Professional Documents
Culture Documents
New Content To Foundation Tier Only #1 of 2: GCSE (9-1) Maths Revision Poster
New Content To Foundation Tier Only #1 of 2: GCSE (9-1) Maths Revision Poster
Uploaded by
Ehan MalikCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Sacred Sex Rites of Ishtar by Annie Dieu-Le-Veut - PDF Version 1Document177 pagesThe Sacred Sex Rites of Ishtar by Annie Dieu-Le-Veut - PDF Version 1ashwinNo ratings yet
- EFQM Business Excellence ModelDocument5 pagesEFQM Business Excellence Modelmarrisha26No ratings yet
- Base Rate Percentage + Ratio and ProportionDocument15 pagesBase Rate Percentage + Ratio and Proportionrommel legaspiNo ratings yet
- Robot Project Report RoboticsDocument34 pagesRobot Project Report Roboticsdcrust_amit82% (11)
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesDetailed Lesson Plancess100% (5)
- Edexcel 1. NumberDocument10 pagesEdexcel 1. Numbernanamd96No ratings yet
- Chapter Summary: Number 1: Working With FractionsDocument5 pagesChapter Summary: Number 1: Working With FractionsEmmanuel NWANAFORONo ratings yet
- Find + 5: Business Math Example: 3 8 5 9 6Document3 pagesFind + 5: Business Math Example: 3 8 5 9 6Pherngy CadanoNo ratings yet
- Math 10 FinalsDocument2 pagesMath 10 FinalsKrystel MamarilNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Simple and Compound InterestDocument7 pagesWeek 6 Simple and Compound InterestRia KhyleNo ratings yet
- CH 03Document42 pagesCH 03Kat FishNo ratings yet
- Business Mathematics: Ratio, Proportion, and Percent 7.1. RATIODocument6 pagesBusiness Mathematics: Ratio, Proportion, and Percent 7.1. RATIOMiss Jennelyn100% (2)
- Math HandbookDocument24 pagesMath HandbookMariama BooneNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic and StatisticsDocument4 pagesArithmetic and StatisticsDaniel S. Macaraeg100% (1)
- Live Online Content: Aclc College of MandaueDocument26 pagesLive Online Content: Aclc College of MandaueMary April Repuela GapoNo ratings yet
- Live Online Content: Aclc College of MandaueDocument26 pagesLive Online Content: Aclc College of MandaueMary April Repuela GapoNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Arithmetic and StatisticsDocument4 pagesLecture - Arithmetic and Statisticsryner ainsworthNo ratings yet
- Business Math Lesson GuideDocument9 pagesBusiness Math Lesson GuideKaye VillaflorNo ratings yet
- PDF Csec Mathematics June 2017 Paper 1 Solution 2017 CompressDocument9 pagesPDF Csec Mathematics June 2017 Paper 1 Solution 2017 CompressMickellSZNNo ratings yet
- PDF Csec Mathematics June 2017 Paper 1 Solution 2017 CompressDocument9 pagesPDF Csec Mathematics June 2017 Paper 1 Solution 2017 CompressMickellSZNNo ratings yet
- Fractions & Percentages: Keywords What Do I Need To Be Able To Do? @whisto - MathsDocument1 pageFractions & Percentages: Keywords What Do I Need To Be Able To Do? @whisto - MathsEmrah ozkanNo ratings yet
- Heep 209Document28 pagesHeep 209Jyoti GuptaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 - Conversion Among Fractions, Decimals and PercentDocument27 pagesWEEK 1 - Conversion Among Fractions, Decimals and PercentPrincess Joan Cornejo-Dela LunaNo ratings yet
- Comparing Quantities Ratio: "How Many Times One Quantity Is of The Other"Document3 pagesComparing Quantities Ratio: "How Many Times One Quantity Is of The Other"davethiyaguNo ratings yet
- 131427614.H Percentage BasicsDocument38 pages131427614.H Percentage BasicsShane Rajapaksha100% (1)
