNo ratings yet
- Trial Exam DCS Che 12 2022 FinalDocument11 pagesTrial Exam DCS Che 12 2022 Finalnavin chhetriNo ratings yet
- Practice Sheet, CH # 9, C-I, Chemical KineticsDocument5 pagesPractice Sheet, CH # 9, C-I, Chemical Kineticsfreeacount468No ratings yet
- Class-12 Chemistry ElectroDocument4 pagesClass-12 Chemistry ElectroHemant ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- West Bengal University of TechnologyDocument4 pagesWest Bengal University of Technologysayan_dasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Equilibrium Reactions Which Factor Influences The Value of The Equilibrium Constant For A Reversible Reaction?Document10 pagesChemistry Equilibrium Reactions Which Factor Influences The Value of The Equilibrium Constant For A Reversible Reaction?Anivia12No ratings yet
- Trial Exam DCS Che 12 2022 Final (MA)Document19 pagesTrial Exam DCS Che 12 2022 Final (MA)navin chhetriNo ratings yet
- Test On Chemical KineticsDocument4 pagesTest On Chemical Kineticsdevansh dewanNo ratings yet
- Class Test Chapter 1 ChemistryDocument1 pageClass Test Chapter 1 ChemistryKhaskhali FamilyNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document6 pagesProblem Set 1XeDz DomingoNo ratings yet
- Chem. Assig.Document8 pagesChem. Assig.aryan asliaNo ratings yet
- Kinetics Lec-1 NEET ChalisaDocument35 pagesKinetics Lec-1 NEET Chalisaashustarguy005No ratings yet
- Taller CineticaQuimicaDocument27 pagesTaller CineticaQuimicaFelipeNo ratings yet
- GZB - Xii - WS-8 - Chemistry - Chemical Kinetics - OctoberDocument3 pagesGZB - Xii - WS-8 - Chemistry - Chemical Kinetics - OctoberSaman PanwarNo ratings yet
- Concordia Colleges BWP: 1 Year Chemistry Chapter#11Document2 pagesConcordia Colleges BWP: 1 Year Chemistry Chapter#11Hafiz ZainNo ratings yet
- Question On Chemical Kinetics-MA 2022Document12 pagesQuestion On Chemical Kinetics-MA 2022Sangay ChodenNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice AnswersDocument16 pagesMultiple Choice AnswersholdonpainendsNo ratings yet
- Kinetic For A2Document23 pagesKinetic For A2alvin2282No ratings yet
- CH 12 Prac Test Kinetics1Document15 pagesCH 12 Prac Test Kinetics1NolemNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics: (Physical Chemistry)Document26 pagesChemical Kinetics: (Physical Chemistry)keshavNo ratings yet
- MCH 05 2020 April Final Exam Option OneDocument20 pagesMCH 05 2020 April Final Exam Option Onepaul kapambweNo ratings yet
- Kinetics IntroductionDocument55 pagesKinetics IntroductionAgano juma mwakasendoNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Ut-1 Question Paper ChemistryDocument19 pagesClass 12 Ut-1 Question Paper ChemistryArun singhNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 CHEMICAL KINETICS 2017Document10 pagesUnit 4 CHEMICAL KINETICS 2017Gaurav SharmaNo ratings yet
- I. Select The Most Appropriate Answer: Marks ScoredDocument5 pagesI. Select The Most Appropriate Answer: Marks Scoredshishir kafleNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Chemistry Revision Assignment For Test 11Document6 pages1st Year Chemistry Revision Assignment For Test 11Syed Moeen NaqviNo ratings yet
- Answer: A: General Chemistry Exam Practice Questions - CH 14Document10 pagesAnswer: A: General Chemistry Exam Practice Questions - CH 14فاطمة كليبNo ratings yet
- Circle The Correct Answer Choice For Each of The Following QuestionsDocument5 pagesCircle The Correct Answer Choice For Each of The Following QuestionsRonnyNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument3 pagesChemical Kineticsvivek daveNo ratings yet
- Bioprocess Principles & Ipc QPDocument2 pagesBioprocess Principles & Ipc QPmayank kushwahaNo ratings yet
- 2 July Physical Pharmaceutics 403 TDocument2 pages2 July Physical Pharmaceutics 403 TRaja RajaNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY 12th SubejctiveDocument3 pagesCHEMISTRY 12th SubejctiveVivek SanwalNo ratings yet
- Kinetic 1 LDocument3 pagesKinetic 1 Leman abdulghanyNo ratings yet
- Big Idea 4 AnswersDocument4 pagesBig Idea 4 AnswersSreeyaNo ratings yet
