Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2nd Quarter Examination in Physical Science 12 (2019-2020)
2nd Quarter Examination in Physical Science 12 (2019-2020)
Uploaded by
Teresa Marie CorderoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Diagnostic Test Physical ScienceDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Test Physical SciencePilar Angelie Palmares Villarin67% (3)
- CHM-2045 Exam 1 Sample QuestionsDocument7 pagesCHM-2045 Exam 1 Sample QuestionsFrankNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Long TestDocument2 pagesScience 8 Long TestKarena Wahiman100% (1)
- Summative Test Science 9Document2 pagesSummative Test Science 9jennifer lacambra75% (4)
- Organic Chem (Online Review)Document211 pagesOrganic Chem (Online Review)Spencer Thomas100% (1)
- Physical Science DefinitionsDocument8 pagesPhysical Science DefinitionsJason KampsNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument193 pagesOrganic ChemistryThilagaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Chemistry Second Quarter TestDocument10 pagesReviewer Chemistry Second Quarter TestmichaelalangcasNo ratings yet
- Pre Test Grade 11Document4 pagesPre Test Grade 11anon_409285199100% (1)
- Chemical Reaction Practice TestDocument9 pagesChemical Reaction Practice TestMarivic Bernardo GalvezNo ratings yet
- Science 2Document17 pagesScience 2Ralph NilloNo ratings yet
- Week 1 and 2 Summative TestDocument4 pagesWeek 1 and 2 Summative TestJulie Anne Portal - OdascoNo ratings yet
- Mastery Test in Physical Science - Gr.11Document3 pagesMastery Test in Physical Science - Gr.11kert mendozaNo ratings yet
- Paul Vincent Laureta - GAT-Week 5Document3 pagesPaul Vincent Laureta - GAT-Week 5Paul Vincent Laureta0% (1)
- Week 5 and 6 Summative TestDocument2 pagesWeek 5 and 6 Summative TestJulie Anne Portal - OdascoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 2019Document5 pagesPhysical Science 2019L Lawliet100% (1)
- Test Questions ScienceDocument4 pagesTest Questions ScienceEsmeey Castañares100% (1)
- Chemistry: NameDocument3 pagesChemistry: NameHaseeb JaveedNo ratings yet
- Summative 2 Physical Science Answer KeyDocument2 pagesSummative 2 Physical Science Answer KeygjarandiaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Exam Drill IDocument6 pagesChemistry - Exam Drill IJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Exam Drill IDocument6 pagesChemistry - Exam Drill IJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Summative Test in Science 9Document3 pagesSecond Quarter Summative Test in Science 9Rowella Lagalo100% (1)
- CHEM51Document5 pagesCHEM51Reiniel Cirujano AntonioNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Second Quarterly Examinations Questionnaire General DirectionsDocument3 pagesScience 9 Second Quarterly Examinations Questionnaire General DirectionsBert RoseteNo ratings yet
- Matter and Chemical Change ReviewDocument4 pagesMatter and Chemical Change ReviewjacquelinebicekNo ratings yet
- 1 Chemistry Jdjei Opek JeiDocument3 pages1 Chemistry Jdjei Opek JeiMahater SalicNo ratings yet
- 1st PT 2019-2020 Physical Science 11Document4 pages1st PT 2019-2020 Physical Science 11Gerald Balmaceda100% (1)
- Test Bank Physical Science 1stDocument10 pagesTest Bank Physical Science 1stJay MeeNo ratings yet
- 3rd QE PhySciDocument2 pages3rd QE PhySciCHRISTINE MAE PASTERNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Test Questions Humss 1 & Abm 3Document9 pagesUnit 5 - Test Questions Humss 1 & Abm 3Neil GabatoNo ratings yet
- MACROCOSM GRADE 7 - 1stgradingDocument6 pagesMACROCOSM GRADE 7 - 1stgradingpaulaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1Document3 pagesChemistry 1Fahad HADJI USOPHNo ratings yet
- 1 ST Quiz Reviewer BioDocument7 pages1 ST Quiz Reviewer BioAdrienne GabayNo ratings yet
- Chem G7C ReviewDocument10 pagesChem G7C ReviewOng Ern HweeNo ratings yet
- SASE Chemistry W - Key Ans.Document4 pagesSASE Chemistry W - Key Ans.Hiraya ManawariNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Unit B ExamDocument8 pagesScience 9 Unit B Examapi-427321002No ratings yet
- Physical-Science-2019 ExamDocument5 pagesPhysical-Science-2019 ExamL LawlietNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry Answer Key Blue PacopDocument30 pagesPharmaceutical Chemistry Answer Key Blue PacopJeannie UyNo ratings yet
