Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concept Map Part LL
Concept Map Part LL
Uploaded by
api-663568963Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graph Concept MapDocument5 pagesCoronary Artery Bypass Graph Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (1)
- CC Concept MapDocument11 pagesCC Concept Mapapi-546355187No ratings yet
- Lucas Meyer Cosmetics B-White Marketing Brochure Low ResDocument4 pagesLucas Meyer Cosmetics B-White Marketing Brochure Low Resapi-291771056No ratings yet
- Endocrine System Coloring Activity - LDocument3 pagesEndocrine System Coloring Activity - LBriannaCarpenterNo ratings yet
- Mastectomy ConsentDocument2 pagesMastectomy ConsentrealshinjaeNo ratings yet
- Medical English ExercisesDocument54 pagesMedical English ExercisesCarmen100% (1)
- First Aid Emergencies: Call/DialDocument5 pagesFirst Aid Emergencies: Call/DialKhalilahmad Khatri100% (1)
- Concept Map Critical CareDocument6 pagesConcept Map Critical Careapi-508559825No ratings yet
- Concept Map CCDocument4 pagesConcept Map CCapi-738778945No ratings yet
- Simple Tools in HD MonitoringDocument66 pagesSimple Tools in HD MonitoringGHALEB A. AlmekhlafiNo ratings yet
- Concept Map CompletedDocument5 pagesConcept Map Completedapi-730811728No ratings yet
- Assessment and Concept Map Care Plan For Critical Care PatientDocument11 pagesAssessment and Concept Map Care Plan For Critical Care Patientapi-546697029No ratings yet
- Approach To Patient With Dyspnea & Ankle Swellling: Dr. Mudhafar Barzani MBCHB, DM, PHD, FRCP Ass. Prof. in CardiologyDocument55 pagesApproach To Patient With Dyspnea & Ankle Swellling: Dr. Mudhafar Barzani MBCHB, DM, PHD, FRCP Ass. Prof. in CardiologyDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- CC Concept MapDocument6 pagesCC Concept Mapapi-741058487No ratings yet
- Assessment and Concept Map Care PlanDocument6 pagesAssessment and Concept Map Care Planapi-508445604No ratings yet
- Assessment and Concept Map Care Plan For Critical Care PatientDocument8 pagesAssessment and Concept Map Care Plan For Critical Care Patientapi-593853954No ratings yet
- Concept Map Template - Andreanna TocickiDocument5 pagesConcept Map Template - Andreanna Tocickiapi-741174198No ratings yet
- Concept Map Templatef21Document4 pagesConcept Map Templatef21api-741272284No ratings yet
- CC - Concept MapDocument2 pagesCC - Concept Mapapi-546518436No ratings yet
- CHF Cardiomegaly Volume OverloadDocument1 pageCHF Cardiomegaly Volume Overloadnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Concept Map Template Final 2Document6 pagesCritical Care Concept Map Template Final 2api-740444719No ratings yet
- Complex Care Clinical Concept Map Sara Ciletti Youngstown State UniversityDocument9 pagesComplex Care Clinical Concept Map Sara Ciletti Youngstown State Universityapi-590353096No ratings yet
- Concept Map Critical CareDocument6 pagesConcept Map Critical Careapi-498759347No ratings yet
- CC Concept Map Part LL 1Document5 pagesCC Concept Map Part LL 1api-604539767No ratings yet
- Step 1. Write The Key Problems The Patient Has Based On The Data Collected. The KeyDocument7 pagesStep 1. Write The Key Problems The Patient Has Based On The Data Collected. The Keyapi-594625714No ratings yet
- Assessment and Concept Map Care Plan: Joseph GorospeDocument5 pagesAssessment and Concept Map Care Plan: Joseph Gorospeapi-497389977No ratings yet
- Complex Care Lab: Concept MapDocument6 pagesComplex Care Lab: Concept Mapapi-604569933No ratings yet
- Concept Map Done Updated PDFDocument6 pagesConcept Map Done Updated PDFapi-655682809No ratings yet
- PERFUSION monitoring-SYSTEMIC-ghalebDocument49 pagesPERFUSION monitoring-SYSTEMIC-ghalebGHALEB A. AlmekhlafiNo ratings yet
- ccpc15 Shock Syndromes WorkbookDocument40 pagesccpc15 Shock Syndromes WorkbookJeremy HamptonNo ratings yet