- Kinetics Multiple Choice and Free Response With KeyDocument29 pagesKinetics Multiple Choice and Free Response With KeyPatrícia Cardoso GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- o6qCo1WM19qPS7UpMm41Whdw2jhS6i2R 8F9KryfZS2eKzl9OH9mqk9cDocument27 pageso6qCo1WM19qPS7UpMm41Whdw2jhS6i2R 8F9KryfZS2eKzl9OH9mqk9cAZAIN K.O.No ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics AssignmentDocument3 pagesChemical Kinetics Assignmentjainaba mohamedNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Engineering MCQs PDFDocument62 pagesChemical Reaction Engineering MCQs PDFKamran Islam100% (2)
- DPP (Chemistry) Chemical KineticsDocument6 pagesDPP (Chemistry) Chemical KineticsNavinNo ratings yet
- AP Chem Ch12 Practice QuizDocument8 pagesAP Chem Ch12 Practice QuizlhijeanNo ratings yet
- FTW1Document52 pagesFTW1pubgkrpg09No ratings yet
- L18 CVD and Catalyst DeactivationDocument17 pagesL18 CVD and Catalyst DeactivationjeffreypabzNo ratings yet
- CMC Chapter 16 (1) - 1Document84 pagesCMC Chapter 16 (1) - 1Raghad AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemistry Faculty of Science and Mathematics Universiti Pendidikan Sultan Idris SKU1023 SEM 2 2017/2018Document3 pagesDepartment of Chemistry Faculty of Science and Mathematics Universiti Pendidikan Sultan Idris SKU1023 SEM 2 2017/2018Marco AdenNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Mind MapDocument1 pageChemical Kinetics Mind MapSamridhi MoudgilNo ratings yet
- SABONDocument11 pagesSABONKarl Sebastien Dejito ConosNo ratings yet
- CH307 Inorganic Kinetics: Dr. Andrea Erxleben Room C150 Andrea - Erxleben@nuigalway - IeDocument50 pagesCH307 Inorganic Kinetics: Dr. Andrea Erxleben Room C150 Andrea - Erxleben@nuigalway - Ieneel721507No ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics NumDocument3 pagesChemical Kinetics NumVANESSA JOHNS CLASS XINo ratings yet
- Kinetics of Reaction: The Iodine Clock RotationDocument13 pagesKinetics of Reaction: The Iodine Clock RotationDavid Lemuel del PradoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 InhibitorsDocument12 pagesLesson 6 Inhibitorstbrook2017No ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Engineering (CRE) Is TheDocument24 pagesChemical Reaction Engineering (CRE) Is TheVaibhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - Chemical Kinetics Answers - Suggested 2022Document12 pagesTutorial 1 - Chemical Kinetics Answers - Suggested 2022Phương LêNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Chemical KineticsDocument7 pagesChapter 4 - Chemical KineticsMADHAVNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Reaction Rate 22-23Document92 pages1.1 Reaction Rate 22-23m-423224No ratings yet
- 4 Chemical KineticsDocument96 pages4 Chemical Kineticsforojaypee2002No ratings yet
- PhysicalScience11 - Module5 - Collision Theory - CatalystDocument16 pagesPhysicalScience11 - Module5 - Collision Theory - CatalystRenny Romero Luzada100% (11)
- 5 Yield PDFDocument2 pages5 Yield PDFNur AishaNo ratings yet
- Collision TheoryDocument66 pagesCollision TheoryPAUL BENEDICT MORENO MENDOZANo ratings yet
- Q: 2 Attempt Any Three of The Following Question (12) : InstructionsDocument2 pagesQ: 2 Attempt Any Three of The Following Question (12) : InstructionsSmruthi SuvarnaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetic Isotope EffectDocument43 pagesChemical Kinetic Isotope Effecttumman lal SahuNo ratings yet
- CH6 Pt. 2Document6 pagesCH6 Pt. 2Ken LaguiabNo ratings yet
- ch16 Lecture 8e GOODDocument105 pagesch16 Lecture 8e GOODJana Mae Catot AcabalNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - Topic 11 Kinetics - Edexcel IAL Chemistry A-LevelDocument69 pagesFlashcards - Topic 11 Kinetics - Edexcel IAL Chemistry A-LevelzuveriaNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Collision Theory Rates of ReactionDocument6 pages6.1 Collision Theory Rates of ReactionMarshNo ratings yet
- Practice Rate Law ProblemsDocument6 pagesPractice Rate Law ProblemsPatriciaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial For Chapter 23Document9 pagesTutorial For Chapter 23Thurgah VshinyNo ratings yet
- (Final Version) Lesson 3 - Kinetics of Homogeneous ReactionDocument27 pages(Final Version) Lesson 3 - Kinetics of Homogeneous Reaction霓裳羽衣No ratings yet