Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organic Chemistry - Petroleum/Crude Oil
Organic Chemistry - Petroleum/Crude Oil
Uploaded by
anya de silvaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Organic Chemistry - Petroleum/Crude Oil
Organic Chemistry - Petroleum/Crude Oil
Uploaded by
anya de silvaCopyright:
Available Formats
Organic Chemistry – Petroleum/Crude Oil
Students should be able to:
(a) state that the naphtha fraction from crude oil is the main source of hydrocarbons
used as the feedstock for the production of a wide range of organic compounds
(b) describe the issues relating to the competing uses of oil as an energy source
and as a chemical feedstock
Introduction to Organic Chemistry
What are organic compounds?
All organic compounds contain carbon. Most organic compounds also contain hydrogen.
Hydrocarbons are compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen only.
Organic compounds may also contain other elements like oxygen (for example, alcohols and
organic acids) and nitrogen (for example, amino acids).
Organic compounds are found in all animals and plants, and even things like plastics and medicines.
However, not all carbon-containing compounds are organic compounds. For example, carbon
dioxide, carbon monoxide and carbonates are not classified as organic compounds.
Formation of Petroleum and Natural Gas
Petroleum and natural gas are mixtures of hydrocarbons, mainly
alkanes. Millions of years ago, dead plants and animals formed layers,
for example, at the bottom of the sea, and were buried under mud and
sand. The dead and decaying plants and animals were subject to great
heat and pressure, and were slowly converted to a dark, sticky liquid,
called petroleum or crude oil. Some of it was changed to a gas called
natural gas.
Petroleum and natural gas are often found together, held in between
layers of non-porous rock, hundreds or thousands of metres below the Figure 1 Extraction of
surface of the earth. These fuels are extracted by drilling deep Petroleum and Natural
wells through the rock. Gas
2022 Secondary 4 Chemistry (6092) 1
Fractional Distillation of Petroleum
Petroleum is a mixture of different alkanes with different boiling points.
Petroleum can be separated into useful fractions (or parts) using fractional distillation.
The separation into fractions is based on the different range of boiling points.
Each fraction consists of a mixture of hydrocarbons which boils over a certain temperature
range.
Hydrocarbons more carbon atoms have higher boiling points whereas those with fewer carbon
atoms have lower boiling points.
Process :
1. Petroleum is heated in a furnace and vapourised. The hot vapour will flow up the fractionating
column and start to cool down.
2. Each fraction condenses at a different temperature and comes out of the column at different
height depending on their boiling points.
3. The hydrocarbons with the lower boiling point range will distill over at the top of the column,
where the temperature is lower, while the ones with the higher boiling point range will distil over
at the bottom where the temperature is higher.
4. The process is called selective condensation.
2022 Secondary 4 Chemistry (6092) 2
The Different Fractions and Their Uses
Fraction No. of Boiling Point Uses
carbon Range (ºC)
atoms (n)
Petroleum gas 1–4 < 40 Fuel for cooking
Petrol 5 – 10 40 – 75 Fuel for car engines
(Gasoline)
Naphtha 7 – 14 75 – 150 Feedstock (raw material) for
petrochemicals (E.g. plastics, detergents,
alcohol, drugs)
Kerosene 11 – 16 160 – 250 Fuel for jet engines; cooking and heating
(Paraffin)
Diesel 16 – 20 250 – 300 Fuel for diesel engines of buses, taxis and
lorries
Lubricating oil 20 – 35 300 – 350 Lubricants for machines; making of waxes
and polishes
Bitumen >70 > 350 Make road surfaces
All the fractions are insoluble in water and burn in air.
As n increases per molecule,
the boiling points increases.(Relative molecular mass and molecular size increases, IMF/VDW
forces strengthen, more energy needed to break the IMF/VDW forces, bp increases)
the liquids become more viscous (flow less easily).
the liquids burn less easily, meaning flammability decreases. (more bonds to be broken, Ea
increases)
when the liquids burn, they burn with a more sooty flame, ie. more carbon produced.
(percentage by mass of carbon increases so more oxygen needed for complete combustion per
unit mass of hydrocarbon)
Issues related to Fossil Fuels
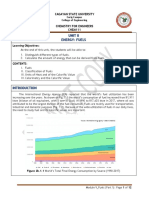
Petroleum is a finite non-renewable resource and the world’s petroleum reserves are depleting.