- OB Care Plan: Assessment DataDocument10 pagesOB Care Plan: Assessment Dataapi-520858833No ratings yet
- 2.5.3.1 Hipertensi EsensialDocument156 pages2.5.3.1 Hipertensi Esensialshafiqah zawiraNo ratings yet
- Complete Critical Care Concept MapDocument6 pagesComplete Critical Care Concept Mapapi-663631864No ratings yet
- Complex Care Concept MapDocument6 pagesComplex Care Concept Mapapi-740628337No ratings yet
- Handout 5 CardioVascular System Overview (Recovered)Document7 pagesHandout 5 CardioVascular System Overview (Recovered)Orlyn Joy TanaweNo ratings yet
- Clinical Judgment Plan of Care Long FormDocument12 pagesClinical Judgment Plan of Care Long Formapi-699835864No ratings yet
- Concept Map f21 FinishedDocument5 pagesConcept Map f21 Finishedapi-601070065No ratings yet
- Case 2 Cardiac TamponadeDocument8 pagesCase 2 Cardiac TamponadeJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Shock - BASIC Course 2022Document22 pagesShock - BASIC Course 2022R MANo ratings yet
- CC Concept MapDocument9 pagesCC Concept Mapapi-606252228No ratings yet
- Shock and Inotropes With DR Sumesh AroraDocument54 pagesShock and Inotropes With DR Sumesh AroraAhmed AhmedNo ratings yet
- NCM118 (Midterms) Activity 6: Case Analysis: Assessment Finding Physiologic Basis Nursing InterventionDocument2 pagesNCM118 (Midterms) Activity 6: Case Analysis: Assessment Finding Physiologic Basis Nursing InterventionKyla TuanNo ratings yet
- Terapi Cairan PD Syok KardiogenikDocument27 pagesTerapi Cairan PD Syok KardiogenikSri AsmawatiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan PT1Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan PT1Trexie ScattNo ratings yet
- CC Concept Map 3-1-24Document6 pagesCC Concept Map 3-1-24api-739624128No ratings yet
- "Mayroong Namuong Dugo Sa Utak Niya Kaya Hindi Maayos Ang Daloy NG Dugo Rito" As Verbalized by The Patient's MotherDocument6 pages"Mayroong Namuong Dugo Sa Utak Niya Kaya Hindi Maayos Ang Daloy NG Dugo Rito" As Verbalized by The Patient's MotherAllisson BeckersNo ratings yet
- Final Draft Concept MapDocument15 pagesFinal Draft Concept Mapapi-546712849No ratings yet
- CC Concept MapDocument5 pagesCC Concept Mapapi-663024375No ratings yet
- Risk NCP Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesRisk NCP Decreased Cardiac OutputMICHELLE FACTONo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Submitted byDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Submitted byKarl Angelo MontanoNo ratings yet
- Shock in Covid PatientDocument21 pagesShock in Covid PatientGHALEB A. AlmekhlafiNo ratings yet
- A. Identity: The Patient Said Had Been Hospitalized With The Same ComplaintDocument7 pagesA. Identity: The Patient Said Had Been Hospitalized With The Same ComplaintWindasariNo ratings yet
- Syock & ManagementDocument34 pagesSyock & ManagementIndra Anwari RukmanNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure Novotel BJMDocument20 pagesHeart Failure Novotel BJMFiqhiyatun PerdaniNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 17 May 2024Document7 pagesAdobe Scan 17 May 2024AmanyNo ratings yet
- Case 5Document14 pagesCase 5Mary Grace TirolNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Final Copy1Document7 pagesConcept Map Final Copy1api-608271845No ratings yet
- 9 - Role of Non InvasiveDocument46 pages9 - Role of Non InvasiveHavara Kausar AkbarNo ratings yet
- Concept Map FinalDocument5 pagesConcept Map Finalapi-545001894No ratings yet
- Sepsis Emergency-Avepa 2020 1. Systemic Inflammation (Sirs)Document3 pagesSepsis Emergency-Avepa 2020 1. Systemic Inflammation (Sirs)Yaiza Garcia CasadoNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Concept MapDocument6 pagesCritical Care Concept Mapapi-740642728No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Management of Systematic Lupus ErythematosusDocument53 pagesNursing Care Management of Systematic Lupus ErythematosusDana Marie LeanoNo ratings yet
