Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Development and Function of Immune System: Summary By: Noor Alsheikh
Development and Function of Immune System: Summary By: Noor Alsheikh
Uploaded by
Noor AlsheikhCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Fahim Halim Khan - Elements of Immunology-Pearson Education (2011)Document509 pagesFahim Halim Khan - Elements of Immunology-Pearson Education (2011)yusra nadeem50% (2)
- 2013fall IndianpolisORGN AbstractsDocument368 pages2013fall IndianpolisORGN AbstractstinperasovicNo ratings yet
- Hematology Mudit Khanna PDFDocument40 pagesHematology Mudit Khanna PDFSylvia DiamondNo ratings yet
- Immuno Virology BacteriologyDocument309 pagesImmuno Virology BacteriologyJulianna MacintyreNo ratings yet
- Summary ImmunologyDocument1 pageSummary ImmunologyNoor AlsheikhNo ratings yet
- Immunology 2Document30 pagesImmunology 2ukashazam19No ratings yet
- 4 ImmunityDocument5 pages4 Immunityziadnasef186No ratings yet
- Difference Between Humoral Immunity and Cell Mediated ImmunityDocument3 pagesDifference Between Humoral Immunity and Cell Mediated ImmunityAloke SahaNo ratings yet
- Micro F2.Chapter 7 - 2022Document4 pagesMicro F2.Chapter 7 - 2022عبدالرحمن عابدNo ratings yet
- Sesi 1 - DR - Umi - Imunologi Transfusi DarahDocument46 pagesSesi 1 - DR - Umi - Imunologi Transfusi DarahWanda RyNo ratings yet
- Lactation Biology Animal Science 337: Immunology BasicsDocument30 pagesLactation Biology Animal Science 337: Immunology BasicsSoraya AyaNo ratings yet
- Imunology Review Mention Two Component of The Acquired Immune System!Document6 pagesImunology Review Mention Two Component of The Acquired Immune System!Fatmala Umi MaisarahNo ratings yet
- Cytokines in Health and DiseasesDocument22 pagesCytokines in Health and DiseasesProvidence UzomaNo ratings yet
- DR - Irma-Dasar Imunologi Dan Reaksi HipersensitivitasDocument89 pagesDR - Irma-Dasar Imunologi Dan Reaksi Hipersensitivitasvandhani79No ratings yet
- L5 Is Adaptive ImmunityDocument3 pagesL5 Is Adaptive ImmunityErickson MoragaNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Agustin AC Agustin AM Balmaceda Cerezo Caluya DolorosoDocument24 pagesImmunology: Agustin AC Agustin AM Balmaceda Cerezo Caluya DolorosoConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- 5a. Mekanisme Imunitas Seluler Dan HumoralDocument32 pages5a. Mekanisme Imunitas Seluler Dan HumoralGaluh Apsari SyafranNo ratings yet
- 19 - Lecture - PPT Lymphatic ImmunityDocument191 pages19 - Lecture - PPT Lymphatic ImmunityGwyneth Adrienne Leigh VillapandoNo ratings yet
- Viral Immunity: Rajiv Gandhi College of Veterinary and Animal ScienceDocument14 pagesViral Immunity: Rajiv Gandhi College of Veterinary and Animal SciencesangeethabalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Elements of Host Protective Responses - ClinicalKeyDocument12 pagesChapter 7. Elements of Host Protective Responses - ClinicalKeyد. محمد سند راشد الحصينيNo ratings yet
- 4.cytokines - MamounDocument26 pages4.cytokines - Mamounrozaadil99No ratings yet
- ISBBhandoutDocument55 pagesISBBhandoutRed GillianNo ratings yet
- Study Guide: Cytokines Associated With Innate ImmunityDocument12 pagesStudy Guide: Cytokines Associated With Innate ImmunityxxxxxxxNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 2024Document25 pagesLecture 6 2024emanelshimy51No ratings yet
- Acquired ImmunityDocument16 pagesAcquired ImmunityMohammed Hashem100% (1)