The supply of petroleum is being depleted very rapidly, and there is a need for its conservation.
Petroleum, besides being used as fuel, has other important uses like being used as a raw material
for the manufacture of essential chemical compounds like medicine and plastics.
Combustion of petroleum also contributes to pollution (due to the production of CO and C) and
global warming (due to the production of CO2).
One way of conserving petroleum is to cut down on its use as a fuel.
We can also save fossil fuels by using alternative energy sources, like solar energy and nuclear
energy.
2022 Secondary 4 Chemistry (6092) 3
Alternative Fuels
One possible source of alternative fuel comes from plants. In Malaysia, palm oil is being used to
run vehicles fitted with special engines. In Brazil, ethanol is being used as a fuel.
Another important fuel is methane, which is the gas produced when organic matter (waste material
from plants and animals) is allowed to decay in the absence of air. Biogas contains about 50%
methane.
Another possible fuel is hydrogen, which can be obtained from water. Hydrogen, when burnt,
produces only steam, which is a non-pollutant. Hydrogen also produces more energy per gram when
burnt, than any other common fuel.
Advantages of using hydrogen as an alternative fuel:
1. Clean fuel, producing only water.
2. Renewable, can be manufactured. (Note that this only applies if hydrogen is obtained from
water instead of petroleum)
3. Produces more energy per unit mass (reaction is more exothermic).
Classification of Organic Compounds
Organic compounds are divided into 2 main categories – hydrocarbons and non-hydrocarbons. They
are then divided further into different homologous series.
Organic Compounds
Hydrocarbons Non-hydrocarbons
Alkanes Alkenes Alkynes Alcohols Carboxylic acids Esters
in sy
Definitions :
1. A homologous series is a family of organic compounds which conform to the general formula
and each member differs from the next by a –CH2 group.
2. Compounds in the same homologous series contain the same functional group and have similar
chemical properties.
3. A functional group is an atom or a group of atoms that gives a molecule its characteristic
properties.
2022 Secondary 4 Chemistry (6092) 4
Figure 3. Different functional groups
In general, organic compounds in the same homologous series have a few properties in common:
They have the same functional group, so they have similar chemical properties.
There is a gradual change in their physical properties.
2022 Secondary 4 Chemistry (6092) 5
Naming Organic Compounds
The name of an organic compound is divided into 2 parts. The first part (prefix) tells us the number
of carbon atoms in the compound.
Prefix meth- eth- prop- but- pent- hex- hept- oct- non- dec-
No. of 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
carbon
atoms
The second part (suffix) tells us the functional group of the compound.
Suffix -ane -ene -ol -oic acid
Homologous series alkane alkene alcohol carboxylic acid
For example,
prop ene
eth ol
H H H H
H
H C C C H C C O H
H H H H
propene ethanol
Figure 4. Naming of organic compounds
Propene is an alkene with three carbon atoms per molecule, while ethanol is an alcohol with two
carbon atoms per molecule.