- Licensure Examination For Teachers General Education - MathematicsDocument31 pagesLicensure Examination For Teachers General Education - MathematicsJhay B. MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Briefing Paper For The Directors of Newton Media Supplies LTDDocument3 pagesBriefing Paper For The Directors of Newton Media Supplies LTDYashmi BhanderiNo ratings yet
- Percentages PDFDocument7 pagesPercentages PDFPrashanthNo ratings yet
- Decimals Comp PacketDocument33 pagesDecimals Comp Packetapi-235199292No ratings yet
- Business Mathematics Learning AccountDocument60 pagesBusiness Mathematics Learning AccountLibbyNo ratings yet
- Business Math - Module 1 - Fractions, Decimals, PercentsDocument4 pagesBusiness Math - Module 1 - Fractions, Decimals, PercentsChristine Marie CabilinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Answers To Questions and Problems: Managerial Economics and Business Strategy, 8eDocument16 pagesChapter 3: Answers To Questions and Problems: Managerial Economics and Business Strategy, 8eRomel BucaloyNo ratings yet
- RRPSC WordsumsDocument34 pagesRRPSC Wordsumslilandre092No ratings yet
- MATH 6 - T.JanenDocument30 pagesMATH 6 - T.JanenJanen Vea Padua DavidNo ratings yet
- Business Math 01Document50 pagesBusiness Math 01Isabel Grace VictorNo ratings yet
- 0580 Igcse MathsDocument13 pages0580 Igcse MathsHoang MinhNo ratings yet
- (Week 1) : TOPIC TITLE: Introduction: Fraction, Decimal, andDocument10 pages(Week 1) : TOPIC TITLE: Introduction: Fraction, Decimal, andReaganRicafortNo ratings yet
- November Exam Summary 2023Document9 pagesNovember Exam Summary 2023cassidykpvv1No ratings yet
- Decimals, Fractions, Consum ArithmDocument6 pagesDecimals, Fractions, Consum ArithmAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- CA Final SFM Concept & Formulae BookletDocument121 pagesCA Final SFM Concept & Formulae BookletShivaji hariNo ratings yet
- Math 6 Q2 Module 4Document14 pagesMath 6 Q2 Module 4Leo CerenoNo ratings yet
- Dosage Calculations 1: Dr. A CoxDocument33 pagesDosage Calculations 1: Dr. A CoxKimora Jay DupreNo ratings yet
- Math Fractions, Decimals and Percentages CLSPDocument34 pagesMath Fractions, Decimals and Percentages CLSPBeeha AzmanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Decimals, Fractions, and Percentages: Place ValueDocument7 pages1.1 Decimals, Fractions, and Percentages: Place ValueJustin MattiesNo ratings yet
- HO3 Decimals, Powers, RootsDocument2 pagesHO3 Decimals, Powers, Rootspavan guptaNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet in Math7Document4 pagesLearning Activity Sheet in Math7Raphy BrionesNo ratings yet
- Percentage Profit and LossDocument7 pagesPercentage Profit and LossRahulNo ratings yet
- BusMath (SHS) Fractions, Decimals, PercentageDocument23 pagesBusMath (SHS) Fractions, Decimals, PercentageAnonymous qh2BZqNo ratings yet
- Dee Hwa Liong Academy: Fractions, Decimals, and PercentagesDocument9 pagesDee Hwa Liong Academy: Fractions, Decimals, and PercentageskelvinNo ratings yet
- Business Math ReviewerDocument6 pagesBusiness Math ReviewerabigailyaunNo ratings yet
- Abm 005 - ReviewerDocument6 pagesAbm 005 - ReviewerMary Beth Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Standard FormDocument22 pagesStandard FormHala HassanNo ratings yet
- Brbmath NotesDocument25 pagesBrbmath NotestenderjuicyiyyyNo ratings yet
- Reading3 3BDocument5 pagesReading3 3BSphamandla MakalimaNo ratings yet
- Fractions, Percentages and DecimalsDocument17 pagesFractions, Percentages and DecimalsTheresa NelNo ratings yet
