Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Permeability
Permeability
Uploaded by
Srimonta RoyCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Sensors 19 03631Document24 pagesSensors 19 03631Praveen Kumar JeyaprakashNo ratings yet
- Sensors 19 03631Document24 pagesSensors 19 03631Alam Castillo HerreraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computational Fluid DynamicsDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Computational Fluid DynamicsJonyzhitop TenorioNo ratings yet
- Conclusions and RecommendationsDocument2 pagesConclusions and RecommendationsLndIngenieriaNo ratings yet
- Definition of CFDDocument2 pagesDefinition of CFDKabir ShafayatNo ratings yet
- Feature Based VisualisationDocument18 pagesFeature Based VisualisationRider RanjithNo ratings yet
- What Is CFDDocument2 pagesWhat Is CFDJerry MateoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3, CFD TheoryDocument32 pagesChapter 3, CFD TheoryAnil Frivolous AbstemiousNo ratings yet
- Loosely Coupled MethodDocument18 pagesLoosely Coupled MethodMadhu Kiran Reddy MuliNo ratings yet
- Fluid AssignmentDocument23 pagesFluid AssignmentYush KumarNo ratings yet
- Euclid - Jam.1350488796 GoodDocument14 pagesEuclid - Jam.1350488796 GoodWei GaoNo ratings yet
- Gradual Variation Analysis For Groundwater Flow: Lchen@udc - EduDocument12 pagesGradual Variation Analysis For Groundwater Flow: Lchen@udc - EduAna Beatriz Rubio ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Fluidos y Aplicacion BiomecanicaDocument6 pagesFluidos y Aplicacion BiomecanicaSheyla Balvin RojasNo ratings yet
- ATOMIZAÇÃO phd8Document9 pagesATOMIZAÇÃO phd8eustaccoNo ratings yet
- CFD Short Notes-QuestionsDocument8 pagesCFD Short Notes-Questionsaaron prakashNo ratings yet
- Grwater Model PDFDocument55 pagesGrwater Model PDFmartin andres zapata hoyosNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Eqt 534: Finite Difference Method For Partial Differential Equations Name: Nurul Izham Bin M Shukeri MATRIC NO: 1632121977 Lecturer: Dr. Nursalasawati RusliDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 Eqt 534: Finite Difference Method For Partial Differential Equations Name: Nurul Izham Bin M Shukeri MATRIC NO: 1632121977 Lecturer: Dr. Nursalasawati RusliSyaza Label HijabNo ratings yet
- What Is CFD?: Fluid DynamicsDocument2 pagesWhat Is CFD?: Fluid DynamicsVasanth AradhyaNo ratings yet
- Water: A Novel, Coupled CFD-DEM Model For The Flow Characteristics of Particles Inside A PipeDocument23 pagesWater: A Novel, Coupled CFD-DEM Model For The Flow Characteristics of Particles Inside A PipemnoNo ratings yet
- A Review On The Numerical Inversion Methods of Relative Permeability CurvesDocument6 pagesA Review On The Numerical Inversion Methods of Relative Permeability Curvesjsotofmet4918No ratings yet
- CPK GW ModellingDocument12 pagesCPK GW ModellingBALJINDER SINGHNo ratings yet
- A Kinematic Controller For Liquid Pouring BetweenDocument22 pagesA Kinematic Controller For Liquid Pouring BetweenAhmad Shuja ChughtaiNo ratings yet
- Computational Fluid Mechanics Simulation and Computation With Gambit and FluentDocument69 pagesComputational Fluid Mechanics Simulation and Computation With Gambit and FluentYush KumarNo ratings yet
- Computational Fluid DynamicsDocument4 pagesComputational Fluid DynamicsAravind ManneNo ratings yet
- 2016 TVC Video Based Fluid ReconstructionDocument14 pages2016 TVC Video Based Fluid Reconstruction会爆炸的小米NoteNo ratings yet
- Importance of CFDDocument1 pageImportance of CFDHamood Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Predicting High-Resolution Turbulence Details in Space and TimeDocument16 pagesPredicting High-Resolution Turbulence Details in Space and TimeasdfNo ratings yet
- Difference Between FEM FDM and FVMDocument5 pagesDifference Between FEM FDM and FVMRafael Santos RoqueNo ratings yet
- Fluids: Application of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Proxy Modeling For Fluid Flow in Porous MediaDocument17 pagesFluids: Application of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Proxy Modeling For Fluid Flow in Porous MediaramatamaNo ratings yet
- Basie Ro 2017Document4 pagesBasie Ro 2017Nazario HuarachiNo ratings yet
- Multiscale Fluid Mechanics and Modeling: SciencedirectDocument15 pagesMultiscale Fluid Mechanics and Modeling: SciencedirectdiegoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Control Using The Adjoint MethodDocument8 pagesFluid Control Using The Adjoint MethodAmir JoonNo ratings yet