- Ashley Wolanzyk Concept MapDocument5 pagesAshley Wolanzyk Concept Mapapi-455796674No ratings yet
- Concept Map PedsDocument6 pagesConcept Map Pedsapi-498759347No ratings yet
- Renin Angiotensin System and the HeartFrom EverandRenin Angiotensin System and the HeartWalmor C. De MelloNo ratings yet
- Ysu Nurs 3749 Poster - RecellDocument1 pageYsu Nurs 3749 Poster - Recellapi-663568963No ratings yet
- Paris Concept MapDocument3 pagesParis Concept Mapapi-663568963No ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument12 pagesCase Studyapi-663568963No ratings yet
- Transitions ResumeDocument1 pageTransitions Resumeapi-663568963No ratings yet
- 989104Document188 pages989104diyan110No ratings yet
- CAREGIVING NC II - Week7Document12 pagesCAREGIVING NC II - Week7Lignerrac Anipal UtadNo ratings yet
- Gen Psych Reviewer #2: Good luck with the test yall (づⴲ□ⴲ) づDocument25 pagesGen Psych Reviewer #2: Good luck with the test yall (づⴲ□ⴲ) づLucy WatsonNo ratings yet
- Plant Structures and FunctionsDocument20 pagesPlant Structures and FunctionsBriana RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Acute InflammationDocument71 pagesAcute Inflammationsi_miaomiao100% (1)
- Science of GlutathioneDocument4 pagesScience of GlutathioneDavid OrtmanNo ratings yet
- Sensation and Perception: A Unit Lesson Plan For High School Psychology TeachersDocument46 pagesSensation and Perception: A Unit Lesson Plan For High School Psychology TeachersLune NoireNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum: John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center For Neurobiology & Behavior Columbia UniversityDocument21 pagesCerebellum: John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center For Neurobiology & Behavior Columbia UniversitySasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- Posterior Malleolus FractureDocument9 pagesPosterior Malleolus FracturekenthepaNo ratings yet
- Supraglottoplasty For Laryngomalacia PDFDocument7 pagesSupraglottoplasty For Laryngomalacia PDFVeronica GaticaNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram of The Pathophysiology of Toxic Shock SyndromeDocument2 pagesSchematic Diagram of The Pathophysiology of Toxic Shock SyndromeRan MaNo ratings yet
- Blooms TaxonomyDocument7 pagesBlooms Taxonomyapi-394677350No ratings yet
- MICROB3 - Chapter3 - Cell Structure and FunctionDocument40 pagesMICROB3 - Chapter3 - Cell Structure and FunctionAdriana Corrêa0% (1)
- Specialize Immunity at Epithelial Barriers and in Immune Privilege TissuesDocument27 pagesSpecialize Immunity at Epithelial Barriers and in Immune Privilege TissuesUmar UsmanNo ratings yet
- 1) Vasoplegia During Cardiac Surgery Current Concepts and Management 2010Document5 pages1) Vasoplegia During Cardiac Surgery Current Concepts and Management 2010Carolina QuirogaNo ratings yet
- The MidbrainDocument3 pagesThe MidbrainAshly Kate AbarientosNo ratings yet
- High-Yield Cell and Molecular Biology $24.95: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 1999, 128 Pages, ISBN 0683303597Document1 pageHigh-Yield Cell and Molecular Biology $24.95: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 1999, 128 Pages, ISBN 0683303597AjeyJhaNo ratings yet
- Dendritic Cells PDFDocument370 pagesDendritic Cells PDFAnonymous YQawhb100% (1)
- Dna Repair MechanismsDocument49 pagesDna Repair MechanismsayeshaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Cardio and CPRDocument35 pagesChapter 5 Cardio and CPRAjay Pal NattNo ratings yet
- Australian Prescriber (1988) ClearanceDocument2 pagesAustralian Prescriber (1988) Clearance1234choco100% (1)
- Anatomical Observations of The Subarachnoid Cisterns of The Brain During SurgeryDocument5 pagesAnatomical Observations of The Subarachnoid Cisterns of The Brain During SurgeryMatheus FernandesNo ratings yet
