Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 viewsUntitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
dhwiwdh The best statement is 3. The document states that intermediate filaments are the most stable (not dynamic) types of cytoskeleton and play a structural role by resisting tension on the cell.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Human Genetics Concepts and Applications 11Th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument29 pagesHuman Genetics Concepts and Applications 11Th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFmagdalavicemanocgp100% (13)
- Plant Pigments and Photosynthesis Lab ReportDocument4 pagesPlant Pigments and Photosynthesis Lab ReportAnthony64% (22)
- AP Biology Name - Chapter 6 Guided Reading AssignmentDocument6 pagesAP Biology Name - Chapter 6 Guided Reading AssignmentRobert Ladaga33% (3)
- CytoskeletonDocument65 pagesCytoskeletonSapana SubediNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument24 pagesCell StructureA. AsadiNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton SNDocument3 pagesCytoskeleton SNsamy gNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument2 pagesAmino Acids and ProteinsyejiNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument40 pagesConnective TissueMoayad albeshriNo ratings yet
- BM 1 1 CytoskeletonDocument24 pagesBM 1 1 CytoskeletonSanthoshi Sadhanaa SankarNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton Motor Proteins and ECM - SCDocument77 pagesCytoskeleton Motor Proteins and ECM - SCAlice RizzoNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton DADocument35 pagesCytoskeleton DAAnonymous NVBCqKWHNo ratings yet
- Cytology - 1Document13 pagesCytology - 1Sumayya KabeerNo ratings yet
- Cell and EpitheliumDocument11 pagesCell and EpitheliumMichael DamazoNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument52 pagesConnective TissueMaxamed Faarax XaashiNo ratings yet
- CytoskeletonDocument6 pagesCytoskeletonPreethaNo ratings yet
- 6 10-CytoplasmDocument27 pages6 10-CytoplasmAbbas TalibNo ratings yet
- General Characteristics: of Mitochondria 1 Methods of StudyDocument7 pagesGeneral Characteristics: of Mitochondria 1 Methods of StudypaulaNo ratings yet
- Cy To SkeletonDocument21 pagesCy To SkeletonJisna JaisonNo ratings yet
- C & M Bio CytoskeletonDocument40 pagesC & M Bio CytoskeletonA PNo ratings yet
- BIO 35 Chapter 1B - Cell Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument11 pagesBIO 35 Chapter 1B - Cell Anatomy and PhysiologyJake EverettNo ratings yet
- Techno-1.1-The CellDocument37 pagesTechno-1.1-The CellMark DeGrootteNo ratings yet
- CytosceletonDocument41 pagesCytosceletonaidar.seralinNo ratings yet
- MembrDocument43 pagesMembrnadaahmd2040No ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton MADocument22 pagesCytoskeleton MAsema raraNo ratings yet
- CytoskeletonDocument27 pagesCytoskeletonserenity limNo ratings yet
- Reflective Journal For Module 2 Unit 1: Name: Yulo, Ires A. Section: BSED-SCI.3-BDocument6 pagesReflective Journal For Module 2 Unit 1: Name: Yulo, Ires A. Section: BSED-SCI.3-Bguirillita acutNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton and Cell Motility 1Document40 pagesCytoskeleton and Cell Motility 1Muhamad Farhan RLNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy: The CellDocument33 pagesHuman Anatomy: The CellramadanNo ratings yet
- 11.sitoskeleton Dan Pergerakan Sel-Dr - IsraDocument40 pages11.sitoskeleton Dan Pergerakan Sel-Dr - IsraTa RaNo ratings yet
- BY2201 EmmaC CytoskeletonIandIIDocument62 pagesBY2201 EmmaC CytoskeletonIandIIRebecca ReillyNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology - Part 1: 1) Plasma Membrane 2) CytoskeletonDocument18 pagesCell Biology - Part 1: 1) Plasma Membrane 2) CytoskeletonBeTy AgustinNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 CellsDocument1 pageTopic 2 CellsKandy Anne Castillo AbuanNo ratings yet
- Muscular TDocument18 pagesMuscular TSumayya KabeerNo ratings yet
- 2cytology Cytoskel Receptor Transp (3) 1Document43 pages2cytology Cytoskel Receptor Transp (3) 1m.mansoor3377No ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton PRESENTATIONDocument36 pagesCytoskeleton PRESENTATIONChaudryNomiNo ratings yet