- Pratiwi S Gunawan, BDS., DDS., MDSC, PHDDocument53 pagesPratiwi S Gunawan, BDS., DDS., MDSC, PHDBima Ewando KabanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document58 pagesChapter 2LA TSHTTNo ratings yet
- Micro F2.chapter 8 - 2022Document3 pagesMicro F2.chapter 8 - 2022Gamal Eldien ElsaiedNo ratings yet
- Isabela State University: Immunology (Bs Psych 2)Document8 pagesIsabela State University: Immunology (Bs Psych 2)Charlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Summary Chart: Fundamental ConceptsDocument3 pagesSummary Chart: Fundamental ConceptsChrystelle Mariano TibayNo ratings yet
- Parcial 3 Inmunología T Cell DevelopmentDocument4 pagesParcial 3 Inmunología T Cell Developmentjuan mondaNo ratings yet
- Immune: Immunis (Latin) Exemption From Charges (Taxes, Expenses)Document31 pagesImmune: Immunis (Latin) Exemption From Charges (Taxes, Expenses)Anonymous wVgEAr6No ratings yet
- Stevens (Science) Med TechDocument31 pagesStevens (Science) Med TechnotsoninjaninjaNo ratings yet
- Ishaque PK Pondicherry UniversityDocument34 pagesIshaque PK Pondicherry UniversityRiska Resty WasitaNo ratings yet
- Immunology: E. A. JalalDocument60 pagesImmunology: E. A. JalalazlinnursulianyNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Immune SystemDocument28 pagesAdaptive Immune SystemRiana AgathaNo ratings yet
- 07 Mikrobiologi Endodontik (PPT 2 Imunologi)Document88 pages07 Mikrobiologi Endodontik (PPT 2 Imunologi)Nahdah Zhafirah SyamNo ratings yet
- Immunology 3Document116 pagesImmunology 3ahmed_abu_alrobNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Dr. E. Okon, MRCSDocument28 pagesImmunology: Dr. E. Okon, MRCSEdwin OkonNo ratings yet
- Functions of TH Cells, Th1 and Th2 Cells, Macrophages, TC Cells, and NK Cells ImmunoregulationDocument19 pagesFunctions of TH Cells, Th1 and Th2 Cells, Macrophages, TC Cells, and NK Cells Immunoregulationmohammed agungNo ratings yet
- Cells & Organs of The Immune System, Cellular ImmunityDocument53 pagesCells & Organs of The Immune System, Cellular ImmunityfrenchaticiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document2 pagesChapter 14Nona PeriarceNo ratings yet
- Prelim - Adaptive Immune ResponseDocument12 pagesPrelim - Adaptive Immune ResponseJustin BellosaNo ratings yet
- 12 13 2006 Life Science Introduction To Immune 2006Document99 pages12 13 2006 Life Science Introduction To Immune 2006api-3696530No ratings yet
- Handout For Innate 1, Innate 2 and AdaptiveDocument26 pagesHandout For Innate 1, Innate 2 and Adaptive7231598No ratings yet
- LymphocytesDocument5 pagesLymphocytesLilyNo ratings yet
- Cytokines: Cytokine Source Target/Effect OtherDocument1 pageCytokines: Cytokine Source Target/Effect OthermcwnotesNo ratings yet
- Immunology High Yield For STEP 1Document13 pagesImmunology High Yield For STEP 1lourdesfercabNo ratings yet
- Immunopathology: Normal Immune ResponseDocument13 pagesImmunopathology: Normal Immune ResponseChinedu H. DuruNo ratings yet
- Linfocitos B y T-DepuratedDocument18 pagesLinfocitos B y T-DepuratedByron Emerson Gonzales GonzalesNo ratings yet
- General Features of The Immune SystemDocument6 pagesGeneral Features of The Immune SystemMinerva Bautista RoseteNo ratings yet
- JSD 1 15Document10 pagesJSD 1 15freeda.ampottiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Eight: CytokineDocument6 pagesChapter Eight: CytokineNur LiyanaNo ratings yet
- InterleucinasDocument1 pageInterleucinasSofía RivasNo ratings yet
- Cell - Cytokine TablesDocument6 pagesCell - Cytokine Tablesnaazaninrahat76No ratings yet
- Essay ImmuneDocument8 pagesEssay ImmuneAishah Najihah100% (1)