- GCSE StandardFormDocument26 pagesGCSE StandardFormdishapanditNo ratings yet
- Ws Financial-Maths Simple-And-Compound 19 5 20 gr12Document7 pagesWs Financial-Maths Simple-And-Compound 19 5 20 gr12anelethusi.544No ratings yet
- Rounding Decimals NotesDocument3 pagesRounding Decimals NotesSharath ChanderNo ratings yet
- Gre-Cheet SheetDocument1 pageGre-Cheet SheetParvej KhanNo ratings yet
- Bond & Stock Sample Problemsv1.1Document4 pagesBond & Stock Sample Problemsv1.1An HoàiNo ratings yet
- GCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 7From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 7No ratings yet
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 8From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 8No ratings yet
- New Content To Foundation Tier Only #2 of 2: GCSE (9-1) Maths Revision PosterDocument1 pageNew Content To Foundation Tier Only #2 of 2: GCSE (9-1) Maths Revision PosterEhan MalikNo ratings yet
- GCSE (9-1) Maths Revision Poster: New Common Content To Foundation and Higher Tier #2 of 2Document1 pageGCSE (9-1) Maths Revision Poster: New Common Content To Foundation and Higher Tier #2 of 2Ehan MalikNo ratings yet
- New Content To Higher Tier Only #2 of 2: GCSE (9-1) Maths Revision PosterDocument1 pageNew Content To Higher Tier Only #2 of 2: GCSE (9-1) Maths Revision PosterEhan MalikNo ratings yet
- New Content To Higher Tier Only #1 of 2: GCSE (9-1) Maths Revision PosterDocument1 pageNew Content To Higher Tier Only #1 of 2: GCSE (9-1) Maths Revision PosterEhan MalikNo ratings yet
- Small Signal Model of Boost DC-DC Converter Operating in CCMDocument3 pagesSmall Signal Model of Boost DC-DC Converter Operating in CCMtinhmaixatoi2006No ratings yet
- Solar Design LeedDocument10 pagesSolar Design Leedapi-465215783No ratings yet
- Class 9 Science 3Document7 pagesClass 9 Science 3chandralok_kumarNo ratings yet
- Figure 1 Concept of Structure and Function: Philippine-EagleDocument8 pagesFigure 1 Concept of Structure and Function: Philippine-EagleShekaina Faith Cuizon Lozada100% (2)
- Lecture 15Document20 pagesLecture 15Yavuz KaplanNo ratings yet
- 3 Legged 5 Why - Effective Root Cause AnalysisDocument40 pages3 Legged 5 Why - Effective Root Cause AnalysisJohn OoNo ratings yet
- PARAS, Mark Heinrich B. - Exercise 3 - Lecture Biochemistry CHEM 40 BSN 1EDocument4 pagesPARAS, Mark Heinrich B. - Exercise 3 - Lecture Biochemistry CHEM 40 BSN 1EMark Heinrich B. ParasNo ratings yet
- MSI K9A2 CF Series ManualDocument89 pagesMSI K9A2 CF Series ManualDosije218No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Entrepreneurship Theory Process and Practice 10th Edition by KuratkoDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Entrepreneurship Theory Process and Practice 10th Edition by Kuratkosanityenhanceqould1100% (54)
- ADUPPUDocument3 pagesADUPPUAnanthakrishnan KarurNo ratings yet
- Circus ThesisDocument6 pagesCircus ThesisSomeoneWriteMyPaperSingapore100% (2)
- AV Control Receiver: Operating InstructionsDocument32 pagesAV Control Receiver: Operating InstructionsCuthbert Marshall100% (1)
- Cu ZN 10Document2 pagesCu ZN 10wjjt6chgtmNo ratings yet
- Fdpc8016S: Powertrench Power Clip 25V Asymmetric Dual N-Channel MosfetDocument12 pagesFdpc8016S: Powertrench Power Clip 25V Asymmetric Dual N-Channel MosfetRDNo ratings yet
- Islamic WorldviewDocument74 pagesIslamic Worldviewvera290690100% (1)
- Piping Info - Carbon Steel & Stainless Steel Guide SpacingDocument2 pagesPiping Info - Carbon Steel & Stainless Steel Guide SpacingpalluraviNo ratings yet
