Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
Rasheda PickettCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Clil Lesson Plan TemplateDocument5 pagesClil Lesson Plan Templatesandovalz24433% (3)
- Becoming The Perfect Daughter - Spacer XDocument414 pagesBecoming The Perfect Daughter - Spacer XSergio Seferino33% (3)
- Administering An IntradermalDocument7 pagesAdministering An IntradermalCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Colloidalt Gold and Silver - Production of Colloidal Gold With Electrolysis and Green SynthesisDocument14 pagesColloidalt Gold and Silver - Production of Colloidal Gold With Electrolysis and Green SynthesisDevon Narok100% (1)
- IntramuscularDocument4 pagesIntramusculargaatgaatNo ratings yet
- PRS Ear Instillation - GlovaDocument3 pagesPRS Ear Instillation - GlovaAndrea Colleen GlovaNo ratings yet
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology College of NursingDocument47 pagesMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology College of NursingBella OllieNo ratings yet
- Animals Are People TooDocument2 pagesAnimals Are People TooTashini LileeNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Shortcuts Part 1 PDFDocument102 pagesEnglish Grammar Shortcuts Part 1 PDFRitesh Sahu100% (3)
- Terex RT 780. 80 Ton RTDocument20 pagesTerex RT 780. 80 Ton RTBhavana Kewlani67% (3)
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Ins Tute of Technology College of NursingDocument4 pagesMindanao State University - Iligan Ins Tute of Technology College of NursingNessy Nicholle SatruionNo ratings yet
- Administering Medication Via A SmallDocument6 pagesAdministering Medication Via A SmallAndrea Bayaga WaganNo ratings yet
- Checklist With Rationale For Intradermal & Intramuscular InjectionDocument8 pagesChecklist With Rationale For Intradermal & Intramuscular InjectionClarice Jamille RazonNo ratings yet
- Administering Medication Via Small-Volume Nebulizer DefinitionDocument5 pagesAdministering Medication Via Small-Volume Nebulizer DefinitionNessy Nicholle SatruionNo ratings yet
- Adding Medication To IV Fluid ContainerDocument14 pagesAdding Medication To IV Fluid Containerjennielunay00No ratings yet
- RLE PrelimsDocument8 pagesRLE PrelimsNicole VallejosNo ratings yet
- ID Checklist RATIONALEDocument42 pagesID Checklist RATIONALEAT4-11 HUMSS 2 CEDRICK ILAONo ratings yet
- Administering Nasal MedicationsDocument4 pagesAdministering Nasal MedicationsNessy Nicholle SatruionNo ratings yet
- Procedure Checklist Oral Medication AdministrationDocument4 pagesProcedure Checklist Oral Medication AdministrationRochel HatagueNo ratings yet
- Administering Medication Via A Metered Dose InhalerDocument7 pagesAdministering Medication Via A Metered Dose InhalerGio TalomiaNo ratings yet
- Iv Drug Preperation: Gina S. Cuenca, RN, MNDocument49 pagesIv Drug Preperation: Gina S. Cuenca, RN, MNJainah Rose Ferrer GubacNo ratings yet
- NUR 204.administering Medications by IV Bolus or Push Through IV InfusionDocument42 pagesNUR 204.administering Medications by IV Bolus or Push Through IV InfusionKouta SanNo ratings yet
- Administering Oral Medication (Print)Document5 pagesAdministering Oral Medication (Print)Binoy Serino100% (1)
- Instilling Otic/Ear Drops Procedure RationaleDocument12 pagesInstilling Otic/Ear Drops Procedure RationaleBSN2-F MASINING NA PAGPAPAHAYAGNo ratings yet
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology College of NursingDocument5 pagesMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology College of NursingNessy Nicholle SatruionNo ratings yet
- Procedure Oral Medication Administration RevisedDocument4 pagesProcedure Oral Medication Administration Revised4rrzbdpg8bNo ratings yet
- Administration of IV Medication e ToolDocument6 pagesAdministration of IV Medication e ToolMaria Sofia Stephanie SatoriNo ratings yet
- Intra MuscularDocument4 pagesIntra MuscularAT4-11 HUMSS 2 CEDRICK ILAONo ratings yet
- Adding Medications To Intravenous Fluid ContainersDocument2 pagesAdding Medications To Intravenous Fluid ContainersJemina Rafanan RacadioNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Western Mindanao State University College of Nursing Zamboanga CityDocument12 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Western Mindanao State University College of Nursing Zamboanga CityChristine Joy MolinaNo ratings yet
- Administering Cytotoxic Drug by Bolus InjectionDocument2 pagesAdministering Cytotoxic Drug by Bolus InjectionErika GusiNo ratings yet