- Spe 79709 Pa P PDFDocument9 pagesSpe 79709 Pa P PDFtomk2220No ratings yet
- Water: Calibration Procedure For Water Distribution Systems: Comparison Among Hydraulic ModelsDocument18 pagesWater: Calibration Procedure For Water Distribution Systems: Comparison Among Hydraulic ModelsWaheed AhmadNo ratings yet
- Presentation On CFD 2Document17 pagesPresentation On CFD 220MVB325 Md Abdur RahimNo ratings yet
- C CC C C CDocument6 pagesC CC C C Canushka56No ratings yet
- NHT 2023Document11 pagesNHT 2023Bishwajit MajiNo ratings yet
- Modeling Solid-Liquid Settling System As A Two-Phase Flow ProblemDocument6 pagesModeling Solid-Liquid Settling System As A Two-Phase Flow ProblemNagaswarupini SundarajNo ratings yet
- CFD IntroductionDocument1 pageCFD IntroductionbennyNo ratings yet
- Particle-Based Liquid Control Using Animation TemplatesDocument10 pagesParticle-Based Liquid Control Using Animation TemplatesBozko LPNo ratings yet
- Simon Stegmaier, Ulrich Rist and Thomas Ertl - Opening The Can of Worms: An Exploration Tool For Vortical FlowsDocument8 pagesSimon Stegmaier, Ulrich Rist and Thomas Ertl - Opening The Can of Worms: An Exploration Tool For Vortical FlowsJuaxmawNo ratings yet
- Simulation AnswersDocument13 pagesSimulation AnswerspgkortzasNo ratings yet
- DEM ReportDocument37 pagesDEM ReportMostafa TaghaviNo ratings yet
- Zhi Quan Leong, Dev Ranmuthugala, Irene Penesis and Hung Duc Nguyen University of Tasmania / Australian Maritime College E-Mail(s)Document7 pagesZhi Quan Leong, Dev Ranmuthugala, Irene Penesis and Hung Duc Nguyen University of Tasmania / Australian Maritime College E-Mail(s)pvdaiNo ratings yet
- Water Resources Research - 2013 - Sheng - Dynamic Coupling of Pore Scale and Reservoir Scale Models For Multiphase FlowDocument16 pagesWater Resources Research - 2013 - Sheng - Dynamic Coupling of Pore Scale and Reservoir Scale Models For Multiphase Flowvcox4460No ratings yet
- Water 10 01440Document16 pagesWater 10 01440مهندس ابينNo ratings yet
- Methods of Analysis: NPTEL, IIT Kharagpur, Prof. Gargi Das, Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument3 pagesMethods of Analysis: NPTEL, IIT Kharagpur, Prof. Gargi Das, Department of Chemical Engineeringأحمد إبراهيم شواربNo ratings yet
- Use of Computational Fluid Dynamics CFD in Teaching Fluid MechanicsDocument13 pagesUse of Computational Fluid Dynamics CFD in Teaching Fluid MechanicsRayner BarrosNo ratings yet
- CFDDocument2 pagesCFDRatnakar ChodapaneediNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: Components of Set-UpDocument7 pagesAcknowledgement: Components of Set-UpSaurabh SumanNo ratings yet
- HD4Document1 pageHD4bennyNo ratings yet
- Example-Based Turbulence Style Transfer: Syuhei Sato, Yoshinori Dobashi, Theodore Kim, Tomoyuki NishitaDocument9 pagesExample-Based Turbulence Style Transfer: Syuhei Sato, Yoshinori Dobashi, Theodore Kim, Tomoyuki Nishitabob sunNo ratings yet
- TUBO - MIDTERM LectureDocument1 pageTUBO - MIDTERM LectureZy LangNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computational Fluid DynamicsDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Computational Fluid DynamicsArchana RajputNo ratings yet
- Journal of Computational Physics: Xiaosong Sun, Mikio Sakai, Yoshinori YamadaDocument30 pagesJournal of Computational Physics: Xiaosong Sun, Mikio Sakai, Yoshinori YamadaMuhammad Adnan LaghariNo ratings yet
- 2016 - TompsonDocument10 pages2016 - TompsonJosephNo ratings yet
- A Computational Model For Suspended Large Rigid Bodies in 3D Unsteady Viscous Flows XiaoDocument32 pagesA Computational Model For Suspended Large Rigid Bodies in 3D Unsteady Viscous Flows XiaowatersakanaNo ratings yet