- MUGETADocument8 pagesMUGETAdaudimgetamafweleNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Science 9Document5 pagesReviewer Science 9emmanvillafuerteNo ratings yet
- MidtermDocument6 pagesMidtermJAnnisCatianNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practice Test With Answer For Physical Science Major 1 PDFDocument6 pagesChemistry Practice Test With Answer For Physical Science Major 1 PDFOvelia KayuzakiNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter TQ Science 7Document4 pages1st Quarter TQ Science 7Thyra PastorNo ratings yet
- Sample Question With Tos in Science 8 For 3RD QuarterDocument2 pagesSample Question With Tos in Science 8 For 3RD QuarterRe BornNo ratings yet
- Module 5n6 Answer Sheet Is Anatomy and Physiology (Abegail C. Relunia - Bsed 3c-Science)Document6 pagesModule 5n6 Answer Sheet Is Anatomy and Physiology (Abegail C. Relunia - Bsed 3c-Science)Abegail ReluniaNo ratings yet
- Individual Quiz 2019Document1 pageIndividual Quiz 2019joan marie PeliasNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 3rd Quarter ExamDocument4 pagesPhysical Science 3rd Quarter Examjeddah noa lorzano100% (1)
- Atoms, Elements, and Compounds-Chapter 6Document8 pagesAtoms, Elements, and Compounds-Chapter 6Araas AraasNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Class - 7 SUBJECT-Science CHAPTER - 3, Chemical Substances and Processes A. Fill in The BlanksDocument3 pagesWorksheet Class - 7 SUBJECT-Science CHAPTER - 3, Chemical Substances and Processes A. Fill in The BlanksRenee DisaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Study GuideDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Study GuideportbluepicklesNo ratings yet
- QUIZ#2 - Matter and The Molecules of LifeDocument14 pagesQUIZ#2 - Matter and The Molecules of LifeLouiza Angelina LayugNo ratings yet
- Pre Test Physci Q3Document3 pagesPre Test Physci Q3MICHELLE DE GUZMAN SOTTONo ratings yet
- SPT11 PDFDocument2 pagesSPT11 PDFLeeann LeeNo ratings yet
- I. Choosing The Best Answer and Filling in The Answer SheetDocument3 pagesI. Choosing The Best Answer and Filling in The Answer SheetPham Van Tin B1909842No ratings yet
- Q1, Gen Chem 2 Sy 2022-2023Document4 pagesQ1, Gen Chem 2 Sy 2022-2023Jenny Vhie S. VinagreraNo ratings yet
- TQ G9Q2Document4 pagesTQ G9Q2Veronica PabillenaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer (Chemistry)Document10 pagesScience Reviewer (Chemistry)CHRISTIAN NOE BONGALBALNo ratings yet
- I. Multiple Choice: Read Each Item Carefully. Write The Letter of The Best AnswerDocument4 pagesI. Multiple Choice: Read Each Item Carefully. Write The Letter of The Best AnswerGerald BalmacedaNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Encircle The Letter That Corresponds To Your AnswerDocument3 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Encircle The Letter That Corresponds To Your AnswerJohnnard BelenNo ratings yet
- Basic Education Department (SHS) : Qualifying Examination - ChemistryDocument3 pagesBasic Education Department (SHS) : Qualifying Examination - Chemistryismael jaafarNo ratings yet
- (MSU SASE) Chemistry-1Document4 pages(MSU SASE) Chemistry-1Arice MontiponNo ratings yet
- Long TestDocument3 pagesLong TestMarvin SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Organic Reaction Mechanisms 1982: An annual survey covering the literature dated December 1981 through November 1982From EverandOrganic Reaction Mechanisms 1982: An annual survey covering the literature dated December 1981 through November 1982A. C. KnipeNo ratings yet
- Oral RecitationDocument1 pageOral RecitationTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Final Exam in Chem 1Document2 pagesFinal Exam in Chem 1Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- First Quarterly Examination in Science 10Document2 pagesFirst Quarterly Examination in Science 10Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- SECOND QUARTERLY EXAMINATION IN SCIENCE 8 (Simplicity)Document2 pagesSECOND QUARTERLY EXAMINATION IN SCIENCE 8 (Simplicity)Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- First Final Examination in Science 7Document8 pagesFirst Final Examination in Science 7Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Long Test in Science 7Document1 pageLong Test in Science 7Teresa Marie Cordero100% (1)
