Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
Saurish SakhreOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Untitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
Saurish SakhreCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
Minerals can't be synthesized ( since the definition fo minerals clearly
mentions that minerals are the compounds of metals associated with their earthly
impurities and if we synthesize metals , they'll not be associated with any earthly
impurities )
Right ma'am
2. If we are asked to write the reaction of Baeyer's process for one mark , which
reaction should we write since there are 3 reactions ( under Baeyer's process )
mentioned or should I simply combine all the reactions since no new reactants need
to be introduced as the products of the preceding reaction will serve as the
reactants for the succeeding reaction
3. Page 136
What is meant by 'agitation' here
4. Page 136
Do I need to learn the reactions of the alternative method of Baeyer's process
5. Page 137
Are carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide the impurities associated with the oxygen
liberated at the anode
6. The melting point of the mixture of alumina , cryolite , and fluorspar is 950 C
whereas the meting point of Aluminium is 660 C so wouldn't it volatize out
7. Why do we prefer to use several graphite electrodes instead of a single big
graohite electrode
8. Is only Magnalium light , hard , tough , and corrosion resistant or is Duralumin
the same ( since it's not clearly given in the book if the properties specified are
only of magnalium or they are shared by both Duralumin and Magnalium )
9. Page 149 Preparation of Hydrogen Chloride gas by direct combination
What is meant by 'burning jet of hydrogen'
10. Page 150 Laboratory prepration of hydrogen chloride gas Observation
Isn't sulphuric acid a dehydrating agent
11. The formation of ammonium chloride through the reaction of hydrogen chloride
and ammonia is a reversile process
Right ma'am
12. Is the fomration of HCl in the presence of diffused sunlight a reversible
process
13. Page 154 Special arrangement
Instead of using the term 'rim of the trough' , can we use 'water level of the
water contained in the trough'
14. Give an example of a constant boiling mixture
15. Corundum is another name for alumina
Right ma'am
16. Do I have to learn all the scientists who discovered a compound or defined its
properties ( names of scientists that are given at the start of the chapters of the
'Study of Compounds' unit )
17. Lime water is another name for slaked lime
Right ma'am
18. Is Red lead ( Pb3O4 ) a precipitate
19. Difference between residue and precipitate
20. What is the oxidizing agent used in the formation of aqua regia
21. Nitrosyl chloride and chlorine are strong oxidizing agents which enable them to
dissolve noble metals leading to the formation of their chlorides or is it only the
nascent chlorine which has a part and nitrosyl chloride doesn't have a part in it
Right ma'am
22. Page 225 Numbering of Carbon atoms
Instead of writing 4 - ethyl 3 - methyl heptane , can we write 3 - methyl 4 -
ethyl heptane
23. What is meant by 'attacking reagent'
24. Page 228 Sources Fire damps
What are coal pockets
25. Why is methane called marsh gas ( keywords required ) ( because it is formed by
the decay of organic matter ) )
26. Alkanes are called parafins and alkenes are called olefins but what are alkynes
called
27. Page 232 Sources
What is thermal cracking
28. Pd represents which element
29. Page 234
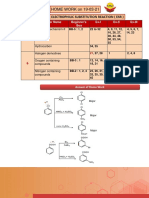
Explain the chemical test given under Halogenation
30. Page 234 Halogenation
Why is the reaction of iodine difficult
31. Page 234 Halogenation
For the other two reactions they have written inert solvent on the arrow but
for the iodine reaction they haven't even though the solvent used is the same ,
i.e. , carbon tetrachloride
32. Why is the first member of a homologous series always the most important
33. Do I have to mentioned potassium oxide and alumina as promoters and haematite
as the catalyst when I'm asked to write the catalysts and promoters used in the
Haber's process or is mentioning Molybdenum as the promoter and finely divided iron
as the catalyst sufficient
34. Does haematite and potassium oxide and alumina have to be used along with
molybdenum and finely divided iron or are they substitutes of Molybdenum and finely
divided iron
35. Page 184 Laboratory method Procedure
What is a glass retort
36. What is the colour of FeSO4 solution
37. CO2 + NO2 ----> _
38. NO2 + H2O ----> _
39. Page 191 Ionization of Nitric acid Pure or concentrated nitric acid
Explain
40. Why is C + 4 HNO3 ----> CO2 + 2H2O + 4NO2 and not C + HNO3 ----> H2CO3 + NO2
( the reaction is not balanced )
41. On page 192 , they've written that nitric acid reacts with copper to form
nitric oxide but on the next page , the product formed on reaction of copper and
nitric acid is written as nitrogen dioxide . What is correct
42. Pure nitric acid ( 98 percent purity ) is called fuming nitric acid . Why
43. How can we differentiate between dilute acids and concentrated acids
44. Page 206 Contact tower point 3
Explain
45. Page 207 Temperature point 2
A rise of 10C doubles the speed of the process but at what temperature should
we increase it by 10C
46.
