Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physical Science Worksheet
Physical Science Worksheet
Uploaded by
Mary GoresCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Performance Performance Enhancing Notes: Chemistry Grade 10 - 11Document238 pagesPerformance Performance Enhancing Notes: Chemistry Grade 10 - 11Nadi Makasaki95% (43)
- Polar and Nonpolar Molecules AP PogilDocument6 pagesPolar and Nonpolar Molecules AP PogilLily Stanton67% (3)
- Physical Science: Quarter 3/module 5/week 3: General Types of Intermolecular ForcesDocument12 pagesPhysical Science: Quarter 3/module 5/week 3: General Types of Intermolecular ForcesJennie KimNo ratings yet
- 01 Chapter 01 How The Elements Found in The Universe Were FormedDocument73 pages01 Chapter 01 How The Elements Found in The Universe Were FormedKyra Lim100% (1)
- 1 - KMTDocument45 pages1 - KMTEllysa Jade VelascoNo ratings yet
- Polarity of Molecules and Its PropertiesDocument34 pagesPolarity of Molecules and Its PropertiesNica Floresta - MendozaNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem ReviewerDocument10 pagesGen Chem ReviewerLawrence Angelo Mana-ayNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Intermolecular Forces of AttractionDocument43 pagesLesson 3 - Intermolecular Forces of AttractionFreshieeNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 3Document4 pagesPhysical Science Week 3John Matthew De JesusNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces:: Attraction in Molecular LevelDocument34 pagesIntermolecular Forces:: Attraction in Molecular LevelKelly MarceloNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Smile 2Document12 pagesPhysical Science Smile 2DYLANNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 5 6Document3 pagesSyllabus 5 6Victor John DagalaNo ratings yet
- Covalent MoleculesDocument3 pagesCovalent MoleculesElizabeth PhillipsNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Intermolecular Forces of Solids & LiquidsDocument4 pagesUnit 1 Intermolecular Forces of Solids & LiquidsMoira Nadeen NicolasoraNo ratings yet
- 4 - States of Matter - Theory - (1-41)Document43 pages4 - States of Matter - Theory - (1-41)eerannaNo ratings yet
- How The Properties of Matter Relate To Their Chemical StructureDocument99 pagesHow The Properties of Matter Relate To Their Chemical StructureElpi Ferrer80% (5)
- Gc12-Lesson 1.1Document63 pagesGc12-Lesson 1.1Hebron Seth TagpunoNo ratings yet
- WWPWPWDocument30 pagesWWPWPWRaven LampaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 4: Name: Rico R. Candelario Grade & Section: 12 St. Gabriel HUMSSDocument4 pagesPhysical Science Week 4: Name: Rico R. Candelario Grade & Section: 12 St. Gabriel HUMSSRico R. CandelarioNo ratings yet
- Physical Science - M3 - Polarity of MoleculesDocument15 pagesPhysical Science - M3 - Polarity of MoleculesJodi RempilloNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document4 pagesModule 1welpNo ratings yet
- PS Q3 Module3 WK3Document12 pagesPS Q3 Module3 WK3Jason PojasNo ratings yet
- CH 6. State of Matter (Chem +1) PDFDocument46 pagesCH 6. State of Matter (Chem +1) PDFDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsDocument5 pagesKinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsJohn Ahron BalinoNo ratings yet
- Flexible Learning Activity No. 1 in Physical Science 3rd GradingDocument6 pagesFlexible Learning Activity No. 1 in Physical Science 3rd GradingGeizel GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Q3 Module 3 Polar or Nonpolar: Prepared By: Engr. Erwin D. Rubio JRDocument25 pagesQ3 Module 3 Polar or Nonpolar: Prepared By: Engr. Erwin D. Rubio JRGumban Aaron Frances M.No ratings yet
