Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ambot:' : Applied Economics Supply Force Supply - P F (QS)
Ambot:' : Applied Economics Supply Force Supply - P F (QS)
Uploaded by
cali k0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesThe document discusses the economic concept of supply. It defines supply as the quantity of a good or service offered for sale during a given period of time. Six key variables that influence supply are identified: price of the good, input prices, prices of related goods, technological advances, expected future price, and number of firms producing the product. A general supply function is defined relating quantity supplied to these six variables. The relationship between each variable and quantity supplied is characterized by slope parameters. The document also distinguishes between changes in quantity supplied, which occur when price changes, and changes in supply, which occur when other determinants of supply change.
Original Description:
Original Title
Untitled
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the economic concept of supply. It defines supply as the quantity of a good or service offered for sale during a given period of time. Six key variables that influence supply are identified: price of the good, input prices, prices of related goods, technological advances, expected future price, and number of firms producing the product. A general supply function is defined relating quantity supplied to these six variables. The relationship between each variable and quantity supplied is characterized by slope parameters. The document also distinguishes between changes in quantity supplied, which occur when price changes, and changes in supply, which occur when other determinants of supply change.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesAmbot:' : Applied Economics Supply Force Supply - P F (QS)
Ambot:' : Applied Economics Supply Force Supply - P F (QS)
Uploaded by
cali kThe document discusses the economic concept of supply. It defines supply as the quantity of a good or service offered for sale during a given period of time. Six key variables that influence supply are identified: price of the good, input prices, prices of related goods, technological advances, expected future price, and number of firms producing the product. A general supply function is defined relating quantity supplied to these six variables. The relationship between each variable and quantity supplied is characterized by slope parameters. The document also distinguishes between changes in quantity supplied, which occur when price changes, and changes in supply, which occur when other determinants of supply change.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
ambot:’>
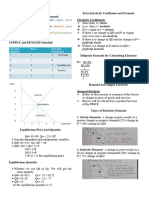
APPLIED ECONOMICS - P = f(Qs)
SUPPLY FORCE
Supply
~Quantity supplied (Qs)
- amount of a good or service offered for sale during
a given period of time
~Six variables that influence Qs
- Price of good or service (P)
- Input prices (PI )
- Prices of goods related to production (Pr)
- Technological advances (T)
- Expected future price of the product (Pe) ~Graphing Supply Curves
- Number of firms producing the product (F) - point on a direct supply curve shows either:
~General supply function o maximum amount of a good that will be
offered for sale at a given price
- Qs = f (P, PI, Pr, T, Pe, F)
- Qs = h + kP + lPI + mPr + nT + rPe + sF o minimum price necessary to induce
producers to voluntarily offer a particular
~k, l, m, n, r, & s are slope parameters quantity for sale
- measure the effect on Qs of changing one of the
- variables while holding the others constant
~Sign of parameter shows how a variable is related to Qs
- Positive sign indicates direct relationship
- Negative sign indicates inverse relationship
~General Supply Function
- Change in quantity supplied
o occurs when price changes
o movement along the supply curve
- Change in supply
o occurs when one of the other variables, or
determinants of supply, changes
o supply curve shifts rightward or leftward
~Direct Supply Function
- The direct supply function, or simply supply,
shows how quantity supplied, Qs, is related to
product price, P, when all other variables are held
constant.