- Optical Flow: Exploring Dynamic Visual Patterns in Computer VisionFrom EverandOptical Flow: Exploring Dynamic Visual Patterns in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- PN Junction Theory For Semiconductor Diodes 2Document3 pagesPN Junction Theory For Semiconductor Diodes 2Srimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- Group C (150815 150817 150818 150819 150820Document1 pageGroup C (150815 150817 150818 150819 150820Srimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Basics & Semiconductor Physics Tutorial 1Document5 pagesSemiconductor Basics & Semiconductor Physics Tutorial 1Srimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- Why Do Semiconductors Have A Band Gap - QuoraDocument2 pagesWhy Do Semiconductors Have A Band Gap - QuoraSrimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode As Voltage Regulator Tutorial 4Document5 pagesZener Diode As Voltage Regulator Tutorial 4Srimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- Group B (150810,150811,150812,150813,150814)Document1 pageGroup B (150810,150811,150812,150813,150814)Srimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- ReservoirDocument1 pageReservoirSrimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- Group No E (150827,150828, 140807, 140813, 140820)Document1 pageGroup No E (150827,150828, 140807, 140813, 140820)Srimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- Group No A (150801,02,03,06,08,09)Document1 pageGroup No A (150801,02,03,06,08,09)Srimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- Lubricant TestDocument1 pageLubricant TestSrimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- SaturationDocument1 pageSaturationSrimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledSrimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 01 PDFDocument16 pagesAssignment - 01 PDFSrimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- PorosityDocument1 pagePorositySrimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- Conventional and Unconventional GasDocument2 pagesConventional and Unconventional GasSrimonta RoyNo ratings yet
Permeability
Permeability
Uploaded by
Srimonta RoyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Permeability
Permeability
Uploaded by
Srimonta RoyCopyright:
Available Formats
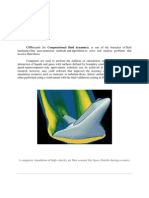
The permeability method, also known as the equivalent fluid method or the fictitious
fluid method, is a numerical technique used in computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to
model the flow of fluids around solid objects. It is often used when the object's
geometry is complex, and analytical solutions are not feasible.
The method involves replacing the solid object with a fictitious fluid that has the same
geometry as the object. The properties of this fictitious fluid, such as its density and
viscosity, are chosen to be similar to those of the fluid that is actually present. The
equations of motion for the fluid flow are then solved using computational techniques,
taking into account the presence of the fictitious fluid.
The main advantage of the permeability method is that it allows for the simulation of
complex geometries that would be difficult to model using other techniques.
Additionally, the method is computationally efficient and can provide results quickly.
However, there are some limitations to the method. One of the most significant
limitations is that it assumes that the flow around the object is two-dimensional and
steady, which is not always the case in real-world situations. Additionally, the accuracy of
the method depends on the choice of properties for the fictitious fluid, which can be
challenging to determine in some cases.
You might also like
- Sensors 19 03631Document24 pagesSensors 19 03631Praveen Kumar JeyaprakashNo ratings yet
- Sensors 19 03631Document24 pagesSensors 19 03631Alam Castillo HerreraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computational Fluid DynamicsDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Computational Fluid DynamicsJonyzhitop TenorioNo ratings yet
- Conclusions and RecommendationsDocument2 pagesConclusions and RecommendationsLndIngenieriaNo ratings yet
- Definition of CFDDocument2 pagesDefinition of CFDKabir ShafayatNo ratings yet
- Feature Based VisualisationDocument18 pagesFeature Based VisualisationRider RanjithNo ratings yet
- What Is CFDDocument2 pagesWhat Is CFDJerry MateoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3, CFD TheoryDocument32 pagesChapter 3, CFD TheoryAnil Frivolous AbstemiousNo ratings yet
- Loosely Coupled MethodDocument18 pagesLoosely Coupled MethodMadhu Kiran Reddy MuliNo ratings yet
- Fluid AssignmentDocument23 pagesFluid AssignmentYush KumarNo ratings yet
- Euclid - Jam.1350488796 GoodDocument14 pagesEuclid - Jam.1350488796 GoodWei GaoNo ratings yet
- Gradual Variation Analysis For Groundwater Flow: Lchen@udc - EduDocument12 pagesGradual Variation Analysis For Groundwater Flow: Lchen@udc - EduAna Beatriz Rubio ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Fluidos y Aplicacion BiomecanicaDocument6 pagesFluidos y Aplicacion BiomecanicaSheyla Balvin RojasNo ratings yet