- CHP No 4Document58 pagesCHP No 4asad saleemNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument15 pagesSCIENCEPaula DecenaNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces of AttractionDocument41 pagesIntermolecular Forces of AttractionDon King EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- MODULEDocument7 pagesMODULEht6pfpkvhkNo ratings yet
- Second Midterm ReviewDocument90 pagesSecond Midterm ReviewEvelyn Montserrat Gómez ZentenoNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument22 pagesIntermolecular ForcesJianne Therese VillalvaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 3Document18 pagesPhysical Science Week 3RAINIER DE JESUSNo ratings yet
- Polarity of Molecule (Autosaved)Document40 pagesPolarity of Molecule (Autosaved)Yson GonzalesNo ratings yet
- PHSC - L3 Bond Polarity and Properties of CompoundsDocument31 pagesPHSC - L3 Bond Polarity and Properties of CompoundsRegene SoledadNo ratings yet
- My Learning Episodes: The Learners Demonstrate Understanding Of..Document8 pagesMy Learning Episodes: The Learners Demonstrate Understanding Of..Radzmiya SulaymanNo ratings yet
- GS PDFDocument41 pagesGS PDFdivakarsNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Bonding in SolidsDocument27 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Bonding in Solidsmhay martinezNo ratings yet
- 4 14 Chemical Bonding 4 Intermolecular Forces JLDocument46 pages4 14 Chemical Bonding 4 Intermolecular Forces JLFN5052023 PRAMITA MAHENDRANNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Polarity of Molecules and Its PropertiesDocument38 pagesWeek 2 Polarity of Molecules and Its Propertieslily smithNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular 2Document2 pagesIntermolecular 2tgeorgina630No ratings yet
- PolarityDocument20 pagesPolarityYsabela MataNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Intermolecular Forces-2Document11 pages3.1 Intermolecular Forces-2faridaisepicNo ratings yet
- Elements and Their Corresponding ColorDocument6 pagesElements and Their Corresponding ColorAdonis MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Part II Microscopic World I NotesDocument32 pagesPart II Microscopic World I NotesHon KwanNo ratings yet
- 115 Intermolecular Force Worksheet KeyDocument2 pages115 Intermolecular Force Worksheet Keyada wangNo ratings yet
- Intramolecular Forces and Intermolecular ForcesDocument12 pagesIntramolecular Forces and Intermolecular ForcesDuyen Nguyen100% (1)
- 4.7 Intermolecular ForcesDocument5 pages4.7 Intermolecular ForcesrachpNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Modules Week 2Document6 pagesPhysical Science Modules Week 2RODJHEN ANNE P. BARQUILLANo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Atomic Structure NotesDocument22 pagesTopic 2 Atomic Structure NotesAMAN AHMADNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Chemical BondingDocument29 pagesWeek 3 - Chemical BondingNthabelengNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Recapping Important Concepts: 2P32 Winter Term 2012-13 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Dr. M. PilkingtonDocument13 pagesLecture 1 - Recapping Important Concepts: 2P32 Winter Term 2012-13 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Dr. M. PilkingtonS K Mishra0% (1)
- Notes VSEPR (CH 6)Document21 pagesNotes VSEPR (CH 6)Nestor BalboaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 in Physical ScienceDocument8 pagesModule 5 in Physical ScienceDarlyn MontillaNo ratings yet
