Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
165 viewsGRADE 12 - Physical Science - Second Quarterly Examination
GRADE 12 - Physical Science - Second Quarterly Examination
Uploaded by
Nil PadillaThe document is a 30 question multiple choice quiz on physical sciences topics including astronomy, physics, and Einstein's theory of relativity. It covers concepts like the shape of the Earth, planetary motion, Galileo's assertions about falling bodies, reflection and refraction of light, and Einstein's mass-energy equivalence formula. Students are asked to choose the correct answer for each question from the options provided.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- POGIL - KinematicsDocument4 pagesPOGIL - KinematicsmagiclcjNo ratings yet
- Transfer Function Models Representing The Dynamics of A MissileDocument15 pagesTransfer Function Models Representing The Dynamics of A MissileD.Viswanath100% (7)
- L8 - Example For Jacobian of RobotsDocument8 pagesL8 - Example For Jacobian of RobotsZul Fadhli100% (1)
- General Physics 1 - Budget of WorkDocument11 pagesGeneral Physics 1 - Budget of Workanon_145781083No ratings yet
- BeerVM11e PPT Ch11Document92 pagesBeerVM11e PPT Ch11brayanNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter Test PHYSICS 12Document4 pages4th Quarter Test PHYSICS 12Cris ElcarteNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Physical ScienceDocument5 pagesSummative Test Physical ScienceARNEL METILLONo ratings yet
- Origin of The Solar SystemDocument3 pagesOrigin of The Solar SystemZercyNice Imbong CarreonNo ratings yet
- Activity 8d. Convection CurrentDocument5 pagesActivity 8d. Convection CurrentGUILLER BELENNo ratings yet
- LP Phy Sci Q2-M5 (W2)Document4 pagesLP Phy Sci Q2-M5 (W2)MARIA DINA TAYACTACNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Physical Science Q2Document2 pagesWeek 1 - Physical Science Q2Gemma Quiocho-CardenasNo ratings yet
- Dlp-Investigating Principles Governing MotionDocument8 pagesDlp-Investigating Principles Governing MotionAngel GaluteraNo ratings yet
- Template 7e'sDocument2 pagesTemplate 7e'smaricris olayonNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Physical Science mhelDSDocument16 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Physical Science mhelDSRommelyn RosasNo ratings yet
- InnovationDocument2 pagesInnovationDoodz O MadronioNo ratings yet
- Physical Science DLL q2 (Week 4)Document2 pagesPhysical Science DLL q2 (Week 4)Esmale RyaNo ratings yet
- DLL - Speed, Velocity and AccelerationDocument2 pagesDLL - Speed, Velocity and AccelerationCyril Alba ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Quarter 3 LASDocument35 pagesPhysical Science Quarter 3 LASDrama LlamaNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Day 1Document5 pagesWeek 5 - Day 1RAMIL BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Free FallDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Free FallQueencess Ara TorresNo ratings yet
- Physical Science: Quarter 2 - Module 13 Special Theory of RelativityDocument21 pagesPhysical Science: Quarter 2 - Module 13 Special Theory of RelativityLlahona FajardoNo ratings yet
- psdll11 28 18Document2 pagespsdll11 28 18Christine De San JoseNo ratings yet
- Sample Lesson Exemplar - The Composition of The EarthDocument3 pagesSample Lesson Exemplar - The Composition of The EarthRommel DaysonNo ratings yet
- PDF Answerkey Earthlifescience - CompressDocument11 pagesPDF Answerkey Earthlifescience - CompressAlvin PaboresNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification 1 Semester/ 2 Quarterly Assessment Grade 12 Subject: Physical ScienceDocument5 pagesTable of Specification 1 Semester/ 2 Quarterly Assessment Grade 12 Subject: Physical ScienceArlance Sandra Marie MedinaNo ratings yet
- Week 7 - Physical-ScienceDocument1 pageWeek 7 - Physical-ScienceKayla TiquisNo ratings yet
- Marinduque National High School: Department of Education MIMAROPA Region Isok 1, Boac, MarinduqueDocument4 pagesMarinduque National High School: Department of Education MIMAROPA Region Isok 1, Boac, MarinduqueMaria Joy VelascoNo ratings yet