- Innate and Adaptive Immunity: - Innate Is FIRST LINE OF DEFENCE: No Prior Exposure Needed - Comprised OfDocument31 pagesInnate and Adaptive Immunity: - Innate Is FIRST LINE OF DEFENCE: No Prior Exposure Needed - Comprised OfBegumHazinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 - The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body DefensesDocument2 pagesChapter 21 - The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body DefensesChryza Faith QuicoyNo ratings yet
- Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)Document8 pagesMajor Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)Rishav GautamNo ratings yet
- 1 Pendahuluan Imunologi Klinis-Imunitas UmumDocument36 pages1 Pendahuluan Imunologi Klinis-Imunitas UmumAniend Uchuz ChizNo ratings yet
- Preclinical Immunology and Microbiology Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1From EverandPreclinical Immunology and Microbiology Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Immunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityFrom EverandImmunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityNo ratings yet
- Transfer Factors: Properties, Mechanism of Action and Its Clinical ApplicationsFrom EverandTransfer Factors: Properties, Mechanism of Action and Its Clinical ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Transfusion SummaryDocument3 pagesTransfusion SummaryNoor AlsheikhNo ratings yet
- Calcium Metabolism QuestionsDocument1 pageCalcium Metabolism QuestionsNoor AlsheikhNo ratings yet
- Transfusion: Summary By: Noor AlsheikhDocument4 pagesTransfusion: Summary By: Noor AlsheikhNoor AlsheikhNo ratings yet
- Myeloid Neoplastic Disorders SummaryDocument5 pagesMyeloid Neoplastic Disorders SummaryNoor AlsheikhNo ratings yet
- Summary ImmunologyDocument1 pageSummary ImmunologyNoor AlsheikhNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Related DrugsDocument5 pagesReproductive System Related DrugsNoor AlsheikhNo ratings yet
- Test 1 - APQ Model Answers-1Document14 pagesTest 1 - APQ Model Answers-1Matsiri ImmanuelNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument92 pagesImmunology[161]Shuaib AktherNo ratings yet
- Brochure Services IHC StainsDocument16 pagesBrochure Services IHC StainsYousra ZeidanNo ratings yet
- Aging, Inflammation, Immunity and Periodontal Disease PDFDocument22 pagesAging, Inflammation, Immunity and Periodontal Disease PDFCayadi Sidarta Antonius PocipNo ratings yet
- Biology - Google Drive 123456Document168 pagesBiology - Google Drive 123456Nirmal ChakravarthyNo ratings yet
- SBRC HematologyOncology 2Document80 pagesSBRC HematologyOncology 2dalia khamoNo ratings yet
- Question PaperDocument16 pagesQuestion PaperAashi AkterNo ratings yet
- Antigen AntibodiesDocument65 pagesAntigen AntibodiespradeepbawaneNo ratings yet
- The Pathogenesis of Immune Thrombocytopaenic Purpura: ReviewDocument11 pagesThe Pathogenesis of Immune Thrombocytopaenic Purpura: ReviewNaomi ThamNo ratings yet
- Full HD English Editorials 2-1-2022Document25 pagesFull HD English Editorials 2-1-2022uihuyhyubuhbNo ratings yet
- Becker Immunology Microbiology 2013Document454 pagesBecker Immunology Microbiology 2013Goose ChapmanNo ratings yet
- Types of Leucocytes (White Blood Cells) : Lymphocytes: Monocytes: Basophils: Neutrophils: EosinophilsDocument4 pagesTypes of Leucocytes (White Blood Cells) : Lymphocytes: Monocytes: Basophils: Neutrophils: Eosinophilsjust-maybe202No ratings yet
- USMLE Step 1 Uworld NotesDocument26 pagesUSMLE Step 1 Uworld NotesSweta DabhiNo ratings yet