- Physical-Science-SHS-6.1-Types-of-Intermolecular-Forces-of-AttractionDocument20 pagesPhysical-Science-SHS-6.1-Types-of-Intermolecular-Forces-of-AttractionJoseph De ChavezNo ratings yet
- Physical Science HandoutsDocument5 pagesPhysical Science HandoutsEllaNatividad100% (1)
- The Kinetic Molecular Model and Intermolecular Forces of Attraction in MatterDocument104 pagesThe Kinetic Molecular Model and Intermolecular Forces of Attraction in MatterMiguel TatlonghariNo ratings yet
- PHYSCI - First Quarter NotesDocument7 pagesPHYSCI - First Quarter NotesCjNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem IiDocument8 pagesGen Chem Iiirizharanda98No ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY 3rd Quarter ReviewerDocument9 pagesCHEMISTRY 3rd Quarter ReviewerJanelle NopuetoNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- MB Online Basketball League Liability Waver FormDocument1 pageMB Online Basketball League Liability Waver FormMary GoresNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledMary GoresNo ratings yet
- Merry Christmas Happy HolidaysDocument4 pagesMerry Christmas Happy HolidaysMary GoresNo ratings yet
- Ses05 004Document29 pagesSes05 004Mary GoresNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledMary GoresNo ratings yet
- Set 1 Navneet PhysicsDocument5 pagesSet 1 Navneet Physicswww.rajdeepsarkar999No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 LaserDocument19 pagesChapter 7 LaserYohannesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 6+7 B-I)Document2 pagesChemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 6+7 B-I)XXXNo ratings yet
- Structural, Elastic, Electronic, Magnetic and Thermoelectric Properties of New Quaternary Heusler Compounds Cozrmnx (X Al, Ga, Ge, In)Document36 pagesStructural, Elastic, Electronic, Magnetic and Thermoelectric Properties of New Quaternary Heusler Compounds Cozrmnx (X Al, Ga, Ge, In)yasmine bouldiabNo ratings yet
- Questions Periodic Table of Elements Get The Table Organized in TimeDocument3 pagesQuestions Periodic Table of Elements Get The Table Organized in TimeJonathan ApiladoNo ratings yet
- Overview:: Book Title:-Physics For Joint Entrance Examination JEEDocument6 pagesOverview:: Book Title:-Physics For Joint Entrance Examination JEEkunalNo ratings yet
- Prolate-Oblate Difference Its Effect: and Energy Levels and Quadrupole MomentsDocument3 pagesProlate-Oblate Difference Its Effect: and Energy Levels and Quadrupole MomentsMarwa Moustafa Abdel-HafezNo ratings yet
- Physical World NotesDocument5 pagesPhysical World NotesAdorned. pearlNo ratings yet
- Physics: FiitjeeDocument1,319 pagesPhysics: FiitjeeBISWAJEET100% (2)
- 2018 A Level Solutions (Compiled)Document38 pages2018 A Level Solutions (Compiled)Faith SeahNo ratings yet
- Che1501 TL 102 2023 0 BDocument32 pagesChe1501 TL 102 2023 0 BBrandon MakamaNo ratings yet
- Zeal Study SSLC SCIENCE All Lessons 2mark Answers New 30.10.22Document45 pagesZeal Study SSLC SCIENCE All Lessons 2mark Answers New 30.10.22DevapriyaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry JokesDocument30 pagesChemistry JokesDiane TNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument19 pagesPeriodic TableFilmodeNo ratings yet
- Jamb-Chemistry-Past-Questions-11-15 UnibenpgDocument55 pagesJamb-Chemistry-Past-Questions-11-15 UnibenpgEhigie promiseNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Part BDocument56 pagesUnit 2 Part B소피아No ratings yet
- Physics 403. Modern Physics Laboratory: Eugene V Colla, Anne SicklesDocument56 pagesPhysics 403. Modern Physics Laboratory: Eugene V Colla, Anne Sicklesally claveriaNo ratings yet
