Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pcol
Pcol
Uploaded by
Ynah Celeste0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageThis document contains notes on pharmacology topics including:
1. Pharmaceutics which involves the breakdown of medications and mechanisms of absorption like pinocytosis and diffusion.
2. Pharmacokinetics which studies the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of drugs in the body.
3. Pharmacodynamics which examines the actions and effects of drugs on the body including their primary and secondary effects.
Original Description:
Pharmacology
Original Title
pcol
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains notes on pharmacology topics including:
1. Pharmaceutics which involves the breakdown of medications and mechanisms of absorption like pinocytosis and diffusion.
2. Pharmacokinetics which studies the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of drugs in the body.
3. Pharmacodynamics which examines the actions and effects of drugs on the body including their primary and secondary effects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pagePcol
Pcol
Uploaded by
Ynah CelesteThis document contains notes on pharmacology topics including:
1. Pharmaceutics which involves the breakdown of medications and mechanisms of absorption like pinocytosis and diffusion.
2. Pharmacokinetics which studies the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of drugs in the body.
3. Pharmacodynamics which examines the actions and effects of drugs on the body including their primary and secondary effects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
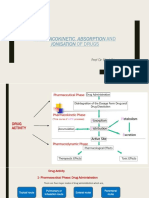
PHARMACOLOGY (TAKE DOWN NOTES) TO REVIEW!
Pharmaceutics – break down of the capsule 1. Medications to prevent heat, cure –
* Pinocytosis – passive, active pharmacotherapy
Kinetics – absorption, distribution, 2. Effects of the body on the drugs –
metabolism, excretion pharmacokinetics
Pharmacodynamics – action of drug on the 3. Known as undesirable effects – toxicology
body 4. Losartan, lowers bp – pharmacokinetics
Passive – diffusion (has high and low 5. Receptor – pharmacodynamics
concentration) 6. Stomach ulcer, otc mefenamic acid –
*blood cloth – example of diffusion, pharmacokinetics
high concentration 7. Oral has higher drugs – false
Active – need enzymes, proteins 8. Infants drug metabolism does not happen
Kinocytosis – inside the cell, cells carry the due to immature liver function – false
drug into membrane 9. Actions of the drug on the body –
Distribution – the drugs become available pharmacodynamics
to body fluid 10. Physical nature of drugs –
*when blood decrease, the distribution pharmacokinetics
of blood will be delayed 11. Enantiomers – disarrange
Metabolism – the body inactivates or 12. Response is too small for clinical benefits –
biotransform the drugs ; 12 hrs/ 6 hrs (half minimum effect concentration
life) until it eliminates 13. Drug with material design to dissolve in the
Elimination – 4.5 – 8 normal urine PH intestine – enteric coated preparation
14. Sublingual need – 30 mins, then re-assess
Creatinine clearance – before giving toxic
15. 3 existing vascular – placental, blood-brain
drugs
barriers,
Normal GFR – 90 above; increased
16. Consideration – age, sex, nutritional status
creatinine level in blood and urine
17. Highest drug concentration – peak level
Pharmacodynamics – study of the drugs
18. Withdraws blood sample – half life
Drug response:
19. Withdraw before next administration –
Primary – desirable effect on
through
the patient
20. Adverse reaction – unexpected
Secondary effect – can be
21. Drug interaction – drug-drug, drug-
desirable or not
food/beverage, drug-condition interaction
Chemical – composition of molecular
22. The greater the agent, the lower the
Generic – lower case letters on drugs