- Naming CompoundsDocument2 pagesNaming CompoundsTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Pretest in Physical Science 12Document3 pagesPretest in Physical Science 12Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Examination in Science 9Document2 pagesSecond Quarter Examination in Science 9Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- TOS Grade 10 (1st Quarter 2019-2020)Document3 pagesTOS Grade 10 (1st Quarter 2019-2020)Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument9 pagesCHEMISTRYTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- CELL OrganellesDocument5 pagesCELL OrganellesTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Activity 1Document2 pagesEndocrine Activity 1Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table (Chemical Bonding)Document8 pagesPeriodic Table (Chemical Bonding)Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Levels of Biological OrganizationDocument6 pagesLevels of Biological OrganizationTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- First Quarterly Examination in Science 7 (2019-2020)Document2 pagesFirst Quarterly Examination in Science 7 (2019-2020)Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIONDocument8 pagesREPRODUCTIONTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- CARBONDocument1 pageCARBONTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- WHLP Activity Sheet 1 (Circulatory)Document1 pageWHLP Activity Sheet 1 (Circulatory)Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument47 pagesAtomic StructureTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- MICROSCOPEDocument5 pagesMICROSCOPETeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Activity in MicroscopeDocument2 pagesActivity in MicroscopeTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Concentration of SolutionsDocument30 pagesConcentration of SolutionsTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Ways of Separating MixturesDocument23 pagesWays of Separating MixturesTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Grade 9Document56 pagesChemistry Grade 9wafa sheikhNo ratings yet
- Solid Solution For Catalytic Ammonia Synthesis FromDocument8 pagesSolid Solution For Catalytic Ammonia Synthesis FromAhmad AlShahrourNo ratings yet
- Vsepr: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular GeometryDocument16 pagesVsepr: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular GeometrySandra Enn BahintingNo ratings yet
- Coordination ChemistryDocument19 pagesCoordination ChemistryPrityyyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry OpenStaxDocument1,413 pagesChemistry OpenStaxreklaminisNo ratings yet
- 202-Nya TH Ea F14Document5 pages202-Nya TH Ea F14Julien SiinoNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 - Integrated Science Consolidated CurriculumDocument12 pagesGrade 8 - Integrated Science Consolidated Curriculumshonaishot hottieNo ratings yet
- PS SIR Inorganic QUESTION 100Document10 pagesPS SIR Inorganic QUESTION 100Arya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Protonation and Geometry of Histidine Rings: Research PapersDocument11 pagesProtonation and Geometry of Histidine Rings: Research Papersrufus991No ratings yet
- Chemistry Important QuestionsDocument13 pagesChemistry Important QuestionsSadnanSadiqueNo ratings yet
- Valence Bond Theory: 4 Meet On Chemical Bond CourseDocument52 pagesValence Bond Theory: 4 Meet On Chemical Bond Courselina lathifaNo ratings yet
- Dae Footwear PDFDocument140 pagesDae Footwear PDFFarid ElkhshabNo ratings yet
- Class XI Chemistry Worksheet 2021Document43 pagesClass XI Chemistry Worksheet 2021Muffadal AlaviNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY HotsDocument143 pagesCHEMISTRY HotsJaved Sheikh0% (1)
- FullDocument1,175 pagesFull43 Trần Công VinhNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0167732220370549 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0167732220370549 Maintuangsiong ShuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Linetics MCQS Set ExamDocument16 pagesChemical Linetics MCQS Set ExamAsim MushtaqNo ratings yet
- SR AIIMS S60 - NEET Part Test - 2 (03!01!23) SyllabusDocument1 pageSR AIIMS S60 - NEET Part Test - 2 (03!01!23) SyllabusAdithya BharadwajNo ratings yet
- MO TheoryDocument34 pagesMO TheoryKhoerunnisaWulanSafitriNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - Structure of SubstancesDocument16 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Structure of SubstancesChemistryKlipz100% (6)