- Arihant Term 2 Physics Class 12Document176 pagesArihant Term 2 Physics Class 12Javin GargNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry MCQDocument19 pagesClass 12 Chemistry MCQTayseer SaudiaNo ratings yet
- PH501Document1 pagePH501MAUSAM KatariyaNo ratings yet
- Emg 1204 Introduction To Materials Science Tutorial I Attempt All These Questions Question OneDocument2 pagesEmg 1204 Introduction To Materials Science Tutorial I Attempt All These Questions Question Onesteve gateriNo ratings yet
- U3 Chemical Bonding Review, IB10Document35 pagesU3 Chemical Bonding Review, IB10Liang LuNo ratings yet
- 2018 JC1 H1 Chem EOY P1 P2 Answers With CommentsDocument17 pages2018 JC1 H1 Chem EOY P1 P2 Answers With CommentsSeth LimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 CHM138Document76 pagesChapter 2 CHM138Isaac LibuNo ratings yet
- Aadil Vahora: AnandDocument10 pagesAadil Vahora: AnandAadil VahoraNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics Topic 4 Atomic Structure Knowledge OrganiserDocument3 pagesAQA Physics Topic 4 Atomic Structure Knowledge OrganiserGabriel HoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Module 5Document15 pagesGeneral Chemistry Module 5Junelle Ramos Aquino0% (2)
- 500 MCQDocument55 pages500 MCQkirki pNo ratings yet
Physical Science Worksheet
Physical Science Worksheet
Uploaded by
Mary GoresOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physical Science Worksheet
Physical Science Worksheet
Uploaded by
Mary GoresCopyright:
Available Formats
iPHYSICAL SCIENCE WORKSHEET
NAME: _Kc Almasan____________________________________________________________
GRADE & SECTION: _11-Empathy_____________________________________________
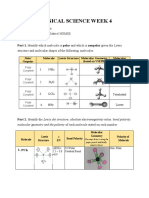
I. Consider the following substances. In the first column labeled Molecular Polarity, indicate whether
molecule is POLAR MOLECULE or NONPOLAR MOLECULE. In the second column labeled Bond
Polarity, indicate whether the bonds are POLAR or NONPOLAR. And in the last column write the IMFA
present on each substance.
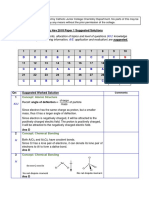
Substance Molecular Polarity Bond Polarity IMFA Present
London dispersion
1. HF Polar molecule Polar forces
Dipole-Dipole
2. PCl5 Polar molecule Polar interaction
London dispersion forces
Nonpolar molecule Nonpolar
3. CH4
Dipole-Dipole interaction
Polar molecule Polar
4. NH3
Hydrogen bonding
Nonpolar molecule Nonpolar
5. Fe O2
2t
II. Answer the following questions.
1. Explain the three intramolecular bonds (ionic, covalent, and metallic bond).
Metal and non-metal is the ionic bond, atoms for atoms. The covalent bond is a combination
of two non-metal in a covalent molecule. and the force that holds an atom together is the
metallic bond.
2. How and why has the Atomic Theory changed over time?
The atomic model has changed since the atomic model was invented on theories and
discoveries. Following the discovery of many subatomic particles, quantum mechanics'
influence on the likelihood that electrons would be found at a specific area led to the
development of the most recent atomic model, the electron cloud.
3. How did Ernest Rutherford and JJ Thomson made a contribution in the Atoms and Atomic Theory?
Thomson's plum pudding model of the atom had negatively-charged electrons embedded within
a positively-charged "soup." Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed that the atom is mostly
empty space with a tiny, dense, positively-charged nucleus. Based on these results, Rutherford
proposed the nuclear model of the atom.
