Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Leading and Lagging Fleet Indicators
Leading and Lagging Fleet Indicators
Uploaded by
jadwa consultingOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Leading and Lagging Fleet Indicators
Leading and Lagging Fleet Indicators
Uploaded by
jadwa consultingCopyright:
Available Formats
Innovative Strategies for the Road Ahead
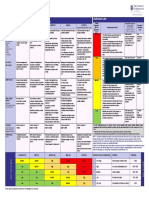
LEADING & LAGGING
FLEET MANAGEMENT
PERFORMANCE INDICATORS
Innovative Strategies for the Road Ahead
Leading and lagging indicators are two types of measurements used when assessing performance in a
business or organisation. A leading indicator is a predictive measurement, for example; the percentage of
people wearing safety belts in a vehicle is a leading safety indicator. A lagging indicator is an output measu-
rement, for example; the number of road traffic crashes is a lagging safety indicator.
The difference between the two is a leading indicator can influence change and a lagging indicator can only
record what has happened. In this document examples are provided for the priority areas in fleet manage-
ment: cost efficiency, effectiveness, safety and environmental impact.
Some indicators are cross-cutting; meaning that they influence more than one priority area.
This list is not exhaustive but serves to give inspiration about leading and lagging indicators.
Priority area Leading Lagging
Average age per vehicle Total Cost of Ownership
Cost-efficiency
Total Fleet Cost as % of the
Liters of fuel per 100 kms
Programme Cost
Unscheduled repair costs per
vehicle
Number of eco-driving training
hours
Maintenance done according to
training schedule
Utilisation rate per vehicle
Number of trips made as % of
Effectiveness Vehicle availability
number of trips requested
Maintenance done according to
Number of trip requests per year
training schedule
Utilization rate per vehicle Average procurement time per vehicle
% of managers with adequate
Crashes per 100.000 kilometers driven
Safety fleet safety training
Programme delivery days lost through
sickness absence (% of total work days
% of staff with adequate fleet lost by sickness absence; this can also
safety training be specified further, e.g. for short- term
sickness and long-term sickness
absence)
Innovative Strategies for the Road Ahead
Priority area Leading Lagging
% of management meetings in Number of crashes resulting in
wherein fleet safety is addressed injuries
Safety
% of management-staff meetings Number of crashes resulting in
wherein fleet safety is addressed fatalities
% of business partners (contractors,
suppliers, etc.) evaluated and
Number of speeding events
selected on the basis of their safety
performance
Number of near-miss reports
Number of fleet safety
assessments
Safety climate (measured through
staff survey
Liters of fuel per 100 kilometers CO2 emissions per kilometre
Average sustainable fleet training
Kilometres driven per vehicle type
hours per staff member
Environmental
impact
% of drivers who received eco-driving Kilometres driven per euro
training emission standard
Kilometres driven through
% of vehicles fitted with vehicle
vehicle sharing with other UN
tracking systems
agencies
% of operating offices with fleet Passenger kilometres per liter
emission reduction targets of fuel
% of petrol vehicles as a total of vehi- CO2 emissions from idling as a
cles percentage of total emissions
% of vehicles beyond disposal policy
% of vehicles included in carpool
You might also like
- Books Villains of All Nations Atlantic Pirates in The Golden AgeDocument4 pagesBooks Villains of All Nations Atlantic Pirates in The Golden AgeVoislav0% (3)
- Multivac 225/245Document28 pagesMultivac 225/245freddyoviedo33% (3)