- Chemistryh Subject Syllabus For A Level Form V-VI - 2018 PDFDocument90 pagesChemistryh Subject Syllabus For A Level Form V-VI - 2018 PDFMaryNo ratings yet
- Full Download Biology 3rd Edition Brooker Solutions ManualDocument18 pagesFull Download Biology 3rd Edition Brooker Solutions Manualmaurineheckathorneus100% (40)
- Yr 12 Chemistry PP1Document11 pagesYr 12 Chemistry PP1NjoroNo ratings yet
- Answers To Eocqs: Cambridge International As Level ChemistryDocument3 pagesAnswers To Eocqs: Cambridge International As Level ChemistryRaihanNo ratings yet
- Iit Chemistry: Goc (Electronic Effect)Document35 pagesIit Chemistry: Goc (Electronic Effect)swadhin100% (1)
- SamajDocument21 pagesSamajAnand SwarnkarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding PDFDocument14 pagesChemical Bonding PDFsiddhant shuklaNo ratings yet
2nd Quarter Examination in Physical Science 12 (2019-2020)
2nd Quarter Examination in Physical Science 12 (2019-2020)
Uploaded by
Teresa Marie CorderoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2nd Quarter Examination in Physical Science 12 (2019-2020)
2nd Quarter Examination in Physical Science 12 (2019-2020)
Uploaded by
Teresa Marie CorderoCopyright:
Available Formats
2nd Quarter Examination in Physical Science 12
I. MULTIPLE CHOICE: Write the letter of the correct answer before the number.
1. An attraction between atoms that allows the formation of substances that contain two or more atoms.
a. Electronegativity b. Chemical Bond c. Organic Compound d. None of the above
2. The ability of an atom to draw electrons toward itself.
a. Electronegativity b. Chemical Bond c. Organic Compound d. None of the above
3. H20 is a polar bond. What type of intermolecular forces is present between the atoms of H20?
a. Dispersion Forces b. Ion-Dipole Interaction c. London Dispersion d. Dipole-Dipole Interaction
4. Carbohydrates provide our body with heat and energy. Carbohydrates are also called as___________.
a. Amino acids b. Saccharides c. Nucleotides d. Fats
5. A type of nucleic acid that contains our genetic information.
a. DNA b. RNA c. PMA d. NPA
6. Monosaccharides are single unit sugars. Which of the following is the formula for monosaccharides?
a. C12H22O11 b. C6H10O5 c. C6H12O6 d. C5H10O5
7. These are attractive forces found between molecules.
a. Chemical Bond b. Electronegativity c. Intermolecular forces d. Hydrocarbons
8. The energy required to activate molecules or atom to a condition in which they can undergo chemical reaction.
a. Potential Energy b. Kinetic Energy c. Solar Energy d. Activation Energy
9. These are compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen only.
a. Organic compound b. Hydrocarbon c. Inorganic Compound d. Teflon
10. Refers to two or more units of sugar.
a. Polysaccharide b. Disaccharide c. Monosaccharide d. Trisaccharide
11. These are substances that stop or slow down the rate of chemical reaction.
a. Exhibitor b. Catalysts c. Inhibitor d. Catalysis
12. A type of bond that occurs between a metal and a nonmetal.
a. Polar bond b. Covalent Bond c. Ionic bond d. Metallic Bond
13. These are charged particles that gains electrons.
a. Cations b. Anions c. Neutrons d. Protons
14. A level of protein structure wherein it contains a structure of either alpha helix or pleated sheets of amino acids.
a. Primary Structure b. Secondary Structure c. Tertiary Structure d. Quaternary Structure
15. A change in which one or more new substances are formed.
a. Physical Change b. Climate Change c. Chemical Change d. All of the above
II. IDENTIFICATION
1. Refers to the passing of traits from parents to offspring.
2. These are biological catalysts.
3. These are attractive forces that occur between nonpolar molecules.
4. A milk sugar that is formed from the combination of glucose and galactose.
5. The Greek word for lipids which means fat or lard.
6. The term used when substances possess the properties of both hydrophilic and hydrophobic
7. These are the building blocks of proteins.
8. A theory that explains the rate of reaction of substances or compounds.
9. A primary monosaccharide found in fruits.
10. A reaction wherein heat is released to the surroundings.
11. A special type of dipole-dipole that occurs only in molecules that contain hydrogen atom bonded to small, highly
electronegative atom.