You might also like
- Performance Performance Enhancing Notes: Chemistry Grade 10 - 11Document238 pagesPerformance Performance Enhancing Notes: Chemistry Grade 10 - 11Nadi Makasaki95% (43)
- Polar and Nonpolar Molecules AP PogilDocument6 pagesPolar and Nonpolar Molecules AP PogilLily Stanton67% (3)
- Physical Science: Quarter 3/module 5/week 3: General Types of Intermolecular ForcesDocument12 pagesPhysical Science: Quarter 3/module 5/week 3: General Types of Intermolecular ForcesJennie KimNo ratings yet
- 01 Chapter 01 How The Elements Found in The Universe Were FormedDocument73 pages01 Chapter 01 How The Elements Found in The Universe Were FormedKyra Lim100% (1)
- 1 - KMTDocument45 pages1 - KMTEllysa Jade VelascoNo ratings yet
- Polarity of Molecules and Its PropertiesDocument34 pagesPolarity of Molecules and Its PropertiesNica Floresta - MendozaNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem ReviewerDocument10 pagesGen Chem ReviewerLawrence Angelo Mana-ayNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Intermolecular Forces of AttractionDocument43 pagesLesson 3 - Intermolecular Forces of AttractionFreshieeNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 3Document4 pagesPhysical Science Week 3John Matthew De JesusNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces:: Attraction in Molecular LevelDocument34 pagesIntermolecular Forces:: Attraction in Molecular LevelKelly MarceloNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Smile 2Document12 pagesPhysical Science Smile 2DYLANNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 5 6Document3 pagesSyllabus 5 6Victor John DagalaNo ratings yet
- Covalent MoleculesDocument3 pagesCovalent MoleculesElizabeth PhillipsNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Intermolecular Forces of Solids & LiquidsDocument4 pagesUnit 1 Intermolecular Forces of Solids & LiquidsMoira Nadeen NicolasoraNo ratings yet
- 4 - States of Matter - Theory - (1-41)Document43 pages4 - States of Matter - Theory - (1-41)eerannaNo ratings yet
- How The Properties of Matter Relate To Their Chemical StructureDocument99 pagesHow The Properties of Matter Relate To Their Chemical StructureElpi Ferrer80% (5)
- Gc12-Lesson 1.1Document63 pagesGc12-Lesson 1.1Hebron Seth TagpunoNo ratings yet
- WWPWPWDocument30 pagesWWPWPWRaven LampaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 4: Name: Rico R. Candelario Grade & Section: 12 St. Gabriel HUMSSDocument4 pagesPhysical Science Week 4: Name: Rico R. Candelario Grade & Section: 12 St. Gabriel HUMSSRico R. CandelarioNo ratings yet
- Physical Science - M3 - Polarity of MoleculesDocument15 pagesPhysical Science - M3 - Polarity of MoleculesJodi RempilloNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document4 pagesModule 1welpNo ratings yet
- PS Q3 Module3 WK3Document12 pagesPS Q3 Module3 WK3Jason PojasNo ratings yet
- CH 6. State of Matter (Chem +1) PDFDocument46 pagesCH 6. State of Matter (Chem +1) PDFDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsDocument5 pagesKinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsJohn Ahron BalinoNo ratings yet
- Flexible Learning Activity No. 1 in Physical Science 3rd GradingDocument6 pagesFlexible Learning Activity No. 1 in Physical Science 3rd GradingGeizel GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Q3 Module 3 Polar or Nonpolar: Prepared By: Engr. Erwin D. Rubio JRDocument25 pagesQ3 Module 3 Polar or Nonpolar: Prepared By: Engr. Erwin D. Rubio JRGumban Aaron Frances M.No ratings yet
- CHP No 4Document58 pagesCHP No 4asad saleemNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument15 pagesSCIENCEPaula DecenaNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces of AttractionDocument41 pagesIntermolecular Forces of AttractionDon King EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- MODULEDocument7 pagesMODULEht6pfpkvhkNo ratings yet