- Wang Et Al 2022 Bottom-Up and Cognitive Top-Down Emotion RegulationDocument19 pagesWang Et Al 2022 Bottom-Up and Cognitive Top-Down Emotion RegulationThiago CardosoNo ratings yet
- MangasinoroDocument8 pagesMangasinoroEd MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy GlossaryDocument132 pagesAnatomy GlossaryMansoor ShahzadNo ratings yet
Concept Map Part LL
Concept Map Part LL
Uploaded by
api-663568963Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Concept Map Part LL
Concept Map Part LL
Uploaded by
api-663568963Copyright:
Available Formats
1
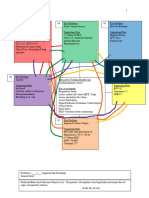
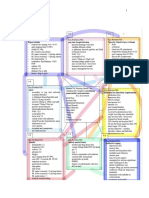
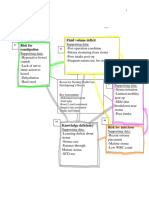
# Key Problem/ND # Key Problems/ND # Key Problem/ND
Risk for dec cardiac output Impaired gas exchange Risk for infection
Supporting data: Supporting data: Supporting data:
BP: 64/38 Diminished breath sounds WBC: 12.9
MAP: 46 Dyspnea Neutrophils: 12.38
Hemodynamic instability BiPAP requiring 50% FiO2 Cefepime IV 50mL/hr
Atrial fibrillation with RVR SPO2: 97% Vancomycin IV 200mL/hr
HR: 151 Tachypnea Diabetic
Cardiomegaly on CXR RR: 27
# Key Problem/ND:
# Key Problem/ND
Risk for fluid volume overload
Risk for electrolyte
Supporting data:
imbalance
AKI
Reason For Needing Health Care Supporting data:
Electrolyte imbalance
(Medical Dx/ Surgery) BUN: 77
BUN: 77
Septic shock, AKI, BP of 64/38 in emergency Creatinine: 2.55
Creatinine: 2.55
department Calcium: 7.9
Albumin: 1.8
Phosphate: 6.4
2+ pitting edema in lower
Focused assessment: Afib RVR
extremities
Cardiovascular, BP Muscle weakness
24 hour output 65mL
Allergies:
NKA
# Key Problem/ND # Key Problem/ND # Key Problem/ND
Anxiety Risk for shock Deficient knowledge
Supporting data: Supporting data: Supporting data:
Yelling out for help BP: 64/38 Confusion
Confusion MAP: 46 Ammonia: 56
Ammonia: 56 Hemodynamic instability Altered mental status
BiPAP on for entire shift Altered mental status Impaired verbal communication
Confusion
Poor oxygenation
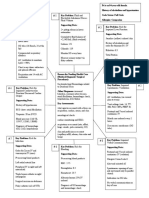
Problem #1: Risk for dec cardiac output
General Goal: Maintain an adequate blood pressure with a MAP >65
P. Schuster, Concept Mapping: A Critical Thinking Approach, Davis, 2002.
2
Predicted Behavioral Outcome Objective (s): The patient will have a MAP that consistently a over 65 on the
day of care.
Nursing Interventions Patient Responses
1. Assess blood pressure 1. BP 102/56
2. Assess heart rate and rhythm 2. HR 151, afib RVR
3. Check peripheral pulses 3. Radial +2, pedal +1; bilaterally
4. Monitor for neuro changes 4. Pt had new onset of confusion
5. Assess SpO2 5. 97% on BiPAP FiO2 50%
6. Monitor urine output 6. 65mL in 24 prior to shift start
Evaluation of outcome objectives: Patients blood pressure has improved since her arrival in the ED. Was 64/38
with a MAP of 46, now it is 102/56 with a MAP of 75
Problem #2: Impaired gas exchange
General Goal: Maintain adequate oxygenation
Predicted Behavioral Outcome Objective (s): The patient will maintain an SpO2 greater than 93% on the day
of care.
Nursing Interventions Patient Responses
1. Administer O2 as needed 1. SpO2 97% on BiPap FiO2 50%
2. Assess respiratory rate 2. Respiratory rate was 27/min
3. Assess respiratory effort 3. Breathing was labored
4. Auscultation respirations 4. Breath sounds were diminished
5. Monitor for neuro changes 5. New onset of confusion and restless
Evaluation of outcome objectives: Patient required BiPap with an FiO2 of 50% to maintain adequate
oxygenation of greater than 93% SpO2.
Problem #3: Risk for shock
General Goal: Display adequate perfusion
P. Schuster, Concept Mapping: A Critical Thinking Approach, Davis, 2002.
3
Predicted Behavioral Outcome Objective (s): The patient will have palpable peripheral pulses and have an
adequate BP on the day of care.