concentration – false
packaging
23. Some drugs are eliminated without
Trade name – capslock/ bold letter
undergoing metabolism – false
24. A drug maybe eliminated without
NATURE OF DRUGS
undergoing metabolism – false
Sterile – disarranged molecule
25. Herbal produced are safer than medical
Enantiomers – mirror life/image drugs – false
Onset – minimum effect of drug 26. After taking long lasting insulin, the
Peak – maximum patient’s blood pressure lowers after 20
Duration of action – after observing onset mins – pharmacodynamics
effect until least 27. Partial agonist have lower maximal – true
Half life (peak concentration) – withdraw 28. Drugs with zero order eliminations have
blood during peak time before constant half life – false
administering next dose 29. Pharmacognosy is the study of drug made
1st dose – withdraw from natural substances/sources – true
Through – withdraw before 2nd dose (?) 30. When a drug is distributed in the body, it
Enteric – coated (dissolves at intestine, means that it has reached the tissues and
should not crush the drug) cells – true
Sustained – release 31. About 12% - pharmacokinetics
Distribution of drugs – delayed 32. Drugs can turned on the body’s
Absorption – delayed if the patient is too physiological functions – true
young or too old because of gastric
contents QUIZ 2
Dose adjustment – in pain Enumeration: component required on all labels
You might also like
- CSHP Template For Residential - New (Repaired)Document5 pagesCSHP Template For Residential - New (Repaired)Jo An Valdez0% (1)
- I. Introduction - Basic PharmacologyDocument4 pagesI. Introduction - Basic Pharmacologymdgayas70100% (2)
- Urban Land Use - Community-Based PlanningDocument316 pagesUrban Land Use - Community-Based PlanningAnonymous 5poler100% (1)
- PharmacologyDocument8 pagesPharmacologyJi-Han Abalo ImnidaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology LecturesDocument7 pagesPharmacology LecturesMutya XDNo ratings yet
- Midterm PharmacologyDocument8 pagesMidterm PharmacologyMae Ysobel HalangdonNo ratings yet
- Review Guide in Pharmacology Prelim ExamDocument6 pagesReview Guide in Pharmacology Prelim ExamDela Cruz, Maria Roanne M.No ratings yet
- CHP 1Document9 pagesCHP 1Nida RidzuanNo ratings yet
- Pharma Week 1-5Document33 pagesPharma Week 1-5Krystel Anne Milan100% (1)
- PHARMACOLOGY Midterm LectureDocument5 pagesPHARMACOLOGY Midterm LectureSana ChanNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Quick TestDocument27 pagesPharmacology Quick TestAassh DcmbrNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology TrancesDocument27 pagesPharmacology TrancesMAZON, DHANYCIA XYREENNo ratings yet
- Responses To Drug Administration:: Factors Affecting Drug ResponseDocument4 pagesResponses To Drug Administration:: Factors Affecting Drug ResponseThea GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PharmaDocument5 pagesReviewer PharmaRica ParcasioNo ratings yet
- Ncm106pharma PrelimDocument9 pagesNcm106pharma PrelimKM PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Final Coverage FundaDocument3 pagesFinal Coverage FundaGlory NeriNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology SupplementalsDocument4 pagesNursing Pharmacology SupplementalsYla ReyesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology Supplemental Videos TranscriptDocument3 pagesNursing Pharmacology Supplemental Videos TranscriptYla ReyesNo ratings yet
- Introduction Pharma Ppt. StudentDocument77 pagesIntroduction Pharma Ppt. StudentKwebblekop JordiNo ratings yet
- MODULE 9. MedicationDocument22 pagesMODULE 9. MedicationShain TuliaoNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 Pharmacology Lec 1 and 2Document4 pagesNCM 106 Pharmacology Lec 1 and 2christyl necesitoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Week 2 Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument4 pagesPharmacology Week 2 Cheat Sheet: by ViaVijungcoNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument7 pagesPharmacologyraquel maniegoNo ratings yet