2022 Secondary 4 Chemistry (6092) 6
You might also like
- CHAPTER 4 Fuels and It's Supply System For SI and CI EnginesDocument102 pagesCHAPTER 4 Fuels and It's Supply System For SI and CI EnginesRushabh Patel100% (1)
- IGCSE Chemistry - Organic ChemistryDocument31 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Organic ChemistryChemistryKlipz98% (42)
- Liquid and Gaseous FuelsDocument84 pagesLiquid and Gaseous Fuelsmohamed abdalla abo assyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of FuelDocument6 pagesChemistry of FuelIsaiah Danniel PerezNo ratings yet
- As Topic 5 Notes - AlkanesDocument5 pagesAs Topic 5 Notes - AlkanesKavisha AshaNo ratings yet
- IC Engine FuelDocument116 pagesIC Engine FueluchihaenomiNo ratings yet
- As Topic 5 Notes - AlkanesDocument5 pagesAs Topic 5 Notes - AlkanesRaiyan RahmanNo ratings yet
- Hyrocarbona 1Document10 pagesHyrocarbona 1jpkaomeNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument10 pagesOrganic ChemistrySayeef MahdiNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 - Organic Chemistry IDocument17 pagesTopic 6 - Organic Chemistry Ijulian maltoNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1: Context, Introduction To Petroleum Engineering, Present and Future ScenarioDocument37 pagesUNIT 1: Context, Introduction To Petroleum Engineering, Present and Future ScenarioJITENDRA PRATAP SINGHNo ratings yet
- FEI CSEC Chemistry Handbook Section B - Organic Chemistry and Section CDocument134 pagesFEI CSEC Chemistry Handbook Section B - Organic Chemistry and Section CMarques GrantNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument16 pagesOrganic ChemistryaquamogolwaneNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SME Notes (Organic Chemmistry)Document14 pagesChemistry SME Notes (Organic Chemmistry)Sayeef MahdiNo ratings yet
- Petro Unit 1Document38 pagesPetro Unit 1ethanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project: By: Ouail BalahDocument9 pagesChemistry Project: By: Ouail BalahOuail BalahNo ratings yet
- 4.C Alkanes ASDocument13 pages4.C Alkanes ASytshortsfromopus65No ratings yet
- Chapter (14) Organic ကျက်စာDocument12 pagesChapter (14) Organic ကျက်စာMoun Lynn SythuNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Chap 06Document12 pagesOrganic Chemistry Chap 06Daniya Sohail Sohail HashimNo ratings yet
- Topic 5a - Introduction To Organic Chemistry Revision Notes: 1) FormulaeDocument5 pagesTopic 5a - Introduction To Organic Chemistry Revision Notes: 1) FormulaeThuvarakaNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument24 pagesOrganic ChemistryEMMANUEL FESTUSNo ratings yet
- Carbon CompoundDocument78 pagesCarbon CompoundYRaj FimmNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry '13Document33 pagesOrganic Chemistry '13Princess KimNo ratings yet
- Alkanes ClassDocument27 pagesAlkanes ClassRyan JamesNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry The Three Stages of RefiningDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistry The Three Stages of RefiningCeyda ErdoğanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document15 pagesChapter 2vinNo ratings yet
- AFL Units 1 To 3 NOLDocument47 pagesAFL Units 1 To 3 NOLpavanraneNo ratings yet
- Notes Lecture - Introduction To HydrocarbonsDocument24 pagesNotes Lecture - Introduction To HydrocarbonsGothic_VampiressNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class 10 Chapter 11Document14 pagesChemistry Class 10 Chapter 11Rahim BakhshNo ratings yet
- Module 9 - UNIT II - Fuels (Part 1)Document12 pagesModule 9 - UNIT II - Fuels (Part 1)Jhess GaliciaNo ratings yet
- c21 - An Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument5 pagesc21 - An Introduction To Organic ChemistrygarethongshNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1 The Fuel and Energy RelationshipDocument10 pages1.1.1 The Fuel and Energy RelationshipRomeo San GasparNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument14 pagesChemistry NotesMina TadrosNo ratings yet
- iGCSE Chemistry Organic ChemDocument96 pagesiGCSE Chemistry Organic Chemreem.halawiNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 Carbon The Chemical Basis of Organic ChemistryDocument16 pagesLESSON 1 Carbon The Chemical Basis of Organic ChemistryShannNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument12 pagesOrganic ChemistryYoviNo ratings yet
