Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Histolytica. This Can Be Accomplished Using
Histolytica. This Can Be Accomplished Using
Uploaded by
Lingayo, Deseree C.Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Histolytica. This Can Be Accomplished Using
Histolytica. This Can Be Accomplished Using
Uploaded by
Lingayo, Deseree C.Copyright:
Available Formats
Salabao, Miccah Ysabel L.
(BS BIOLOGY4A)
Laboratory Activity 1 (PARASITOLOGY)
Amoeba
c. Laboratory Diagnosis
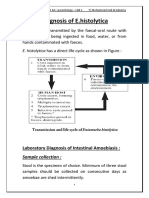
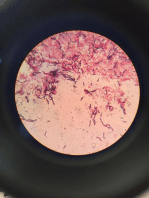
Microscopic identification of cysts and trophozoites in the stool is the common method for diagnosing E.
histolytica. This can be accomplished using:
Fresh stool: wet mounts and permanently stained preparations (e.g., trichrome).
Concentrates from fresh stool: wet mounts, with or without iodine stain, and permanently
stained preparations (e.g., trichrome). Concentration procedures, however, are not useful for
demonstrating trophozoites.
In addition, E. histolytica trophozoites can also be identified in aspirates or biopsy samples obtained
during colonoscopy or surgery.
d. Epidemiology
Transmission can occur through fecal-oral route (ingestion of food and water, contaminated with feces
containing E. histolytica cysts). Sexual transmission can also occur
e. Prevention and Control
Containment requirements: Containment Level 2 facilities, equipment, and operational practices for
work involving infectious or potentially infectious materials, animals, or cultures.
Protective clothing: Lab coat. Gloves when direct skin contact with infected materials or animals is
unavoidable. Eye protection must be used where there is a known or potential risk of exposure to
splashes.
Other precautions: All procedures that may produce aerosols, or involve high concentrations or large
volumes should be conducted in a biological safety cabinet (BSC). The use of needles, syringes, and
other sharp objects should be strictly limited. Additional precautions should be considered with work
involving animals or large-scale activities.
f. Pathology
Asymptomatic patients carrying the pathogen can be treated with luminal amebicides (kills cysts) such
as oral paromomycin, oral diloxanide furoate, and oral iodoquinol. Amebic dysentery/colitis or amebic
abscess can be treated with tissue amebicides (kills trophozoites) such as oral metronidazole, or oral
tinidazole. Oral paromomycin, diloxanidfuroate or iodoquinol are prescribed for elimination of cysts
following treatment with tissue amebicides. Therapeutic aspiration/drainage of an amebic liver may be
required, alone or along with antiparasitic therapy, in patients who do not respond to therapy.
References:
https://www.cdc.gov/dpdx/amebiasis/index.html
https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/laboratory-biosafety-biosecurity/pathogen-safety-
data-sheets-risk-assessment/entamoeba-histolytica-pathogen-safety-data-sheet.html
You might also like
- Microbiology Lab Manual - Revised Spring 2013Document117 pagesMicrobiology Lab Manual - Revised Spring 2013Mbiko SabeyoNo ratings yet
- Icru 89 (229-260)Document32 pagesIcru 89 (229-260)Christian Ordoñez100% (1)
- Amoebiasis ..ParasitologyDocument7 pagesAmoebiasis ..ParasitologyBenard NyaumaNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle and Infection Mode From Entamoeba HistolyticaDocument30 pagesLife Cycle and Infection Mode From Entamoeba HistolyticaSynthesis is What MattersNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Amoebiasis: Entamoeba HistolyticaDocument7 pagesLesson 3 Amoebiasis: Entamoeba HistolyticaAstrid FausziaNo ratings yet