Nursing Interventions Patient Responses
1. Administer phenylephrine 1. Vasoconstriction of vessels
2. Administer norepinephrine 2. Improvement of BP to stable level
3. Monitor BP closely via A-line 3. BP ranged from 94 SBP to 51 DBP
4. Monitor heart rate 4. HR ranged from 93-151, irregular,afib
5. Monitor bowel sounds 5. Active, no ileus
Evaluation of outcome objectives: Patients pulses were all palpable, extremities cool due to vasopressors.
Problem #4: Risk for fluid volume overload
General Goal: Patient will achieve fluid balance
Predicted Behavioral Outcome Objective (s): The patient will have a urine output greater than 30mL/hr on the
day of care.
Nursing Interventions Patient Responses
1. Monitor daily weights 1. Weighed gained 1kg since yesterday
2. Monitor I&O 2. 24hr intake:3926mL, output:65mL
3. Check CXR 3. Pulmonary vascular congestion
4. Assess for peripheral edema 4. +1 pitting on LLE & RLE
5. Auscultate lung sounds 5. Diminished with fine crackles
6. Assess for JVD 6. No JVD noted
7. Administer albumin 7. Removal of fluid in 3rd space
Evaluation of outcome objectives: Patients output is poor and pt is fluid overloaded as evidenced by 2nd and
3rd spacing.
P. Schuster, Concept Mapping: A Critical Thinking Approach, Davis, 2002.
4
Problem #5: Risk for infection
General Goal: Reduce complications from infection
Predicted Behavioral Outcome Objective (s): The patient will maintain immune response on the day of care.
Nursing Interventions Patient Responses
1. Monitor temperature 1. Temp 101.8 on arrival, 99.2 today
2. Monitor sputum color 2. Sputum tan/green
3. Monitor WBC count 3. WBC count 12.9
4. Administer antibiotics 4. Cefepime and vancomycin given
Evaluation of outcome objectives: Patients WBC count increased from previous shift indicating an immune
response to the infection.
Problem # 6: Risk for electrolyte imbalance
General Goal: Maintain electrolyte levels within the normal ranges
Predicted Behavioral Outcome Objective (s): The patient will tolerate electrolyte solutions on the day of care.
Nursing Interventions Patient Responses
1. Monitor electrolyte levels 1. CL, PO4, and Ca abnormal
2. Monitor renal function 2. Creatinine 2.55, BUN 77
3. Assess GFR 3. GFR 18
4. Administer isotonic solution 4. 0.9 NS given for electrolyte balance
Evaluation of outcome objectives: Patients electrolyte imbalance had improved slightly from previous day.
Problem #7: Anxiety
General Goal: Patient will tolerate treatments with minimal anxiety
P. Schuster, Concept Mapping: A Critical Thinking Approach, Davis, 2002.
5
Predicted Behavioral Outcome Objective (s): The patient will reduce calls for help and be oriented to know
she’s being helped on the day of care.
Nursing Interventions Patient Responses
1. Assess heart rate 1. HR ranged from 93-151
2. Assess respiratory rate 2. RR ranged from 24-27
3. Monitor for confusion 3. Pt was very confused and not oriented
4. Administer lactulose for confusion 4. First dose given, no effect at this time
5. Maintain a calm environment 5. Pt was inconsolable
Evaluation of outcome objectives: Patient was not oriented and shouted out over us when we tried to console
her. Patient was most relaxed when she fell asleep.
Problem #8: Deficient knowledge
General Goal: Treat patients confusion so they can learn of their condition.
Predicted Behavioral Outcome Objective (s): The patient will respond to their lactulose and respond on the
day of care.
Nursing Interventions Patient Responses
1. Keep patients comfortable 1. Pt was repositioned, pillow support
2. Maintain a calm environment 2. BiPap seemed to overstimulate pt
3. Include patient in plan of care 3. Pt was explained everything we did
4. Treat confusion 4. Lactulose given
5. Monitor ammonia 5. Ammonia 56
6. Provide clear, simple explanations 6. Pt showed no understanding
Evaluation of outcome objectives: Patients high ammonia level needs treated and is a likely catalyst for her
new onset confusion. Treating this is a priority to get her in a better place mentally.