- Prepared By:-: Priyanka Yadav M.Sc. Life Sciences Ist SemDocument37 pagesPrepared By:-: Priyanka Yadav M.Sc. Life Sciences Ist SemleartaNo ratings yet
- 3 CellsDocument6 pages3 CellsEly FructuosoNo ratings yet
- February 27, 2012 - Chapter 7: Inside The CellDocument4 pagesFebruary 27, 2012 - Chapter 7: Inside The CellVincent Troy SantosNo ratings yet
- The Cytoskeleton Is A Network of Filament and Tubules That Extends Throughout A CellDocument9 pagesThe Cytoskeleton Is A Network of Filament and Tubules That Extends Throughout A CellHania GulNo ratings yet
- Centro, MF. Module - 6.Document9 pagesCentro, MF. Module - 6.jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Question Sheet+ Notes All TopicsDocument19 pagesQuestion Sheet+ Notes All TopicsSidraNo ratings yet
- 8 Cell - The Unit of Life-NotesDocument6 pages8 Cell - The Unit of Life-NotesBhavanya RavichandrenNo ratings yet
- 8 Cell - The Unit of Life-NotesDocument6 pages8 Cell - The Unit of Life-NotesdeveshjayakumaryadavNo ratings yet
- 3011 Doc 20240327 Wa0021.Document24 pages3011 Doc 20240327 Wa0021.vavc720No ratings yet
- MODULE 2.2 Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument11 pagesMODULE 2.2 Cellular Level of OrganizationKate Andrea PanizalesNo ratings yet
- M PRtpbo Fxo F46 YBll E9 HDocument5 pagesM PRtpbo Fxo F46 YBll E9 Hrudrakumbhar2005No ratings yet
- The CytoskeletonDocument9 pagesThe CytoskeletonElena OlmedoNo ratings yet
- The CytoskeletonDocument63 pagesThe CytoskeletonAmara TargaryenNo ratings yet
- The CytoskeletonDocument31 pagesThe CytoskeletonSanthoshsv 143No ratings yet
- Connective Tissue (CT)Document37 pagesConnective Tissue (CT)Fady FadyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document153 pagesLecture 3Miya GordNo ratings yet
- 2.4 - Eukaryotic Cell StructureDocument12 pages2.4 - Eukaryotic Cell Structurejpvnym85gdNo ratings yet
- 6.1-How Are Cells Studied?: Magnification Resolution Contrast Electron Microscope (EM)Document7 pages6.1-How Are Cells Studied?: Magnification Resolution Contrast Electron Microscope (EM)Sadasivarao GaddeNo ratings yet
- Thecytoskeleton PPTDocument11 pagesThecytoskeleton PPTseenu mohapatra100% (1)
- Module 2.2 Cellular Basis of LifeDocument10 pagesModule 2.2 Cellular Basis of LifechellesuguitanNo ratings yet
- IkatDocument38 pagesIkatReenha TrisnawatiNo ratings yet
- Summary NotesDocument14 pagesSummary NotesNo-Face. PersonaNo ratings yet
- Cell The Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesCell The Unit of LifeRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Unit 2 - Cell Structure and FunctionDocument12 pagesAP Biology Unit 2 - Cell Structure and FunctionSam SankarNo ratings yet
- From Tubulin to Thought: The Nexus of Cytoskeleton Microtubules and Brain Complexity.From EverandFrom Tubulin to Thought: The Nexus of Cytoskeleton Microtubules and Brain Complexity.No ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- ParaphrasingDocument12 pagesParaphrasingdhwiwdhNo ratings yet
- To CommunicationDocument63 pagesTo CommunicationdhwiwdhNo ratings yet
- 5 Minute Self Introduction Speech TemplateDocument2 pages5 Minute Self Introduction Speech TemplatedhwiwdhNo ratings yet
- Glutamato Deamination by Oxidation Is Readily ReversibleDocument9 pagesGlutamato Deamination by Oxidation Is Readily ReversibledhwiwdhNo ratings yet
- Valid and Invalid Arguments: CS 202 Epp Section 1.3 Aaron BloomfieldDocument17 pagesValid and Invalid Arguments: CS 202 Epp Section 1.3 Aaron BloomfielddhwiwdhNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitleddhwiwdhNo ratings yet
- Biology Depth Study - Cystic FibrosisDocument7 pagesBiology Depth Study - Cystic FibrosisDog DogNo ratings yet
- Neurohealth Properties of Hericium Erinaceus MycelDocument11 pagesNeurohealth Properties of Hericium Erinaceus Myceldokan42No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan PatrickDocument4 pagesLesson Plan PatrickPatrick Jerome SilvanoNo ratings yet
- Cell SignalingDocument87 pagesCell SignalingZaw Linn PhyoNo ratings yet
- Mineralocorticoids: Shajeer. SDocument42 pagesMineralocorticoids: Shajeer. SShajeer SalimNo ratings yet
