Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HHIS Lec (Week 10)
HHIS Lec (Week 10)
Uploaded by
FelicityOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HHIS Lec (Week 10)
HHIS Lec (Week 10)
Uploaded by
FelicityCopyright:
Available Formats
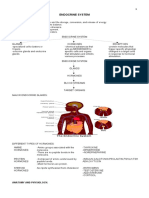
HHIS 221: Human histology
2nd Year|2nd Semester| A.Y 2022 – 2023
Week 10: ENDOCRINE GLANDS
Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis)
- Base of the brain (sella turcica) of the Basophils;
sphenoid bone
Gonadotrophs
- Hypo means under
- Physis means growth - Secretes FSH and LH
- Weigh about 0.5g - Large, round, granular
- deep purple-black cytoplasm
Thyrotrophs
NEUROHYPOPHYSIS OR POSTERIOR
PITUITARY GLAND - Secretes TSH
- Small, angular, oval nucleus,
Oxytocin
- Very dense deep purple-black granular
- Stimulates contractions of the uterus during cytoplasm
labor
- Causes milk ejection
Pars Tuberalis
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
- smaller funnel shaped region surrounding
- Can inhibit urine production
around infundibulum
- In large amounts, causes vasoconstriction
- highly vascular rise
leading to increased blood pressure
- most of the cells of the Pars Tuberalis is
(vasopressin)
Gonadotrophs
ADENOHYPOPHYSIS OR ANTERIOR
Pars Intermedia
PITUITARY GLAND
- Narrow zone between the Pars Distalis and
Pars Distalis – 70% of Adenohypophysis
the Pars Nervosa
Chromophobe Cells - affinity for standard - Contains with Basophilic cells
histological dyes. - Line with the simple cuboidal epithelium
- Synthesizes Melanocyte Simulating
Chromophil Cells - Consist of:
Hormone
Acidophils;
Somatotrophs
- Secretes growth hormone
MEDICAL CONDITIONS OF THE
- Medium, oval/angular,
ANTERIOR PITUITARY
- Orange cytoplasm, prominent nucleoli
Mammotrophs
Gigantism – excessive production of growth
- Secrete prolactin hormone in children before closing of the long
- Large, polygonal/angular bone of the epiphysial plate
- purple-pink cytoplasm, green nuclei
Acromegaly – excessive production of growth
hormone in adult with musculoskeletal horology
and other medical consequences
HHIS 221: Human histology
2nd Year|2nd Semester| A.Y 2022 – 2023
Week 10: ENDOCRINE GLANDS
Pineal Gland Parathyroid Glands
- Also known as epiphysis cerebri - 4 small ovoid masses located on the back of
- Found on the 3rd ventricle; Attached to the the thyroid gland, one at each end of the
brain by a stalk upper and lower poles
- Age causes an increase in the amount of
- The parenchyma of the glands consists of 2
connective tissue in the pineal body and the
types of cells:
formation of calcified bodies called Brain
Sands/ Psamomma Bodies/ Corpora Chief/ Principal Cells
Arenacea
Oxyphil Cells
Thyroid Gland
Adrenal Glands
- Located in the cervical region anterior to the
cricoid cartilage of larynx - Also known as Suprarenal Glands
- Consists of 2 lateral lobes connected by a - Paired organs
narrow isthmus
- Weighs 25-40 grams; covered by a fibrous
capsule 2 CONCENTRIC REGIONS
- Contain 20M – 30M thyroid follicle Adrenal Cortex
2 types of cells: - outer glandular region in three layers
- Follicular cells/Thyrocytes - yellowish peripheral region
- Parafollicular cells/C cells - Cells of the adrenal cortex have
characteristic features of steroid-secreting
cells
MEDICAL CONDITIONS AFFECTING THE
THYROID GLAND
3 Concentric Zones:
1. Goiter – Cause by chronic dietary ironic Zona Glomerulosa (Outermost)
deficiency - 15% of the cortex
2. Graves Disease - hyperthyroidism; causes - Composed of columnar/pyramidal shaped
exophthalmic goiter-edema behind eyes causes
cell
bulging; hyperactivity, arrythmias.