- Slht-Tve 10 Q3 M2Document13 pagesSlht-Tve 10 Q3 M2Jecel Feb BiangosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Static and Dynamic Characteristics of SignalsDocument18 pagesChapter 2 Static and Dynamic Characteristics of SignalsDiyaa AhmedNo ratings yet
- Sesiones de Technical EnglishDocument90 pagesSesiones de Technical EnglishBill Klinthon Chiara100% (1)
- Tenant Fit-Out Manual: January 2017Document53 pagesTenant Fit-Out Manual: January 2017Rohan BagadiyaNo ratings yet
- Grover WasherDocument51 pagesGrover WasherFourHorsemenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document9 pagesChapter 1Dary OngNo ratings yet
- GPX SBRO 004 E Rev.0.1Document4 pagesGPX SBRO 004 E Rev.0.1OperacionesNo ratings yet
- Training Modules For Group B Officers & Group C Supervisors of S&T DepartmentDocument59 pagesTraining Modules For Group B Officers & Group C Supervisors of S&T DepartmentMayank TripathiNo ratings yet
- Intrauterine Growth RestrictionDocument7 pagesIntrauterine Growth RestrictionNurfazlinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One ReaserchDocument54 pagesChapter One Reaserchkassahun meseleNo ratings yet
New Content To Foundation Tier Only #1 of 2: GCSE (9-1) Maths Revision Poster
New Content To Foundation Tier Only #1 of 2: GCSE (9-1) Maths Revision Poster
Uploaded by
Ehan MalikOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
New Content To Foundation Tier Only #1 of 2: GCSE (9-1) Maths Revision Poster
New Content To Foundation Tier Only #1 of 2: GCSE (9-1) Maths Revision Poster
Uploaded by
Ehan MalikCopyright:
Available Formats
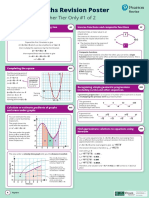
GCSE (9-1) Maths Revision Poster Revise
New Content to Foundation Tier Only #1 of 2
Standard form N9 Compound interest and reverse percentages R16
Writing numbers in standard form In Compound Interest, interest is added The normal price of a coat is £45
to the account at the end of each year so The price is reduced by 15% in a sale.
You can count the number of places that the Numbers in standard form a new calculation must be worked out.
decimal point has to move to make a number that have two parts The multiplier for a 15% decrease is 0.85
is greater than or equal to 1, and less than 10. The table shows how an investment of
£40 000 grows with a compound interest
3 jumps 7900 ˃ 10 This part is rate of 3% per annum (per year). × 0.85
This part
so the power a number
is a power £45
7900 = 7.9 × 103 is positive ≥1 and less
of 10. End of Balance
than 10. year
4 jumps 0.00035 < 1 15% OFF
so the power 1 40 000 × 1.03 = 41 200 = £38.25
7.3 × 10 – 6
0.00035 = 3.5 × 10 -4 is negative 2 41 200 × 1.03 = 42 346 ÷ 0.85
3 42 346 × 1.03 = 43 709.08
To covert a number in standard form to an ordinary number, you can count the
number of places the decimal point has to move. If you are given a final amount, divide by
The multiplier for a 3% increase is 1.03
the multiplier to find the original amount.
If the power is positive then the decimal point
7.9 x 103 = 7900 moves to the right that number of places
If the power is negative then the decimal point
7 . 9 x 1 0 -3 = 0.079 moves to the right that number of places Factorise quadratic expressions A4
To factorise an expression in
the form x2 + bx + c you need to Example: x2 + 5 x + 6
Direct and Inverse proportion R10 find two numbers that add up 2 and 3 add to make 5 and
(numeric and algebraic) to make b, and that multiply multiply to make 6
to make c.