- Second Midterm ReviewDocument90 pagesSecond Midterm ReviewEvelyn Montserrat Gómez ZentenoNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument22 pagesIntermolecular ForcesJianne Therese VillalvaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 3Document18 pagesPhysical Science Week 3RAINIER DE JESUSNo ratings yet
- Polarity of Molecule (Autosaved)Document40 pagesPolarity of Molecule (Autosaved)Yson GonzalesNo ratings yet
- PHSC - L3 Bond Polarity and Properties of CompoundsDocument31 pagesPHSC - L3 Bond Polarity and Properties of CompoundsRegene SoledadNo ratings yet
- My Learning Episodes: The Learners Demonstrate Understanding Of..Document8 pagesMy Learning Episodes: The Learners Demonstrate Understanding Of..Radzmiya SulaymanNo ratings yet
- GS PDFDocument41 pagesGS PDFdivakarsNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Bonding in SolidsDocument27 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Bonding in Solidsmhay martinezNo ratings yet
- 4 14 Chemical Bonding 4 Intermolecular Forces JLDocument46 pages4 14 Chemical Bonding 4 Intermolecular Forces JLFN5052023 PRAMITA MAHENDRANNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Polarity of Molecules and Its PropertiesDocument38 pagesWeek 2 Polarity of Molecules and Its Propertieslily smithNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular 2Document2 pagesIntermolecular 2tgeorgina630No ratings yet
- PolarityDocument20 pagesPolarityYsabela MataNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Intermolecular Forces-2Document11 pages3.1 Intermolecular Forces-2faridaisepicNo ratings yet
- Elements and Their Corresponding ColorDocument6 pagesElements and Their Corresponding ColorAdonis MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Part II Microscopic World I NotesDocument32 pagesPart II Microscopic World I NotesHon KwanNo ratings yet
- 115 Intermolecular Force Worksheet KeyDocument2 pages115 Intermolecular Force Worksheet Keyada wangNo ratings yet
- Intramolecular Forces and Intermolecular ForcesDocument12 pagesIntramolecular Forces and Intermolecular ForcesDuyen Nguyen100% (1)
- 4.7 Intermolecular ForcesDocument5 pages4.7 Intermolecular ForcesrachpNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Modules Week 2Document6 pagesPhysical Science Modules Week 2RODJHEN ANNE P. BARQUILLANo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Atomic Structure NotesDocument22 pagesTopic 2 Atomic Structure NotesAMAN AHMADNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Chemical BondingDocument29 pagesWeek 3 - Chemical BondingNthabelengNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Recapping Important Concepts: 2P32 Winter Term 2012-13 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Dr. M. PilkingtonDocument13 pagesLecture 1 - Recapping Important Concepts: 2P32 Winter Term 2012-13 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Dr. M. PilkingtonS K Mishra0% (1)
- Notes VSEPR (CH 6)Document21 pagesNotes VSEPR (CH 6)Nestor BalboaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 in Physical ScienceDocument8 pagesModule 5 in Physical ScienceDarlyn MontillaNo ratings yet
- Physical-Science-SHS-6.1-Types-of-Intermolecular-Forces-of-AttractionDocument20 pagesPhysical-Science-SHS-6.1-Types-of-Intermolecular-Forces-of-AttractionJoseph De ChavezNo ratings yet
- Physical Science HandoutsDocument5 pagesPhysical Science HandoutsEllaNatividad100% (1)
- The Kinetic Molecular Model and Intermolecular Forces of Attraction in MatterDocument104 pagesThe Kinetic Molecular Model and Intermolecular Forces of Attraction in MatterMiguel TatlonghariNo ratings yet
- PHYSCI - First Quarter NotesDocument7 pagesPHYSCI - First Quarter NotesCjNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem IiDocument8 pagesGen Chem Iiirizharanda98No ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY 3rd Quarter ReviewerDocument9 pagesCHEMISTRY 3rd Quarter ReviewerJanelle NopuetoNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- MB Online Basketball League Liability Waver FormDocument1 pageMB Online Basketball League Liability Waver FormMary GoresNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledMary GoresNo ratings yet