- (19th of 19 Chapters) Organic Chemistry Part 1 of 3 - GCE O Level Chemistry LectureDocument37 pages(19th of 19 Chapters) Organic Chemistry Part 1 of 3 - GCE O Level Chemistry LectureChengeto MatandaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: TerminologiesDocument14 pagesOrganic Chemistry: TerminologiesGirvin DjapardiNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument24 pagesOrganic ChemistryNivas KaruppananNo ratings yet
- 6 184623437Document24 pages6 184623437Dr.Srinivasa Rao K.V.N100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry CurrentDocument48 pagesOrganic Chemistry CurrentBierzo JomarNo ratings yet
- IVAN Organic ChemistryDocument11 pagesIVAN Organic ChemistryYoviNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Organic ChemistryDocument31 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Organic ChemistryddddddffdfdfNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument10 pagesChemistry Notesxd OptimusNo ratings yet
- CIE IGCSE Organic Chemistry (2023-2025)Document13 pagesCIE IGCSE Organic Chemistry (2023-2025)abiharehan196No ratings yet
- Oil Refinary Dr Adndn 2016-مهمةDocument234 pagesOil Refinary Dr Adndn 2016-مهمةHmid AljbreNo ratings yet
- Topic 14. Organic ChemistryDocument24 pagesTopic 14. Organic ChemistryBashar Abu HijlehNo ratings yet
- L02 - w3 - 01 - Fuels Energy - RelationsDocument6 pagesL02 - w3 - 01 - Fuels Energy - RelationsJohn Rave Manuel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Saturated HydrocarbonsDocument17 pagesChapter 12 Saturated HydrocarbonsChristian Guimmayen ArizoNo ratings yet
- HYDROCARBONS Module3Document22 pagesHYDROCARBONS Module3Mugara Waitega PeterNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Notes - Part 1Document14 pagesOrganic Chemistry Notes - Part 1idkNo ratings yet
- Mod 1 Revision Guide Organic2Document6 pagesMod 1 Revision Guide Organic2Saifulahmed49No ratings yet
- Znotes ChemDocument7 pagesZnotes ChemCaylinNo ratings yet
- CHP 3 Organic Compounds PDFDocument54 pagesCHP 3 Organic Compounds PDFzubair.gs-017No ratings yet
- 8 Fuels and Earth SciencesDocument6 pages8 Fuels and Earth SciencessophiederryNo ratings yet
- AS Chemistry - Revision Notes Unit 3 - Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument6 pagesAS Chemistry - Revision Notes Unit 3 - Introduction To Organic ChemistryRaiyan RahmanNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument4 pagesOrganic ChemistrybethanyNo ratings yet
- Alkanes PDFDocument15 pagesAlkanes PDFAnkitBanerjee100% (1)
- Igcse Separate Sciences Topic C14: Organic Chemistry Revision NotesDocument9 pagesIgcse Separate Sciences Topic C14: Organic Chemistry Revision NotesJamiu Yusuf AsukuNo ratings yet
- Crude Petroleum analysis handbook: Crude oil Quality control, #1From EverandCrude Petroleum analysis handbook: Crude oil Quality control, #1Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- How Well Would Budget 2023 Achieve Its Aims On Markets?: Market: ChildcareDocument7 pagesHow Well Would Budget 2023 Achieve Its Aims On Markets?: Market: Childcareanya de silvaNo ratings yet
- 2023 JC1 H1 Price Mechanism and Its Applications Part 1 Lecture Notes - Uploaded VersionDocument46 pages2023 JC1 H1 Price Mechanism and Its Applications Part 1 Lecture Notes - Uploaded Versionanya de silvaNo ratings yet
- 2006 AJC H2 MY SolnDocument9 pages2006 AJC H2 MY Solnanya de silvaNo ratings yet
- 2022 4E Bio6093 Prelim - P2Document23 pages2022 4E Bio6093 Prelim - P2anya de silvaNo ratings yet
- 2022 Sec 4IP Bio EOY Paper 2 - Mark Scheme - Updated 131022Document14 pages2022 Sec 4IP Bio EOY Paper 2 - Mark Scheme - Updated 131022anya de silvaNo ratings yet
- 2022 Sec 4IP Bio EOY Paper 2Document20 pages2022 Sec 4IP Bio EOY Paper 2anya de silvaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledanya de silvaNo ratings yet
- Sec 4 Alkenes NotesDocument12 pagesSec 4 Alkenes Notesanya de silvaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledanya de silvaNo ratings yet