P. Schuster, Concept Mapping: A Critical Thinking Approach, Davis, 2002.
You might also like
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graph Concept MapDocument5 pagesCoronary Artery Bypass Graph Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (1)
- CC Concept MapDocument11 pagesCC Concept Mapapi-546355187No ratings yet
- Lucas Meyer Cosmetics B-White Marketing Brochure Low ResDocument4 pagesLucas Meyer Cosmetics B-White Marketing Brochure Low Resapi-291771056No ratings yet
- Endocrine System Coloring Activity - LDocument3 pagesEndocrine System Coloring Activity - LBriannaCarpenterNo ratings yet
- Mastectomy ConsentDocument2 pagesMastectomy ConsentrealshinjaeNo ratings yet
- Medical English ExercisesDocument54 pagesMedical English ExercisesCarmen100% (1)
- First Aid Emergencies: Call/DialDocument5 pagesFirst Aid Emergencies: Call/DialKhalilahmad Khatri100% (1)
- Concept Map Critical CareDocument6 pagesConcept Map Critical Careapi-508559825No ratings yet
- Concept Map CCDocument4 pagesConcept Map CCapi-738778945No ratings yet
- Simple Tools in HD MonitoringDocument66 pagesSimple Tools in HD MonitoringGHALEB A. AlmekhlafiNo ratings yet
- Concept Map CompletedDocument5 pagesConcept Map Completedapi-730811728No ratings yet
- Assessment and Concept Map Care Plan For Critical Care PatientDocument11 pagesAssessment and Concept Map Care Plan For Critical Care Patientapi-546697029No ratings yet
- Approach To Patient With Dyspnea & Ankle Swellling: Dr. Mudhafar Barzani MBCHB, DM, PHD, FRCP Ass. Prof. in CardiologyDocument55 pagesApproach To Patient With Dyspnea & Ankle Swellling: Dr. Mudhafar Barzani MBCHB, DM, PHD, FRCP Ass. Prof. in CardiologyDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- CC Concept MapDocument6 pagesCC Concept Mapapi-741058487No ratings yet
- Assessment and Concept Map Care PlanDocument6 pagesAssessment and Concept Map Care Planapi-508445604No ratings yet
- Assessment and Concept Map Care Plan For Critical Care PatientDocument8 pagesAssessment and Concept Map Care Plan For Critical Care Patientapi-593853954No ratings yet
- Concept Map Template - Andreanna TocickiDocument5 pagesConcept Map Template - Andreanna Tocickiapi-741174198No ratings yet
- Concept Map Templatef21Document4 pagesConcept Map Templatef21api-741272284No ratings yet
- CC - Concept MapDocument2 pagesCC - Concept Mapapi-546518436No ratings yet
- CHF Cardiomegaly Volume OverloadDocument1 pageCHF Cardiomegaly Volume Overloadnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Concept Map Template Final 2Document6 pagesCritical Care Concept Map Template Final 2api-740444719No ratings yet
- Complex Care Clinical Concept Map Sara Ciletti Youngstown State UniversityDocument9 pagesComplex Care Clinical Concept Map Sara Ciletti Youngstown State Universityapi-590353096No ratings yet
- Concept Map Critical CareDocument6 pagesConcept Map Critical Careapi-498759347No ratings yet
- CC Concept Map Part LL 1Document5 pagesCC Concept Map Part LL 1api-604539767No ratings yet
- Step 1. Write The Key Problems The Patient Has Based On The Data Collected. The KeyDocument7 pagesStep 1. Write The Key Problems The Patient Has Based On The Data Collected. The Keyapi-594625714No ratings yet
- Assessment and Concept Map Care Plan: Joseph GorospeDocument5 pagesAssessment and Concept Map Care Plan: Joseph Gorospeapi-497389977No ratings yet
- Complex Care Lab: Concept MapDocument6 pagesComplex Care Lab: Concept Mapapi-604569933No ratings yet
- Concept Map Done Updated PDFDocument6 pagesConcept Map Done Updated PDFapi-655682809No ratings yet
- PERFUSION monitoring-SYSTEMIC-ghalebDocument49 pagesPERFUSION monitoring-SYSTEMIC-ghalebGHALEB A. AlmekhlafiNo ratings yet
- ccpc15 Shock Syndromes WorkbookDocument40 pagesccpc15 Shock Syndromes WorkbookJeremy HamptonNo ratings yet
- OB Care Plan: Assessment DataDocument10 pagesOB Care Plan: Assessment Dataapi-520858833No ratings yet