- AMOEBIASISDocument4 pagesAMOEBIASISBryan MasikaNo ratings yet
- AmoebiasisDocument4 pagesAmoebiasisnamanNo ratings yet
- 04 Lec - Giardiasis & TrichmoniasisDocument25 pages04 Lec - Giardiasis & Trichmoniasisمصطفي خندقاويNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: Laboratory ManualDocument23 pagesMicrobiology: Laboratory ManualDevindraPrptNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Lab Trans (Prelims)Document35 pagesMicrobiology Lab Trans (Prelims)Dhawell AnnNo ratings yet
- Entamoeba HistolyticaDocument22 pagesEntamoeba HistolyticaMercilie EbioNo ratings yet
- 12 - 2022 Lactobacilli, CorynebacteriaDocument55 pages12 - 2022 Lactobacilli, CorynebacteriaroshnayimNo ratings yet
- Clinical Parasitology IIIDocument6 pagesClinical Parasitology IIINkopengieh Rene PochiekenNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Parasitology Given Parasites Identify The Following A. Common Name B. Geographical Distribution in The PhilippinesDocument29 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology Given Parasites Identify The Following A. Common Name B. Geographical Distribution in The PhilippinesTea-yuhNo ratings yet
- Specimen Collections in The Medical Microbiology and parasitologyNOTESDocument43 pagesSpecimen Collections in The Medical Microbiology and parasitologyNOTESPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- Uid 1776Document12 pagesUid 1776IsaacJ22No ratings yet
- Part-2-ParasitologyDocument33 pagesPart-2-ParasitologyAli AhmedNo ratings yet
- Jsimposium Tifoid FeverDocument4 pagesJsimposium Tifoid FeverWawan BwNo ratings yet
- Parasitology: Entamoeba HistolyticaDocument9 pagesParasitology: Entamoeba Histolyticaعلي حسين عودة العلياويNo ratings yet
- Medical Parasitology: HNS 212: Introduction To Medical ProtozoologyDocument132 pagesMedical Parasitology: HNS 212: Introduction To Medical ProtozoologyJOSEPH NDERITUNo ratings yet
- طفيليات عملي الحكمة المعمل 3 صيدلةDocument4 pagesطفيليات عملي الحكمة المعمل 3 صيدلةMohammed AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Glanders: C H A P T E R 2 - 5 - 1 1Document10 pagesGlanders: C H A P T E R 2 - 5 - 1 1Ryan ChenNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology HandoutsDocument30 pagesBacteriology HandoutsMarco Tolentino100% (8)
- Pratical 1, 2,3, 4 ParasitologyDocument23 pagesPratical 1, 2,3, 4 ParasitologyDOUMBOUYA SIDIKINo ratings yet
- Group1 ProtozoanMicrosDocument3 pagesGroup1 ProtozoanMicrosLuke Jovanni TAOCNo ratings yet
- Amoebiasis: Dr. Syifa Musyika, SPPD KgehDocument24 pagesAmoebiasis: Dr. Syifa Musyika, SPPD Kgehdian ilmaniarNo ratings yet
- Stool Specimen CollectionDocument8 pagesStool Specimen CollectionPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- MicrobesDocument6 pagesMicrobesemms meNo ratings yet
- ISOSPORADocument16 pagesISOSPORAAbdirashidNo ratings yet
- 2421 Lab ManualDocument116 pages2421 Lab Manuallpalo004No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - RELIABLE DIAGNOSIS OF PARASITIC INFECTIONSDocument31 pagesLecture 3 - RELIABLE DIAGNOSIS OF PARASITIC INFECTIONSNida RidzuanNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercises Intro To MicrobiologyDocument71 pagesLab Exercises Intro To MicrobiologyAygul RamankulovaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Diagnostic Medical MicrobiologyDocument4 pagesPrinciples of Diagnostic Medical MicrobiologyTarequl Islam NishadNo ratings yet
- Envr133 Lab3 Enterococci&FSDocument6 pagesEnvr133 Lab3 Enterococci&FSAbhishek BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Protozoal Gastrointestinal InfectionsDocument3 pagesProtozoal Gastrointestinal InfectionssivaNo ratings yet