- Sec 4 Ecology NotesDocument21 pagesSec 4 Ecology Notesanya de silvaNo ratings yet
- Key Factors Limiting Refining Capacity in AfricaDocument12 pagesKey Factors Limiting Refining Capacity in AfricaMugabi Kolping FrancisNo ratings yet
- BC Royalty Review Independent AssessmentDocument106 pagesBC Royalty Review Independent AssessmentAlaskaHighwayNews100% (1)
- Oil and Gas Technology Update - 26 Oktober 2016 - P9 City Plaza - PATRIA - LNG Iso Tank DevelopmentDocument19 pagesOil and Gas Technology Update - 26 Oktober 2016 - P9 City Plaza - PATRIA - LNG Iso Tank Developmentagung100% (1)
- Attachment 05 - BFD, ELD and P&I Diagrams-PearlDocument77 pagesAttachment 05 - BFD, ELD and P&I Diagrams-Pearlum er100% (1)
- Pgas-kj-c004-Ecv-dg-105 - Metering Shelter PJB Muara Karang - As Built Drawing - FTHDocument10 pagesPgas-kj-c004-Ecv-dg-105 - Metering Shelter PJB Muara Karang - As Built Drawing - FTHIwan NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Group News - March 2014Document17 pagesGroup News - March 2014Lopez Gardo0% (1)
- Workflow of The in Situ Combustion EOR Method in VDocument20 pagesWorkflow of The in Situ Combustion EOR Method in VRonald GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Biomethane Plants Based On Municipal Solid WasteDocument17 pagesBiomethane Plants Based On Municipal Solid WasteRocky KhareNo ratings yet
- Rapport Annuel 2020 - enDocument79 pagesRapport Annuel 2020 - enDavid GatesNo ratings yet
- Asia Pac Offshore Newsletter Issue 120 END MAY 2018Document20 pagesAsia Pac Offshore Newsletter Issue 120 END MAY 2018Abdullah FathanNo ratings yet
- 240 East Med Gas DiplomacyDocument49 pages240 East Med Gas DiplomacyMohamed AliNo ratings yet
- Cambay 101Document7 pagesCambay 101Sanjeev Singh NegiNo ratings yet
- Cracking Hydrocarbon Feedstock With A Heavy TailDocument4 pagesCracking Hydrocarbon Feedstock With A Heavy TailGhasem BashiriNo ratings yet
- MEED Qatar 2022 Sample PagesDocument26 pagesMEED Qatar 2022 Sample PagesvadivvelkavinNo ratings yet
- 2 Rajiv Aggarwal Bio CNG A Green Alternate To Fossil FuelsDocument28 pages2 Rajiv Aggarwal Bio CNG A Green Alternate To Fossil FuelsGaneshkumar AmbedkarNo ratings yet
- A Novel Concept For Offshore Production of Liquefied Natural GasDocument4 pagesA Novel Concept For Offshore Production of Liquefied Natural Gasbkonly4uNo ratings yet
- DPR Ambala KurukshetraDocument85 pagesDPR Ambala KurukshetraAbdul Wajid AliNo ratings yet
- Corporate Social Responsibility Initiatives at ExxonMobilpgdm 22-24Document19 pagesCorporate Social Responsibility Initiatives at ExxonMobilpgdm 22-24Amit RajNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Geology: Assignment: 1Document9 pagesPetroleum Geology: Assignment: 1Afiq AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Data Overview - Multimedia OfficerDocument2 pagesData Overview - Multimedia Officercochrane perkasaNo ratings yet
- Sonatrach Antisurge PDFDocument214 pagesSonatrach Antisurge PDFBerhoof Dalch100% (1)
- OCIMF PublicationsDocument8 pagesOCIMF PublicationsSahil BiswasNo ratings yet
- Honeywell Modular GasProcessing Plants BrochureDocument8 pagesHoneywell Modular GasProcessing Plants BrochureCHE.ENG1734No ratings yet
- Prelude FLNG Terminal Information Book CondensateDocument82 pagesPrelude FLNG Terminal Information Book CondensateSnow JohnNo ratings yet
- Future Need For Petroleum Engineering: June 2021Document15 pagesFuture Need For Petroleum Engineering: June 2021David BonsuNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - 2009 FLNG FLNG Safe Tandem Offloading of LNG SeoulpptDocument27 pagesDokumen - Tips - 2009 FLNG FLNG Safe Tandem Offloading of LNG SeoulpptOlusegun OyebanjiNo ratings yet
- Condensate Stabilizer Unit: Key BenefitsDocument2 pagesCondensate Stabilizer Unit: Key Benefitsgurbuz sakmakNo ratings yet
- WHP12S 30 103 0012 - B1Document1 pageWHP12S 30 103 0012 - B1DonnyNo ratings yet
- Well Control Incident TrollDocument44 pagesWell Control Incident TrollFaniyi Hussein KehindeNo ratings yet
- Hazard and Operability Study With Quantitative Risk Assessment of Propane YardDocument7 pagesHazard and Operability Study With Quantitative Risk Assessment of Propane YardSUNDARAMAHALINGAM ANo ratings yet