Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Balance System - Petroleum Equipment Institute
Balance System - Petroleum Equipment Institute
Uploaded by
Enrique Armando0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pagesBalance systems use vapor pressure created during refueling to transfer vapors from a vehicle's fuel tank to an underground storage tank without external power. As gasoline flows into the vehicle tank, the rising liquid pushes vapors into the nozzle and back through the dispenser piping to the underground tank. This creates a closed system where vapors in one tank flow to the other tank due to pressure from the in-flow and out-flow of liquid between the two tanks.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBalance systems use vapor pressure created during refueling to transfer vapors from a vehicle's fuel tank to an underground storage tank without external power. As gasoline flows into the vehicle tank, the rising liquid pushes vapors into the nozzle and back through the dispenser piping to the underground tank. This creates a closed system where vapors in one tank flow to the other tank due to pressure from the in-flow and out-flow of liquid between the two tanks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pagesBalance System - Petroleum Equipment Institute
Balance System - Petroleum Equipment Institute
Uploaded by
Enrique ArmandoBalance systems use vapor pressure created during refueling to transfer vapors from a vehicle's fuel tank to an underground storage tank without external power. As gasoline flows into the vehicle tank, the rising liquid pushes vapors into the nozzle and back through the dispenser piping to the underground tank. This creates a closed system where vapors in one tank flow to the other tank due to pressure from the in-flow and out-flow of liquid between the two tanks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
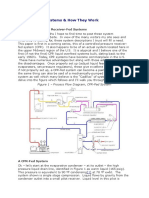
Balance System - Petroleum
Equipment Institute
A method used in gasoline vapor recovery which permits vapors in
the tank being filled to be transferred to another tank without
intervention of any external power source.
In Stage II vapor recovery systems, vapors present in the vehicle fuel
tank must be removed from the tank without being allowed to escape
into the atmosphere. When the balance refueling process begins, the
vapor recovery nozzle is inserted into the fill pipe of the vehicle’s
tank. The nozzle bellows makes a tight connection with the fill pipe.
As gasoline flows through the nozzle and into the tank, the rising level
of liquid forces the vapors, present in the tank, into the bellows that
surround a vapor port on the nozzle. The continuing pressure created
by the rising liquid pushes the displaced vapors back through the
bellows, through the vapor-return port of the nozzle, and then on
through the vapor-return portion of the dispenser hose.
The same pressure source continues to push the vapors on through
the piping in the dispenser and then through the vapor-return pipe
under the driveway, all the way back to the underground tank from
which the liquid is flowing.
This arrangement constitutes a closed system. Vapors displaced while
filling one tank (the vehicle tank) will follow the path of least
resistance and flow back through the system into an underground
storage tank.
Thus, vapors in the vehicle tank are transferred to the underground
storage tank without the help of any type of secondary power source.
The transfer is accomplished entirely as a result of the normal in-flow
:
of liquid into the vehicle tank and the offsetting liquid out-flow from
the storage tank. Because of this balance–liquid in, vapor out and
liquid out, vapor in–the method is referred to as a balance system.
Stage II balance systems, employed for most underground tank
installations, are less efficient when used with aboveground tanks
because of the thermal effects of the sun and the higher pressure
required to force vapors upward into aboveground tanks.
:
You might also like
- Closed and Open Feed SystemDocument7 pagesClosed and Open Feed SystemRoneil BaculioNo ratings yet
- Gas Pressure Recirculation Systems - An American PhenomenaDocument16 pagesGas Pressure Recirculation Systems - An American PhenomenaJim Wright, P.E.No ratings yet
- Carrier Chapter 3 Piping DesignDocument22 pagesCarrier Chapter 3 Piping DesignAhmad Al-rifaiNo ratings yet
- Change of Cargo Grades or Preparation For DrydockDocument3 pagesChange of Cargo Grades or Preparation For DrydockAlice Mano JiamaNo ratings yet
- Hydropneumatic Schemematics331 380Document2 pagesHydropneumatic Schemematics331 380wnewell1No ratings yet