12. A bond which occurs only in non-metals.
13. These are charged particles that lose electrons.
14. These are the starting materials used in a chemical reaction.
15. Collisions resulting in a reaction that successfully forms the expected product.
16. The catalysis wherein the reactants and the catalyst are in different phases.
17. A bond found in polypeptide chain of amino acids.
18. -19. The substances or molecules that possess the force of ion-dipole interaction.
20. A reaction wherein heat is absorbed by the object from the surroundings. .
III. SOLVING: Given the electronegativity of each element, solve for the electronegativity difference of the
compounds and give the type of bond present in each compound.
C=2.5 K=0.8 S= 2.5 I=2.7 Cs=0.8 Br=2.8 N=3.0 Ca=1.3 Cl=3.0
COMPOUND ELECTRONEGATIVITY TYPE OF BOND
DIFFERENCE
CS2 1. 6.
CsBr 2. 7.
N2 3. 8.
CaCl 4. 9.
KI 5. 10.
IV. MATCHING TYPE: Match Column A to Column B. Write the letter of the correct answer before the
number.
Column A Column B
1. Hydrogen bonding occurs only when bonded to a. C, H, N, O
these electronegative atoms b. Gaseous Solutions
2. These are solutions in which water is the solvent. c. F, N, O
3. The new materials formed after the chemical d. Liquid solution
reaction. e. Inhibitor
4. A substance that increases the rate of a chemical f. Catalyst
reaction. g. Law of Multiple Proportion
5. The law which states that the mass of reactants is h. Law of Conservation of Mass
equal to the mass of the products in a chemical i. Law of Conservation of Energy
reaction. j. Reactants
k. Products
Column A Column B
6. Tarnishing of silver bracelet a. Chemical Change
7. Melting of butter b. Physical Change
8. Burning of wood
9. Frying a fish in a pan a. Exothermic Reaction
10. Putting a warm damp towel in the forehead b. Endothermic Reaction
V. BALANCING EQUATIONS: Balance the following equations.
1. Fe + Cl2 FeCl3
2. C + SO2 CS2 + CO
3. Ag + S Ag2S
4. Zn + CuSO4 Cu + ZnSO4
5. Fe2O3 + C Fe + CO
Prepared by:
TERESA MARIE Y. CORDERO
Subject Teacher
Approved by:
MRS. BERNIE G. LOQUINARIO
Head Teacher III
You might also like
- Diagnostic Test Physical ScienceDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Test Physical SciencePilar Angelie Palmares Villarin67% (3)
- CHM-2045 Exam 1 Sample QuestionsDocument7 pagesCHM-2045 Exam 1 Sample QuestionsFrankNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Long TestDocument2 pagesScience 8 Long TestKarena Wahiman100% (1)
- Summative Test Science 9Document2 pagesSummative Test Science 9jennifer lacambra75% (4)
- Organic Chem (Online Review)Document211 pagesOrganic Chem (Online Review)Spencer Thomas100% (1)
- Physical Science DefinitionsDocument8 pagesPhysical Science DefinitionsJason KampsNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument193 pagesOrganic ChemistryThilagaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Chemistry Second Quarter TestDocument10 pagesReviewer Chemistry Second Quarter TestmichaelalangcasNo ratings yet
- Pre Test Grade 11Document4 pagesPre Test Grade 11anon_409285199100% (1)
- Chemical Reaction Practice TestDocument9 pagesChemical Reaction Practice TestMarivic Bernardo GalvezNo ratings yet
- Science 2Document17 pagesScience 2Ralph NilloNo ratings yet
- Week 1 and 2 Summative TestDocument4 pagesWeek 1 and 2 Summative TestJulie Anne Portal - OdascoNo ratings yet
- Mastery Test in Physical Science - Gr.11Document3 pagesMastery Test in Physical Science - Gr.11kert mendozaNo ratings yet
- Paul Vincent Laureta - GAT-Week 5Document3 pagesPaul Vincent Laureta - GAT-Week 5Paul Vincent Laureta0% (1)
- Week 5 and 6 Summative TestDocument2 pagesWeek 5 and 6 Summative TestJulie Anne Portal - OdascoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 2019Document5 pagesPhysical Science 2019L Lawliet100% (1)
- Test Questions ScienceDocument4 pagesTest Questions ScienceEsmeey Castañares100% (1)
- Chemistry: NameDocument3 pagesChemistry: NameHaseeb JaveedNo ratings yet