- PDF Parenteral 024144Document46 pagesPDF Parenteral 024144Jamilah SidicNo ratings yet
- IV Meds in Volumetric Set C RationaleDocument2 pagesIV Meds in Volumetric Set C RationalePascal Marie IzhaqNo ratings yet
- VASQUEZ - BSN2A - Priming, Starting, and Discontinuation of IV Solution (Procedure and Rationale)Document5 pagesVASQUEZ - BSN2A - Priming, Starting, and Discontinuation of IV Solution (Procedure and Rationale)Mari Sheanne M. VasquezNo ratings yet
- OM VP and ID P and RDocument5 pagesOM VP and ID P and RTamara Kate HalicanNo ratings yet
- Children's Community Nursing Team - SOP 11 - Intravenous Medication Via A Central Venous LineDocument8 pagesChildren's Community Nursing Team - SOP 11 - Intravenous Medication Via A Central Venous Linezaenal abidinNo ratings yet
- Albumin Piggyback Procedure ChecklistDocument3 pagesAlbumin Piggyback Procedure ChecklistAljane VistoNo ratings yet
- Bns Respi Cardio ProceduresDocument60 pagesBns Respi Cardio Proceduressinuaish syaNo ratings yet
- Procedures RationaleDocument3 pagesProcedures RationaleJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- Rectal Suppository Procedure With Rationale 1Document5 pagesRectal Suppository Procedure With Rationale 1yuuki konnoNo ratings yet
- Administration Eye DropsDocument13 pagesAdministration Eye DropsyaraNo ratings yet
- Adding Medications To An Existing IvfDocument2 pagesAdding Medications To An Existing Ivfpretty_maryNo ratings yet
- Module-Intradermal Etool PDFDocument7 pagesModule-Intradermal Etool PDFErika Danalle ArceoNo ratings yet
- Eye Ear Med Instillation Procedure RationaleDocument6 pagesEye Ear Med Instillation Procedure Rationaleyuuki konnoNo ratings yet
- Drug Admin (Dragged) 4Document1 pageDrug Admin (Dragged) 4ebray7472No ratings yet
- Mixing InsulinDocument2 pagesMixing Insulinadrian lozanoNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes Checklist ProceduresDocument4 pagesFluid and Electrolytes Checklist ProceduresJamaica Leslie Noveno0% (1)
- Administering Oral Medications: Melendez, Anna Carmela PDocument19 pagesAdministering Oral Medications: Melendez, Anna Carmela PAnna Carmela P. MelendezNo ratings yet
- Tri LalaDocument5 pagesTri LalaHarvey T. Dato-onNo ratings yet
- Administrasi Vaksin PDFDocument34 pagesAdministrasi Vaksin PDFerindah puspowatiNo ratings yet
- IV InjectionDocument10 pagesIV Injectionpreeti sharmaNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Therapy: Level 1 NSL Manual: FundamentalsDocument8 pagesIntravenous Therapy: Level 1 NSL Manual: FundamentalsPrecious Ingrid Dolor DenostaNo ratings yet
- 12 Rights of Administering Medication PDF Dose (Biochemistry) ChemistryDocument1 page12 Rights of Administering Medication PDF Dose (Biochemistry) ChemistryTina Michelle DazaNo ratings yet
- Sajo College of Nursing Sciences Birnin Kebbi, Kebbi State: Unit IxDocument22 pagesSajo College of Nursing Sciences Birnin Kebbi, Kebbi State: Unit IxyusufNo ratings yet
- CUNANAN - Changing Monitoring Discontinuing IVFDocument6 pagesCUNANAN - Changing Monitoring Discontinuing IVFAbbyNo ratings yet
- Administering Medications by Intravenous Bolus or Push Through An Intravenous InfusionDocument3 pagesAdministering Medications by Intravenous Bolus or Push Through An Intravenous Infusionchalinsammy1No ratings yet
- 029 Medication TrayDocument3 pages029 Medication TrayS BindhiyaNo ratings yet
- Nur 1208 2021 Prep of MedsDocument38 pagesNur 1208 2021 Prep of MedsDannielle EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- IntradermalDocument7 pagesIntradermalKyle Dapulag100% (1)
- Checklists For Midterm 2: Common Steps For Preparing MedicationsDocument45 pagesChecklists For Midterm 2: Common Steps For Preparing MedicationsPatricia Anne Nicole CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Medications Name: Date: Oral MedicationsDocument21 pagesMedications Name: Date: Oral MedicationsDONITA DALUMPINESNo ratings yet
- IthinkaboutyoualotDocument5 pagesIthinkaboutyoualotpgumbanNo ratings yet
- Checklist Administering An Intramuscular InjectionDocument3 pagesChecklist Administering An Intramuscular InjectionCAMPOSANO, JHANNA MARIENo ratings yet
- IV TherapyDocument7 pagesIV TherapyJerika Shane MañosoNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Crisis: Information and Help in the 2020 Pandemic - What Everyone Should KnowFrom EverandCoronavirus Crisis: Information and Help in the 2020 Pandemic - What Everyone Should KnowNo ratings yet