- Score Report - Immunology & Serology at Free Online Quiz SchoolDocument29 pagesScore Report - Immunology & Serology at Free Online Quiz SchoolThomas Giang100% (1)
- Full Download Book Immunology 9Th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Immunology 9Th Edition PDFtommy.peacock526100% (29)
- Immunology WorksheetDocument3 pagesImmunology WorksheetJavia CampbellNo ratings yet
- Human Health and DiseasesDocument24 pagesHuman Health and DiseasesAnujith AnuNo ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Immunology A Short Course 7th Edition All ChapterDocument26 pagesFull Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Immunology A Short Course 7th Edition All Chapterfooleexstyle100% (7)
- Immunology OutlineDocument43 pagesImmunology OutlinekudosforkimNo ratings yet
- Microbio Halo HaloDocument94 pagesMicrobio Halo HaloCARRAO, Samuel Jr.No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 16 MicroparaDocument46 pagesCHAPTER 16 MicroparaKathlyn LopeñaNo ratings yet
- DBT BET Question Paper 2010 With Answer KeyDocument24 pagesDBT BET Question Paper 2010 With Answer KeyAbhay Kumar100% (3)
- Antibody Production and Purification Technical Handbook, Version 2Document41 pagesAntibody Production and Purification Technical Handbook, Version 2bh14561No ratings yet
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)Document38 pagesChronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)Vikkineshwaran Siva Subramaniam100% (2)
- The Blood: Rubie Maranan-Causaren, MSDocument73 pagesThe Blood: Rubie Maranan-Causaren, MSlady ann jimenez100% (3)
- 415 MSC Zoology PDFDocument43 pages415 MSC Zoology PDFravi kothapallyNo ratings yet
Development and Function of Immune System: Summary By: Noor Alsheikh
Development and Function of Immune System: Summary By: Noor Alsheikh
Uploaded by
Noor AlsheikhOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Development and Function of Immune System: Summary By: Noor Alsheikh
Development and Function of Immune System: Summary By: Noor Alsheikh
Uploaded by
Noor AlsheikhCopyright:
Available Formats
Week 10
Immunology
Development and function of
immune system
Summary by: Noor Alsheikh
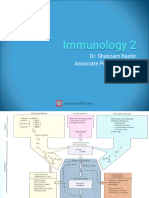
The differentiation is under the influence of:
1-growth factors:
Stem cell factor, IL-1, 3, 4, 6, 7, GM-CSF
Hemopoitic stem 2-cell-cell interactions.
cell
lymphoid myeloid
progenitor cell progenitor cell
B cell
T cell -Cytokines for development:
-Develops in thymus (thymulin, thymopoiten and a1 & B4 thymosin) No receptors for specific antigens, They include:
IL-7, BCGF, IL-1,2,4,6 Phagocytes
-Attracted by integrins and chemotactic factors like B2 microglobulin -Stages of development:
-Innervated by ANS, so affected by stress - By the process of Phagocytosis
Pro B cell: heavy chain - The major phagocytic cells are the monocytes, macrophages
Pre B cell: light chain, IgM, Iga, IgB and neutrophils.
Development in stages: Immature: IgM/ IgD
-Stage I: IL-1 and TNF removes CD34 and double negative -Mac-1 (CD11b-CD18) is an important CD marker for
Mature: expressing both apoptosis to self reactive mononuclear phagocytes
-Stage II: IL-7 gives T cell receptor, CD3 and double positive (4
5-15%, Act as APC and express IgM and IgG
and 8)
Cells markers: CD19,20,79 Antigen presenting cells (APC)
-Stage III:
Stimulated by following cytokines: -They process and present antigen to TH cells and Tc cells.
Positive selection, if cell binds to:
clonal proliferation: IL-2,4,13 -Examples: are dendritic cells,monocytes, macrophages, B-cells.