- Secrete; Mineralocorticoids and Aldosterone
3. Hypothyroidism – reduces the thyroid
hormone level cause by local inflammation - Responsible for electrolyte and water
balance in the body
HHIS 221: Human histology
2nd Year|2nd Semester| A.Y 2022 – 2023
Week 10: ENDOCRINE GLANDS
Type 2 Diabetes – Non-Insulin dependent, occurs
most commonly with obesity
Zona Fasciculata (Middle)
Placenta
- Cells are arranged in straight cords
- 55% - 80% of the cortex - Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
- Secrete; Glucocorticoids and Cortisol - helps thicken the uterine lining to support
- Induce fat mobilization and muscle growing embryo during pregnancy; stop
proteolysis menstruation
Zona Reticularis (Innermost)
- Smaller cells in the network of irregular
cords
- 10% of the cortex
- Secrete; sex hormones/androgens
Adrenal Medulla
- inner neural tissue region
- reddish brown central area
Islets of Langerhans / Pancreatic Islets
- The pancreas is a mixed gland
- The islets of the pancreas produce hormones
Insulin – allows glucose to cross plasma
membranes into cells from Beta Cells
Glucagon – allows glucose to enter the blood
from Alpha Cells
Somatostatin – secretes from Delta Cells
These hormones are antagonists that maintain Other Endocrine Products
blood sugar homeostasis
MEDICAL CONDITIONS AFFECTING THE
PANCREAS
Diabetes Mellitus – Loss of insulin, elevated
blood sugar or hypoglycemia
Type 1 Diabetes – Insulin dependent, loss of beta
cells
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology ReviewerDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Reviewermashup100% (14)
- Endocrine, USMLE ENDPOINTDocument73 pagesEndocrine, USMLE ENDPOINTDaNy Chiriac67% (3)
- Clinical OSCE NotesDocument49 pagesClinical OSCE Notesrandom.mail.scsm711250% (2)
- Endocrine Gland....Document62 pagesEndocrine Gland....Sabita TripathiNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Endocrine System: Ma. Minda Luz M. Manuguid, M.DDocument27 pagesHistology of The Endocrine System: Ma. Minda Luz M. Manuguid, M.Dchocoholic potchiNo ratings yet
- W4-15 Endocrine and Alimentary Layers of The Neck Lecture PDFDocument75 pagesW4-15 Endocrine and Alimentary Layers of The Neck Lecture PDFSAHIL AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Describe and Explained Organs Belong To Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesDescribe and Explained Organs Belong To Endocrine SystemnilaahanifahNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument30 pagesEndocrineRola TawfikNo ratings yet
- C10 Endocrine SystemDocument24 pagesC10 Endocrine Systemwajomi100% (1)
- Neurohistology Lecture 3 Endocrine SystemDocument32 pagesNeurohistology Lecture 3 Endocrine Systemisicheipraise3No ratings yet
- Dr. Ahmed Ammar: General ConceptsDocument19 pagesDr. Ahmed Ammar: General ConceptsAmy AmyNo ratings yet
- Somatic Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesSomatic Nervous SystemGuenNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland: 2.2 BasophilsDocument15 pagesPituitary Gland: 2.2 BasophilsJR BetonioNo ratings yet
- Midterm Endocrine SystemDocument90 pagesMidterm Endocrine SystemSandra OnceNo ratings yet
- Endo Reviewer 1Document8 pagesEndo Reviewer 1ANA DelafuenteNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemRoeisa SalinasNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Animal ScienceDocument15 pagesEndocrine System Animal ScienceJairus LampanoNo ratings yet
- HISTOLOGY 4 - Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesHISTOLOGY 4 - Endocrine SystemGauri SulekhaNo ratings yet
- Inbound 2262520782433835641Document5 pagesInbound 2262520782433835641Jannah MoralesNo ratings yet
- (Histo) Endocrine SystemDocument34 pages(Histo) Endocrine SystemAfiqah AliasNo ratings yet
- ReviewDocument6 pagesReviewAlbisladys Castellanos PujolsNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Endocrine System PPT 2023Document70 pagesAnatomy Endocrine System PPT 2023bereket bekeleNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Histology NotesDocument5 pagesEndocrine Histology NotesJulie TranNo ratings yet