- Corona Virus: Information You Need and How to Protect Yourself and Your Fellow Human BeingsFrom EverandCorona Virus: Information You Need and How to Protect Yourself and Your Fellow Human BeingsNo ratings yet
- 12 - Safe Handling of Sharps - March 3 - Low ResDocument2 pages12 - Safe Handling of Sharps - March 3 - Low ResRasheda PickettNo ratings yet
- Dates Lab Clin Clin Tasks Attempted 1 2 3 4 5 6 7: UWISON Revised 2014-2015,2018 IM MedicationDocument4 pagesDates Lab Clin Clin Tasks Attempted 1 2 3 4 5 6 7: UWISON Revised 2014-2015,2018 IM MedicationRasheda PickettNo ratings yet
- Patient Care Checklist: Objective: Student Will Demonstrate Competence in CollectingDocument4 pagesPatient Care Checklist: Objective: Student Will Demonstrate Competence in CollectingRasheda PickettNo ratings yet
- Case Study PPT - PDF HIV With Opportunistic Infection - Madayag March 2023Document71 pagesCase Study PPT - PDF HIV With Opportunistic Infection - Madayag March 2023Rasheda PickettNo ratings yet
- Administration of DdaDocument4 pagesAdministration of DdaRasheda PickettNo ratings yet
- Best Practice GuidelinesDocument2 pagesBest Practice GuidelinesRasheda PickettNo ratings yet
- Growth and DevelopementDocument50 pagesGrowth and DevelopementRasheda Pickett100% (1)
- 2019 Hematology (1) (Autosaved)Document67 pages2019 Hematology (1) (Autosaved)Rasheda PickettNo ratings yet
- NURS 4018 Course OutlineDocument3 pagesNURS 4018 Course OutlineRasheda PickettNo ratings yet
- CLIENT DATABASE 2019 - PeadsDocument7 pagesCLIENT DATABASE 2019 - PeadsRasheda PickettNo ratings yet
- Corperate Strategy 2017Document7 pagesCorperate Strategy 2017Rasheda PickettNo ratings yet
- MANDAYADocument22 pagesMANDAYAAndengBaduriaNo ratings yet
- TP-L3-402 Nursing Admin Checklist 5.1Document2 pagesTP-L3-402 Nursing Admin Checklist 5.1عبيدة محمد ابو عابدNo ratings yet
- Mintmade FashionDocument15 pagesMintmade FashionJack ZNo ratings yet
- Teletek Rreater Panel ManualDocument20 pagesTeletek Rreater Panel Manualiphonekaan34No ratings yet
- Ilumi Catalogue 2018 Q4Document84 pagesIlumi Catalogue 2018 Q4ha huynh100% (1)
- AHU Datasheet Sample Detailed Page 1 of 6 1635440149Document1 pageAHU Datasheet Sample Detailed Page 1 of 6 1635440149alim khanNo ratings yet
- Cad Cam Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesCad Cam Lecture NotesSantosh SantuNo ratings yet
- Desert Magazine 1942 FebruaryDocument68 pagesDesert Magazine 1942 Februarydm1937100% (5)
- Intro To Signal Processing 2021Document510 pagesIntro To Signal Processing 2021crypto fanbaby0% (1)
- Durag Opacity Monitor (D R290) Service Manual PDFDocument40 pagesDurag Opacity Monitor (D R290) Service Manual PDFchergui.adelNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - From The Perspective of PsychologyDocument37 pagesLesson 4 - From The Perspective of PsychologyPoeil Sergio MoldezNo ratings yet
- JTAG - WikipediaDocument16 pagesJTAG - Wikipediasantosh soodNo ratings yet
- Issues in Urban Planning in India Explained PointwiseDocument6 pagesIssues in Urban Planning in India Explained PointwiseAnchal kumariNo ratings yet
- Basketball (Exercises)Document3 pagesBasketball (Exercises)marian marianNo ratings yet
- Elios Manual - AoSenMa gc035 Drón PDFDocument29 pagesElios Manual - AoSenMa gc035 Drón PDFtrebronXNo ratings yet
- Dinas Kesehatan Kota Tomohon Jurusan Analis Kesehatan Poltekkes Kemenkes Manado Jurusan Kesehatan Lingkungan Poltekkes Kemenkes ManadoDocument10 pagesDinas Kesehatan Kota Tomohon Jurusan Analis Kesehatan Poltekkes Kemenkes Manado Jurusan Kesehatan Lingkungan Poltekkes Kemenkes ManadoNova RizkenNo ratings yet
- Wobenzym PSDocument3 pagesWobenzym PSManish PrakashNo ratings yet
- PLAINCRETE Blocks Matibay Pa!: Load Bearing Reinforced Concrete Blocks Money ConstructontheDocument7 pagesPLAINCRETE Blocks Matibay Pa!: Load Bearing Reinforced Concrete Blocks Money ConstructontheJim Bryan RazNo ratings yet
- Inflation AccountingDocument9 pagesInflation AccountingyasheshgaglaniNo ratings yet
- Q3 Summative Test 1,2 3 PDFDocument8 pagesQ3 Summative Test 1,2 3 PDFZDMon TVNo ratings yet
- Solvents Used in PharmacyDocument19 pagesSolvents Used in PharmacyMuhammad Mustafa IjazNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Work, Potential Energy, and Potential Electrostatic WorkDocument22 pagesElectrostatic Work, Potential Energy, and Potential Electrostatic WorkwonuNo ratings yet
- Class 6 NSTSE PQP 10-Papers 2019-20 2-In-A4 PDFDocument85 pagesClass 6 NSTSE PQP 10-Papers 2019-20 2-In-A4 PDFSanjib Mandal100% (3)