- Defining Artificial LiftDocument2 pagesDefining Artificial LiftDIEGONo ratings yet
- EvapEmission PDFDocument8 pagesEvapEmission PDFpivillamilNo ratings yet
- Change of Cargo Grades or Preparation For Drydock - LPG Tanker ProcedureDocument6 pagesChange of Cargo Grades or Preparation For Drydock - LPG Tanker ProcedureLukasz ZablockiNo ratings yet
- Cargo and Ballast Pumps For Chemical TankersDocument10 pagesCargo and Ballast Pumps For Chemical TankersSnehilNo ratings yet
- Vacuum PumpDocument8 pagesVacuum PumpVineeth VsNo ratings yet
- Aspirator Assist - Petroleum Equipment InstituteDocument1 pageAspirator Assist - Petroleum Equipment InstituteEnrique ArmandoNo ratings yet
- Lovely Professional University: Term Paper OF Modern Physics & Electronic ON Vacuum PumpsDocument17 pagesLovely Professional University: Term Paper OF Modern Physics & Electronic ON Vacuum PumpsEr Vijay ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Conceptual DesignDocument4 pagesConceptual Designemmanuel limaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Part of Quiz-1Document2 pagesAssignment Part of Quiz-1Bilal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Basic Hydraulic SystemsDocument21 pagesBasic Hydraulic Systemsdane63No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Fuel Supply SystemDocument14 pagesChapter 2 - Fuel Supply SystemLalith Koushik GanganapalliNo ratings yet
- Gas Powered Liquid Recirculation Compared To Mechanical PumpsDocument28 pagesGas Powered Liquid Recirculation Compared To Mechanical PumpsJim Wright, P.E.No ratings yet
- Gas Pressure Recirculation Systems An American PhenomenaDocument16 pagesGas Pressure Recirculation Systems An American PhenomenaChristina ArgesanuNo ratings yet
- Boiler Feed Pump Recirculation ValvesDocument16 pagesBoiler Feed Pump Recirculation ValvesShameer Majeed100% (1)
- Components of Retail Motor-Fuel Dispensing UnitDocument28 pagesComponents of Retail Motor-Fuel Dispensing UnitkuraimundNo ratings yet
- Hydropneumatic Tank Control Systems: Drinking Water Tech TipsDocument2 pagesHydropneumatic Tank Control Systems: Drinking Water Tech TipsBlancaNo ratings yet
- Exhaust and Pollution Control SystemDocument24 pagesExhaust and Pollution Control SystemOne Love Jah LoveNo ratings yet
- SimpleDocument49 pagesSimpleDima Al KibbiNo ratings yet
- March23, 1954 J. L, Dunnlgan Y 2,672,853: Sealed Cooling System For Internal-Combustion EnginésDocument3 pagesMarch23, 1954 J. L, Dunnlgan Y 2,672,853: Sealed Cooling System For Internal-Combustion Enginésmonem2014No ratings yet
- College of Engineering and ArchitectureDocument16 pagesCollege of Engineering and Architecturemalyn gorospeNo ratings yet
- VDU Technical Description: Chemex Modular, LLCDocument4 pagesVDU Technical Description: Chemex Modular, LLCmigelNo ratings yet
- Ammonia SystemDocument7 pagesAmmonia Systemsirsa11No ratings yet
- Production Facility Design PDFDocument34 pagesProduction Facility Design PDFQaiser Hafeez100% (1)
- Cargo Oil Pump Tanker VesselsDocument8 pagesCargo Oil Pump Tanker VesselsŘhýđm Šâűřābh100% (1)
- Cargo Oil Pump Tanker VesselsDocument8 pagesCargo Oil Pump Tanker VesselsŘhýđm ŠâűřābhNo ratings yet
- Eductor Jet PumpDocument2 pagesEductor Jet PumpPiyapiya Oh PiyapiyaNo ratings yet
- 2.2.1. Pengertian Gas Lift (GL)Document10 pages2.2.1. Pengertian Gas Lift (GL)HENRY ARDIANNo ratings yet
- Liquid Transfer Vapor RecoveryDocument7 pagesLiquid Transfer Vapor RecoverymusaveerNo ratings yet
- Assign 1Document15 pagesAssign 1Aakarshit JainNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Inert Gas SystemDocument8 pages1.6 Inert Gas SystemAbcdNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument2 pagesAbstractZeshan JamilNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics of Car EnginesDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics of Car EnginesRaaidhAhmedNo ratings yet
- 2017 - OGMP TGD7 Liquids Unloading - CCAC PDFDocument18 pages2017 - OGMP TGD7 Liquids Unloading - CCAC PDFManuel ChNo ratings yet
- Charging Refrigerants Into HVACDocument12 pagesCharging Refrigerants Into HVACRay NamuNo ratings yet
- Slug CatcherDocument3 pagesSlug Catcherwkhan_55No ratings yet
- Types of NH3 SystemsDocument8 pagesTypes of NH3 Systemsrdany3437No ratings yet
- Kettle Type Reboiler WorkingDocument7 pagesKettle Type Reboiler WorkingCepi Sindang KamulanNo ratings yet
- How Fuel PumpDocument3 pagesHow Fuel PumpCarlos Carvajal AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Off Gas CoolingDocument9 pagesOff Gas CoolingAnonymous zwSP5gvNo ratings yet