- BotulismDocument29 pagesBotulismRohan TejaNo ratings yet
- Yers I NiosisDocument4 pagesYers I NiosisCharleen Joyce UsacdinNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On AmeobiasisDocument34 pagesA Case Study On AmeobiasisKhemz Dalde LimNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology Pa Exam Topics: Laboratory Diagnosis in Infections Cause byDocument20 pagesBacteriology Pa Exam Topics: Laboratory Diagnosis in Infections Cause byCristina KepteaNo ratings yet
- Entamoeba Histolytica Exists in Two Forms - Trophozoite and Cyst. The Trophozoite and Cyst Measure 20Document2 pagesEntamoeba Histolytica Exists in Two Forms - Trophozoite and Cyst. The Trophozoite and Cyst Measure 20Joan BarcenasNo ratings yet
- Grp02ClinPara PDFDocument68 pagesGrp02ClinPara PDFJeddhie MoraNo ratings yet
- Amebia PDFDocument6 pagesAmebia PDF04lubna_869632400No ratings yet
- Amoebiasis Case StudyDocument12 pagesAmoebiasis Case StudyGrace NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Lab Manual - Spring 2012Document114 pagesMicrobiology Lab Manual - Spring 2012occbuzi100% (3)
- Mls306 Histopath Lab PrelimsDocument4 pagesMls306 Histopath Lab PrelimsEvanka BaguistanNo ratings yet
- Ear Cultures Principle: 3.6.12 Sop: Ear Culture Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesEar Cultures Principle: 3.6.12 Sop: Ear Culture Page 1 of 2SemeeeJuniorNo ratings yet
- Lec 39. Parasitol Protozoa of SI, Protozoa, Nematodes LIDocument51 pagesLec 39. Parasitol Protozoa of SI, Protozoa, Nematodes LIkareemosama9916No ratings yet
- CHN Food and WaterDocument4 pagesCHN Food and WatertimmybunsenNo ratings yet
- 7.0 FlagellatesDocument7 pages7.0 FlagellatesHenry KarokiNo ratings yet
- Other Gram Negative Enteric PathogensDocument51 pagesOther Gram Negative Enteric Pathogensyosef awokeNo ratings yet
- Extraintestinal AmoebiasisDocument38 pagesExtraintestinal AmoebiasisMuhammad Afiq AbdulhanNo ratings yet
- Genus: Entamoeba Coli: Lecturer: Nerran K.F.AL-Rubaey Practical Parasites Lab - 2Document6 pagesGenus: Entamoeba Coli: Lecturer: Nerran K.F.AL-Rubaey Practical Parasites Lab - 2Chairut ChampoonoteNo ratings yet
- Zoo143 Clinical Parasitology Topic: Parasites of Clinical SignificanceDocument13 pagesZoo143 Clinical Parasitology Topic: Parasites of Clinical SignificanceChristian Martell LiwagNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Lab Manual and GuideDocument117 pagesMicrobiology Lab Manual and GuideSelvaraju Parthibhan100% (2)
- Kemiii OoooDocument17 pagesKemiii Oooosgfdjwwt88No ratings yet
- Diarrhea in Kittens and Young Cats - WSAVA2011 - VINDocument4 pagesDiarrhea in Kittens and Young Cats - WSAVA2011 - VINkukuhamru19No ratings yet
- AmebiasisDocument32 pagesAmebiasisRizty Mayang FachleviNo ratings yet
- Micro NoeDocument63 pagesMicro NoejoseNo ratings yet
- Practical Manual for Detection of Parasites in Feces, Blood and Urine SamplesFrom EverandPractical Manual for Detection of Parasites in Feces, Blood and Urine SamplesNo ratings yet
- 911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!From Everand911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Curriculum ImplementionDocument9 pagesCurriculum ImplementionLingayo, Deseree C.No ratings yet
- Curriculum Evaluation Through Learning Assessment ACT.Document2 pagesCurriculum Evaluation Through Learning Assessment ACT.Lingayo, Deseree C.No ratings yet
- Curricular Reform in Teacher EducationDocument3 pagesCurricular Reform in Teacher EducationLingayo, Deseree C.No ratings yet
- Contemporary 1Document16 pagesContemporary 1Lingayo, Deseree C.No ratings yet