- Mikyas. 2020. Positive Science or Interpretive UnderstandingDocument16 pagesMikyas. 2020. Positive Science or Interpretive UnderstandingMikyas AberaNo ratings yet
Untitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
Rasheda PickettOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Untitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
Rasheda PickettCopyright:
Available Formats
The University of the West Indies
Faculty of Medical Sciences
The UWI School of Nursing, Mona
Year II
BScN
Administering Piggyback Intermittent IVI of Medication
With intermittent IVI of medication, the drug is mixed with a small amount of IV solution (50
mL to 100 mL), and administered over a short period of time. The administration may be done
using an infusion pump or by gravity infusion.
Considerations
Infusion pump:- The nurse is required to program the infusion rate into the pump.
Gravity infusion:- The nurse is required to calculate the infusion rate in drops per minute.
The IV piggyback delivery system requires the intermittent or additive solution to be placed
higher than the primary solution container, if using a short secondary infusion tubing.
Equipment
Medication
Small-volume bag/bottle (labeled)
Secondary infusion tubing
Connector (needle/needleless)
Alcohol swabs
IV pole
Medication Kardex
Tape
PPE (as required)
Assessment
Assess the patient for any allergies.
Assess the appropriateness of the drug for the patient.
Assess the compatibility of the ordered drug, diluents, and the infusing IV fluid.
UWISON Revised 2018 Page 1
Assess the IV site, noting any swelling, coolness, leakage of fluid at site, redness, or pain.
Assess the patient’s vital signs before administration of the medication (especially if they may be
affected by the drug).
Verify patient’s name, dose, route, and time of administration.
Check the expiration date (before administering the medication).
Assess the patient’s knowledge of the medication.
Nursing Diagnoses
Risk for Allergy Response
Risk for Infection
Risk for Injury
Knowledge Deficit
Procedure
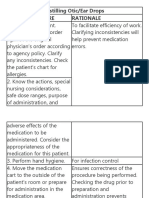
Action Rationale
1. Ensure the drug is prescribed To prevent medication error
2. Perform hand hygiene This prevents the spread of microorganisms.
3. Gather equipment. Prepare Preparation promotes efficient time
medication cart/tray with the management and organized approach to the
necessary equipment and supplies. task.
4. Check the Kardex/medication order This helps to identify any errors.
for completeness and accuracy.
Check the patient’s chart for
allergies. To prevent complication(s)Assessment is a
prerequisite to administration of medications.
UWISON Revised 2018 Page 2
5. Wash hands
Introduce yourself then identify Identifying yourself is an essential first step
the patient using at least two in establishing the therapeutic nurse-patient
identifiers relationship (RNAO, 2015). Patient
identification validates the correct patient
and correct procedure. Pulling the curtains
promotes patient’s privacy.
o Check the name and identification
number on the patient’s It ensures the right patient receives the
identification band. medications and helps prevent errors.
This is the most reliable method.
o Ask the patient to state his or her
name.
This requires a response from the patient, but
illness and strange surrounding often cause
o If the patient cannot identify him patients to be confused.
or herself, verify the patient’s
This is another way to double check identity.
identification with the staff
member who knows the patient
for the second source. .
6. Complete necessary assessments Assessment is a prerequisite to
before administering medications. administration of medication
Check allergy bracelet or ask patient
about allergies.
Educate patient about medication
To inform and alleviate any fears and
increase patient compliance
7. Perform hand hygiene To prevent the spread of microorganisms
8. Select the appropriate medication This is a part of the first check of the label
from stock. which helps to prevent medication errors
9. Compare the label with the order on This is the second check of the label which
the Kardex. Check the expiry date and helps to prevent medication error
perform calculations, verify
UWISON Revised 2018 Page 3
calculations with another nurse.
10. Know the actions, special nursing To evaluate the therapeutic effect of the
considerations, safe dose range and medication and to educate the patient.
purpose of administration and adverse
effects of the medications to be
administered.
11. Withdraw the medication from the
ampoule or vial.