- Design of Plumbing Systems For Multi-Storey Buildings PDFDocument14 pagesDesign of Plumbing Systems For Multi-Storey Buildings PDFpequenita34100% (4)
- Sucker Rod PumpDocument28 pagesSucker Rod Pumpakshitppe11100% (1)
- Gas Lift OperDocument3 pagesGas Lift OperMikhaelrams RamsNo ratings yet
- 300 Level ReportDocument47 pages300 Level ReportGildaZoe Ighoraye100% (1)
- Coaxial - Petroleum Equipment InstituteDocument2 pagesCoaxial - Petroleum Equipment InstituteEnrique ArmandoNo ratings yet
- How Does The Carburetor Works: A) TemperatureDocument5 pagesHow Does The Carburetor Works: A) TemperatureKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- (Oto-Hui - Com) Doosan Hydraulic BasicDocument76 pages(Oto-Hui - Com) Doosan Hydraulic Basiceng_ebrahim_2000100% (2)
- Various Valves Arrangement For Machinery Spaces Piping SystemDocument10 pagesVarious Valves Arrangement For Machinery Spaces Piping SystemRaj GraffitiNo ratings yet
- Aerospace ReservoirsDocument8 pagesAerospace ReservoirsSandeep LeeNo ratings yet
- Tanker Questions From Ship EducationDocument33 pagesTanker Questions From Ship EducationAshok YNo ratings yet
- Module-4 Liquid Propellant RocketDocument5 pagesModule-4 Liquid Propellant RocketmaniNo ratings yet
- All Types PumpsDocument61 pagesAll Types PumpsstabinmathewNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Pneu Conveyor 1Document17 pagesJurnal Pneu Conveyor 1Zulfahmi AmriNo ratings yet
- Ocr A Level Biology A 2Nd Edition Sue Hocking Download PDF ChapterDocument51 pagesOcr A Level Biology A 2Nd Edition Sue Hocking Download PDF Chaptermarie.jauregui723100% (6)
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitFrom EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitNo ratings yet
- Dissolution of Gases in Liquids and the Formation of Dispersion Systems in the Mode of Torsion-Oriented TurbulizationFrom EverandDissolution of Gases in Liquids and the Formation of Dispersion Systems in the Mode of Torsion-Oriented TurbulizationNo ratings yet
- Aspirator Assist - Petroleum Equipment InstituteDocument1 pageAspirator Assist - Petroleum Equipment InstituteEnrique ArmandoNo ratings yet
- Coaxial - Petroleum Equipment InstituteDocument2 pagesCoaxial - Petroleum Equipment InstituteEnrique ArmandoNo ratings yet
- Vertical High Thrust Motors: Installation, Operation and Maintenance ManualDocument76 pagesVertical High Thrust Motors: Installation, Operation and Maintenance ManualEnrique ArmandoNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics, Plato's Cave and The Blind Piranha - Scientific AmericanDocument6 pagesQuantum Mechanics, Plato's Cave and The Blind Piranha - Scientific AmericanEnrique ArmandoNo ratings yet
- Piping & Instrumentation Diagrams Guide - LucidchartDocument12 pagesPiping & Instrumentation Diagrams Guide - LucidchartEnrique ArmandoNo ratings yet
- Bonded Sump Entry Fitting Termination Style Spec Sheet-2Document4 pagesBonded Sump Entry Fitting Termination Style Spec Sheet-2Enrique ArmandoNo ratings yet
- Red Thread IIA Piping System Spec SheetDocument2 pagesRed Thread IIA Piping System Spec SheetEnrique ArmandoNo ratings yet
- Catalog U Line Contender Factory Sealed 20 Amp Plugs Receptacles Appleton en Us 7438326Document6 pagesCatalog U Line Contender Factory Sealed 20 Amp Plugs Receptacles Appleton en Us 7438326Enrique ArmandoNo ratings yet
- Rotron Regenerative Blowers CatalogDocument2 pagesRotron Regenerative Blowers CatalogEnrique ArmandoNo ratings yet
- Executive Order G-70-150-AD: 1. ApplicabilityDocument10 pagesExecutive Order G-70-150-AD: 1. ApplicabilityEnrique ArmandoNo ratings yet
- Executive Order G-70-150-Ad Exhibit 1 Vaporvac System Equipment ListDocument3 pagesExecutive Order G-70-150-Ad Exhibit 1 Vaporvac System Equipment ListEnrique ArmandoNo ratings yet
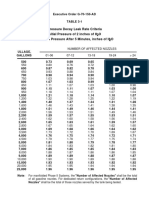
- Pressure Decay Leak Rate Criteria Initial Pressure of 2 Inches of H2O Minimum Pressure After 5 Minutes, Inches of H2ODocument1 pagePressure Decay Leak Rate Criteria Initial Pressure of 2 Inches of H2O Minimum Pressure After 5 Minutes, Inches of H2OEnrique ArmandoNo ratings yet
- Executive Order G-70-150-Ad Exhibit 2 Specifications For The Vaporvac Bootless Nozzle SystemDocument5 pagesExecutive Order G-70-150-Ad Exhibit 2 Specifications For The Vaporvac Bootless Nozzle SystemEnrique ArmandoNo ratings yet
- Understanding Units of Gas ConcentrationDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Units of Gas ConcentrationEnrique ArmandoNo ratings yet
- Veeder-Root Specification Sheet 8600 & 8601 Series Consoles: Standard FeaturesDocument2 pagesVeeder-Root Specification Sheet 8600 & 8601 Series Consoles: Standard FeaturesEnrique ArmandoNo ratings yet