- Qs = f(P)
~Inverse Supply Function
- price (P) is plotted on the vertical axis & quantity
supplied (Qs) is plotted on the horizontal axis
ambot:’>
SEATWORKS
You might also like
- Application of CalculusDocument7 pagesApplication of CalculusNoramira Ahmad Tajuddin88% (16)
- Syllabus of BSC Nursing, Kathmandu UniversityDocument191 pagesSyllabus of BSC Nursing, Kathmandu UniversityKamal Raj Chapagain94% (18)
- Chapter 10-Understanding A Firm's Financial Statements: True/FalseDocument23 pagesChapter 10-Understanding A Firm's Financial Statements: True/FalseKhang ToNo ratings yet
- CKE6150 Spare Parts ManualDocument74 pagesCKE6150 Spare Parts ManualVanessa RiveraNo ratings yet
- Quantity DemandedDocument4 pagesQuantity DemandedYusra PangandamanNo ratings yet
- Demand, Supply and Equilibrium in The MarketDocument18 pagesDemand, Supply and Equilibrium in The MarketRana BasitNo ratings yet
- Economics: 讲师: CherieDocument306 pagesEconomics: 讲师: CherieEvelyn YangNo ratings yet
- Socstud ReviewerDocument9 pagesSocstud ReviewerCRAIG MIKEL P YUNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Demand, Supply Market EquilibriumDocument37 pagesChapter 2 Demand, Supply Market EquilibriumNadeen ZNo ratings yet
- Demand Supply and Market Equilibrium StudentsDocument25 pagesDemand Supply and Market Equilibrium StudentsOliver TalipNo ratings yet
- Demand Supply and Market EquilibriumDocument30 pagesDemand Supply and Market EquilibriumOliver TalipNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document60 pagesChapter 02judeaharmony.wamildaNo ratings yet
- Markets: Demand, Supply, and ElasticityDocument45 pagesMarkets: Demand, Supply, and ElasticityGoutam ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document55 pagesChapter 2Ana Leah DelfinNo ratings yet
- MGEC Concepts PrimerDocument2 pagesMGEC Concepts PrimerDevbratRathNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply AnalysisDocument31 pagesDemand and Supply AnalysisUsman WaheedNo ratings yet
- Demand Supply EquilibriumDocument18 pagesDemand Supply EquilibriumGeorgiana IlieNo ratings yet
- Chap 6 ElasticityDocument26 pagesChap 6 ElasticityShivkarthik G SNo ratings yet
- Best Notes of Theory of SupplyDocument5 pagesBest Notes of Theory of Supplyshakuntala197804No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document3 pagesChapter 2trucle22725No ratings yet
- ch12 Nicholson 3dec2020Document62 pagesch12 Nicholson 3dec2020Jahanzeb KhanNo ratings yet
- Supply For International ClassDocument29 pagesSupply For International ClassNAJLA RIZKIA RAMADHANINo ratings yet
- Midterms Basic Microeconomics ReviewerDocument3 pagesMidterms Basic Microeconomics ReviewerPrince LitchNo ratings yet
- ECON254 Lecture4 CompetitionDocument37 pagesECON254 Lecture4 CompetitionKhalid JassimNo ratings yet
- Apeco SemisDocument6 pagesApeco SemisAthena Francine LangiNo ratings yet
- Demand Analysis: Demand Desire + Ability To Pay + Willingness To Pay Demand Is Relative Term - Price Time PlaceDocument44 pagesDemand Analysis: Demand Desire + Ability To Pay + Willingness To Pay Demand Is Relative Term - Price Time PlaceAbhishek GargNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Basics of Supply and Demand 20190829 MDocument17 pagesCH 2 Basics of Supply and Demand 20190829 MRodney ManuelNo ratings yet
- 02 Demand and Supply AnalysisDocument33 pages02 Demand and Supply AnalysisRajeev SinghNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Topic 2 Demand and Supply Functions (Microeconomics)Document14 pagesLesson 3 - Topic 2 Demand and Supply Functions (Microeconomics)Marianne Jade HonorarioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document41 pagesChapter 2Heap Ke XinNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes EconS301 Fall2010 AllDocument182 pagesLecture Notes EconS301 Fall2010 AllFelix MunozNo ratings yet
- Econ330 notesPartIDocument115 pagesEcon330 notesPartIĐoàn Ngọc Thành Lộc0% (1)