- PS - Quarter 2 - Week 1Document6 pagesPS - Quarter 2 - Week 1edgardo viadorNo ratings yet
- Session 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4: I. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesSession 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4: I. ObjectivesSherwin SantosNo ratings yet
- Universe and The Solar SystemDocument16 pagesUniverse and The Solar SystemJennifer MagangoNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test in PhySciDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Test in PhySciJuliane Rebecca PitlongayNo ratings yet
- Third Periodical PhysciDocument4 pagesThird Periodical PhysciMiss RonaNo ratings yet
- GenPhysics2 Module 2Document20 pagesGenPhysics2 Module 2I can see your pixels 2No ratings yet
- DLL Mod.4 3RD QRTR G10Document7 pagesDLL Mod.4 3RD QRTR G10Sarah Candelaria ArcellanaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Exam in PhySciDocument4 pages3rd Quarter Exam in PhySciyvetteNo ratings yet
- Math9 - Q4 - Mod5 - Wk5 - Real Life Problems Involving Right Triangles - v5Document36 pagesMath9 - Q4 - Mod5 - Wk5 - Real Life Problems Involving Right Triangles - v5Sam dela CernaNo ratings yet
- Shs-Tos Earth and Life ScienceDocument1 pageShs-Tos Earth and Life SciencerichardsamranoNo ratings yet
- 2022 23 DLL WK3 Q2 EALS Nov. 14 18 2022 Modified 4Document6 pages2022 23 DLL WK3 Q2 EALS Nov. 14 18 2022 Modified 4glaiza.riveraNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in PHYSICAL SCIENCEDocument3 pagesSummative Test in PHYSICAL SCIENCEMaelNo ratings yet
- Bow MilDocument1 pageBow MilScarletBeauty Enriquez-DiagbelNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Physical Science Q2 Wk7 GLAKDocument16 pagesGrade 12 Physical Science Q2 Wk7 GLAKJose GulitiwNo ratings yet
- Earth Life Science DLL Week 2Document8 pagesEarth Life Science DLL Week 2Janice Danieles Siano-TahuyanNo ratings yet
- MATATAG Accomplishment ReportDocument5 pagesMATATAG Accomplishment Reportbauder langkiaNo ratings yet
- DLL PHY-SCI (Aug Week2)Document5 pagesDLL PHY-SCI (Aug Week2)Jesse GabrielNo ratings yet
- PT G8 ScienceDocument5 pagesPT G8 ScienceJoville Palermo UrsolinoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Quarter 3 Week 2: Not For SaleDocument7 pagesPhysical Science Quarter 3 Week 2: Not For SaleChristien Kate GonzalesNo ratings yet
- LP Phy Sci Q2-M3 (W1)Document3 pagesLP Phy Sci Q2-M3 (W1)MARIA DINA TAYACTACNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Earth and Life Science Grade-11Document5 pagesDepartment of Education: Earth and Life Science Grade-11Ro ZenNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Week 4 DLLDocument6 pagesEarth and Life Week 4 DLLReyes CzarinaNo ratings yet
- EALS 1st Quarter Exam SY 2022-2023Document5 pagesEALS 1st Quarter Exam SY 2022-2023Maria Lourdes PunayNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Accomplishment Report School Year 2020-2021 Grade I - RosalDocument36 pagesDepartment of Education: Accomplishment Report School Year 2020-2021 Grade I - RosalCandida Ortaliza CuagdanNo ratings yet
- LIGHT Quiz - Secondary 2Document6 pagesLIGHT Quiz - Secondary 2priyaNo ratings yet
- Budget-of-Work-Earth and Life ScienceDocument5 pagesBudget-of-Work-Earth and Life Sciencejoei Arquero100% (1)
- Physical Science - Day 56Document6 pagesPhysical Science - Day 56Maria Sheila OtlangNo ratings yet
- 2weekly Home Learning Plan For Modular DistanceDocument8 pages2weekly Home Learning Plan For Modular DistanceRica Mae EsmenosNo ratings yet
- Final Semi Detailed Lesson Plan TemplateDocument10 pagesFinal Semi Detailed Lesson Plan TemplateJessie GernaleNo ratings yet
- 2023-2024-DLL-WK4Q2-EALS-Nov.27-31, 2023Document5 pages2023-2024-DLL-WK4Q2-EALS-Nov.27-31, 2023glaiza.riveraNo ratings yet
- DLP Science 8 Wk1D5 3rd QTRDocument1 pageDLP Science 8 Wk1D5 3rd QTRLianne Marie CabanginNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Genral Physics 2Document4 pagesLesson Plan Genral Physics 2Ron Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 BUDGET OF WORK IN ScienceDocument7 pagesGrade 7 BUDGET OF WORK IN ScienceYanika BarasNo ratings yet