- Summative 2 Physical Science Answer KeyDocument2 pagesSummative 2 Physical Science Answer KeygjarandiaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Exam Drill IDocument6 pagesChemistry - Exam Drill IJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Exam Drill IDocument6 pagesChemistry - Exam Drill IJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Summative Test in Science 9Document3 pagesSecond Quarter Summative Test in Science 9Rowella Lagalo100% (1)
- CHEM51Document5 pagesCHEM51Reiniel Cirujano AntonioNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Second Quarterly Examinations Questionnaire General DirectionsDocument3 pagesScience 9 Second Quarterly Examinations Questionnaire General DirectionsBert RoseteNo ratings yet
- Matter and Chemical Change ReviewDocument4 pagesMatter and Chemical Change ReviewjacquelinebicekNo ratings yet
- 1 Chemistry Jdjei Opek JeiDocument3 pages1 Chemistry Jdjei Opek JeiMahater SalicNo ratings yet
- 1st PT 2019-2020 Physical Science 11Document4 pages1st PT 2019-2020 Physical Science 11Gerald Balmaceda100% (1)
- Test Bank Physical Science 1stDocument10 pagesTest Bank Physical Science 1stJay MeeNo ratings yet
- 3rd QE PhySciDocument2 pages3rd QE PhySciCHRISTINE MAE PASTERNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Test Questions Humss 1 & Abm 3Document9 pagesUnit 5 - Test Questions Humss 1 & Abm 3Neil GabatoNo ratings yet
- MACROCOSM GRADE 7 - 1stgradingDocument6 pagesMACROCOSM GRADE 7 - 1stgradingpaulaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1Document3 pagesChemistry 1Fahad HADJI USOPHNo ratings yet
- 1 ST Quiz Reviewer BioDocument7 pages1 ST Quiz Reviewer BioAdrienne GabayNo ratings yet
- Chem G7C ReviewDocument10 pagesChem G7C ReviewOng Ern HweeNo ratings yet
- SASE Chemistry W - Key Ans.Document4 pagesSASE Chemistry W - Key Ans.Hiraya ManawariNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Unit B ExamDocument8 pagesScience 9 Unit B Examapi-427321002No ratings yet
- Physical-Science-2019 ExamDocument5 pagesPhysical-Science-2019 ExamL LawlietNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry Answer Key Blue PacopDocument30 pagesPharmaceutical Chemistry Answer Key Blue PacopJeannie UyNo ratings yet
- MUGETADocument8 pagesMUGETAdaudimgetamafweleNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Science 9Document5 pagesReviewer Science 9emmanvillafuerteNo ratings yet
- MidtermDocument6 pagesMidtermJAnnisCatianNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practice Test With Answer For Physical Science Major 1 PDFDocument6 pagesChemistry Practice Test With Answer For Physical Science Major 1 PDFOvelia KayuzakiNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter TQ Science 7Document4 pages1st Quarter TQ Science 7Thyra PastorNo ratings yet
- Sample Question With Tos in Science 8 For 3RD QuarterDocument2 pagesSample Question With Tos in Science 8 For 3RD QuarterRe BornNo ratings yet
- Module 5n6 Answer Sheet Is Anatomy and Physiology (Abegail C. Relunia - Bsed 3c-Science)Document6 pagesModule 5n6 Answer Sheet Is Anatomy and Physiology (Abegail C. Relunia - Bsed 3c-Science)Abegail ReluniaNo ratings yet
- Individual Quiz 2019Document1 pageIndividual Quiz 2019joan marie PeliasNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 3rd Quarter ExamDocument4 pagesPhysical Science 3rd Quarter Examjeddah noa lorzano100% (1)
- Atoms, Elements, and Compounds-Chapter 6Document8 pagesAtoms, Elements, and Compounds-Chapter 6Araas AraasNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Class - 7 SUBJECT-Science CHAPTER - 3, Chemical Substances and Processes A. Fill in The BlanksDocument3 pagesWorksheet Class - 7 SUBJECT-Science CHAPTER - 3, Chemical Substances and Processes A. Fill in The BlanksRenee DisaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Study GuideDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Study GuideportbluepicklesNo ratings yet