You might also like
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 1: Properties of The Three States of MatterDocument24 pagesScience: Quarter 3 - Module 1: Properties of The Three States of Matternadia doropan67% (3)
- Jamb Chemistry 2021 Key PointsDocument15 pagesJamb Chemistry 2021 Key PointsAbiodun BamideleNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument12 pagesChemistrythakurbaliram97No ratings yet
- Important Questions ScieceDocument11 pagesImportant Questions Scieceabhinavgautharaju11111No ratings yet
- Chemistry ExDocument12 pagesChemistry ExAmit KingNo ratings yet
- 5 6176732192253674928Document14 pages5 6176732192253674928Manu ShreeNo ratings yet
- Full Portion Chapterwise Important QuestionsDocument144 pagesFull Portion Chapterwise Important Questionsм.ѕυяуαα X C 29No ratings yet
- Test Chemistry ICSE Class VIII 2023Document3 pagesTest Chemistry ICSE Class VIII 2023Ananthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledSaurish SakhreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 HydrogenDocument3 pagesChapter 4 HydrogenvenusrinivassNo ratings yet
- Halogen Derivative of AlkaneDocument29 pagesHalogen Derivative of AlkaneDeepti Kaskar60% (5)
- Senior ChemistryDocument12 pagesSenior ChemistryDanny 341No ratings yet
- Chemistry ClassX AssignmentDocument6 pagesChemistry ClassX AssignmentBharatiyaNaariNo ratings yet
- Sy Chemistry Q. Bank Sem 1 2023-24Document7 pagesSy Chemistry Q. Bank Sem 1 2023-24Kia AsherNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE PAPER-05 (Solved) Class - XII: 8. What Is The Effect of Temperature On The Solubility of A Solid in A Solvent?Document10 pagesSAMPLE PAPER-05 (Solved) Class - XII: 8. What Is The Effect of Temperature On The Solubility of A Solid in A Solvent?Gaurav RoyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (Class XII)Document4 pagesChemistry (Class XII)Sumathi SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Chemsitry Question Bank em 218992Document71 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Chemsitry Question Bank em 218992TharaneshNo ratings yet
- 12th CHEMISTRY - 2mark Golden Questions - 2023Document4 pages12th CHEMISTRY - 2mark Golden Questions - 2023Ragavi100% (1)
- Senior Chemistry QuizDocument5 pagesSenior Chemistry Quizchinyembakelvin947No ratings yet
- SR Inter CHEMISTRY IMP-New With 70% Syllabus-Converted-1Document6 pagesSR Inter CHEMISTRY IMP-New With 70% Syllabus-Converted-1B. SwapnaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Question PaperDocument17 pagesChemical Reaction Question PapershivamNo ratings yet
- Science Passing - ChemestryDocument15 pagesScience Passing - Chemestryrevathishetty340No ratings yet
- Half Yearly Chapterwise Important QuestionsDocument4 pagesHalf Yearly Chapterwise Important Questionsfood loverNo ratings yet
- Model Paper With SolutionsDocument16 pagesModel Paper With SolutionsHoly GhostNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 17Document17 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 17jashwanth kumar58No ratings yet
- 12 2008 Chemistry 3 PDFDocument17 pages12 2008 Chemistry 3 PDFjashwanth kumar58No ratings yet
- Check List To Score ADocument14 pagesCheck List To Score AAnizah AsiminNo ratings yet
- 2010 12 Lyp Chemistry 01 PDFDocument17 pages2010 12 Lyp Chemistry 01 PDFanush JainNo ratings yet
- VivaDocument4 pagesVivagilchristNo ratings yet
- Pratice Questions Class 10Document14 pagesPratice Questions Class 10Dps BhangraNo ratings yet
- Studies of Heavy Metals: Unit - 7Document3 pagesStudies of Heavy Metals: Unit - 7Rabin KCNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-1 Important Questions IPE 2023-1Document2 pagesChemistry-1 Important Questions IPE 2023-1telukuntlasaivardhanNo ratings yet