- Geraldine Esperanza - Individual Workplace Application PlanDocument3 pagesGeraldine Esperanza - Individual Workplace Application PlanJohn Warren Paras100% (1)
- Physical Science 3rd Quarter ExamDocument1 pagePhysical Science 3rd Quarter ExamVERNA LOUNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 PS Q4Document3 pagesGrade 12 PS Q4JosephineNo ratings yet
- 4TH QRTR ExamDocument2 pages4TH QRTR ExamAlexander AlcazarinNo ratings yet
- Summative TestDocument2 pagesSummative TestMikee MercadoNo ratings yet
- GRADE 11 - Earth and Life Sciences ExaminationDocument2 pagesGRADE 11 - Earth and Life Sciences ExaminationNil PadillaNo ratings yet
- GRADE 10 - Mathematics - Second Quarterly ExaminationDocument2 pagesGRADE 10 - Mathematics - Second Quarterly ExaminationNil PadillaNo ratings yet
- GRADE 11 - General Mathematics ExaminationDocument4 pagesGRADE 11 - General Mathematics ExaminationNil PadillaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - Mathematics - Second Quarter ExaminationDocument4 pagesGrade 9 - Mathematics - Second Quarter ExaminationNil Padilla0% (1)
- Mecanica de FluidosDocument6 pagesMecanica de FluidosAndrés sanchezNo ratings yet
- Flow Past NACA 0012 Airfoil TestDocument14 pagesFlow Past NACA 0012 Airfoil TestArthur Saw Sher-QenNo ratings yet
- 1-Froude NumberDocument2 pages1-Froude NumberM JunaidNo ratings yet
- 6 D KljenakSymp2008 PDocument0 pages6 D KljenakSymp2008 PMma Best SportNo ratings yet
- DynamicsDocument10 pagesDynamicsPaul AndersNo ratings yet
- 2 Point SourcesDocument16 pages2 Point SourcesJULIETHERESE MNo ratings yet
- PDF Beer Dinamica 9e Manual de Soluciones c15bDocument67 pagesPDF Beer Dinamica 9e Manual de Soluciones c15bOliver AlexisNo ratings yet
- Rotation 032224Document16 pagesRotation 032224zed santosNo ratings yet
- Torsional Rigidity CalculactionsDocument1 pageTorsional Rigidity Calculactionsapi-556772195No ratings yet
- Engineering Dynamics BEM2013/EM210 Chapter 15 Kinetics of A ParticleDocument21 pagesEngineering Dynamics BEM2013/EM210 Chapter 15 Kinetics of A ParticlemahrusNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of FluidDocument94 pagesMechanics of FluidSanket SubhadeepNo ratings yet
- SOW MCO F4 Physics 2020 (LATEST 17OGOS2020)Document39 pagesSOW MCO F4 Physics 2020 (LATEST 17OGOS2020)syafiqahdaudNo ratings yet
- Accessible Physics - A Guided Coursebook For A-Level (PDFDrive)Document233 pagesAccessible Physics - A Guided Coursebook For A-Level (PDFDrive)Ashraf ToorNo ratings yet
- Interference LightDocument36 pagesInterference Lightvishwanath c kNo ratings yet
- Extra Tryout Physics (Type G) : Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument24 pagesExtra Tryout Physics (Type G) : Multiple Choice QuestionsBELVIN TANNADINo ratings yet
- Hme1 Projectile MotionDocument19 pagesHme1 Projectile MotionkheyNo ratings yet
- Classifying Angles: Classify Each Angle As Acute, Obtuse, Right, or StraightDocument2 pagesClassifying Angles: Classify Each Angle As Acute, Obtuse, Right, or StraightBlack Ink Tutorials & ServicesNo ratings yet
- Subjective Assignment Newton Laws of MotionDocument3 pagesSubjective Assignment Newton Laws of MotionAniket PalNo ratings yet
- Stockhausen - UnityDocument13 pagesStockhausen - Unityjeanjean33No ratings yet
- Lecture20 - Angular Momentum and Vector PrecessionDocument31 pagesLecture20 - Angular Momentum and Vector PrecessionkoreyhintonNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: ME8511 Kinematics and Dynamics LabDocument7 pagesSyllabus: ME8511 Kinematics and Dynamics LabAmarnath PalaniNo ratings yet
- Experimental Measurement Moment of InertiaDocument34 pagesExperimental Measurement Moment of InertiayogagaNo ratings yet
- 4 Angular Kinematics of Human MovementDocument55 pages4 Angular Kinematics of Human MovementzainabnoorNo ratings yet
- Force Analysis - Basic ConceptsDocument24 pagesForce Analysis - Basic ConceptsTaylan KaraçelikNo ratings yet
GRADE 12 - Physical Science - Second Quarterly Examination
GRADE 12 - Physical Science - Second Quarterly Examination