- Merry Christmas Happy HolidaysDocument4 pagesMerry Christmas Happy HolidaysMary GoresNo ratings yet
- Ses05 004Document29 pagesSes05 004Mary GoresNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledMary GoresNo ratings yet
- Set 1 Navneet PhysicsDocument5 pagesSet 1 Navneet Physicswww.rajdeepsarkar999No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 LaserDocument19 pagesChapter 7 LaserYohannesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 6+7 B-I)Document2 pagesChemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 6+7 B-I)XXXNo ratings yet
- Structural, Elastic, Electronic, Magnetic and Thermoelectric Properties of New Quaternary Heusler Compounds Cozrmnx (X Al, Ga, Ge, In)Document36 pagesStructural, Elastic, Electronic, Magnetic and Thermoelectric Properties of New Quaternary Heusler Compounds Cozrmnx (X Al, Ga, Ge, In)yasmine bouldiabNo ratings yet
- Questions Periodic Table of Elements Get The Table Organized in TimeDocument3 pagesQuestions Periodic Table of Elements Get The Table Organized in TimeJonathan ApiladoNo ratings yet
- Overview:: Book Title:-Physics For Joint Entrance Examination JEEDocument6 pagesOverview:: Book Title:-Physics For Joint Entrance Examination JEEkunalNo ratings yet
- Prolate-Oblate Difference Its Effect: and Energy Levels and Quadrupole MomentsDocument3 pagesProlate-Oblate Difference Its Effect: and Energy Levels and Quadrupole MomentsMarwa Moustafa Abdel-HafezNo ratings yet
- Physical World NotesDocument5 pagesPhysical World NotesAdorned. pearlNo ratings yet
- Physics: FiitjeeDocument1,319 pagesPhysics: FiitjeeBISWAJEET100% (2)
- 2018 A Level Solutions (Compiled)Document38 pages2018 A Level Solutions (Compiled)Faith SeahNo ratings yet
- Che1501 TL 102 2023 0 BDocument32 pagesChe1501 TL 102 2023 0 BBrandon MakamaNo ratings yet
- Zeal Study SSLC SCIENCE All Lessons 2mark Answers New 30.10.22Document45 pagesZeal Study SSLC SCIENCE All Lessons 2mark Answers New 30.10.22DevapriyaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry JokesDocument30 pagesChemistry JokesDiane TNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument19 pagesPeriodic TableFilmodeNo ratings yet
- Jamb-Chemistry-Past-Questions-11-15 UnibenpgDocument55 pagesJamb-Chemistry-Past-Questions-11-15 UnibenpgEhigie promiseNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Part BDocument56 pagesUnit 2 Part B소피아No ratings yet
- Physics 403. Modern Physics Laboratory: Eugene V Colla, Anne SicklesDocument56 pagesPhysics 403. Modern Physics Laboratory: Eugene V Colla, Anne Sicklesally claveriaNo ratings yet
- Arihant Term 2 Physics Class 12Document176 pagesArihant Term 2 Physics Class 12Javin GargNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry MCQDocument19 pagesClass 12 Chemistry MCQTayseer SaudiaNo ratings yet
- PH501Document1 pagePH501MAUSAM KatariyaNo ratings yet
- Emg 1204 Introduction To Materials Science Tutorial I Attempt All These Questions Question OneDocument2 pagesEmg 1204 Introduction To Materials Science Tutorial I Attempt All These Questions Question Onesteve gateriNo ratings yet
- U3 Chemical Bonding Review, IB10Document35 pagesU3 Chemical Bonding Review, IB10Liang LuNo ratings yet
- 2018 JC1 H1 Chem EOY P1 P2 Answers With CommentsDocument17 pages2018 JC1 H1 Chem EOY P1 P2 Answers With CommentsSeth LimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 CHM138Document76 pagesChapter 2 CHM138Isaac LibuNo ratings yet
- Aadil Vahora: AnandDocument10 pagesAadil Vahora: AnandAadil VahoraNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics Topic 4 Atomic Structure Knowledge OrganiserDocument3 pagesAQA Physics Topic 4 Atomic Structure Knowledge OrganiserGabriel HoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Module 5Document15 pagesGeneral Chemistry Module 5Junelle Ramos Aquino0% (2)
- 500 MCQDocument55 pages500 MCQkirki pNo ratings yet