So x2 + 5 x + 6 = (x + 2) (x + 3)
If two quantities are in direct proportion then,
for example, one doubles so will the other. Example question ing bracket Check by expanding
pand s
Number of tickets Total cost The number of days, d, that Ex
bought it will take to build a house is
3 £135 Expanding
given by d = 720/n where n is 2x ( x + 3 ) = 2x 2 + 6x
×2 ×2 the number of workers used
each day. How many days will
it take 8 workers to build the
(x + 2) (x +3) = x 2 + 3x + 2x + 6
6 £270 house? Facto ing
ris = x 2 +5x +6
If two quantities are in inverse proportion then, for 720 ÷ 8 = 90
example, when one doubles the other one will halve.
What if 10 workers were used?
Average speed Time taken
720 ÷ 10 = 72
40 km/h 2 hours
As the number of workers
Plot cubic and reciprocal graphs, recognise A12
×2 ÷2 increases, then number of quadratic and cubic graphs
days decreases.
80 km/h 1 hour
To plot cubic and reciprocal graphs substitute values of x to find values of y then plotting
points to draw the graph.
Solve simultaneous equations A19 Graphs that contain an y The points where y = x2 – 6x
x3 term and no higher 1 crosses the x-axis are the
y=
are cubic graphs. x solutions to the quadratic
The most common method for solving equation x2 – 6x = 0. The
simultaneous equations is the elimination 3x + y = 20 × by 4 to y
y = 4 – x3 x x-coordinate of the turning
method. make 4y 0 point is halfway between
x + 4y = 14 in each 2 these points.
equation y=–
x y
Multiply one or both equations to make 12x + 4y = 80 y = x2 –6x
coefficients of one variable equal 0 x
– x + 4y = 14 Subtract the Graphs of the form Line of
equations symmetry
k
11x = 66 and solve y = x3 + 2 x3 y= x
Add or subtract the equations to eliminate x 0 6
x=6 are reciprocal graphs. Turning
one of the variables (3, –9) Point
3 × 6 + y = 20 Substitute
back into
Solve, then substitute back into one equation
18 + y = 20 one of the
to find the value of the other variable y=2 equations
Trigonometric ratios in right-angled triangles G20
For right-angled triangles only:
Solve quadratic equations by factorisation A18 Use SOH CAH TOA to remember the rules for sin, cos and tan:
To solve the equation x2 + 6x + 5 = 0 we need to follow these steps. opp
1 sin x =
hyp
hypotenuse
1 2 3 opposite
adj
Factorise the Set each factor Solve the two linear equations 2 cos x =
hyp
left-hand side of equal to zero: to find the two solutions:
x
the equation: (x + 5) = 0 x+5=0 x+1=0 opp
3 tan x =
(x + 5) (x + 1) = 0 adj
(x + 1) = 0 x = −5 or x = −1 adjacent
N Number A Algebra R Ratio G Geometry Pearson Education Ltd is committed
to reducing its impact on the
environment by using responsibly
sourced and recycled paper.