Uploaded by
Nil Padilla0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
165 views2 pagesThe document is a 30 question multiple choice quiz on physical sciences topics including astronomy, physics, and Einstein's theory of relativity. It covers concepts like the shape of the Earth, planetary motion, Galileo's assertions about falling bodies, reflection and refraction of light, and Einstein's mass-energy equivalence formula. Students are asked to choose the correct answer for each question from the options provided.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document is a 30 question multiple choice quiz on physical sciences topics including astronomy, physics, and Einstein's theory of relativity. It covers concepts like the shape of the Earth, planetary motion, Galileo's assertions about falling bodies, reflection and refraction of light, and Einstein's mass-energy equivalence formula. Students are asked to choose the correct answer for each question from the options provided.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
165 views2 pagesGRADE 12 - Physical Science - Second Quarterly Examination
GRADE 12 - Physical Science - Second Quarterly Examination
Uploaded by
Nil PadillaThe document is a 30 question multiple choice quiz on physical sciences topics including astronomy, physics, and Einstein's theory of relativity. It covers concepts like the shape of the Earth, planetary motion, Galileo's assertions about falling bodies, reflection and refraction of light, and Einstein's mass-energy equivalence formula. Students are asked to choose the correct answer for each question from the options provided.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
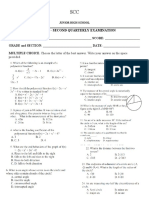
SCC
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL
GRADE 12 - SECOND QUARTERLY EXAMINATION
Physical Sciences
NAME: _____________________________________________ SCORE: ______________________
GRADE and SECTION: _______________________________ DATE: _______________________
MULTIPLE CHOICE. ENCIRCLE the letter corresponding to the correct answer for each of the questions provided.
1. Which BEST explains why the Earth is not disk-shaped?
a. Stars are viewed differently when traveling north and south
b. The shadow cast by the Earth during lunar eclipse is circular
c. The shadows cast in two different cities during solstice differed in length
d. The only shape that cast a circular shadow in whatever direction is a sphere
2. Which of the following is in annual motion?
a. Moonrise c. Sunset
b. Eastward rise of stars d. Vernal Equinox
3. What astronomical event was NOT known to men before the advent of telescopes?
a. Solar Eclipse c. Retrograde of Mars
b. Summer Solstice d. Rotation of the Sun
4. Which presents a system with elliptical orbit?
a. Copernician c. Ptolemaic
b. Keplerian d. Tychonic
5. Which presents the heliocentric model of the universe?
a. Copernician c. Ptolemaic
b. Keplerian d. Tychonic
6. Which presents a geo-heliocentric model of the solar system?
a. Copernician c. Ptolemaic
b. Keplerian d. Tychonic
7. Which of the following is TRUE about Galileo’s assertion about free-falling bodies?
a. Bodies will fall on the surface of the Earth at a constant acceleration
b. Bodies will fall on the surface of the Earth at a constant speed
c. Bodies will fall on the surface of the Earth at a constant velocity
d. Bodies will fall on the surface of the Earth at a constant projectile
8. Which of the following is NOT considered part of Aristotelian’s natural motion?
a. A book resting at the top of the table c. An apple falling from a tree
b. Pushing a cart d. Smoke naturally rises
9. Which of the following is NOT an assertion of Galileo?
a. A body that is in uniform motion will move a distance that is proportional to the time it will take to travel.
b. A uniformly accelerating body will travel at a speed proportional to time.
c. An object in motion will keep moving; and the external force is not necessary to maintain the motion.
d. A body will fall on the surface of the Earth at a constant speed.