- Nursing PharmacologyDocument4 pagesNursing PharmacologyAshley Jane MacapayadNo ratings yet
- Unit #1 IntroductionDocument22 pagesUnit #1 IntroductionSaima VictorNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - PrelimsDocument9 pagesPharmacology - PrelimsLou KristofferNo ratings yet
- WWWWWWWDocument12 pagesWWWWWWWPrincess Diana Bernardino100% (1)
- Pharmacology (Prelim)Document2 pagesPharmacology (Prelim)Sheena Marie M. TarleNo ratings yet
- Lec1 PDFDocument26 pagesLec1 PDFDeary DearyNo ratings yet
- Unit #1 IntroductionDocument22 pagesUnit #1 IntroductionSaima VictorNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Unit 1Document63 pagesPharmacology Unit 1mesfin ashenafNo ratings yet
- 216 - Pharma First WeekDocument4 pages216 - Pharma First WeekJessielyn FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology ReviewerDocument24 pagesPharmacology ReviewergreinabelNo ratings yet
- Introduction On DrugsDocument2 pagesIntroduction On DrugsAdya AeshaNo ratings yet
- Sources of New Drugs: Molecular Pharmacology Combinatorial SynthesisDocument14 pagesSources of New Drugs: Molecular Pharmacology Combinatorial SynthesisJasper JangNo ratings yet
- Ios g56fBJEDfmJmkl6UDocument207 pagesIos g56fBJEDfmJmkl6UBawan ZahirNo ratings yet
- Vice and Drug Education and Control-RkDocument21 pagesVice and Drug Education and Control-RkROSES KISSES SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PharmacologyDocument45 pagesIntroduction To Pharmacologysandeepv08No ratings yet
- Notes in PharmacologyDocument96 pagesNotes in Pharmacologydmd_2dd50% (2)
- Notes in PharmacologyDocument95 pagesNotes in PharmacologyMylz MendozaNo ratings yet
- General PharmacologyDocument8 pagesGeneral PharmacologysekarenthangavelNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetic, Absorption and Ionisation of DrugsDocument31 pagesPharmacokinetic, Absorption and Ionisation of DrugsAli ElmehdawiNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument20 pagesPharmacologyKan JiNo ratings yet
- Pcol Quiz 1Document11 pagesPcol Quiz 1SmartieNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 PharmacodynamicsDocument12 pagesMODULE 2 PharmacodynamicsKyser DalitNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of PharmacologyDocument75 pagesBasic Principles of PharmacologyJessica Febrina Wuisan100% (1)
- Vice and Drug Education and ControlDocument7 pagesVice and Drug Education and ControlAimae Eata EalaNo ratings yet
- General Intro To Cology-1Document110 pagesGeneral Intro To Cology-1Sehrish RajpootNo ratings yet
- Review-Guide-in-Pharmacology-Prelim-Exam 2Document7 pagesReview-Guide-in-Pharmacology-Prelim-Exam 2Marie Allen MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Ncma216 PrelimDocument44 pagesNcma216 Prelimroldanmarygrace023No ratings yet
- Trans 1 Medication Administration 1Document23 pagesTrans 1 Medication Administration 1Germin CesaNo ratings yet
- Dalam Pengelolaan Farmakoterapi Pasien-: Fifi Luthfiyah Nutrition Departement On Poltekkes MataramDocument33 pagesDalam Pengelolaan Farmakoterapi Pasien-: Fifi Luthfiyah Nutrition Departement On Poltekkes MataramputryNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pharmacology AntibioticDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Pharmacology AntibioticZaira Reine SantosNo ratings yet
- Drug Education and Vice Control 2Document6 pagesDrug Education and Vice Control 2Catherine AcedoNo ratings yet
- Pharm Exam I NotesDocument19 pagesPharm Exam I Noteskatiana louisNo ratings yet
- Lab PharmacoDocument51 pagesLab PharmacoanaNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument5 pagesPharmacologyCassandra NicoleNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology (Laden Saleh) FinalDocument235 pagesPharmacology (Laden Saleh) FinalLaden SalehNo ratings yet