- Genbio2 Lesson 1 Plant and Animal Nutrition Part 1Document32 pagesGenbio2 Lesson 1 Plant and Animal Nutrition Part 1crystal janr macalisangNo ratings yet
- Biology 9 O Level Test PaperDocument10 pagesBiology 9 O Level Test PaperAllam S/o Mumtaz Ali TunioNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Starch DigestionDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Starch DigestionNikki Ticman100% (1)
- WHLP StemDocument8 pagesWHLP Stemcristina maquintoNo ratings yet
- Physci 111A Lecture 1 XX PDFDocument31 pagesPhysci 111A Lecture 1 XX PDFJASMINE LOUIENo ratings yet
- Introduction To CytogeneticsDocument39 pagesIntroduction To CytogeneticsAnderson AliNo ratings yet
- IBO 2010 Korea Theory Paper 1Document61 pagesIBO 2010 Korea Theory Paper 1Bikash Ranjan RayNo ratings yet
- Biotechnologies: Past History, Present State and Future ProspectsDocument16 pagesBiotechnologies: Past History, Present State and Future ProspectsJuana RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Protocolo Purificacion Desde GelDocument3 pagesProtocolo Purificacion Desde GelAriel ArayaNo ratings yet
- Fisiopatologia Da Dor - Clinical PainDocument8 pagesFisiopatologia Da Dor - Clinical PainEnzoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Basis of Life Organic Compounds: By: Ej R. Agsalda Bsbio-1Document15 pagesChemical Basis of Life Organic Compounds: By: Ej R. Agsalda Bsbio-1Ej AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- BME 553 Exam IDocument12 pagesBME 553 Exam Imgnieves11No ratings yet
- Potent Half-Sandwich Iridium (III) and Ruthenium (II) Anticancer Complexes Containing A P O-Chelated LigandDocument10 pagesPotent Half-Sandwich Iridium (III) and Ruthenium (II) Anticancer Complexes Containing A P O-Chelated LigandFernandaIbarraVázquezNo ratings yet
- Various Expression SystemDocument15 pagesVarious Expression SystemVamsi K KuchibhotlaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Microbiological Methods: SciencedirectDocument7 pagesJournal of Microbiological Methods: Sciencedirectfrancis3ndourNo ratings yet
- 09 Regulation of Gene ExpressionDocument42 pages09 Regulation of Gene ExpressionFirst Anonym877No ratings yet
- General Information On Cancer: Accumulation of Mutations Uncontrolled Cell DivisionDocument24 pagesGeneral Information On Cancer: Accumulation of Mutations Uncontrolled Cell DivisionMario and Krinon MocciaNo ratings yet
- Glutathione FinalDocument33 pagesGlutathione Finalapi-103232543No ratings yet
- Otot 2Document106 pagesOtot 2anita parwatiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2B Guided Notes 2022Document6 pagesUnit 2B Guided Notes 2022Victoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Postharvest Biology and Technology: A A A B C A D DDocument10 pagesPostharvest Biology and Technology: A A A B C A D DRestrepo JuanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Dna Isolation & PurificationDocument10 pagesPrinciples of Dna Isolation & PurificationRatish Singh50% (2)
- Dna Gel Electrophoresis: Gateway To Various Biotechnology InvestigationsDocument16 pagesDna Gel Electrophoresis: Gateway To Various Biotechnology InvestigationsNasrullah RoslanNo ratings yet
Untitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
dhwiwdh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views32 pages The best statement is 3. The document states that intermediate filaments are the most stable (not dynamic) types of cytoskeleton and play a structural role by resisting tension on the cell.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document The best statement is 3. The document states that intermediate filaments are the most stable (not dynamic) types of cytoskeleton and play a structural role by resisting tension on the cell.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views32 pagesUntitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
dhwiwdh The best statement is 3. The document states that intermediate filaments are the most stable (not dynamic) types of cytoskeleton and play a structural role by resisting tension on the cell.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 32
Cytoskeleton & Cell inclusions
1- Cytoskeleton: Types, structure & functions.