MHC 1 -> CD8
IgE plasma cell: IL-4,13 -Follicular dendritic cells are APC, which stores antigens and
MHC2 -> CD4
IgG plasma cell: IL-4,10,IFN gamma present them to B-cells (Important for memory).
negative selection:
IgA plasma cell: TGFB and IL-5
if high interaction with self peptide -> apoptosis
-Maturation happens in secondary follicles Eosinophils
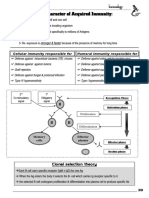
-Primary antibody response: early IgM then IgG -They are Granular WBC ( 2-5% of leukocytes in healthy
T cells either: -Secondary antibody response: memory cells secrete IgG that individual)
T helper (CD4): reacts by binding to MHC 2 on APC response longer, better affinity -They increase in number in allergic and parasitic diseases.
Activated by IL-2
-They have receptors for IgG and IgE antibodies (Fc receptors)
Types: Innate lymphoid cells and receptors for complement.
Th1: cell mediated immunity, secrtes: IL-2, IFN gamma, TNF
-When stimulated, they release granules and toxins such as
Th2: humoral immunity (AB), secretes: IL-4,5,6,10
major basic protein and Eosinophil cationic proteins by
Th9,17, 22…
exocytosis.
T killer (CD8): reacts by binding to MHC 1 on all cells
Activated by IL-2, IL-6 from Th cells
Basophils and Mast Cells
Actions: perforin & granzymes, fas and fas ligand, TNF & TNF-R,
-Basophils and mast cells are similar in function and
lso secretes INF gamma as antiviral agent
Function: defence, wound healing and maintenance of morphology.
epithelial integrity -Basophils are found in the circulation, whereas mast cells are
found in the mucosa and connective tissue and live longer.
Therapeutic application: -Release of mast cell granules lead to vasodilatation, increased
-Transplantation: anti-CD3, anti-CD4 and anti-CD8 monoclonal antibodies vascular permeability, smooth muscle contraction and WBC
-Hypersensitivity: Monoclonal antibody therapy for allergy. chemotaxis.
- Autoimmunity: The use of anti-TNF antibodies (Humira) in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. -the symptoms of allergy and are important for immunity against
-Immunity to tumour: Blocking inhibition by CTLA-4 (using antagonistic antibodies against CTLA-4: FDA approved parasite.
for melanoma in 2011 (ipilimumab) -have receptors for IgE antibody and for complement .
-Stem cell therapy: current and future
You might also like
- Fahim Halim Khan - Elements of Immunology-Pearson Education (2011)Document509 pagesFahim Halim Khan - Elements of Immunology-Pearson Education (2011)yusra nadeem50% (2)
- 2013fall IndianpolisORGN AbstractsDocument368 pages2013fall IndianpolisORGN AbstractstinperasovicNo ratings yet
- Hematology Mudit Khanna PDFDocument40 pagesHematology Mudit Khanna PDFSylvia DiamondNo ratings yet
- Immuno Virology BacteriologyDocument309 pagesImmuno Virology BacteriologyJulianna MacintyreNo ratings yet
- Summary ImmunologyDocument1 pageSummary ImmunologyNoor AlsheikhNo ratings yet
- Immunology 2Document30 pagesImmunology 2ukashazam19No ratings yet
- 4 ImmunityDocument5 pages4 Immunityziadnasef186No ratings yet
- Difference Between Humoral Immunity and Cell Mediated ImmunityDocument3 pagesDifference Between Humoral Immunity and Cell Mediated ImmunityAloke SahaNo ratings yet
- Micro F2.Chapter 7 - 2022Document4 pagesMicro F2.Chapter 7 - 2022عبدالرحمن عابدNo ratings yet
- Sesi 1 - DR - Umi - Imunologi Transfusi DarahDocument46 pagesSesi 1 - DR - Umi - Imunologi Transfusi DarahWanda RyNo ratings yet
- Lactation Biology Animal Science 337: Immunology BasicsDocument30 pagesLactation Biology Animal Science 337: Immunology BasicsSoraya AyaNo ratings yet