- 2.5.3.1 Hipertensi EsensialDocument156 pages2.5.3.1 Hipertensi Esensialshafiqah zawiraNo ratings yet
- Complete Critical Care Concept MapDocument6 pagesComplete Critical Care Concept Mapapi-663631864No ratings yet
- Complex Care Concept MapDocument6 pagesComplex Care Concept Mapapi-740628337No ratings yet
- Handout 5 CardioVascular System Overview (Recovered)Document7 pagesHandout 5 CardioVascular System Overview (Recovered)Orlyn Joy TanaweNo ratings yet
- Clinical Judgment Plan of Care Long FormDocument12 pagesClinical Judgment Plan of Care Long Formapi-699835864No ratings yet
- Concept Map f21 FinishedDocument5 pagesConcept Map f21 Finishedapi-601070065No ratings yet
- Case 2 Cardiac TamponadeDocument8 pagesCase 2 Cardiac TamponadeJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Shock - BASIC Course 2022Document22 pagesShock - BASIC Course 2022R MANo ratings yet
- CC Concept MapDocument9 pagesCC Concept Mapapi-606252228No ratings yet
- Shock and Inotropes With DR Sumesh AroraDocument54 pagesShock and Inotropes With DR Sumesh AroraAhmed AhmedNo ratings yet
- NCM118 (Midterms) Activity 6: Case Analysis: Assessment Finding Physiologic Basis Nursing InterventionDocument2 pagesNCM118 (Midterms) Activity 6: Case Analysis: Assessment Finding Physiologic Basis Nursing InterventionKyla TuanNo ratings yet
- Terapi Cairan PD Syok KardiogenikDocument27 pagesTerapi Cairan PD Syok KardiogenikSri AsmawatiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan PT1Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan PT1Trexie ScattNo ratings yet
- CC Concept Map 3-1-24Document6 pagesCC Concept Map 3-1-24api-739624128No ratings yet
- "Mayroong Namuong Dugo Sa Utak Niya Kaya Hindi Maayos Ang Daloy NG Dugo Rito" As Verbalized by The Patient's MotherDocument6 pages"Mayroong Namuong Dugo Sa Utak Niya Kaya Hindi Maayos Ang Daloy NG Dugo Rito" As Verbalized by The Patient's MotherAllisson BeckersNo ratings yet
- Final Draft Concept MapDocument15 pagesFinal Draft Concept Mapapi-546712849No ratings yet
- CC Concept MapDocument5 pagesCC Concept Mapapi-663024375No ratings yet
- Risk NCP Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesRisk NCP Decreased Cardiac OutputMICHELLE FACTONo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Submitted byDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Submitted byKarl Angelo MontanoNo ratings yet
- Shock in Covid PatientDocument21 pagesShock in Covid PatientGHALEB A. AlmekhlafiNo ratings yet
- A. Identity: The Patient Said Had Been Hospitalized With The Same ComplaintDocument7 pagesA. Identity: The Patient Said Had Been Hospitalized With The Same ComplaintWindasariNo ratings yet
- Syock & ManagementDocument34 pagesSyock & ManagementIndra Anwari RukmanNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure Novotel BJMDocument20 pagesHeart Failure Novotel BJMFiqhiyatun PerdaniNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 17 May 2024Document7 pagesAdobe Scan 17 May 2024AmanyNo ratings yet
- Case 5Document14 pagesCase 5Mary Grace TirolNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Final Copy1Document7 pagesConcept Map Final Copy1api-608271845No ratings yet
- 9 - Role of Non InvasiveDocument46 pages9 - Role of Non InvasiveHavara Kausar AkbarNo ratings yet
- Concept Map FinalDocument5 pagesConcept Map Finalapi-545001894No ratings yet
- Sepsis Emergency-Avepa 2020 1. Systemic Inflammation (Sirs)Document3 pagesSepsis Emergency-Avepa 2020 1. Systemic Inflammation (Sirs)Yaiza Garcia CasadoNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Concept MapDocument6 pagesCritical Care Concept Mapapi-740642728No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Management of Systematic Lupus ErythematosusDocument53 pagesNursing Care Management of Systematic Lupus ErythematosusDana Marie LeanoNo ratings yet
- Ashley Wolanzyk Concept MapDocument5 pagesAshley Wolanzyk Concept Mapapi-455796674No ratings yet
- Concept Map PedsDocument6 pagesConcept Map Pedsapi-498759347No ratings yet