- QUIZ#2 - Matter and The Molecules of LifeDocument14 pagesQUIZ#2 - Matter and The Molecules of LifeLouiza Angelina LayugNo ratings yet
- Pre Test Physci Q3Document3 pagesPre Test Physci Q3MICHELLE DE GUZMAN SOTTONo ratings yet
- SPT11 PDFDocument2 pagesSPT11 PDFLeeann LeeNo ratings yet
- I. Choosing The Best Answer and Filling in The Answer SheetDocument3 pagesI. Choosing The Best Answer and Filling in The Answer SheetPham Van Tin B1909842No ratings yet
- Q1, Gen Chem 2 Sy 2022-2023Document4 pagesQ1, Gen Chem 2 Sy 2022-2023Jenny Vhie S. VinagreraNo ratings yet
- TQ G9Q2Document4 pagesTQ G9Q2Veronica PabillenaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer (Chemistry)Document10 pagesScience Reviewer (Chemistry)CHRISTIAN NOE BONGALBALNo ratings yet
- I. Multiple Choice: Read Each Item Carefully. Write The Letter of The Best AnswerDocument4 pagesI. Multiple Choice: Read Each Item Carefully. Write The Letter of The Best AnswerGerald BalmacedaNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Encircle The Letter That Corresponds To Your AnswerDocument3 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Encircle The Letter That Corresponds To Your AnswerJohnnard BelenNo ratings yet
- Basic Education Department (SHS) : Qualifying Examination - ChemistryDocument3 pagesBasic Education Department (SHS) : Qualifying Examination - Chemistryismael jaafarNo ratings yet
- (MSU SASE) Chemistry-1Document4 pages(MSU SASE) Chemistry-1Arice MontiponNo ratings yet
- Long TestDocument3 pagesLong TestMarvin SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Organic Reaction Mechanisms 1982: An annual survey covering the literature dated December 1981 through November 1982From EverandOrganic Reaction Mechanisms 1982: An annual survey covering the literature dated December 1981 through November 1982A. C. KnipeNo ratings yet
- Oral RecitationDocument1 pageOral RecitationTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Final Exam in Chem 1Document2 pagesFinal Exam in Chem 1Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- First Quarterly Examination in Science 10Document2 pagesFirst Quarterly Examination in Science 10Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- SECOND QUARTERLY EXAMINATION IN SCIENCE 8 (Simplicity)Document2 pagesSECOND QUARTERLY EXAMINATION IN SCIENCE 8 (Simplicity)Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- First Final Examination in Science 7Document8 pagesFirst Final Examination in Science 7Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Long Test in Science 7Document1 pageLong Test in Science 7Teresa Marie Cordero100% (1)
- Naming CompoundsDocument2 pagesNaming CompoundsTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Pretest in Physical Science 12Document3 pagesPretest in Physical Science 12Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Examination in Science 9Document2 pagesSecond Quarter Examination in Science 9Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- TOS Grade 10 (1st Quarter 2019-2020)Document3 pagesTOS Grade 10 (1st Quarter 2019-2020)Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument9 pagesCHEMISTRYTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- CELL OrganellesDocument5 pagesCELL OrganellesTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Activity 1Document2 pagesEndocrine Activity 1Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table (Chemical Bonding)Document8 pagesPeriodic Table (Chemical Bonding)Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Levels of Biological OrganizationDocument6 pagesLevels of Biological OrganizationTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- First Quarterly Examination in Science 7 (2019-2020)Document2 pagesFirst Quarterly Examination in Science 7 (2019-2020)Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
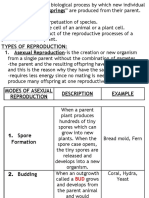