12. When all medications are prepared, Re-checking the helps to prevent medication
recheck the label with the medication errors.
administration record before taking
them to the patient.
13. Perform hand hygiene To prevent the spread of the microorganisms.
14. Take the medication to the patient’s Close observation prevent accidental or
bedside. Keep medications in sight deliberate disarrangement of medication.
at all times.
15. Provide privacy. To maintain the patients dignity
16. Re-identify patient. Check for Assessment is a prerequisite to
allergies. Reinforce information about administration of medication. This is the
medication. Check the medication third check of the medication. This also
against the kardex. prevents medication errors.
Explain procedure, the purpose and Explanation provides rationale, increases
action of each medication to the knowledge and reduces anxiety.
patient. (Can be done on first contact
with the patient).
17. Assess the IV site for the presence of IV medication must be given directly into a
inflammation or infiltration. (Can be vein for safe administration
done on first contact with the patient).
18. Close the clamp on the secondary This prevents fluid entering the system until
infusion tubing. Using aseptic the nurse is ready.
technique, remove the cap on the Maintaining sterility of tubing and
tubing spike, and the cap from the medication port prevents contamination
port of the medication container. (Be
careful not to contaminate either end.)
19. Using a firm push and twisting To ensure that it is properly in place and
motion, attach the tubing to the prevent wasting of medication.
UWISON Revised 2018 Page 4
medication container.
20. Using alcohol swab, cleanse the To prevent the spread of microorganism
access port of the medication
container. Inject medication into
container. Hang piggyback container
on the IV pole.
21. Squeeze drip chamber and release to
fill it about halfway. Open clamp and This removes air from the tubing.
prime tubing. Close clamp.
Attach needless connector or needle
to the end of the tubing (using sterile This preserves sterility of the setup.
technique).
22. Using alcohol swab, clean the access This deters entry of microorganisms when
port on the primary IV infusion piggyback setup is connected to port.
tubing.
23. Close clamp on the primary infusion To prevent mixing of medication with fluid
tubing. and to allow a better flow of medication
24. Connect piggyback setup to the
access port on the primary tubing. Tape stabilizes needle in infusion port and
Use strip of tape to secure secondary prevents it from slipping out.
tubing to primary infusion tubing.
25. Open clamp on the secondary tubing. It is important to verify the safe
Regulate flow at the prescribed rate. administration rate for each drug to prevent
Monitor infusion periodically. effects.
26. Close clamp on piggyback set when
solution is infused.
Dispose of equipment according to
institution’s policy.
27. Open clamp on the primary tubing
and readjust flow rate
28. Wash hands. This prevents the spread of microorganisms.
29. Document procedure. Nursing documentation is a means of inter
and
intra-professional communication which
provides evidence of care and is necessary
for
improved patient care (RNAO, 2007).
UWISON Revised 2018 Page 5
30. Evaluate patient’s response within an For therapeutic and adverse effects from the
appropriate time frame. medications
Documentation.
Record the drug name and dosage, date, time, site of administration in the nurses'
progress notes.
Record each medication given on the Kardex
Document the patient’s tolerance to the procedure.
Document the patient’s response to the medication (the therapeutic and side
effects).
Document the volume of fluid administered on the intake and output chart (as
required).
Reference
Lyn, P. & LeBon, M. (2015) Skills Checklists for Taylor’s Clinical Nursing Skills: A nursing
process approach. (3rd ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams &
Wilkins.
Registered Nurses’ Association of Ontario (RNAO). (2007). Nursing best practice guideline:
Professionalism in Nursing. Retrieved from
http://rnao.ca/sites/rnaoca/files/Professionalism_in_Nursing.pdfRegistered Nurses’
Association of Ontario (RNAO). (2015). Nursing best practice guideline: Person-and Family-
Centred Care. Retrieved from http://rnao.ca/sites/rnao- ca/files/FINAL_Web_Version_1.pdf
UWISON Revised 2018 Page 6
You might also like