10. Rising of smoke is an example of what type of motion according to Aristotle?
a. Natural c. Reaction
b. Normal d. Violent
11. Which of the following is needed to put a body to rest?
a. Inertia c. Gravity
b. Force d. Mass
12. The resistance of a medium in response to movement of a body is known as;
a. Antiperistasis c. Inertia
b. Force d. Gravity
13. What will happen if an external force is acted upon a body at rest?
a. It will move c. nothing will happen
b. It will not move d. it will remain in motion
14. What will happen to the acceleration of the body if a marble moves in a sloped downward plane?
a. Accelerates c. Nothing
b. Decelerates d. Not determined
15. What do you call the phenomenon by which the incident light falling on the surface is sent back into the same
medium?
a. Absorption c. Polarization
b. Reflection d. Refraction
16. What angle is formed by an incoming ray with the normal?
a. Angle of Reflection c. Angle of Incidence
b. Angle of Refraction d. Angle of Equivalence
17. What type of reflection is produced by rough surfaces?
a. Total internal reflection c. Diffuse reflection
b. Dispersion d. Specular reflection
18. Which of the following best describes a Normal line?
a. The path is taken by the rays of light as it approaches the surface
b. Line parallel to the incident and reflected ray
c. An imaginary line is drawn perpendicular to the reflecting surface
d. The total distance traveled by light upon reflecting
19. Which of the following pairs perfectly describes the reflection produced by a smooth surface?
a. Diffuse Reflection: clear and vivid c. Specular Reflection: unclear and vague
b. Diffuse Reflection: unclear and vague d. Specular Reflection: clear and vivid
20. When you see a “wet spot” mirage on the road in front of you, what are you most likely seeing?
a. Sky c. Water
b. Hot air d. Fragment of your imagination
21. White light goes through the filter that can absorb blue light; what color of light can pass through as perceived by
an observer?