- Imunology Review Mention Two Component of The Acquired Immune System!Document6 pagesImunology Review Mention Two Component of The Acquired Immune System!Fatmala Umi MaisarahNo ratings yet
- Cytokines in Health and DiseasesDocument22 pagesCytokines in Health and DiseasesProvidence UzomaNo ratings yet
- DR - Irma-Dasar Imunologi Dan Reaksi HipersensitivitasDocument89 pagesDR - Irma-Dasar Imunologi Dan Reaksi Hipersensitivitasvandhani79No ratings yet
- L5 Is Adaptive ImmunityDocument3 pagesL5 Is Adaptive ImmunityErickson MoragaNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Agustin AC Agustin AM Balmaceda Cerezo Caluya DolorosoDocument24 pagesImmunology: Agustin AC Agustin AM Balmaceda Cerezo Caluya DolorosoConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- 5a. Mekanisme Imunitas Seluler Dan HumoralDocument32 pages5a. Mekanisme Imunitas Seluler Dan HumoralGaluh Apsari SyafranNo ratings yet
- 19 - Lecture - PPT Lymphatic ImmunityDocument191 pages19 - Lecture - PPT Lymphatic ImmunityGwyneth Adrienne Leigh VillapandoNo ratings yet
- Viral Immunity: Rajiv Gandhi College of Veterinary and Animal ScienceDocument14 pagesViral Immunity: Rajiv Gandhi College of Veterinary and Animal SciencesangeethabalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Elements of Host Protective Responses - ClinicalKeyDocument12 pagesChapter 7. Elements of Host Protective Responses - ClinicalKeyد. محمد سند راشد الحصينيNo ratings yet
- 4.cytokines - MamounDocument26 pages4.cytokines - Mamounrozaadil99No ratings yet
- ISBBhandoutDocument55 pagesISBBhandoutRed GillianNo ratings yet
- Study Guide: Cytokines Associated With Innate ImmunityDocument12 pagesStudy Guide: Cytokines Associated With Innate ImmunityxxxxxxxNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 2024Document25 pagesLecture 6 2024emanelshimy51No ratings yet
- Acquired ImmunityDocument16 pagesAcquired ImmunityMohammed Hashem100% (1)
- Pratiwi S Gunawan, BDS., DDS., MDSC, PHDDocument53 pagesPratiwi S Gunawan, BDS., DDS., MDSC, PHDBima Ewando KabanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document58 pagesChapter 2LA TSHTTNo ratings yet
- Micro F2.chapter 8 - 2022Document3 pagesMicro F2.chapter 8 - 2022Gamal Eldien ElsaiedNo ratings yet
- Isabela State University: Immunology (Bs Psych 2)Document8 pagesIsabela State University: Immunology (Bs Psych 2)Charlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Summary Chart: Fundamental ConceptsDocument3 pagesSummary Chart: Fundamental ConceptsChrystelle Mariano TibayNo ratings yet
- Parcial 3 Inmunología T Cell DevelopmentDocument4 pagesParcial 3 Inmunología T Cell Developmentjuan mondaNo ratings yet
- Immune: Immunis (Latin) Exemption From Charges (Taxes, Expenses)Document31 pagesImmune: Immunis (Latin) Exemption From Charges (Taxes, Expenses)Anonymous wVgEAr6No ratings yet
- Stevens (Science) Med TechDocument31 pagesStevens (Science) Med TechnotsoninjaninjaNo ratings yet
- Ishaque PK Pondicherry UniversityDocument34 pagesIshaque PK Pondicherry UniversityRiska Resty WasitaNo ratings yet
- Immunology: E. A. JalalDocument60 pagesImmunology: E. A. JalalazlinnursulianyNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Immune SystemDocument28 pagesAdaptive Immune SystemRiana AgathaNo ratings yet
- 07 Mikrobiologi Endodontik (PPT 2 Imunologi)Document88 pages07 Mikrobiologi Endodontik (PPT 2 Imunologi)Nahdah Zhafirah SyamNo ratings yet
- Immunology 3Document116 pagesImmunology 3ahmed_abu_alrobNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Dr. E. Okon, MRCSDocument28 pagesImmunology: Dr. E. Okon, MRCSEdwin OkonNo ratings yet