- Clil Lesson Plan TemplateDocument5 pagesClil Lesson Plan Templatesandovalz24433% (3)
- Becoming The Perfect Daughter - Spacer XDocument414 pagesBecoming The Perfect Daughter - Spacer XSergio Seferino33% (3)
- Administering An IntradermalDocument7 pagesAdministering An IntradermalCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Colloidalt Gold and Silver - Production of Colloidal Gold With Electrolysis and Green SynthesisDocument14 pagesColloidalt Gold and Silver - Production of Colloidal Gold With Electrolysis and Green SynthesisDevon Narok100% (1)
- IntramuscularDocument4 pagesIntramusculargaatgaatNo ratings yet
- PRS Ear Instillation - GlovaDocument3 pagesPRS Ear Instillation - GlovaAndrea Colleen GlovaNo ratings yet
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology College of NursingDocument47 pagesMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology College of NursingBella OllieNo ratings yet
- Animals Are People TooDocument2 pagesAnimals Are People TooTashini LileeNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Shortcuts Part 1 PDFDocument102 pagesEnglish Grammar Shortcuts Part 1 PDFRitesh Sahu100% (3)
- Terex RT 780. 80 Ton RTDocument20 pagesTerex RT 780. 80 Ton RTBhavana Kewlani67% (3)
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Ins Tute of Technology College of NursingDocument4 pagesMindanao State University - Iligan Ins Tute of Technology College of NursingNessy Nicholle SatruionNo ratings yet
- Administering Medication Via A SmallDocument6 pagesAdministering Medication Via A SmallAndrea Bayaga WaganNo ratings yet
- Checklist With Rationale For Intradermal & Intramuscular InjectionDocument8 pagesChecklist With Rationale For Intradermal & Intramuscular InjectionClarice Jamille RazonNo ratings yet
- Administering Medication Via Small-Volume Nebulizer DefinitionDocument5 pagesAdministering Medication Via Small-Volume Nebulizer DefinitionNessy Nicholle SatruionNo ratings yet
- Adding Medication To IV Fluid ContainerDocument14 pagesAdding Medication To IV Fluid Containerjennielunay00No ratings yet
- RLE PrelimsDocument8 pagesRLE PrelimsNicole VallejosNo ratings yet
- ID Checklist RATIONALEDocument42 pagesID Checklist RATIONALEAT4-11 HUMSS 2 CEDRICK ILAONo ratings yet
- Administering Nasal MedicationsDocument4 pagesAdministering Nasal MedicationsNessy Nicholle SatruionNo ratings yet
- Procedure Checklist Oral Medication AdministrationDocument4 pagesProcedure Checklist Oral Medication AdministrationRochel HatagueNo ratings yet
- Administering Medication Via A Metered Dose InhalerDocument7 pagesAdministering Medication Via A Metered Dose InhalerGio TalomiaNo ratings yet
- Iv Drug Preperation: Gina S. Cuenca, RN, MNDocument49 pagesIv Drug Preperation: Gina S. Cuenca, RN, MNJainah Rose Ferrer GubacNo ratings yet
- NUR 204.administering Medications by IV Bolus or Push Through IV InfusionDocument42 pagesNUR 204.administering Medications by IV Bolus or Push Through IV InfusionKouta SanNo ratings yet
- Administering Oral Medication (Print)Document5 pagesAdministering Oral Medication (Print)Binoy Serino100% (1)
- Instilling Otic/Ear Drops Procedure RationaleDocument12 pagesInstilling Otic/Ear Drops Procedure RationaleBSN2-F MASINING NA PAGPAPAHAYAGNo ratings yet
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology College of NursingDocument5 pagesMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology College of NursingNessy Nicholle SatruionNo ratings yet
- Procedure Oral Medication Administration RevisedDocument4 pagesProcedure Oral Medication Administration Revised4rrzbdpg8bNo ratings yet
- Administration of IV Medication e ToolDocument6 pagesAdministration of IV Medication e ToolMaria Sofia Stephanie SatoriNo ratings yet
- Intra MuscularDocument4 pagesIntra MuscularAT4-11 HUMSS 2 CEDRICK ILAONo ratings yet
- Adding Medications To Intravenous Fluid ContainersDocument2 pagesAdding Medications To Intravenous Fluid ContainersJemina Rafanan RacadioNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Western Mindanao State University College of Nursing Zamboanga CityDocument12 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Western Mindanao State University College of Nursing Zamboanga CityChristine Joy MolinaNo ratings yet
- Administering Cytotoxic Drug by Bolus InjectionDocument2 pagesAdministering Cytotoxic Drug by Bolus InjectionErika GusiNo ratings yet
- PDF Parenteral 024144Document46 pagesPDF Parenteral 024144Jamilah SidicNo ratings yet
- IV Meds in Volumetric Set C RationaleDocument2 pagesIV Meds in Volumetric Set C RationalePascal Marie IzhaqNo ratings yet