- Manage Operational PlanDocument11 pagesManage Operational Planneha100% (1)
- WA Risk Analysis TablesDocument3 pagesWA Risk Analysis TableskanpsnNo ratings yet
- 7 FICO Rollout ProjectDocument39 pages7 FICO Rollout ProjectLokesh Modemz100% (1)
- Auto Updated HSSE DASH BOARDDocument132 pagesAuto Updated HSSE DASH BOARDBorislav VulicNo ratings yet
- MCCG Revised 2007Document23 pagesMCCG Revised 2007finah83100% (2)
- MCCG 2000 Finance CommDocument59 pagesMCCG 2000 Finance CommJiong Xun ChuahNo ratings yet
- 3 - Operational Risk Management - 1Document39 pages3 - Operational Risk Management - 1MikealayNo ratings yet
- Cut-Off Machine ReportDocument27 pagesCut-Off Machine Reportdaniebenade100% (2)
- FPP Risk AssessmentDocument2 pagesFPP Risk AssessmentTrija M RajanNo ratings yet
- PIA Quantitative and Quality AnalysisDocument62 pagesPIA Quantitative and Quality Analysismadnansajid876525% (4)
- Critical Success FactorsDocument1 pageCritical Success Factorsvishmala25No ratings yet
- Enterprise Risk Matrix A3 PDFDocument1 pageEnterprise Risk Matrix A3 PDFDavid VelaNo ratings yet
- QHSE Annual Report 2022Document33 pagesQHSE Annual Report 2022Callif Al AmienNo ratings yet
- Risk Managment Swot AnalysisDocument2 pagesRisk Managment Swot Analysisapi-491553418No ratings yet
- 8 Relative RankingDocument8 pages8 Relative Rankingsyarif hidayatNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Balanced Score CardDocument34 pagesHuman Resource Management: Balanced Score CardLumi LuminitaNo ratings yet
- Project Risk ManagementDocument25 pagesProject Risk ManagementCassandri LabuschagneNo ratings yet
- Ramp Safety CultureDocument11 pagesRamp Safety CultureRumesh ThilakarathnaNo ratings yet
- RISK Mba 17Document22 pagesRISK Mba 17Cecily Sandra100% (1)
- Hazard DatabaseDocument1,140 pagesHazard DatabaseVero ColladoNo ratings yet
- EPAC Return On Investment CalculationDocument12 pagesEPAC Return On Investment CalculationHari Hara SudhanNo ratings yet
- 04RM - Risk-Assessment 2Document32 pages04RM - Risk-Assessment 2Darren TanNo ratings yet
- Qualitative V Quantitative Risk AssessmentDocument5 pagesQualitative V Quantitative Risk AssessmentGundeepNo ratings yet
- Loan Calculator WorksheetDocument1 pageLoan Calculator WorksheetFrancis Vijay Kumar Batta100% (1)
- SDS Ar-Afff 3-3C6Document5 pagesSDS Ar-Afff 3-3C6A K KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Industrial Safety Management Using Innovative and Proactive StrategiesDocument20 pagesIndustrial Safety Management Using Innovative and Proactive StrategiesUdit chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Aviation Safety - Performance Measurement Logic ModelDocument1 pageAviation Safety - Performance Measurement Logic ModelvedatNo ratings yet
- Business Continuity ManagementDocument3 pagesBusiness Continuity ManagementChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- Basis of Presentation: The Health and Safety AuditDocument25 pagesBasis of Presentation: The Health and Safety AuditsivaNo ratings yet
- Step 1: Risk Identification Step 2: Risk Assessment Step 3: Risk Response Step 4: Monitor & ControlDocument28 pagesStep 1: Risk Identification Step 2: Risk Assessment Step 3: Risk Response Step 4: Monitor & ControlAnbuNo ratings yet
- IBM Oil - Elevating Enterpise Risk Management For Market SuccessDocument16 pagesIBM Oil - Elevating Enterpise Risk Management For Market SuccessIBM Chemical and PetroleumNo ratings yet
- Assess Risks and OpportunitiesDocument23 pagesAssess Risks and Opportunitiesurvikp778259No ratings yet
- Organizational ROR As of June 30 2022Document29 pagesOrganizational ROR As of June 30 2022Aimee GozonNo ratings yet