a. Blue b. Green c. Red d. Yellow
22. When green light shines on a red rose, why do petals look black?
a. It absorbs green light c. It reflects green light
b. It reflects the color black d. It absorbs all the colors of the light
23. For you to see a rainbow, where should the sun be positioned?
a. In front of you c. Behind you
b. On your left side d. On your right side
24. It is a combination of two or more waves in one medium.
a. Dispersion c. Interference
b. Scattering d. Diffraction
25. Which is responsible for the spreading of light as it passes through a narrow slit?
a. Refraction c. Diffraction
b. Polarization d. Interference
26. Which is viewed as distortion of space-time?
a. Mass c. Gravity
b. Time d. Force
27. What happens to light as it travels along a massive cosmic body?
a. It bends c. it bounces
b. It reflects d. it disappears
28. What cosmic body can distort space-time the most?
a. Sun c. Earth
b. Moon d. Jupiter
29. In Einstein’s theory of special relativity, E is for energy, m is for mass and c is for _________.
a. Speed of Sound c. Speed of Light
b. Medium in space d. Space-time distortion
30. ___________ refers to the difference in the time interval between two events as perceived by an observer under a
stationary frame
a. Time dilation c. Relativity of Simultaneity
b. Length of Contraction d. Mass Energy Equivalence
You might also like
- POGIL - KinematicsDocument4 pagesPOGIL - KinematicsmagiclcjNo ratings yet
- Transfer Function Models Representing The Dynamics of A MissileDocument15 pagesTransfer Function Models Representing The Dynamics of A MissileD.Viswanath100% (7)
- L8 - Example For Jacobian of RobotsDocument8 pagesL8 - Example For Jacobian of RobotsZul Fadhli100% (1)
- General Physics 1 - Budget of WorkDocument11 pagesGeneral Physics 1 - Budget of Workanon_145781083No ratings yet
- BeerVM11e PPT Ch11Document92 pagesBeerVM11e PPT Ch11brayanNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter Test PHYSICS 12Document4 pages4th Quarter Test PHYSICS 12Cris ElcarteNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Physical ScienceDocument5 pagesSummative Test Physical ScienceARNEL METILLONo ratings yet
- Origin of The Solar SystemDocument3 pagesOrigin of The Solar SystemZercyNice Imbong CarreonNo ratings yet
- Activity 8d. Convection CurrentDocument5 pagesActivity 8d. Convection CurrentGUILLER BELENNo ratings yet
- LP Phy Sci Q2-M5 (W2)Document4 pagesLP Phy Sci Q2-M5 (W2)MARIA DINA TAYACTACNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Physical Science Q2Document2 pagesWeek 1 - Physical Science Q2Gemma Quiocho-CardenasNo ratings yet
- Dlp-Investigating Principles Governing MotionDocument8 pagesDlp-Investigating Principles Governing MotionAngel GaluteraNo ratings yet
- Template 7e'sDocument2 pagesTemplate 7e'smaricris olayonNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Physical Science mhelDSDocument16 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Physical Science mhelDSRommelyn RosasNo ratings yet
- InnovationDocument2 pagesInnovationDoodz O MadronioNo ratings yet
- Physical Science DLL q2 (Week 4)Document2 pagesPhysical Science DLL q2 (Week 4)Esmale RyaNo ratings yet
- DLL - Speed, Velocity and AccelerationDocument2 pagesDLL - Speed, Velocity and AccelerationCyril Alba ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Quarter 3 LASDocument35 pagesPhysical Science Quarter 3 LASDrama LlamaNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Day 1Document5 pagesWeek 5 - Day 1RAMIL BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Free FallDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Free FallQueencess Ara TorresNo ratings yet
- Physical Science: Quarter 2 - Module 13 Special Theory of RelativityDocument21 pagesPhysical Science: Quarter 2 - Module 13 Special Theory of RelativityLlahona FajardoNo ratings yet
- psdll11 28 18Document2 pagespsdll11 28 18Christine De San JoseNo ratings yet
- Sample Lesson Exemplar - The Composition of The EarthDocument3 pagesSample Lesson Exemplar - The Composition of The EarthRommel DaysonNo ratings yet
- PDF Answerkey Earthlifescience - CompressDocument11 pagesPDF Answerkey Earthlifescience - CompressAlvin PaboresNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification 1 Semester/ 2 Quarterly Assessment Grade 12 Subject: Physical ScienceDocument5 pagesTable of Specification 1 Semester/ 2 Quarterly Assessment Grade 12 Subject: Physical ScienceArlance Sandra Marie MedinaNo ratings yet