- VASQUEZ - BSN2A - Priming, Starting, and Discontinuation of IV Solution (Procedure and Rationale)Document5 pagesVASQUEZ - BSN2A - Priming, Starting, and Discontinuation of IV Solution (Procedure and Rationale)Mari Sheanne M. VasquezNo ratings yet
- OM VP and ID P and RDocument5 pagesOM VP and ID P and RTamara Kate HalicanNo ratings yet
- Children's Community Nursing Team - SOP 11 - Intravenous Medication Via A Central Venous LineDocument8 pagesChildren's Community Nursing Team - SOP 11 - Intravenous Medication Via A Central Venous Linezaenal abidinNo ratings yet
- Albumin Piggyback Procedure ChecklistDocument3 pagesAlbumin Piggyback Procedure ChecklistAljane VistoNo ratings yet
- Bns Respi Cardio ProceduresDocument60 pagesBns Respi Cardio Proceduressinuaish syaNo ratings yet
- Procedures RationaleDocument3 pagesProcedures RationaleJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- Rectal Suppository Procedure With Rationale 1Document5 pagesRectal Suppository Procedure With Rationale 1yuuki konnoNo ratings yet
- Administration Eye DropsDocument13 pagesAdministration Eye DropsyaraNo ratings yet
- Adding Medications To An Existing IvfDocument2 pagesAdding Medications To An Existing Ivfpretty_maryNo ratings yet
- Module-Intradermal Etool PDFDocument7 pagesModule-Intradermal Etool PDFErika Danalle ArceoNo ratings yet
- Eye Ear Med Instillation Procedure RationaleDocument6 pagesEye Ear Med Instillation Procedure Rationaleyuuki konnoNo ratings yet
- Drug Admin (Dragged) 4Document1 pageDrug Admin (Dragged) 4ebray7472No ratings yet
- Mixing InsulinDocument2 pagesMixing Insulinadrian lozanoNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes Checklist ProceduresDocument4 pagesFluid and Electrolytes Checklist ProceduresJamaica Leslie Noveno0% (1)
- Administering Oral Medications: Melendez, Anna Carmela PDocument19 pagesAdministering Oral Medications: Melendez, Anna Carmela PAnna Carmela P. MelendezNo ratings yet
- Tri LalaDocument5 pagesTri LalaHarvey T. Dato-onNo ratings yet
- Administrasi Vaksin PDFDocument34 pagesAdministrasi Vaksin PDFerindah puspowatiNo ratings yet
- IV InjectionDocument10 pagesIV Injectionpreeti sharmaNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Therapy: Level 1 NSL Manual: FundamentalsDocument8 pagesIntravenous Therapy: Level 1 NSL Manual: FundamentalsPrecious Ingrid Dolor DenostaNo ratings yet
- 12 Rights of Administering Medication PDF Dose (Biochemistry) ChemistryDocument1 page12 Rights of Administering Medication PDF Dose (Biochemistry) ChemistryTina Michelle DazaNo ratings yet
- Sajo College of Nursing Sciences Birnin Kebbi, Kebbi State: Unit IxDocument22 pagesSajo College of Nursing Sciences Birnin Kebbi, Kebbi State: Unit IxyusufNo ratings yet
- CUNANAN - Changing Monitoring Discontinuing IVFDocument6 pagesCUNANAN - Changing Monitoring Discontinuing IVFAbbyNo ratings yet
- Administering Medications by Intravenous Bolus or Push Through An Intravenous InfusionDocument3 pagesAdministering Medications by Intravenous Bolus or Push Through An Intravenous Infusionchalinsammy1No ratings yet
- 029 Medication TrayDocument3 pages029 Medication TrayS BindhiyaNo ratings yet
- Nur 1208 2021 Prep of MedsDocument38 pagesNur 1208 2021 Prep of MedsDannielle EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- IntradermalDocument7 pagesIntradermalKyle Dapulag100% (1)
- Checklists For Midterm 2: Common Steps For Preparing MedicationsDocument45 pagesChecklists For Midterm 2: Common Steps For Preparing MedicationsPatricia Anne Nicole CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Medications Name: Date: Oral MedicationsDocument21 pagesMedications Name: Date: Oral MedicationsDONITA DALUMPINESNo ratings yet
- IthinkaboutyoualotDocument5 pagesIthinkaboutyoualotpgumbanNo ratings yet
- Checklist Administering An Intramuscular InjectionDocument3 pagesChecklist Administering An Intramuscular InjectionCAMPOSANO, JHANNA MARIENo ratings yet
- IV TherapyDocument7 pagesIV TherapyJerika Shane MañosoNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Crisis: Information and Help in the 2020 Pandemic - What Everyone Should KnowFrom EverandCoronavirus Crisis: Information and Help in the 2020 Pandemic - What Everyone Should KnowNo ratings yet
- Corona Virus: Information You Need and How to Protect Yourself and Your Fellow Human BeingsFrom EverandCorona Virus: Information You Need and How to Protect Yourself and Your Fellow Human BeingsNo ratings yet