- CAP1760 Root Cause Identification Paper (Issue 02 April 19)Document68 pagesCAP1760 Root Cause Identification Paper (Issue 02 April 19)OratexaNo ratings yet
- ISO 14001 Certification ChecklistDocument4 pagesISO 14001 Certification ChecklistEyob SNo ratings yet
- Account and Finance Departmental ObjectiveDocument7 pagesAccount and Finance Departmental ObjectiveVICTORNo ratings yet
- You Exec - Risk Management FreeDocument9 pagesYou Exec - Risk Management FreeJuan GómezNo ratings yet
- HSEQ-HQ-11-03-00 HSE CommitteesDocument6 pagesHSEQ-HQ-11-03-00 HSE CommitteesAHMED AMIRANo ratings yet
- Akzo Nobel Risk ManagementDocument53 pagesAkzo Nobel Risk ManagementdhanuNo ratings yet
- Safety Objectivesand TargetsDocument1 pageSafety Objectivesand Targetsmiko congok3100% (1)
- Stakeholder ManagmentDocument21 pagesStakeholder Managmentsolomon getachewNo ratings yet
- Peration Anagement: Concept of Quality Juran's PrincipleDocument24 pagesPeration Anagement: Concept of Quality Juran's PrincipleAyushi BisenNo ratings yet
- Iso 45001Document1 pageIso 45001Ranjith jNo ratings yet
- Catasthropic Critical Major Moderate Minor: Severity ProbabilityDocument1 pageCatasthropic Critical Major Moderate Minor: Severity ProbabilityArjay LauretaNo ratings yet
- A Study of Risk Management in Construction ProcurementDocument24 pagesA Study of Risk Management in Construction ProcurementIreneNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation StrategyDocument1 pageRisk Assessment and Mitigation StrategySachin SainiNo ratings yet
- Incentive Management and Total RewardDocument11 pagesIncentive Management and Total RewardZayed KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Project Planning - Project Risk ManagementDocument7 pagesChapter 7 - Project Planning - Project Risk ManagementSuada Bőw WéěžýNo ratings yet
- EMS APG Risks and OpportunitiesDocument3 pagesEMS APG Risks and Opportunitiesdio39saiNo ratings yet
- Financial Perspective Kpi LibraryDocument4 pagesFinancial Perspective Kpi LibraryMohamed Yehia0% (1)
- 36 Types of Technology Risk: Simpl IcableDocument25 pages36 Types of Technology Risk: Simpl IcableMichael LimboNo ratings yet
- HYD120SHLP01 Particular Conditions of Contract: Amazon Confidential TATA PROJECTS - RFQ-GC-HYD100-110-120Document43 pagesHYD120SHLP01 Particular Conditions of Contract: Amazon Confidential TATA PROJECTS - RFQ-GC-HYD100-110-120Oklio GistNo ratings yet
- Element 7 SOP Rev 3Document18 pagesElement 7 SOP Rev 3vijay hackerNo ratings yet
- Conducted & Prepared By: Green Circle, IncDocument60 pagesConducted & Prepared By: Green Circle, IncRupal PandyaNo ratings yet
- QSHE - Safety Health KPI 2013Document2 pagesQSHE - Safety Health KPI 2013Andrianto100% (1)
- Guide FoundriesDocument13 pagesGuide Foundriesnadaf2No ratings yet
- FORMULIR CHESM Performance Review Protocol 26 September 2019Document9 pagesFORMULIR CHESM Performance Review Protocol 26 September 2019Slamet RiadiNo ratings yet
- IBM Maximo Asset Configuration Manager A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandIBM Maximo Asset Configuration Manager A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- Agenda SSCCC Board of Directors 2023 02 11Document6 pagesAgenda SSCCC Board of Directors 2023 02 11jadwa consultingNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper On Prioritising Fleet Risk Management - ClementsDocument12 pagesWhitepaper On Prioritising Fleet Risk Management - Clementsjadwa consultingNo ratings yet
- Daily Vehicle Checklist: Date: FLT # Driver/Operator'S NameDocument1 pageDaily Vehicle Checklist: Date: FLT # Driver/Operator'S Namejadwa consultingNo ratings yet
- 3 Actions For DriversDocument4 pages3 Actions For Driversjadwa consultingNo ratings yet