- ATOMIZAÇÃO phd8Document9 pagesATOMIZAÇÃO phd8eustaccoNo ratings yet
- CFD Short Notes-QuestionsDocument8 pagesCFD Short Notes-Questionsaaron prakashNo ratings yet
- Grwater Model PDFDocument55 pagesGrwater Model PDFmartin andres zapata hoyosNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Eqt 534: Finite Difference Method For Partial Differential Equations Name: Nurul Izham Bin M Shukeri MATRIC NO: 1632121977 Lecturer: Dr. Nursalasawati RusliDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 Eqt 534: Finite Difference Method For Partial Differential Equations Name: Nurul Izham Bin M Shukeri MATRIC NO: 1632121977 Lecturer: Dr. Nursalasawati RusliSyaza Label HijabNo ratings yet
- What Is CFD?: Fluid DynamicsDocument2 pagesWhat Is CFD?: Fluid DynamicsVasanth AradhyaNo ratings yet
- Water: A Novel, Coupled CFD-DEM Model For The Flow Characteristics of Particles Inside A PipeDocument23 pagesWater: A Novel, Coupled CFD-DEM Model For The Flow Characteristics of Particles Inside A PipemnoNo ratings yet
- A Review On The Numerical Inversion Methods of Relative Permeability CurvesDocument6 pagesA Review On The Numerical Inversion Methods of Relative Permeability Curvesjsotofmet4918No ratings yet
- CPK GW ModellingDocument12 pagesCPK GW ModellingBALJINDER SINGHNo ratings yet
- A Kinematic Controller For Liquid Pouring BetweenDocument22 pagesA Kinematic Controller For Liquid Pouring BetweenAhmad Shuja ChughtaiNo ratings yet
- Computational Fluid Mechanics Simulation and Computation With Gambit and FluentDocument69 pagesComputational Fluid Mechanics Simulation and Computation With Gambit and FluentYush KumarNo ratings yet
- Computational Fluid DynamicsDocument4 pagesComputational Fluid DynamicsAravind ManneNo ratings yet
- 2016 TVC Video Based Fluid ReconstructionDocument14 pages2016 TVC Video Based Fluid Reconstruction会爆炸的小米NoteNo ratings yet
- Importance of CFDDocument1 pageImportance of CFDHamood Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Predicting High-Resolution Turbulence Details in Space and TimeDocument16 pagesPredicting High-Resolution Turbulence Details in Space and TimeasdfNo ratings yet
- Difference Between FEM FDM and FVMDocument5 pagesDifference Between FEM FDM and FVMRafael Santos RoqueNo ratings yet
- Fluids: Application of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Proxy Modeling For Fluid Flow in Porous MediaDocument17 pagesFluids: Application of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Proxy Modeling For Fluid Flow in Porous MediaramatamaNo ratings yet
- Basie Ro 2017Document4 pagesBasie Ro 2017Nazario HuarachiNo ratings yet
- Multiscale Fluid Mechanics and Modeling: SciencedirectDocument15 pagesMultiscale Fluid Mechanics and Modeling: SciencedirectdiegoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Control Using The Adjoint MethodDocument8 pagesFluid Control Using The Adjoint MethodAmir JoonNo ratings yet
- Spe 79709 Pa P PDFDocument9 pagesSpe 79709 Pa P PDFtomk2220No ratings yet
- Water: Calibration Procedure For Water Distribution Systems: Comparison Among Hydraulic ModelsDocument18 pagesWater: Calibration Procedure For Water Distribution Systems: Comparison Among Hydraulic ModelsWaheed AhmadNo ratings yet
- Presentation On CFD 2Document17 pagesPresentation On CFD 220MVB325 Md Abdur RahimNo ratings yet
- C CC C C CDocument6 pagesC CC C C Canushka56No ratings yet
- NHT 2023Document11 pagesNHT 2023Bishwajit MajiNo ratings yet
- Modeling Solid-Liquid Settling System As A Two-Phase Flow ProblemDocument6 pagesModeling Solid-Liquid Settling System As A Two-Phase Flow ProblemNagaswarupini SundarajNo ratings yet
- CFD IntroductionDocument1 pageCFD IntroductionbennyNo ratings yet
- Particle-Based Liquid Control Using Animation TemplatesDocument10 pagesParticle-Based Liquid Control Using Animation TemplatesBozko LPNo ratings yet
- Simon Stegmaier, Ulrich Rist and Thomas Ertl - Opening The Can of Worms: An Exploration Tool For Vortical FlowsDocument8 pagesSimon Stegmaier, Ulrich Rist and Thomas Ertl - Opening The Can of Worms: An Exploration Tool For Vortical FlowsJuaxmawNo ratings yet
- Simulation AnswersDocument13 pagesSimulation AnswerspgkortzasNo ratings yet
- DEM ReportDocument37 pagesDEM ReportMostafa TaghaviNo ratings yet