2- Centrosome: Structure & function.
3- Cell inclusions: Types.
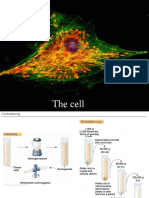
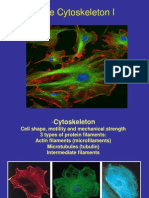
Cytoskeleton
• The cytoskeleton is a network of structural
proteins(non-membranous cell organelles).
Types of cytoskeleton
• 3 types, depending on their thickness& their
structural proteins:
1- Microfilaments.
2- Microtubules.
3- Intermediate filaments.
1-Microfilaments (actin filaments)
• Diameter: 7 nm.
• LM: can be visualized by using
immunohistochemical staining.
1-Microfilaments (actin filaments)
• EM: thin electron dense filaments.
• Structural proteins: monomers of G-actin
(globular actin) polymerize to form F-actin
(filamentous actin) arranged as a double
helix.
They are dynamic structures that can elongate and shorten
Functions of microfilaments
A- Cell motility for:
Cell migration.
Cytoplasmic streaming: during movement
of organelles and transport of vesicles.
Cytokinesis:formation of contractile ring
during cell division.
Muscle contraction associated with
myosin.
B-Structural role:
Maintenance of the cell shape.
Formation the core of microvilli.
2-Microtubules
• Diameter: 25 nm.
• LM picture: by using
immunohistochemical staining.
• EM picture: fine tubules.
• Structural proteins:
A- a globular protein dimer called
tubulin (each is composed of alpha and
beta subunits).
B- Chains of tubulin dimers form a
protofilament.
C- The wall of a microtubule is made up
of 13 protofilaments that run
longitudinally.
Motor proteins associated with microtubules
Kinesin and dynein; they use ATP to
provide energy for movement of vesicles
and organelles along the microtubules.
Microtubules are dynamic structures; can elongate and
shorten
Functions of microtubules
1- Transport: of organelles and
vesicles in the cytoplasm.
2- Structural role:
• Formation of the mitotic spindle.
• Formation of centrioles, cilia &
flagella.
The microtubule organizing centers
1- Centriole which forms the mitotic spindle.
2- The basal bodies of cilia and flagella.
3- Intermediate filaments
• Diameter:10 nm
• LM : by using immunohistochemical staining.
• EM : electron dense filaments thicker than
actin filaments.
• Structural proteins: like woven ropes.
Function of intermediate filaments
• They are the most stable (not dynamic) types of the cytoskeletal
thus they play a structural role .
Classification of intermediate filaments
• According to their protein composition and
their cellular distribution into:
A- Cytoplasmic:
1- Keratin: epithelial cells.
2- Vimentin: in the cells of mesenchymal
origin e.g. fibroblasts.
3- Desmin: muscle cells.
4- Glial fibrillary acidic protein: neuroglia.
5- Neurofilaments: nerve cells.
B- Nuclear:
• Lamins: lining the inner nuclear envelope.