- Functions of TH Cells, Th1 and Th2 Cells, Macrophages, TC Cells, and NK Cells ImmunoregulationDocument19 pagesFunctions of TH Cells, Th1 and Th2 Cells, Macrophages, TC Cells, and NK Cells Immunoregulationmohammed agungNo ratings yet
- Cells & Organs of The Immune System, Cellular ImmunityDocument53 pagesCells & Organs of The Immune System, Cellular ImmunityfrenchaticiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document2 pagesChapter 14Nona PeriarceNo ratings yet
- Prelim - Adaptive Immune ResponseDocument12 pagesPrelim - Adaptive Immune ResponseJustin BellosaNo ratings yet
- 12 13 2006 Life Science Introduction To Immune 2006Document99 pages12 13 2006 Life Science Introduction To Immune 2006api-3696530No ratings yet
- Handout For Innate 1, Innate 2 and AdaptiveDocument26 pagesHandout For Innate 1, Innate 2 and Adaptive7231598No ratings yet
- LymphocytesDocument5 pagesLymphocytesLilyNo ratings yet
- Cytokines: Cytokine Source Target/Effect OtherDocument1 pageCytokines: Cytokine Source Target/Effect OthermcwnotesNo ratings yet
- Immunology High Yield For STEP 1Document13 pagesImmunology High Yield For STEP 1lourdesfercabNo ratings yet
- Immunopathology: Normal Immune ResponseDocument13 pagesImmunopathology: Normal Immune ResponseChinedu H. DuruNo ratings yet
- Linfocitos B y T-DepuratedDocument18 pagesLinfocitos B y T-DepuratedByron Emerson Gonzales GonzalesNo ratings yet
- General Features of The Immune SystemDocument6 pagesGeneral Features of The Immune SystemMinerva Bautista RoseteNo ratings yet
- JSD 1 15Document10 pagesJSD 1 15freeda.ampottiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Eight: CytokineDocument6 pagesChapter Eight: CytokineNur LiyanaNo ratings yet
- InterleucinasDocument1 pageInterleucinasSofía RivasNo ratings yet
- Cell - Cytokine TablesDocument6 pagesCell - Cytokine Tablesnaazaninrahat76No ratings yet
- Essay ImmuneDocument8 pagesEssay ImmuneAishah Najihah100% (1)
- Innate and Adaptive Immunity: - Innate Is FIRST LINE OF DEFENCE: No Prior Exposure Needed - Comprised OfDocument31 pagesInnate and Adaptive Immunity: - Innate Is FIRST LINE OF DEFENCE: No Prior Exposure Needed - Comprised OfBegumHazinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 - The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body DefensesDocument2 pagesChapter 21 - The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body DefensesChryza Faith QuicoyNo ratings yet
- Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)Document8 pagesMajor Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)Rishav GautamNo ratings yet
- 1 Pendahuluan Imunologi Klinis-Imunitas UmumDocument36 pages1 Pendahuluan Imunologi Klinis-Imunitas UmumAniend Uchuz ChizNo ratings yet
- Preclinical Immunology and Microbiology Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1From EverandPreclinical Immunology and Microbiology Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Immunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityFrom EverandImmunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityNo ratings yet
- Transfer Factors: Properties, Mechanism of Action and Its Clinical ApplicationsFrom EverandTransfer Factors: Properties, Mechanism of Action and Its Clinical ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Transfusion SummaryDocument3 pagesTransfusion SummaryNoor AlsheikhNo ratings yet
- Calcium Metabolism QuestionsDocument1 pageCalcium Metabolism QuestionsNoor AlsheikhNo ratings yet
- Transfusion: Summary By: Noor AlsheikhDocument4 pagesTransfusion: Summary By: Noor AlsheikhNoor AlsheikhNo ratings yet