- Endo 1 2005Document53 pagesEndo 1 2005api-3698357No ratings yet
- Body System II 7 Endo 1Document27 pagesBody System II 7 Endo 1rrq8cwk2gnNo ratings yet
- Animal Histology - EndocrineDocument17 pagesAnimal Histology - EndocrineDanielle FletcherNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandsDocument28 pagesEndocrine GlandsVillarosa JayrNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Endokrin Mei 2019Document64 pagesAnatomi Endokrin Mei 2019insiya insiyaNo ratings yet
- ENDODocument18 pagesENDOJoezer Gumangan VeranoNo ratings yet
- 10 Endocrine SystemDocument3 pages10 Endocrine SystemMardy Martin SorianoNo ratings yet
- Endocrinesys TEM: Principles of Chemical CommunicationDocument4 pagesEndocrinesys TEM: Principles of Chemical CommunicationCatherine Joy delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Histologi Sistem EndokrinDocument109 pagesHistologi Sistem EndokrinOlivia Chandra DeviNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesEndocrine Systemrk749vbsk6No ratings yet
- Kelenjar Endokrin HistologiDocument43 pagesKelenjar Endokrin HistologibutterstrikeNo ratings yet
- Endo All MergeDocument586 pagesEndo All MergeShivani DurgeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesEndocrine SystemKimberly Anne SP Padilla100% (2)
- Endocrine SystemDocument43 pagesEndocrine SystemnandaNo ratings yet
- E N D O C R I N E System: Hormonal Control of A. PituitaryDocument3 pagesE N D O C R I N E System: Hormonal Control of A. PituitaryMayet BautistaNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY Endocrine TranscribedDocument9 pagesANATOMY Endocrine TranscribedYanyan PanesNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument21 pagesEndocrine SystemMark DimarucutNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Organs TissuesDocument10 pagesEndocrine Organs TissuesAloysius KalawaNo ratings yet
- Histology Lec-11 EndocrineDocument10 pagesHistology Lec-11 EndocrineKevin C. AguilarNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands - 1st - ChapterDocument12 pagesEndocrine Glands - 1st - Chaptervarun kumarNo ratings yet
- Adrenal GlandDocument47 pagesAdrenal GlandsuthaNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemical Co-Ordination N Integration-Notes Blog (Full Permission)Document3 pages11 Chemical Co-Ordination N Integration-Notes Blog (Full Permission)fariha khanNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus Infundibulum: (Adenohypophysis)Document3 pagesHypothalamus Infundibulum: (Adenohypophysis)jaira_joshbieNo ratings yet
- Endocrine HistologyDocument31 pagesEndocrine HistologymibiteNo ratings yet
- Pituitary GlandDocument66 pagesPituitary GlandAsmita BhattNo ratings yet
- HypothalamusDocument38 pagesHypothalamuscmabdullahNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document9 pagesModule 5CamilleCalmaLenonNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandsDocument24 pagesEndocrine GlandsZoyaNo ratings yet
- Pituitary GlandDocument28 pagesPituitary GlandAzza50% (2)
- U1 - Practice 3 +4 - Medical Terminology - KeyDocument3 pagesU1 - Practice 3 +4 - Medical Terminology - KeyHằng ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System HistologyDocument34 pagesEndocrine System HistologyAnjiZareerNo ratings yet
- Endocrine OctoberDocument70 pagesEndocrine OctoberMohamed FarahatNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Definition & BackgroundDocument11 pagesEndocrine System: Definition & Backgroundعبدالرحمن عدي عبدالفتاحNo ratings yet
- Pituitary TumorsDocument2 pagesPituitary TumorsRama HijaziNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument22 pagesEndocrine SystemRonald A. OganiaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HPA Pathway - and Other Hypothalamic and Pituitary HormonesDocument39 pagesIntroduction To HPA Pathway - and Other Hypothalamic and Pituitary HormoneshumnaNo ratings yet
- Basic HistologyDocument2 pagesBasic HistologyAngel DumalagNo ratings yet
- Endocrine & Respiratory SystemDocument50 pagesEndocrine & Respiratory SystemHana AdivaNo ratings yet
- SodapdfDocument102 pagesSodapdfFelicityNo ratings yet
- MTLB Week 2Document9 pagesMTLB Week 2FelicityNo ratings yet