Intermediate filaments
The intermediate filaments (except for the lamins)
are located in specific tissue types; they can be
used to determine the origin of cancer by
immunohistochemical staining.
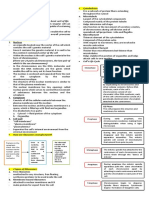
Cytoskeleton Microfilaments Microtubules Intermediate filaments
1- diameter 7 nm. 25 nm. 10 nm.
2- LM Seen only by immunohistochemistry. Seen only by Seen only by
immunohistochemistry immunohistochemistry
3- EM Thin electron dense filaments. Fine tubules. Thicker electron dense
filaments.
4- Structural Monomers of G actin polymerize to form F Tubulin dimer polymerize to Woven ropes.
proteins actin. protofilaments.
13 protofilaments form a
microtubule,
5- Functions Dynamic Dynamic. Not dynamic.
1- Muscle contraction. 1- Transport of organelles & Structural support.
2- Contractile ring in cell division. vesicles.
3- Pseudopodia in migration. 2- Formation of centrioles, cilia
4- Microvilli. & flagella.
5- Cytoplasmic streaming.
Centrosomes
Centrosome
• Definition: a non-membranous organelle.
• EM:
1- It is formed of 2 centrioles, perpendicular
to each other.
2- Each centriole is composed of 9 triplets of
microtubules (a sum of 27 microtubules).
3- Each triplet is composed of three
microtubules (one complete; formed of 13
protofilaments and 2 incomplete;each is
formed of 10 protofilaments).
Functions of centrosome
1- It is the microtubule- organizing
center.
2- Formation of mitotic spindles.
3- Formation of cilia and flagella.
Cytoplasmic inclusions
1- Stored food
A-Glycogen
• Storage form of carbohydrates.
• Function: source of energy.
• Sites: mainly in liver and muscle cells.
• LM:
H&E: not visualized as they dissolve during
preparation of the specimen leaving a pale
vacuolated cytoplasm.
Periodic-acid Schiff: appears magenta red.
Best's carmine:appears bright red.
• EM: dense granules, larger than ribosomes. In
cytoplasm of hepatocytes, glycogen appears
as rosette-shaped aggregates
B-Lipids
• Function:
1- Source of energy.
2- Synthesis of membranes and steroid hormones.
• Sites: stored in the adipocytes; many other cell types
contain few small lipid droplets.
• LM:
H&E: not visualized because they dissolve during
preparation of the specimen leaving a pale vacuolated
cytoplasm.
Osmium tetroxide: appear black.
• EM: grey non- membrane bounded small droplets or
large globules.
C-Proteins
• Site: in protein- synthesizing cells e.g.
salivary gland and pancreas.
• LM: eosinophilic zymogen granules.
• EM: homogenous electron dense
membrane-bounded secretory granules.
2- Pigments
A-Endogenous pigments
1- Hemoglobin: in red blood cells.
2- Hemosiderin: brownish granules in
phagocytic cells of liver and spleen
following phagocytosis of old RBCs.
3- Melanin pigment: brown to black
granules.
4- Lipofuscin pigment: yellow-brown
pigment present in cells with long life
span.
B- Exogenous pigments
1- Tattooing: colored pigments are
injected into the deep layers of the
skin.
2- Dust and smokes: in lung of
smokers and people living in polluted
areas.
Which statement is the best to describe the
intermediate filaments?
1- They are dynamic structure that maintain the cell shape.
2- They are responsible for movement of organelles and vesicles.
3- They are permanent structures that resist tension exerted on the
cell.
4- They form the core of microvilli.
Which statement is the best to describe the
intermediate filaments?
1- They are dynamic structure that maintain the cell shape.
2- They are responsible for movement of organelles and vesicles.
3- They are permanent structures that resist tension exerted on the
cell.
4- They form the core of microvilli.