PEUK A2630a
You might also like
- The Sacred Sex Rites of Ishtar by Annie Dieu-Le-Veut - PDF Version 1Document177 pagesThe Sacred Sex Rites of Ishtar by Annie Dieu-Le-Veut - PDF Version 1ashwinNo ratings yet
- EFQM Business Excellence ModelDocument5 pagesEFQM Business Excellence Modelmarrisha26No ratings yet
- Base Rate Percentage + Ratio and ProportionDocument15 pagesBase Rate Percentage + Ratio and Proportionrommel legaspiNo ratings yet
- Robot Project Report RoboticsDocument34 pagesRobot Project Report Roboticsdcrust_amit82% (11)
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesDetailed Lesson Plancess100% (5)
- Edexcel 1. NumberDocument10 pagesEdexcel 1. Numbernanamd96No ratings yet
- Chapter Summary: Number 1: Working With FractionsDocument5 pagesChapter Summary: Number 1: Working With FractionsEmmanuel NWANAFORONo ratings yet
- Find + 5: Business Math Example: 3 8 5 9 6Document3 pagesFind + 5: Business Math Example: 3 8 5 9 6Pherngy CadanoNo ratings yet
- Math 10 FinalsDocument2 pagesMath 10 FinalsKrystel MamarilNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Simple and Compound InterestDocument7 pagesWeek 6 Simple and Compound InterestRia KhyleNo ratings yet
- CH 03Document42 pagesCH 03Kat FishNo ratings yet
- Business Mathematics: Ratio, Proportion, and Percent 7.1. RATIODocument6 pagesBusiness Mathematics: Ratio, Proportion, and Percent 7.1. RATIOMiss Jennelyn100% (2)
- Math HandbookDocument24 pagesMath HandbookMariama BooneNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic and StatisticsDocument4 pagesArithmetic and StatisticsDaniel S. Macaraeg100% (1)
- Live Online Content: Aclc College of MandaueDocument26 pagesLive Online Content: Aclc College of MandaueMary April Repuela GapoNo ratings yet
- Live Online Content: Aclc College of MandaueDocument26 pagesLive Online Content: Aclc College of MandaueMary April Repuela GapoNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Arithmetic and StatisticsDocument4 pagesLecture - Arithmetic and Statisticsryner ainsworthNo ratings yet
- Business Math Lesson GuideDocument9 pagesBusiness Math Lesson GuideKaye VillaflorNo ratings yet
- PDF Csec Mathematics June 2017 Paper 1 Solution 2017 CompressDocument9 pagesPDF Csec Mathematics June 2017 Paper 1 Solution 2017 CompressMickellSZNNo ratings yet
- PDF Csec Mathematics June 2017 Paper 1 Solution 2017 CompressDocument9 pagesPDF Csec Mathematics June 2017 Paper 1 Solution 2017 CompressMickellSZNNo ratings yet
- Fractions & Percentages: Keywords What Do I Need To Be Able To Do? @whisto - MathsDocument1 pageFractions & Percentages: Keywords What Do I Need To Be Able To Do? @whisto - MathsEmrah ozkanNo ratings yet
- Heep 209Document28 pagesHeep 209Jyoti GuptaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 - Conversion Among Fractions, Decimals and PercentDocument27 pagesWEEK 1 - Conversion Among Fractions, Decimals and PercentPrincess Joan Cornejo-Dela LunaNo ratings yet
- Comparing Quantities Ratio: "How Many Times One Quantity Is of The Other"Document3 pagesComparing Quantities Ratio: "How Many Times One Quantity Is of The Other"davethiyaguNo ratings yet
- 131427614.H Percentage BasicsDocument38 pages131427614.H Percentage BasicsShane Rajapaksha100% (1)
- Licensure Examination For Teachers General Education - MathematicsDocument31 pagesLicensure Examination For Teachers General Education - MathematicsJhay B. MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Briefing Paper For The Directors of Newton Media Supplies LTDDocument3 pagesBriefing Paper For The Directors of Newton Media Supplies LTDYashmi BhanderiNo ratings yet
- Percentages PDFDocument7 pagesPercentages PDFPrashanthNo ratings yet
- Decimals Comp PacketDocument33 pagesDecimals Comp Packetapi-235199292No ratings yet
- Business Mathematics Learning AccountDocument60 pagesBusiness Mathematics Learning AccountLibbyNo ratings yet