- 3 Mark QuestionsDocument5 pages3 Mark QuestionstcesatishNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Important Questions em 218063Document9 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Important Questions em 218063kadachitti2626No ratings yet
- Chemistry Important 2 Mark Questions With AnswersDocument24 pagesChemistry Important 2 Mark Questions With AnswersDipti GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Important QuestionsDocument3 pagesChemistry Important QuestionsAavash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Questions - Answers Bank Class - Xii Subject - Chemistry UNIT-5 (Surface Chemistry)Document6 pagesQuestions - Answers Bank Class - Xii Subject - Chemistry UNIT-5 (Surface Chemistry)Abhay BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument19 pagesChemical Reactionsimraan smNo ratings yet
- Chemistry CHP 1 Important QuestionsDocument3 pagesChemistry CHP 1 Important QuestionsSamanwita KunduNo ratings yet
- 12th CHEMISTRY - Golden 3marks Questions - 2023Document4 pages12th CHEMISTRY - Golden 3marks Questions - 2023coolboy289.mNo ratings yet
- 12th Class Guess Papers 2024 Chemistry LongDocument3 pages12th Class Guess Papers 2024 Chemistry LongMuhammad HaseebNo ratings yet
- PRE TEST ExamDocument3 pagesPRE TEST ExamhaifaniaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Part 2 - Previous Board QuestionDocument13 pagesChemistry Part 2 - Previous Board QuestionSay2LearnNo ratings yet
- Lab Exam. PrefinalDocument1 pageLab Exam. PrefinalAirah Pearl WagaNo ratings yet
- Slide 1Document26 pagesSlide 1ShreyaNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Molecules NotesDocument5 pagesAtoms and Molecules Noteslohitha charyNo ratings yet
- I PUC Model QP AnswerDocument8 pagesI PUC Model QP AnswerSamanth PattarNo ratings yet
- TS SR Chemistry Imp Questions PDFDocument5 pagesTS SR Chemistry Imp Questions PDFUnknown Khan100% (3)
- Test Paper - Chapter - 1 (S - X)Document2 pagesTest Paper - Chapter - 1 (S - X)Víshál RánáNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Test (MMDocument5 pagesChemistry Test (MMVanshika BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 The P Block ElementsDocument25 pagesChapter 7 The P Block Elementspriyanka kNo ratings yet
- SR Chemistry 30-40 MarksDocument5 pagesSR Chemistry 30-40 Markssuranenisannik.bh23No ratings yet
- Ts SR Chemistry Imp Questions 2023-24Document6 pagesTs SR Chemistry Imp Questions 2023-24pandu2006goudNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument9 pagesChemistrySudha NepalNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper-03 CHEMISTRY (Theory) Class - XI: 2 4 X 2 1.33L of Ammonia 3 3Document8 pagesSample Paper-03 CHEMISTRY (Theory) Class - XI: 2 4 X 2 1.33L of Ammonia 3 3SarthakNo ratings yet
- Aliphatics Home PackageDocument6 pagesAliphatics Home PackageelishamahubiNo ratings yet
- Model Paper 5 SchemeDocument12 pagesModel Paper 5 SchemeKalyan ReddyNo ratings yet
- 10th Science Byjus SolutionsDocument159 pages10th Science Byjus SolutionsChinmay B PNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solution For Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument8 pagesNCERT Solution For Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equationssamiksha choudharyNo ratings yet
- To Download Other Subject Question Bank Visit WWW - Eshaale.inDocument18 pagesTo Download Other Subject Question Bank Visit WWW - Eshaale.inSwetha RNNo ratings yet
- Ocio 729: RoctioDocument2 pagesOcio 729: RoctioSaurish SakhreNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledSaurish SakhreNo ratings yet
- First Prelims MathsDocument6 pagesFirst Prelims MathsSaurish SakhreNo ratings yet
- English Language Practice Paper 2Document6 pagesEnglish Language Practice Paper 2Saurish SakhreNo ratings yet
- The Bishop's School, Undri English Language PaperDocument14 pagesThe Bishop's School, Undri English Language PaperSaurish SakhreNo ratings yet