- Contemporary 3Document11 pagesContemporary 3Lingayo, Deseree C.No ratings yet
- Contemporary 5Document9 pagesContemporary 5Lingayo, Deseree C.No ratings yet
- Contemporary 4Document3 pagesContemporary 4Lingayo, Deseree C.No ratings yet
- Contemporary 2Document3 pagesContemporary 2Lingayo, Deseree C.No ratings yet
- Post Partum ComplicationsDocument40 pagesPost Partum ComplicationsMahmoud Abu Al AmrainNo ratings yet
- Final English Medical ExamDocument2 pagesFinal English Medical ExamDayana Andrea Cornejo PalominoNo ratings yet
- Tri AgingDocument92 pagesTri AgingAngelie PantajoNo ratings yet
- Oncology TestDocument32 pagesOncology TestPhilip Gene II MalacasNo ratings yet
- NCP, Ent, Risk For InfectionDocument1 pageNCP, Ent, Risk For InfectionGale DizonNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat High AlertDocument6 pagesDaftar Obat High AlertRestika Eria PutriNo ratings yet
- Proformas 4 ANM GNM 2022Document8 pagesProformas 4 ANM GNM 2022Anuj Kumar MondalNo ratings yet
- Emergency MedicineDocument150 pagesEmergency MedicineDev MartelNo ratings yet
- Liver Stagnation Self Assessment and TrainingDocument3 pagesLiver Stagnation Self Assessment and TrainingEliosNo ratings yet
- USPOREDBA NOVE I STARE DIJAGNOSTIKE LATENTNE TUBERKULOZNE INFEKCIJE (QuantiFERON I PPD)Document7 pagesUSPOREDBA NOVE I STARE DIJAGNOSTIKE LATENTNE TUBERKULOZNE INFEKCIJE (QuantiFERON I PPD)Mijo IlićNo ratings yet
- Adjustment of OHA During Fasting in RamadanDocument2 pagesAdjustment of OHA During Fasting in Ramadanhk.medicinesoptNo ratings yet
- Alicia's CCFP Exam GuideDocument133 pagesAlicia's CCFP Exam Guidejpdavid95No ratings yet
- Emergencies in General PracticeDocument17 pagesEmergencies in General PracticeIoana NavaliciNo ratings yet
- Tylenol - Acetaminophen - Fabros, JennyDocument3 pagesTylenol - Acetaminophen - Fabros, JennyJenny Agustin FabrosNo ratings yet
- Acquired Hemolytic AnemiaDocument48 pagesAcquired Hemolytic AnemiaJeena RajNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CefazolinDocument5 pagesDrug Study - CefazolinNichole DancelNo ratings yet
- Foreigner Physical Examination FormDocument2 pagesForeigner Physical Examination FormArnoldNo ratings yet
- NYSTAGMUSDocument13 pagesNYSTAGMUSwillemlrouxNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis R4PattDocument85 pagesOsteomyelitis R4PattthanawatsimaNo ratings yet
- Agbede DanielDocument18 pagesAgbede DanielDaniel AgbedeNo ratings yet
- Cover-Sblm Bab IDocument17 pagesCover-Sblm Bab ISilmi RamdhaniatiNo ratings yet
- Sciatic Nerve InjuryDocument27 pagesSciatic Nerve Injurytosin mosesNo ratings yet
- Tugas Kelompok 3 Alpha 2017 - Dr. Achmad Ridwan, MO, MSCDocument6 pagesTugas Kelompok 3 Alpha 2017 - Dr. Achmad Ridwan, MO, MSCLivia HanisamurtiNo ratings yet
- FORM MksU4-STUDENTS ENTRANCE MEDICAL EXAMINATIONDocument4 pagesFORM MksU4-STUDENTS ENTRANCE MEDICAL EXAMINATIONRichard OsumoNo ratings yet
- Reported Pathological ChildhoodDocument7 pagesReported Pathological ChildhoodMartha Lucía Triviño LuengasNo ratings yet
- Pidsr Dengue Standard Case DefinitionDocument2 pagesPidsr Dengue Standard Case DefinitionJoe Pete TiuNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Childhood and AdolescenceDocument9 pagesDisorders of Childhood and AdolescenceCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Dissertation On PneumoniaDocument7 pagesDissertation On PneumoniaCustomWrittenPaperLittleRock100% (1)
- Integrated Literature Review of Depression in Elderly People 2167 7182 1000446Document3 pagesIntegrated Literature Review of Depression in Elderly People 2167 7182 1000446LINA VELILLANo ratings yet