- Business Math - Module 1 - Fractions, Decimals, PercentsDocument4 pagesBusiness Math - Module 1 - Fractions, Decimals, PercentsChristine Marie CabilinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Answers To Questions and Problems: Managerial Economics and Business Strategy, 8eDocument16 pagesChapter 3: Answers To Questions and Problems: Managerial Economics and Business Strategy, 8eRomel BucaloyNo ratings yet
- RRPSC WordsumsDocument34 pagesRRPSC Wordsumslilandre092No ratings yet
- MATH 6 - T.JanenDocument30 pagesMATH 6 - T.JanenJanen Vea Padua DavidNo ratings yet
- Business Math 01Document50 pagesBusiness Math 01Isabel Grace VictorNo ratings yet
- 0580 Igcse MathsDocument13 pages0580 Igcse MathsHoang MinhNo ratings yet
- (Week 1) : TOPIC TITLE: Introduction: Fraction, Decimal, andDocument10 pages(Week 1) : TOPIC TITLE: Introduction: Fraction, Decimal, andReaganRicafortNo ratings yet
- November Exam Summary 2023Document9 pagesNovember Exam Summary 2023cassidykpvv1No ratings yet
- Decimals, Fractions, Consum ArithmDocument6 pagesDecimals, Fractions, Consum ArithmAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- CA Final SFM Concept & Formulae BookletDocument121 pagesCA Final SFM Concept & Formulae BookletShivaji hariNo ratings yet
- Math 6 Q2 Module 4Document14 pagesMath 6 Q2 Module 4Leo CerenoNo ratings yet
- Dosage Calculations 1: Dr. A CoxDocument33 pagesDosage Calculations 1: Dr. A CoxKimora Jay DupreNo ratings yet
- Math Fractions, Decimals and Percentages CLSPDocument34 pagesMath Fractions, Decimals and Percentages CLSPBeeha AzmanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Decimals, Fractions, and Percentages: Place ValueDocument7 pages1.1 Decimals, Fractions, and Percentages: Place ValueJustin MattiesNo ratings yet
- HO3 Decimals, Powers, RootsDocument2 pagesHO3 Decimals, Powers, Rootspavan guptaNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet in Math7Document4 pagesLearning Activity Sheet in Math7Raphy BrionesNo ratings yet
- Percentage Profit and LossDocument7 pagesPercentage Profit and LossRahulNo ratings yet
- BusMath (SHS) Fractions, Decimals, PercentageDocument23 pagesBusMath (SHS) Fractions, Decimals, PercentageAnonymous qh2BZqNo ratings yet
- Dee Hwa Liong Academy: Fractions, Decimals, and PercentagesDocument9 pagesDee Hwa Liong Academy: Fractions, Decimals, and PercentageskelvinNo ratings yet
- Business Math ReviewerDocument6 pagesBusiness Math ReviewerabigailyaunNo ratings yet
- Abm 005 - ReviewerDocument6 pagesAbm 005 - ReviewerMary Beth Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Standard FormDocument22 pagesStandard FormHala HassanNo ratings yet
- Brbmath NotesDocument25 pagesBrbmath NotestenderjuicyiyyyNo ratings yet
- Reading3 3BDocument5 pagesReading3 3BSphamandla MakalimaNo ratings yet
- Fractions, Percentages and DecimalsDocument17 pagesFractions, Percentages and DecimalsTheresa NelNo ratings yet
- GCSE StandardFormDocument26 pagesGCSE StandardFormdishapanditNo ratings yet
- Ws Financial-Maths Simple-And-Compound 19 5 20 gr12Document7 pagesWs Financial-Maths Simple-And-Compound 19 5 20 gr12anelethusi.544No ratings yet
- Rounding Decimals NotesDocument3 pagesRounding Decimals NotesSharath ChanderNo ratings yet
- Gre-Cheet SheetDocument1 pageGre-Cheet SheetParvej KhanNo ratings yet
- Bond & Stock Sample Problemsv1.1Document4 pagesBond & Stock Sample Problemsv1.1An HoàiNo ratings yet
- GCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 7From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 7No ratings yet
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 8From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 8No ratings yet
- New Content To Foundation Tier Only #2 of 2: GCSE (9-1) Maths Revision PosterDocument1 pageNew Content To Foundation Tier Only #2 of 2: GCSE (9-1) Maths Revision PosterEhan MalikNo ratings yet