- Crime Detection and InvestigationDocument14 pagesCrime Detection and InvestigationHanimah DimaocorNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology- The Molecular Dance: Understanding Drug Interactions: Harmony and Chaos: The Symphony of Drug InteractionsFrom EverandPharmacology- The Molecular Dance: Understanding Drug Interactions: Harmony and Chaos: The Symphony of Drug InteractionsNo ratings yet
- WIKA GPU-S-3000 SF6 HandlingDocument5 pagesWIKA GPU-S-3000 SF6 HandlingDaniel StaigerNo ratings yet
- Indian Income Tax Return Acknowledgement 2021-22: Assessment YearDocument1 pageIndian Income Tax Return Acknowledgement 2021-22: Assessment YearRia SinghalNo ratings yet
- DNA Packaging Nucleosomes and Chromatin Annunziato 2014Document4 pagesDNA Packaging Nucleosomes and Chromatin Annunziato 2014Fidel Ruiz-RoblesNo ratings yet
- Personal Financial InformationDocument17 pagesPersonal Financial InformationSurajNo ratings yet
- Population Genetics TutorialDocument164 pagesPopulation Genetics TutorialMichelle GNo ratings yet
- Food and Beverage SapDocument52 pagesFood and Beverage SapdamianuskrowinNo ratings yet
- Composite Materials CZ2BDocument20 pagesComposite Materials CZ2BVahid KamraninejadNo ratings yet
- Polymer Degradation and Stability: F. Carrasco, P. Pagès, J. Gámez-Pérez, O.O. Santana, M.L. MaspochDocument10 pagesPolymer Degradation and Stability: F. Carrasco, P. Pagès, J. Gámez-Pérez, O.O. Santana, M.L. MaspochJavier Vallejo MontesinosNo ratings yet
- Sony ST-SA3ESDocument64 pagesSony ST-SA3ESNanoUrraNo ratings yet
- Reologia Do Restylane FinesseDocument8 pagesReologia Do Restylane FinesseRhelvis1No ratings yet
- WEEK 8 Day 3-4Document30 pagesWEEK 8 Day 3-4Estrel Mae PalitayanNo ratings yet
- KASHISHDocument65 pagesKASHISHRavileen AnandNo ratings yet
- Advanced Stat. ResearchDocument6 pagesAdvanced Stat. ResearchYen YenNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Consumer ChemDocument5 pagesLesson Plan in Consumer ChemJessie M. Indolos0% (1)
- Makahiya (Mimosa Pudica) Extract: Its Potential Efficiency in Decreasing The Blood Sugar LevelDocument10 pagesMakahiya (Mimosa Pudica) Extract: Its Potential Efficiency in Decreasing The Blood Sugar LevelJaneNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument60 pagesProject ReportPrashant Bankar33% (6)
- Construction MethodologyDocument102 pagesConstruction MethodologyDagnachew TassewNo ratings yet
- Dish Id RosisDocument28 pagesDish Id RosisDM internaNo ratings yet
- Final Year MBBS Timetable (Online Classes) 2020-21Document2 pagesFinal Year MBBS Timetable (Online Classes) 2020-21em khanNo ratings yet
- Milestii MiciDocument10 pagesMilestii MiciIon CotonețNo ratings yet
- Crime Fighting and Crime Prevention (Criminal Justice)Document127 pagesCrime Fighting and Crime Prevention (Criminal Justice)Dimitrije Živković100% (1)
- New Drugs and Technologies: PrasugrelDocument10 pagesNew Drugs and Technologies: PrasugrelDewi FitrianaNo ratings yet
- 14 Oct - SDRM - Prof. Nirmalya BDocument2 pages14 Oct - SDRM - Prof. Nirmalya BShivam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Contributory NegligenceDocument12 pagesContributory Negligencesai kiran gudisevaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CefurexDocument2 pagesDrug Study CefurexJILLIAN MARIE BARREDONo ratings yet
- Unloading Arm DatasheetDocument2 pagesUnloading Arm DatasheetbecpavanNo ratings yet
- Government of West Bengal: % of Disability (As Per Certificate) Aadhaar Card No (If Yes)Document2 pagesGovernment of West Bengal: % of Disability (As Per Certificate) Aadhaar Card No (If Yes)Brahmankhanda Basapara HIGH SCHOOLNo ratings yet
- KS7D CL29Z40MQDocument84 pagesKS7D CL29Z40MQChris RedfieldNo ratings yet