- English Language Test Position DeterminingDocument5 pagesEnglish Language Test Position DeterminingSaurish SakhreNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledSaurish SakhreNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledSaurish SakhreNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledSaurish SakhreNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledSaurish SakhreNo ratings yet
- Avocado-Flottweg Decanter 2 y 3 PhasesDocument12 pagesAvocado-Flottweg Decanter 2 y 3 PhasesRenzo Saavedra100% (1)
- Headed Studs NELSONDocument1 pageHeaded Studs NELSONNuno Telmo LopesNo ratings yet
- CarcosealunsfDocument2 pagesCarcosealunsfmattiaNo ratings yet
- Royce OverviewDocument8 pagesRoyce OverviewRyan JayNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 PHARMACOLOGY - PrelimsDocument26 pagesNCM 106 PHARMACOLOGY - PrelimsKelsey Macaraig100% (3)
- Prepartion of Folin-Ciocalteu's Phenol ReagentDocument4 pagesPrepartion of Folin-Ciocalteu's Phenol Reagentchokyhara6No ratings yet
- Ignition Transient of Large Solid Rocket MotorDocument98 pagesIgnition Transient of Large Solid Rocket Motorned_marianNo ratings yet
- Thermanit Mts 3 (G Crmo91, Er90s-B9)Document1 pageThermanit Mts 3 (G Crmo91, Er90s-B9)brunizzaNo ratings yet
- Mil DTL 244C - Amendment 1Document40 pagesMil DTL 244C - Amendment 1B.EKICINo ratings yet
- Industrial Pipe Marking Solutions: Oil & GasDocument16 pagesIndustrial Pipe Marking Solutions: Oil & GasHotnCrispy CrispyNo ratings yet
- Classification of Essential OilDocument1 pageClassification of Essential OilElizabelth Woan Chyi75% (4)
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Chemistry 0620/12 March 2019Document38 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Chemistry 0620/12 March 2019aung aungNo ratings yet
- Exploring Chemistry Year 8Document64 pagesExploring Chemistry Year 8Judy KhattabNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Zetamix AluminaDocument2 pagesDatasheet Zetamix Aluminaamandapoly0123No ratings yet
- Nitrate Removal IX SBADocument3 pagesNitrate Removal IX SBAAnandNo ratings yet
- Two-Step: Integrated Process For Production of Xylose, Furfural, and Glucose From Bagasse by Acid HydrolysisDocument6 pagesTwo-Step: Integrated Process For Production of Xylose, Furfural, and Glucose From Bagasse by Acid Hydrolysisprashant balamiNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced Paper 1 2013 PDFDocument41 pagesJEE Advanced Paper 1 2013 PDFK Venkatramana ReddyNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument14 pagesCooling Tower - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRaka Fajar NugrohoNo ratings yet
- MOM II - Module 1Document10 pagesMOM II - Module 1Wolf LordNo ratings yet
- Monod Equation ProblemDocument7 pagesMonod Equation Problemeiddnew100% (1)
- Ethyl Mercaptan - Data SheetDocument1 pageEthyl Mercaptan - Data SheetBn BnNo ratings yet
- CarbochemBrochure English14Document4 pagesCarbochemBrochure English14Hari BudiartoNo ratings yet
- Genome SequencingDocument16 pagesGenome SequencingOhhh OkayNo ratings yet
- Molecular Structure of Solid Liquid and GasDocument2 pagesMolecular Structure of Solid Liquid and GasKoser IrshadNo ratings yet
- 1st Seminar MicroscopeDocument50 pages1st Seminar MicroscopeManas DixitNo ratings yet
- 14 ThermochemistryDocument161 pages14 Thermochemistrysiewkiat0% (1)
- Heat Exchanger Specification Sheet Thermal NEC UnitsDocument1 pageHeat Exchanger Specification Sheet Thermal NEC Unitsmohsen ranjbarNo ratings yet
- Cooling Curve Shape Analysis Can Help Evaluate Quenchants: by M.E. Dakins, G E. Totten and R.W. HeinsDocument2 pagesCooling Curve Shape Analysis Can Help Evaluate Quenchants: by M.E. Dakins, G E. Totten and R.W. Heinsmayin007mixNo ratings yet
- 10th MCQ-QP AnswersDocument5 pages10th MCQ-QP AnswersNARENDRAN S0% (1)