- Demand: - Quantity Demanded (QDocument36 pagesDemand: - Quantity Demanded (QVivek vermaNo ratings yet
- Ashish Sharma PPT 11Document27 pagesAshish Sharma PPT 11Vedantpal Singh ChandrawatNo ratings yet
- Price Elasticity of Demand (E) : - P & Q Are Inversely Related by The Law ofDocument25 pagesPrice Elasticity of Demand (E) : - P & Q Are Inversely Related by The Law ofraja sekharNo ratings yet
- Q α α P α P α M α α α: X d X X Y Y MDocument14 pagesQ α α P α P α M α α α: X d X X Y Y MJolly CharmzNo ratings yet
- Basic Microeconomics Reviewer FinalsDocument3 pagesBasic Microeconomics Reviewer FinalsDearlyne AlmazanNo ratings yet
- Substitutes Compementary: Cross Price Elasticity Kind of GoodDocument6 pagesSubstitutes Compementary: Cross Price Elasticity Kind of GoodlemonNo ratings yet
- 2.3. Elasticity - Measure of ResonsivenessDocument2 pages2.3. Elasticity - Measure of ResonsivenessgebreNo ratings yet
- Micro 101 - Week 4 Market EquilibriumDocument29 pagesMicro 101 - Week 4 Market EquilibriumAbebe AnawutieNo ratings yet
- (By-Dr. Jatin Kumar Lamba) : Chapter-2 Unit 3: Theory of SupplyDocument24 pages(By-Dr. Jatin Kumar Lamba) : Chapter-2 Unit 3: Theory of SupplyDeepak YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Theory of SupplyDocument26 pagesChapter 2-Theory of Supplysassy veganNo ratings yet
- Demand, Supply, and Market EquilibriumDocument28 pagesDemand, Supply, and Market EquilibriumOrion PaxNo ratings yet
- 10 SupplyDocument19 pages10 SupplyKyla DizonNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Dynamics of Demand and SupplyDocument22 pagesModule 3 Dynamics of Demand and SupplyCharice Anne Villamarin100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Demand Supply and Equilibrium Prices 061621Document25 pagesChapter 2 Demand Supply and Equilibrium Prices 061621mc.olalia28No ratings yet
- BHHT1123 Lec4 StudentDocument38 pagesBHHT1123 Lec4 StudentWeiqin ChanNo ratings yet
- Methods of Demand and Supply AnalysisDocument41 pagesMethods of Demand and Supply AnalysisCharbel TresvallesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 An Introduction To Demand and Supply. Market EquilibriumDocument26 pagesChapter 6 An Introduction To Demand and Supply. Market EquilibriumAndreea AnghelNo ratings yet
- Lec-3 (Demand, Supply & Market Equilibrium)Document79 pagesLec-3 (Demand, Supply & Market Equilibrium)MD Shamim HOSSAINNo ratings yet
- EEB - 2608 - Lecture 003 - Theory of SupplyDocument17 pagesEEB - 2608 - Lecture 003 - Theory of SupplyChandan MazumdarNo ratings yet
- Demand & SupplyDocument18 pagesDemand & SupplyBikram SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Demand Schedule and Demand Curve Supply Schedule and The Supply Curve Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument31 pagesDemand Schedule and Demand Curve Supply Schedule and The Supply Curve Elasticity of Demand and SupplyBhavana ChavanNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Supply 2 1Document11 pagesElasticity of Supply 2 1Nguyễn Như NgọcNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document92 pagesCH 10Vanitha NarendrababuNo ratings yet
- (DONE) Econ 201 Final Notes 2Document76 pages(DONE) Econ 201 Final Notes 2Vaga boundedNo ratings yet
- Micro Economics SlidesDocument77 pagesMicro Economics SlidessnuichNo ratings yet
- Report On SupplyDocument6 pagesReport On SupplyPaul Joshua Ofalsa CualNo ratings yet
- Demand AnalysisDocument72 pagesDemand AnalysisSreekanth DogiparthiNo ratings yet
- Cape Econ RevisionsDocument6 pagesCape Econ RevisionsSristi LallNo ratings yet
- Price Elasticity of SupplyDocument11 pagesPrice Elasticity of Supplyirdina athirahNo ratings yet
- Rizal100 PrelimsDocument5 pagesRizal100 Prelimscali kNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledcali kNo ratings yet
- 21ST Century Literature ReviewerDocument4 pages21ST Century Literature Reviewercali kNo ratings yet