- Week 7 - Physical-ScienceDocument1 pageWeek 7 - Physical-ScienceKayla TiquisNo ratings yet
- Marinduque National High School: Department of Education MIMAROPA Region Isok 1, Boac, MarinduqueDocument4 pagesMarinduque National High School: Department of Education MIMAROPA Region Isok 1, Boac, MarinduqueMaria Joy VelascoNo ratings yet
- PS - Quarter 2 - Week 1Document6 pagesPS - Quarter 2 - Week 1edgardo viadorNo ratings yet
- Session 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4: I. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesSession 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4: I. ObjectivesSherwin SantosNo ratings yet
- Universe and The Solar SystemDocument16 pagesUniverse and The Solar SystemJennifer MagangoNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test in PhySciDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Test in PhySciJuliane Rebecca PitlongayNo ratings yet
- Third Periodical PhysciDocument4 pagesThird Periodical PhysciMiss RonaNo ratings yet
- GenPhysics2 Module 2Document20 pagesGenPhysics2 Module 2I can see your pixels 2No ratings yet
- DLL Mod.4 3RD QRTR G10Document7 pagesDLL Mod.4 3RD QRTR G10Sarah Candelaria ArcellanaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Exam in PhySciDocument4 pages3rd Quarter Exam in PhySciyvetteNo ratings yet
- Math9 - Q4 - Mod5 - Wk5 - Real Life Problems Involving Right Triangles - v5Document36 pagesMath9 - Q4 - Mod5 - Wk5 - Real Life Problems Involving Right Triangles - v5Sam dela CernaNo ratings yet
- Shs-Tos Earth and Life ScienceDocument1 pageShs-Tos Earth and Life SciencerichardsamranoNo ratings yet
- 2022 23 DLL WK3 Q2 EALS Nov. 14 18 2022 Modified 4Document6 pages2022 23 DLL WK3 Q2 EALS Nov. 14 18 2022 Modified 4glaiza.riveraNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in PHYSICAL SCIENCEDocument3 pagesSummative Test in PHYSICAL SCIENCEMaelNo ratings yet
- Bow MilDocument1 pageBow MilScarletBeauty Enriquez-DiagbelNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Physical Science Q2 Wk7 GLAKDocument16 pagesGrade 12 Physical Science Q2 Wk7 GLAKJose GulitiwNo ratings yet
- Earth Life Science DLL Week 2Document8 pagesEarth Life Science DLL Week 2Janice Danieles Siano-TahuyanNo ratings yet
- MATATAG Accomplishment ReportDocument5 pagesMATATAG Accomplishment Reportbauder langkiaNo ratings yet
- DLL PHY-SCI (Aug Week2)Document5 pagesDLL PHY-SCI (Aug Week2)Jesse GabrielNo ratings yet
- PT G8 ScienceDocument5 pagesPT G8 ScienceJoville Palermo UrsolinoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Quarter 3 Week 2: Not For SaleDocument7 pagesPhysical Science Quarter 3 Week 2: Not For SaleChristien Kate GonzalesNo ratings yet
- LP Phy Sci Q2-M3 (W1)Document3 pagesLP Phy Sci Q2-M3 (W1)MARIA DINA TAYACTACNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Earth and Life Science Grade-11Document5 pagesDepartment of Education: Earth and Life Science Grade-11Ro ZenNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Week 4 DLLDocument6 pagesEarth and Life Week 4 DLLReyes CzarinaNo ratings yet
- EALS 1st Quarter Exam SY 2022-2023Document5 pagesEALS 1st Quarter Exam SY 2022-2023Maria Lourdes PunayNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Accomplishment Report School Year 2020-2021 Grade I - RosalDocument36 pagesDepartment of Education: Accomplishment Report School Year 2020-2021 Grade I - RosalCandida Ortaliza CuagdanNo ratings yet
- LIGHT Quiz - Secondary 2Document6 pagesLIGHT Quiz - Secondary 2priyaNo ratings yet
- Budget-of-Work-Earth and Life ScienceDocument5 pagesBudget-of-Work-Earth and Life Sciencejoei Arquero100% (1)
- Physical Science - Day 56Document6 pagesPhysical Science - Day 56Maria Sheila OtlangNo ratings yet
- 2weekly Home Learning Plan For Modular DistanceDocument8 pages2weekly Home Learning Plan For Modular DistanceRica Mae EsmenosNo ratings yet
- Final Semi Detailed Lesson Plan TemplateDocument10 pagesFinal Semi Detailed Lesson Plan TemplateJessie GernaleNo ratings yet
- 2023-2024-DLL-WK4Q2-EALS-Nov.27-31, 2023Document5 pages2023-2024-DLL-WK4Q2-EALS-Nov.27-31, 2023glaiza.riveraNo ratings yet