- Zhi Quan Leong, Dev Ranmuthugala, Irene Penesis and Hung Duc Nguyen University of Tasmania / Australian Maritime College E-Mail(s)Document7 pagesZhi Quan Leong, Dev Ranmuthugala, Irene Penesis and Hung Duc Nguyen University of Tasmania / Australian Maritime College E-Mail(s)pvdaiNo ratings yet
- Water Resources Research - 2013 - Sheng - Dynamic Coupling of Pore Scale and Reservoir Scale Models For Multiphase FlowDocument16 pagesWater Resources Research - 2013 - Sheng - Dynamic Coupling of Pore Scale and Reservoir Scale Models For Multiphase Flowvcox4460No ratings yet
- Water 10 01440Document16 pagesWater 10 01440مهندس ابينNo ratings yet
- Methods of Analysis: NPTEL, IIT Kharagpur, Prof. Gargi Das, Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument3 pagesMethods of Analysis: NPTEL, IIT Kharagpur, Prof. Gargi Das, Department of Chemical Engineeringأحمد إبراهيم شواربNo ratings yet
- Use of Computational Fluid Dynamics CFD in Teaching Fluid MechanicsDocument13 pagesUse of Computational Fluid Dynamics CFD in Teaching Fluid MechanicsRayner BarrosNo ratings yet
- CFDDocument2 pagesCFDRatnakar ChodapaneediNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: Components of Set-UpDocument7 pagesAcknowledgement: Components of Set-UpSaurabh SumanNo ratings yet
- HD4Document1 pageHD4bennyNo ratings yet
- Example-Based Turbulence Style Transfer: Syuhei Sato, Yoshinori Dobashi, Theodore Kim, Tomoyuki NishitaDocument9 pagesExample-Based Turbulence Style Transfer: Syuhei Sato, Yoshinori Dobashi, Theodore Kim, Tomoyuki Nishitabob sunNo ratings yet
- TUBO - MIDTERM LectureDocument1 pageTUBO - MIDTERM LectureZy LangNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computational Fluid DynamicsDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Computational Fluid DynamicsArchana RajputNo ratings yet
- Journal of Computational Physics: Xiaosong Sun, Mikio Sakai, Yoshinori YamadaDocument30 pagesJournal of Computational Physics: Xiaosong Sun, Mikio Sakai, Yoshinori YamadaMuhammad Adnan LaghariNo ratings yet
- 2016 - TompsonDocument10 pages2016 - TompsonJosephNo ratings yet
- A Computational Model For Suspended Large Rigid Bodies in 3D Unsteady Viscous Flows XiaoDocument32 pagesA Computational Model For Suspended Large Rigid Bodies in 3D Unsteady Viscous Flows XiaowatersakanaNo ratings yet
- Optical Flow: Exploring Dynamic Visual Patterns in Computer VisionFrom EverandOptical Flow: Exploring Dynamic Visual Patterns in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- PN Junction Theory For Semiconductor Diodes 2Document3 pagesPN Junction Theory For Semiconductor Diodes 2Srimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- Group C (150815 150817 150818 150819 150820Document1 pageGroup C (150815 150817 150818 150819 150820Srimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Basics & Semiconductor Physics Tutorial 1Document5 pagesSemiconductor Basics & Semiconductor Physics Tutorial 1Srimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- Why Do Semiconductors Have A Band Gap - QuoraDocument2 pagesWhy Do Semiconductors Have A Band Gap - QuoraSrimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode As Voltage Regulator Tutorial 4Document5 pagesZener Diode As Voltage Regulator Tutorial 4Srimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- Group B (150810,150811,150812,150813,150814)Document1 pageGroup B (150810,150811,150812,150813,150814)Srimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- ReservoirDocument1 pageReservoirSrimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- Group No E (150827,150828, 140807, 140813, 140820)Document1 pageGroup No E (150827,150828, 140807, 140813, 140820)Srimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- Group No A (150801,02,03,06,08,09)Document1 pageGroup No A (150801,02,03,06,08,09)Srimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- Lubricant TestDocument1 pageLubricant TestSrimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- SaturationDocument1 pageSaturationSrimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledSrimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 01 PDFDocument16 pagesAssignment - 01 PDFSrimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- PorosityDocument1 pagePorositySrimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- Conventional and Unconventional GasDocument2 pagesConventional and Unconventional GasSrimonta RoyNo ratings yet