- REPRODUCTIONDocument8 pagesREPRODUCTIONTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- CARBONDocument1 pageCARBONTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- WHLP Activity Sheet 1 (Circulatory)Document1 pageWHLP Activity Sheet 1 (Circulatory)Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument47 pagesAtomic StructureTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- MICROSCOPEDocument5 pagesMICROSCOPETeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Activity in MicroscopeDocument2 pagesActivity in MicroscopeTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Concentration of SolutionsDocument30 pagesConcentration of SolutionsTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Ways of Separating MixturesDocument23 pagesWays of Separating MixturesTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Grade 9Document56 pagesChemistry Grade 9wafa sheikhNo ratings yet
- Solid Solution For Catalytic Ammonia Synthesis FromDocument8 pagesSolid Solution For Catalytic Ammonia Synthesis FromAhmad AlShahrourNo ratings yet
- Vsepr: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular GeometryDocument16 pagesVsepr: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular GeometrySandra Enn BahintingNo ratings yet
- Coordination ChemistryDocument19 pagesCoordination ChemistryPrityyyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry OpenStaxDocument1,413 pagesChemistry OpenStaxreklaminisNo ratings yet
- 202-Nya TH Ea F14Document5 pages202-Nya TH Ea F14Julien SiinoNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 - Integrated Science Consolidated CurriculumDocument12 pagesGrade 8 - Integrated Science Consolidated Curriculumshonaishot hottieNo ratings yet
- PS SIR Inorganic QUESTION 100Document10 pagesPS SIR Inorganic QUESTION 100Arya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Protonation and Geometry of Histidine Rings: Research PapersDocument11 pagesProtonation and Geometry of Histidine Rings: Research Papersrufus991No ratings yet
- Chemistry Important QuestionsDocument13 pagesChemistry Important QuestionsSadnanSadiqueNo ratings yet
- Valence Bond Theory: 4 Meet On Chemical Bond CourseDocument52 pagesValence Bond Theory: 4 Meet On Chemical Bond Courselina lathifaNo ratings yet
- Dae Footwear PDFDocument140 pagesDae Footwear PDFFarid ElkhshabNo ratings yet
- Class XI Chemistry Worksheet 2021Document43 pagesClass XI Chemistry Worksheet 2021Muffadal AlaviNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY HotsDocument143 pagesCHEMISTRY HotsJaved Sheikh0% (1)
- FullDocument1,175 pagesFull43 Trần Công VinhNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0167732220370549 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0167732220370549 Maintuangsiong ShuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Linetics MCQS Set ExamDocument16 pagesChemical Linetics MCQS Set ExamAsim MushtaqNo ratings yet
- SR AIIMS S60 - NEET Part Test - 2 (03!01!23) SyllabusDocument1 pageSR AIIMS S60 - NEET Part Test - 2 (03!01!23) SyllabusAdithya BharadwajNo ratings yet
- MO TheoryDocument34 pagesMO TheoryKhoerunnisaWulanSafitriNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - Structure of SubstancesDocument16 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Structure of SubstancesChemistryKlipz100% (6)
- Chemistryh Subject Syllabus For A Level Form V-VI - 2018 PDFDocument90 pagesChemistryh Subject Syllabus For A Level Form V-VI - 2018 PDFMaryNo ratings yet
- Full Download Biology 3rd Edition Brooker Solutions ManualDocument18 pagesFull Download Biology 3rd Edition Brooker Solutions Manualmaurineheckathorneus100% (40)
- Yr 12 Chemistry PP1Document11 pagesYr 12 Chemistry PP1NjoroNo ratings yet
- Answers To Eocqs: Cambridge International As Level ChemistryDocument3 pagesAnswers To Eocqs: Cambridge International As Level ChemistryRaihanNo ratings yet
- Iit Chemistry: Goc (Electronic Effect)Document35 pagesIit Chemistry: Goc (Electronic Effect)swadhin100% (1)
- SamajDocument21 pagesSamajAnand SwarnkarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding PDFDocument14 pagesChemical Bonding PDFsiddhant shuklaNo ratings yet