- Author: Kanin (Rays) Business Ethics Common Practices in Business OrganizationDocument3 pagesAuthor: Kanin (Rays) Business Ethics Common Practices in Business Organizationcali kNo ratings yet
- Business Finance ReviewerDocument1 pageBusiness Finance Reviewercali kNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Biology ReviewerDocument7 pages2nd Quarter Biology Reviewercali kNo ratings yet
- Current and Future Trends of Media and InformationDocument2 pagesCurrent and Future Trends of Media and Informationcali kNo ratings yet
- Medium and Techniques ReviewerDocument6 pagesMedium and Techniques Reviewercali kNo ratings yet
- Business Marketing ReviewerDocument3 pagesBusiness Marketing Reviewercali kNo ratings yet
- MIL ReviewerDocument6 pagesMIL Reviewercali kNo ratings yet
- PE ReviewerDocument4 pagesPE Reviewercali kNo ratings yet
- Article (Diseases) 1Document7 pagesArticle (Diseases) 1cali kNo ratings yet
- PR2 NotesDocument9 pagesPR2 Notescali kNo ratings yet
- Rs ReviewerDocument3 pagesRs Reviewercali kNo ratings yet
- Onion AgmarkDocument33 pagesOnion Agmarkseeralan balakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Galle Four GravetsDocument1 pageGalle Four GravetsRavindra KumaraNo ratings yet
- DSC-410 Smoke DetectorDocument4 pagesDSC-410 Smoke DetectorJovany Salazar100% (1)
- Essay On Ratan Tata ...Document3 pagesEssay On Ratan Tata ...GAURAV JAINNo ratings yet
- Statistical Softwares: Excel Stata SpssDocument1 pageStatistical Softwares: Excel Stata SpssJeison Manotas ScarpattisNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Agri Crop 12Document1 pageSummative Test Agri Crop 12CHARISSE VIDENANo ratings yet
- VAC MS Excel-Course Plan 2020Document7 pagesVAC MS Excel-Course Plan 2020BalujagadishNo ratings yet
- QRC Nfpa 7 08Document2 pagesQRC Nfpa 7 08TUZERONo ratings yet
- APUSH Inside-Outside-Inside Discussion InstructionsDocument2 pagesAPUSH Inside-Outside-Inside Discussion InstructionscrolwesNo ratings yet
- COA CH 1Document33 pagesCOA CH 1DesyilalNo ratings yet
- Operational Excellence in Textile Industry Case Study: East AfricaDocument3 pagesOperational Excellence in Textile Industry Case Study: East AfricafarooquintuNo ratings yet
- Mi-171A1 RFM Part-IDocument310 pagesMi-171A1 RFM Part-IJulio Mello50% (2)
- AAM EnglishDocument7 pagesAAM EnglishYannick ÜzümNo ratings yet
- Bangabazar and ChowkbazarDocument13 pagesBangabazar and Chowkbazarprantosaha602No ratings yet
- K3HB-H: Model Number StructureDocument15 pagesK3HB-H: Model Number StructureGustaf Aurellio PanelNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Office Telemetry: Analysis ReportDocument29 pagesMicrosoft Office Telemetry: Analysis ReportdanmierlutNo ratings yet
- Acceptability of Banana Cheese Balls For Students in Colegio de Los BanosDocument4 pagesAcceptability of Banana Cheese Balls For Students in Colegio de Los BanosBSED SOCSTUD I-C Manese,JeremyNo ratings yet
- CNS - Module 2.1-AESDocument17 pagesCNS - Module 2.1-AESNIKSHITH SHETTYNo ratings yet
- AVR700 Owners Manual EnglishDocument26 pagesAVR700 Owners Manual EnglishAussie ChrisNo ratings yet
- S-Airvita User ManualDocument4 pagesS-Airvita User ManualDocMasterNo ratings yet
- Written Works 1ST Quarter CSS9Document7 pagesWritten Works 1ST Quarter CSS9Yne AhuninNo ratings yet
- Shelf-Life and Storage Requirement BS (Updated)Document1 pageShelf-Life and Storage Requirement BS (Updated)Jason Tiongco0% (1)
- Aritificial Vision YOLOV2 Part2Document9 pagesAritificial Vision YOLOV2 Part2David BenavidesNo ratings yet
- It Doesnt Hurt To AskDocument23 pagesIt Doesnt Hurt To Askarun_kejariwalNo ratings yet
- The Republic of Uganda: As BorrowerDocument5 pagesThe Republic of Uganda: As BorrowerBaguma IshaNo ratings yet
- Brief Cop27 Outcomes and Cop28 EngDocument24 pagesBrief Cop27 Outcomes and Cop28 EngVasundhara SaxenaNo ratings yet