- Myeloid Neoplastic Disorders SummaryDocument5 pagesMyeloid Neoplastic Disorders SummaryNoor AlsheikhNo ratings yet
- Summary ImmunologyDocument1 pageSummary ImmunologyNoor AlsheikhNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Related DrugsDocument5 pagesReproductive System Related DrugsNoor AlsheikhNo ratings yet
- Test 1 - APQ Model Answers-1Document14 pagesTest 1 - APQ Model Answers-1Matsiri ImmanuelNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument92 pagesImmunology[161]Shuaib AktherNo ratings yet
- Brochure Services IHC StainsDocument16 pagesBrochure Services IHC StainsYousra ZeidanNo ratings yet
- Aging, Inflammation, Immunity and Periodontal Disease PDFDocument22 pagesAging, Inflammation, Immunity and Periodontal Disease PDFCayadi Sidarta Antonius PocipNo ratings yet
- Biology - Google Drive 123456Document168 pagesBiology - Google Drive 123456Nirmal ChakravarthyNo ratings yet
- SBRC HematologyOncology 2Document80 pagesSBRC HematologyOncology 2dalia khamoNo ratings yet
- Question PaperDocument16 pagesQuestion PaperAashi AkterNo ratings yet
- Antigen AntibodiesDocument65 pagesAntigen AntibodiespradeepbawaneNo ratings yet
- The Pathogenesis of Immune Thrombocytopaenic Purpura: ReviewDocument11 pagesThe Pathogenesis of Immune Thrombocytopaenic Purpura: ReviewNaomi ThamNo ratings yet
- Full HD English Editorials 2-1-2022Document25 pagesFull HD English Editorials 2-1-2022uihuyhyubuhbNo ratings yet
- Becker Immunology Microbiology 2013Document454 pagesBecker Immunology Microbiology 2013Goose ChapmanNo ratings yet
- Types of Leucocytes (White Blood Cells) : Lymphocytes: Monocytes: Basophils: Neutrophils: EosinophilsDocument4 pagesTypes of Leucocytes (White Blood Cells) : Lymphocytes: Monocytes: Basophils: Neutrophils: Eosinophilsjust-maybe202No ratings yet
- USMLE Step 1 Uworld NotesDocument26 pagesUSMLE Step 1 Uworld NotesSweta DabhiNo ratings yet
- Score Report - Immunology & Serology at Free Online Quiz SchoolDocument29 pagesScore Report - Immunology & Serology at Free Online Quiz SchoolThomas Giang100% (1)
- Full Download Book Immunology 9Th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Immunology 9Th Edition PDFtommy.peacock526100% (29)
- Immunology WorksheetDocument3 pagesImmunology WorksheetJavia CampbellNo ratings yet
- Human Health and DiseasesDocument24 pagesHuman Health and DiseasesAnujith AnuNo ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Immunology A Short Course 7th Edition All ChapterDocument26 pagesFull Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Immunology A Short Course 7th Edition All Chapterfooleexstyle100% (7)
- Immunology OutlineDocument43 pagesImmunology OutlinekudosforkimNo ratings yet
- Microbio Halo HaloDocument94 pagesMicrobio Halo HaloCARRAO, Samuel Jr.No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 16 MicroparaDocument46 pagesCHAPTER 16 MicroparaKathlyn LopeñaNo ratings yet
- DBT BET Question Paper 2010 With Answer KeyDocument24 pagesDBT BET Question Paper 2010 With Answer KeyAbhay Kumar100% (3)
- Antibody Production and Purification Technical Handbook, Version 2Document41 pagesAntibody Production and Purification Technical Handbook, Version 2bh14561No ratings yet
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)Document38 pagesChronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)Vikkineshwaran Siva Subramaniam100% (2)
- The Blood: Rubie Maranan-Causaren, MSDocument73 pagesThe Blood: Rubie Maranan-Causaren, MSlady ann jimenez100% (3)
- 415 MSC Zoology PDFDocument43 pages415 MSC Zoology PDFravi kothapallyNo ratings yet