- GCSE (9-1) Maths Revision Poster: New Common Content To Foundation and Higher Tier #2 of 2Document1 pageGCSE (9-1) Maths Revision Poster: New Common Content To Foundation and Higher Tier #2 of 2Ehan MalikNo ratings yet
- New Content To Higher Tier Only #2 of 2: GCSE (9-1) Maths Revision PosterDocument1 pageNew Content To Higher Tier Only #2 of 2: GCSE (9-1) Maths Revision PosterEhan MalikNo ratings yet
- New Content To Higher Tier Only #1 of 2: GCSE (9-1) Maths Revision PosterDocument1 pageNew Content To Higher Tier Only #1 of 2: GCSE (9-1) Maths Revision PosterEhan MalikNo ratings yet
- Small Signal Model of Boost DC-DC Converter Operating in CCMDocument3 pagesSmall Signal Model of Boost DC-DC Converter Operating in CCMtinhmaixatoi2006No ratings yet
- Solar Design LeedDocument10 pagesSolar Design Leedapi-465215783No ratings yet
- Class 9 Science 3Document7 pagesClass 9 Science 3chandralok_kumarNo ratings yet
- Figure 1 Concept of Structure and Function: Philippine-EagleDocument8 pagesFigure 1 Concept of Structure and Function: Philippine-EagleShekaina Faith Cuizon Lozada100% (2)
- Lecture 15Document20 pagesLecture 15Yavuz KaplanNo ratings yet
- 3 Legged 5 Why - Effective Root Cause AnalysisDocument40 pages3 Legged 5 Why - Effective Root Cause AnalysisJohn OoNo ratings yet
- PARAS, Mark Heinrich B. - Exercise 3 - Lecture Biochemistry CHEM 40 BSN 1EDocument4 pagesPARAS, Mark Heinrich B. - Exercise 3 - Lecture Biochemistry CHEM 40 BSN 1EMark Heinrich B. ParasNo ratings yet
- MSI K9A2 CF Series ManualDocument89 pagesMSI K9A2 CF Series ManualDosije218No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Entrepreneurship Theory Process and Practice 10th Edition by KuratkoDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Entrepreneurship Theory Process and Practice 10th Edition by Kuratkosanityenhanceqould1100% (54)
- ADUPPUDocument3 pagesADUPPUAnanthakrishnan KarurNo ratings yet
- Circus ThesisDocument6 pagesCircus ThesisSomeoneWriteMyPaperSingapore100% (2)
- AV Control Receiver: Operating InstructionsDocument32 pagesAV Control Receiver: Operating InstructionsCuthbert Marshall100% (1)
- Cu ZN 10Document2 pagesCu ZN 10wjjt6chgtmNo ratings yet
- Fdpc8016S: Powertrench Power Clip 25V Asymmetric Dual N-Channel MosfetDocument12 pagesFdpc8016S: Powertrench Power Clip 25V Asymmetric Dual N-Channel MosfetRDNo ratings yet
- Islamic WorldviewDocument74 pagesIslamic Worldviewvera290690100% (1)
- Piping Info - Carbon Steel & Stainless Steel Guide SpacingDocument2 pagesPiping Info - Carbon Steel & Stainless Steel Guide SpacingpalluraviNo ratings yet
- Slht-Tve 10 Q3 M2Document13 pagesSlht-Tve 10 Q3 M2Jecel Feb BiangosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Static and Dynamic Characteristics of SignalsDocument18 pagesChapter 2 Static and Dynamic Characteristics of SignalsDiyaa AhmedNo ratings yet
- Sesiones de Technical EnglishDocument90 pagesSesiones de Technical EnglishBill Klinthon Chiara100% (1)
- Tenant Fit-Out Manual: January 2017Document53 pagesTenant Fit-Out Manual: January 2017Rohan BagadiyaNo ratings yet
- Grover WasherDocument51 pagesGrover WasherFourHorsemenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document9 pagesChapter 1Dary OngNo ratings yet
- GPX SBRO 004 E Rev.0.1Document4 pagesGPX SBRO 004 E Rev.0.1OperacionesNo ratings yet
- Training Modules For Group B Officers & Group C Supervisors of S&T DepartmentDocument59 pagesTraining Modules For Group B Officers & Group C Supervisors of S&T DepartmentMayank TripathiNo ratings yet
- Intrauterine Growth RestrictionDocument7 pagesIntrauterine Growth RestrictionNurfazlinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One ReaserchDocument54 pagesChapter One Reaserchkassahun meseleNo ratings yet