- Longer Term Solutions Fleet SafetyDocument2 pagesLonger Term Solutions Fleet Safetyjadwa consultingNo ratings yet
- UNICEF - Methodology For Assessing Procurement Systems (MAPS)Document4 pagesUNICEF - Methodology For Assessing Procurement Systems (MAPS)jadwa consultingNo ratings yet
- 13 Root Cause Analysis QuestionsDocument2 pages13 Root Cause Analysis Questionsjadwa consultingNo ratings yet
- Annex - Aircraft Cargo SpecificationsDocument5 pagesAnnex - Aircraft Cargo Specificationsjadwa consulting0% (1)
- Division 15Document35 pagesDivision 15freannNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi FD15 35Document12 pagesMitsubishi FD15 35hdb jualforkliftNo ratings yet
- CORAL APPENDIX C Communications CZ-2022-1109-029Document96 pagesCORAL APPENDIX C Communications CZ-2022-1109-029CORALationsNo ratings yet
- Curt Gowdy Brochure & MapDocument2 pagesCurt Gowdy Brochure & MapLonebeavNo ratings yet
- Airport VocabularyDocument12 pagesAirport Vocabularypetraonderova67% (3)
- California Reference BookletDocument118 pagesCalifornia Reference BookletVan KochkarianNo ratings yet
- Ferrari IndustrialDocument4 pagesFerrari IndustrialRio ImamNo ratings yet
- Draft Ansi z26 11Document32 pagesDraft Ansi z26 11Nilesh MahajanNo ratings yet
- Greenland 2256 2513 6Document258 pagesGreenland 2256 2513 6seacoastonlineNo ratings yet
- Constructing Rural E-Commerce Logistics Model Based On Ant Colony Algorithm and Artificial Intelligence MethodDocument10 pagesConstructing Rural E-Commerce Logistics Model Based On Ant Colony Algorithm and Artificial Intelligence MethodBryan PabloNo ratings yet
- Tak Tau Apa Di Suruh Upload Ya Ngasal AjaDocument48 pagesTak Tau Apa Di Suruh Upload Ya Ngasal AjaRicky SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Pipe Hot Insulation SpecificationDocument34 pagesPipe Hot Insulation Specificationsadeghmsg100% (1)
- The 30-Year Partnership of Mongolia and The AsianDocument31 pagesThe 30-Year Partnership of Mongolia and The Asianshinkaron88No ratings yet
- Michelin Tire Descriptions and Applications PDFDocument2 pagesMichelin Tire Descriptions and Applications PDFJAVIER BERMUDEZNo ratings yet
- Bell Dashboard 100 ManualDocument24 pagesBell Dashboard 100 ManualDusanMasle50% (2)
- Fatigue and RuttingDocument10 pagesFatigue and RuttingNadeem QureshiNo ratings yet
- KW (Stage Iiia) KW (Stage Iv) : Telescopic Crawler CraneDocument20 pagesKW (Stage Iiia) KW (Stage Iv) : Telescopic Crawler CraneulilkhanNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Hill RoadDocument42 pagesCH 5 Hill RoadSujan Singh100% (3)
- Infiniti HomeLink PDFDocument1 pageInfiniti HomeLink PDFScribdReadersNo ratings yet
- Atlas Copco 100 HP ACDocument66 pagesAtlas Copco 100 HP ACwhalenonNo ratings yet
- 20 - 20A - X20 Times Publication-2Document2 pages20 - 20A - X20 Times Publication-2Peter FormanNo ratings yet
- Irctcs E-Ticketing Service Electronic Reservation Slip (Personal User)Document2 pagesIrctcs E-Ticketing Service Electronic Reservation Slip (Personal User)SAHELI TOUR & TRAVELSNo ratings yet
- Iata Operational Safety AuditDocument46 pagesIata Operational Safety AuditMahmoud Ibrahim100% (2)
- 2001-Xvert SM PDFDocument19 pages2001-Xvert SM PDFqmeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6-1-settlement characteristic and control technology of railway subgrade-传给学生Document63 pagesChapter-6-1-settlement characteristic and control technology of railway subgrade-传给学生Habo TareNo ratings yet
- Crest 10001 Display26c1528 SchematicDocument1 pageCrest 10001 Display26c1528 SchematicHenry Jose Larez RojasNo ratings yet
- School Officials Accept Parcel Tax Defeat: Russian AlligationsDocument28 pagesSchool Officials Accept Parcel Tax Defeat: Russian AlligationsSan Mateo Daily JournalNo ratings yet