- Renin Angiotensin System and the HeartFrom EverandRenin Angiotensin System and the HeartWalmor C. De MelloNo ratings yet
- Ysu Nurs 3749 Poster - RecellDocument1 pageYsu Nurs 3749 Poster - Recellapi-663568963No ratings yet
- Paris Concept MapDocument3 pagesParis Concept Mapapi-663568963No ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument12 pagesCase Studyapi-663568963No ratings yet
- Transitions ResumeDocument1 pageTransitions Resumeapi-663568963No ratings yet
- 989104Document188 pages989104diyan110No ratings yet
- CAREGIVING NC II - Week7Document12 pagesCAREGIVING NC II - Week7Lignerrac Anipal UtadNo ratings yet
- Gen Psych Reviewer #2: Good luck with the test yall (づⴲ□ⴲ) づDocument25 pagesGen Psych Reviewer #2: Good luck with the test yall (づⴲ□ⴲ) づLucy WatsonNo ratings yet
- Plant Structures and FunctionsDocument20 pagesPlant Structures and FunctionsBriana RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Acute InflammationDocument71 pagesAcute Inflammationsi_miaomiao100% (1)
- Science of GlutathioneDocument4 pagesScience of GlutathioneDavid OrtmanNo ratings yet
- Sensation and Perception: A Unit Lesson Plan For High School Psychology TeachersDocument46 pagesSensation and Perception: A Unit Lesson Plan For High School Psychology TeachersLune NoireNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum: John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center For Neurobiology & Behavior Columbia UniversityDocument21 pagesCerebellum: John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center For Neurobiology & Behavior Columbia UniversitySasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- Posterior Malleolus FractureDocument9 pagesPosterior Malleolus FracturekenthepaNo ratings yet
- Supraglottoplasty For Laryngomalacia PDFDocument7 pagesSupraglottoplasty For Laryngomalacia PDFVeronica GaticaNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram of The Pathophysiology of Toxic Shock SyndromeDocument2 pagesSchematic Diagram of The Pathophysiology of Toxic Shock SyndromeRan MaNo ratings yet
- Blooms TaxonomyDocument7 pagesBlooms Taxonomyapi-394677350No ratings yet
- MICROB3 - Chapter3 - Cell Structure and FunctionDocument40 pagesMICROB3 - Chapter3 - Cell Structure and FunctionAdriana Corrêa0% (1)
- Specialize Immunity at Epithelial Barriers and in Immune Privilege TissuesDocument27 pagesSpecialize Immunity at Epithelial Barriers and in Immune Privilege TissuesUmar UsmanNo ratings yet
- 1) Vasoplegia During Cardiac Surgery Current Concepts and Management 2010Document5 pages1) Vasoplegia During Cardiac Surgery Current Concepts and Management 2010Carolina QuirogaNo ratings yet
- The MidbrainDocument3 pagesThe MidbrainAshly Kate AbarientosNo ratings yet
- High-Yield Cell and Molecular Biology $24.95: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 1999, 128 Pages, ISBN 0683303597Document1 pageHigh-Yield Cell and Molecular Biology $24.95: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 1999, 128 Pages, ISBN 0683303597AjeyJhaNo ratings yet
- Dendritic Cells PDFDocument370 pagesDendritic Cells PDFAnonymous YQawhb100% (1)
- Dna Repair MechanismsDocument49 pagesDna Repair MechanismsayeshaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Cardio and CPRDocument35 pagesChapter 5 Cardio and CPRAjay Pal NattNo ratings yet
- Australian Prescriber (1988) ClearanceDocument2 pagesAustralian Prescriber (1988) Clearance1234choco100% (1)
- Anatomical Observations of The Subarachnoid Cisterns of The Brain During SurgeryDocument5 pagesAnatomical Observations of The Subarachnoid Cisterns of The Brain During SurgeryMatheus FernandesNo ratings yet
- Wang Et Al 2022 Bottom-Up and Cognitive Top-Down Emotion RegulationDocument19 pagesWang Et Al 2022 Bottom-Up and Cognitive Top-Down Emotion RegulationThiago CardosoNo ratings yet
- MangasinoroDocument8 pagesMangasinoroEd MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy GlossaryDocument132 pagesAnatomy GlossaryMansoor ShahzadNo ratings yet