- 12 - Safe Handling of Sharps - March 3 - Low ResDocument2 pages12 - Safe Handling of Sharps - March 3 - Low ResRasheda PickettNo ratings yet
- Dates Lab Clin Clin Tasks Attempted 1 2 3 4 5 6 7: UWISON Revised 2014-2015,2018 IM MedicationDocument4 pagesDates Lab Clin Clin Tasks Attempted 1 2 3 4 5 6 7: UWISON Revised 2014-2015,2018 IM MedicationRasheda PickettNo ratings yet
- Patient Care Checklist: Objective: Student Will Demonstrate Competence in CollectingDocument4 pagesPatient Care Checklist: Objective: Student Will Demonstrate Competence in CollectingRasheda PickettNo ratings yet
- Case Study PPT - PDF HIV With Opportunistic Infection - Madayag March 2023Document71 pagesCase Study PPT - PDF HIV With Opportunistic Infection - Madayag March 2023Rasheda PickettNo ratings yet
- Administration of DdaDocument4 pagesAdministration of DdaRasheda PickettNo ratings yet
- Best Practice GuidelinesDocument2 pagesBest Practice GuidelinesRasheda PickettNo ratings yet
- Growth and DevelopementDocument50 pagesGrowth and DevelopementRasheda Pickett100% (1)
- 2019 Hematology (1) (Autosaved)Document67 pages2019 Hematology (1) (Autosaved)Rasheda PickettNo ratings yet
- NURS 4018 Course OutlineDocument3 pagesNURS 4018 Course OutlineRasheda PickettNo ratings yet
- CLIENT DATABASE 2019 - PeadsDocument7 pagesCLIENT DATABASE 2019 - PeadsRasheda PickettNo ratings yet
- Corperate Strategy 2017Document7 pagesCorperate Strategy 2017Rasheda PickettNo ratings yet
- MANDAYADocument22 pagesMANDAYAAndengBaduriaNo ratings yet
- TP-L3-402 Nursing Admin Checklist 5.1Document2 pagesTP-L3-402 Nursing Admin Checklist 5.1عبيدة محمد ابو عابدNo ratings yet
- Mintmade FashionDocument15 pagesMintmade FashionJack ZNo ratings yet
- Teletek Rreater Panel ManualDocument20 pagesTeletek Rreater Panel Manualiphonekaan34No ratings yet
- Ilumi Catalogue 2018 Q4Document84 pagesIlumi Catalogue 2018 Q4ha huynh100% (1)
- AHU Datasheet Sample Detailed Page 1 of 6 1635440149Document1 pageAHU Datasheet Sample Detailed Page 1 of 6 1635440149alim khanNo ratings yet
- Cad Cam Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesCad Cam Lecture NotesSantosh SantuNo ratings yet
- Desert Magazine 1942 FebruaryDocument68 pagesDesert Magazine 1942 Februarydm1937100% (5)
- Intro To Signal Processing 2021Document510 pagesIntro To Signal Processing 2021crypto fanbaby0% (1)
- Durag Opacity Monitor (D R290) Service Manual PDFDocument40 pagesDurag Opacity Monitor (D R290) Service Manual PDFchergui.adelNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - From The Perspective of PsychologyDocument37 pagesLesson 4 - From The Perspective of PsychologyPoeil Sergio MoldezNo ratings yet
- JTAG - WikipediaDocument16 pagesJTAG - Wikipediasantosh soodNo ratings yet
- Issues in Urban Planning in India Explained PointwiseDocument6 pagesIssues in Urban Planning in India Explained PointwiseAnchal kumariNo ratings yet
- Basketball (Exercises)Document3 pagesBasketball (Exercises)marian marianNo ratings yet
- Elios Manual - AoSenMa gc035 Drón PDFDocument29 pagesElios Manual - AoSenMa gc035 Drón PDFtrebronXNo ratings yet
- Dinas Kesehatan Kota Tomohon Jurusan Analis Kesehatan Poltekkes Kemenkes Manado Jurusan Kesehatan Lingkungan Poltekkes Kemenkes ManadoDocument10 pagesDinas Kesehatan Kota Tomohon Jurusan Analis Kesehatan Poltekkes Kemenkes Manado Jurusan Kesehatan Lingkungan Poltekkes Kemenkes ManadoNova RizkenNo ratings yet
- Wobenzym PSDocument3 pagesWobenzym PSManish PrakashNo ratings yet
- PLAINCRETE Blocks Matibay Pa!: Load Bearing Reinforced Concrete Blocks Money ConstructontheDocument7 pagesPLAINCRETE Blocks Matibay Pa!: Load Bearing Reinforced Concrete Blocks Money ConstructontheJim Bryan RazNo ratings yet
- Inflation AccountingDocument9 pagesInflation AccountingyasheshgaglaniNo ratings yet
- Q3 Summative Test 1,2 3 PDFDocument8 pagesQ3 Summative Test 1,2 3 PDFZDMon TVNo ratings yet
- Solvents Used in PharmacyDocument19 pagesSolvents Used in PharmacyMuhammad Mustafa IjazNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Work, Potential Energy, and Potential Electrostatic WorkDocument22 pagesElectrostatic Work, Potential Energy, and Potential Electrostatic WorkwonuNo ratings yet
- Class 6 NSTSE PQP 10-Papers 2019-20 2-In-A4 PDFDocument85 pagesClass 6 NSTSE PQP 10-Papers 2019-20 2-In-A4 PDFSanjib Mandal100% (3)
- Mikyas. 2020. Positive Science or Interpretive UnderstandingDocument16 pagesMikyas. 2020. Positive Science or Interpretive UnderstandingMikyas AberaNo ratings yet