- BIOE Week 13Document3 pagesBIOE Week 13FelicityNo ratings yet
- BIOE Week 14Document4 pagesBIOE Week 14FelicityNo ratings yet
- BACT Week 2Document21 pagesBACT Week 2FelicityNo ratings yet
- Hhis LecDocument1 pageHhis LecFelicityNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument19 pagesEndocrine System Anatomy and PhysiologyJoanna EdenNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Endocrine SystemDocument140 pagesTopic 1 Endocrine SystemmasdfgNo ratings yet
- HP Thyroid Meds Conversion ChartDocument3 pagesHP Thyroid Meds Conversion ChartJeanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Surgery MCQDocument71 pagesEndocrine Surgery MCQShriyansh ChaharNo ratings yet
- Lesiones Cutaneas y Enfermedad Sistemica en Felinos Sep 2017Document13 pagesLesiones Cutaneas y Enfermedad Sistemica en Felinos Sep 2017dayana rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Post-Throidectomy Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesPost-Throidectomy Nursing Care PlanCyrus De AsisNo ratings yet
- Anasurgery MockboardDocument12 pagesAnasurgery MockboardVince CabahugNo ratings yet
- Radiologi EndokrinDocument76 pagesRadiologi EndokrinAndi9993100% (1)
- Endocrine Disease: Anthony P. Heaney, MD, PHD and Glenn D. Braunstein, MDDocument2 pagesEndocrine Disease: Anthony P. Heaney, MD, PHD and Glenn D. Braunstein, MDCharlemagne Charles INo ratings yet
- Evaluation of TSH, T4 and T3 in Human Serum: Standardization On Normal IndividualsDocument6 pagesEvaluation of TSH, T4 and T3 in Human Serum: Standardization On Normal IndividualsTanveerNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Disorders Julie Mann, NP - Case StudyDocument10 pagesEndocrine Disorders Julie Mann, NP - Case Studysimonedarling75% (4)
- Physical Assessment Ears, Eyes, Nose, Throat and Cranial NervesDocument28 pagesPhysical Assessment Ears, Eyes, Nose, Throat and Cranial Nervesjennylyn guadalupeNo ratings yet
- Klasifikasi Prosedur ICD9CMDocument258 pagesKlasifikasi Prosedur ICD9CMJivitaBasarahNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism and Myxedema ComaDocument53 pagesHypothyroidism and Myxedema ComaKuba ArebaNo ratings yet
- Study of Prevalence and Awareness Regarding Thyroid Disorders in People of Western Nepal at Zenus HospitalDocument9 pagesStudy of Prevalence and Awareness Regarding Thyroid Disorders in People of Western Nepal at Zenus HospitalIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Sea Moss GelDocument4 pagesSea Moss GelIsra tanveer100% (1)
- DLL Endocrine DisordersDocument4 pagesDLL Endocrine Disorderskaycin DuzonNo ratings yet
- Ospe Du EntDocument114 pagesOspe Du Entmfshihab3352No ratings yet
- Thyroid ReportDocument31 pagesThyroid ReportMarion PerniaNo ratings yet
- Sujok Therapy and Treatment of Diseases Part IiDocument7 pagesSujok Therapy and Treatment of Diseases Part IiDoctor A SethiNo ratings yet
- Venus, Mundane Chakra To Netzach - Allchin (1982)Document3 pagesVenus, Mundane Chakra To Netzach - Allchin (1982)kalidwadNo ratings yet
- CBD - Ayu Sufiana Mardliyya - 30101607622 - Hyperthyroid - DR Anna - RSISA P21.1Document27 pagesCBD - Ayu Sufiana Mardliyya - 30101607622 - Hyperthyroid - DR Anna - RSISA P21.1Ayu SufianaNo ratings yet
- The Wisdom of Menopause by Christiane Northrup: The Physical Foundation of The Change (Excerpt)Document42 pagesThe Wisdom of Menopause by Christiane Northrup: The Physical Foundation of The Change (Excerpt)Random House Publishing Group92% (12)
- Hypothyroidism in Context: Where We've Been and Where We're GoingDocument12 pagesHypothyroidism in Context: Where We've Been and Where We're Going1130017003 AIMMATUL CHANIFAHNo ratings yet
- Accuprobe: Lab ReportDocument2 pagesAccuprobe: Lab ReportSnju BjajNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument28 pagesThyroid GlandSurvey IndiaNo ratings yet
- MCQs by Jahaan Opal Biology ICSE Class 10Document4 pagesMCQs by Jahaan Opal Biology ICSE Class 10Jahaan OpalNo ratings yet
- A CASE REPORT: Hyperthyroidism in PregnancyDocument46 pagesA CASE REPORT: Hyperthyroidism in PregnancyIrma Permata sariNo ratings yet