- DLP Science 8 Wk1D5 3rd QTRDocument1 pageDLP Science 8 Wk1D5 3rd QTRLianne Marie CabanginNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Genral Physics 2Document4 pagesLesson Plan Genral Physics 2Ron Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 BUDGET OF WORK IN ScienceDocument7 pagesGrade 7 BUDGET OF WORK IN ScienceYanika BarasNo ratings yet
- Geraldine Esperanza - Individual Workplace Application PlanDocument3 pagesGeraldine Esperanza - Individual Workplace Application PlanJohn Warren Paras100% (1)
- Physical Science 3rd Quarter ExamDocument1 pagePhysical Science 3rd Quarter ExamVERNA LOUNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 PS Q4Document3 pagesGrade 12 PS Q4JosephineNo ratings yet
- 4TH QRTR ExamDocument2 pages4TH QRTR ExamAlexander AlcazarinNo ratings yet
- Summative TestDocument2 pagesSummative TestMikee MercadoNo ratings yet
- GRADE 11 - Earth and Life Sciences ExaminationDocument2 pagesGRADE 11 - Earth and Life Sciences ExaminationNil PadillaNo ratings yet
- GRADE 10 - Mathematics - Second Quarterly ExaminationDocument2 pagesGRADE 10 - Mathematics - Second Quarterly ExaminationNil PadillaNo ratings yet
- GRADE 11 - General Mathematics ExaminationDocument4 pagesGRADE 11 - General Mathematics ExaminationNil PadillaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - Mathematics - Second Quarter ExaminationDocument4 pagesGrade 9 - Mathematics - Second Quarter ExaminationNil Padilla0% (1)
- Mecanica de FluidosDocument6 pagesMecanica de FluidosAndrés sanchezNo ratings yet
- Flow Past NACA 0012 Airfoil TestDocument14 pagesFlow Past NACA 0012 Airfoil TestArthur Saw Sher-QenNo ratings yet
- 1-Froude NumberDocument2 pages1-Froude NumberM JunaidNo ratings yet
- 6 D KljenakSymp2008 PDocument0 pages6 D KljenakSymp2008 PMma Best SportNo ratings yet
- DynamicsDocument10 pagesDynamicsPaul AndersNo ratings yet
- 2 Point SourcesDocument16 pages2 Point SourcesJULIETHERESE MNo ratings yet
- PDF Beer Dinamica 9e Manual de Soluciones c15bDocument67 pagesPDF Beer Dinamica 9e Manual de Soluciones c15bOliver AlexisNo ratings yet
- Rotation 032224Document16 pagesRotation 032224zed santosNo ratings yet
- Torsional Rigidity CalculactionsDocument1 pageTorsional Rigidity Calculactionsapi-556772195No ratings yet
- Engineering Dynamics BEM2013/EM210 Chapter 15 Kinetics of A ParticleDocument21 pagesEngineering Dynamics BEM2013/EM210 Chapter 15 Kinetics of A ParticlemahrusNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of FluidDocument94 pagesMechanics of FluidSanket SubhadeepNo ratings yet
- SOW MCO F4 Physics 2020 (LATEST 17OGOS2020)Document39 pagesSOW MCO F4 Physics 2020 (LATEST 17OGOS2020)syafiqahdaudNo ratings yet
- Accessible Physics - A Guided Coursebook For A-Level (PDFDrive)Document233 pagesAccessible Physics - A Guided Coursebook For A-Level (PDFDrive)Ashraf ToorNo ratings yet
- Interference LightDocument36 pagesInterference Lightvishwanath c kNo ratings yet
- Extra Tryout Physics (Type G) : Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument24 pagesExtra Tryout Physics (Type G) : Multiple Choice QuestionsBELVIN TANNADINo ratings yet
- Hme1 Projectile MotionDocument19 pagesHme1 Projectile MotionkheyNo ratings yet
- Classifying Angles: Classify Each Angle As Acute, Obtuse, Right, or StraightDocument2 pagesClassifying Angles: Classify Each Angle As Acute, Obtuse, Right, or StraightBlack Ink Tutorials & ServicesNo ratings yet
- Subjective Assignment Newton Laws of MotionDocument3 pagesSubjective Assignment Newton Laws of MotionAniket PalNo ratings yet
- Stockhausen - UnityDocument13 pagesStockhausen - Unityjeanjean33No ratings yet
- Lecture20 - Angular Momentum and Vector PrecessionDocument31 pagesLecture20 - Angular Momentum and Vector PrecessionkoreyhintonNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: ME8511 Kinematics and Dynamics LabDocument7 pagesSyllabus: ME8511 Kinematics and Dynamics LabAmarnath PalaniNo ratings yet
- Experimental Measurement Moment of InertiaDocument34 pagesExperimental Measurement Moment of InertiayogagaNo ratings yet
- 4 Angular Kinematics of Human MovementDocument55 pages4 Angular Kinematics of Human MovementzainabnoorNo ratings yet
- Force Analysis - Basic ConceptsDocument24 pagesForce Analysis - Basic ConceptsTaylan KaraçelikNo ratings yet