You might also like
- Human Genetics Concepts and Applications 11Th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument29 pagesHuman Genetics Concepts and Applications 11Th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFmagdalavicemanocgp100% (13)
- Plant Pigments and Photosynthesis Lab ReportDocument4 pagesPlant Pigments and Photosynthesis Lab ReportAnthony64% (22)
- AP Biology Name - Chapter 6 Guided Reading AssignmentDocument6 pagesAP Biology Name - Chapter 6 Guided Reading AssignmentRobert Ladaga33% (3)
- CytoskeletonDocument65 pagesCytoskeletonSapana SubediNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument24 pagesCell StructureA. AsadiNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton SNDocument3 pagesCytoskeleton SNsamy gNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument2 pagesAmino Acids and ProteinsyejiNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument40 pagesConnective TissueMoayad albeshriNo ratings yet
- BM 1 1 CytoskeletonDocument24 pagesBM 1 1 CytoskeletonSanthoshi Sadhanaa SankarNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton Motor Proteins and ECM - SCDocument77 pagesCytoskeleton Motor Proteins and ECM - SCAlice RizzoNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton DADocument35 pagesCytoskeleton DAAnonymous NVBCqKWHNo ratings yet
- Cytology - 1Document13 pagesCytology - 1Sumayya KabeerNo ratings yet
- Cell and EpitheliumDocument11 pagesCell and EpitheliumMichael DamazoNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument52 pagesConnective TissueMaxamed Faarax XaashiNo ratings yet
- CytoskeletonDocument6 pagesCytoskeletonPreethaNo ratings yet
- 6 10-CytoplasmDocument27 pages6 10-CytoplasmAbbas TalibNo ratings yet
- General Characteristics: of Mitochondria 1 Methods of StudyDocument7 pagesGeneral Characteristics: of Mitochondria 1 Methods of StudypaulaNo ratings yet
- Cy To SkeletonDocument21 pagesCy To SkeletonJisna JaisonNo ratings yet
- C & M Bio CytoskeletonDocument40 pagesC & M Bio CytoskeletonA PNo ratings yet
- BIO 35 Chapter 1B - Cell Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument11 pagesBIO 35 Chapter 1B - Cell Anatomy and PhysiologyJake EverettNo ratings yet
- Techno-1.1-The CellDocument37 pagesTechno-1.1-The CellMark DeGrootteNo ratings yet
- CytosceletonDocument41 pagesCytosceletonaidar.seralinNo ratings yet
- MembrDocument43 pagesMembrnadaahmd2040No ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton MADocument22 pagesCytoskeleton MAsema raraNo ratings yet
- CytoskeletonDocument27 pagesCytoskeletonserenity limNo ratings yet
- Reflective Journal For Module 2 Unit 1: Name: Yulo, Ires A. Section: BSED-SCI.3-BDocument6 pagesReflective Journal For Module 2 Unit 1: Name: Yulo, Ires A. Section: BSED-SCI.3-Bguirillita acutNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton and Cell Motility 1Document40 pagesCytoskeleton and Cell Motility 1Muhamad Farhan RLNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy: The CellDocument33 pagesHuman Anatomy: The CellramadanNo ratings yet
- 11.sitoskeleton Dan Pergerakan Sel-Dr - IsraDocument40 pages11.sitoskeleton Dan Pergerakan Sel-Dr - IsraTa RaNo ratings yet
- BY2201 EmmaC CytoskeletonIandIIDocument62 pagesBY2201 EmmaC CytoskeletonIandIIRebecca ReillyNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology - Part 1: 1) Plasma Membrane 2) CytoskeletonDocument18 pagesCell Biology - Part 1: 1) Plasma Membrane 2) CytoskeletonBeTy AgustinNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 CellsDocument1 pageTopic 2 CellsKandy Anne Castillo AbuanNo ratings yet
- Muscular TDocument18 pagesMuscular TSumayya KabeerNo ratings yet
- 2cytology Cytoskel Receptor Transp (3) 1Document43 pages2cytology Cytoskel Receptor Transp (3) 1m.mansoor3377No ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton PRESENTATIONDocument36 pagesCytoskeleton PRESENTATIONChaudryNomiNo ratings yet
- Prepared By:-: Priyanka Yadav M.Sc. Life Sciences Ist SemDocument37 pagesPrepared By:-: Priyanka Yadav M.Sc. Life Sciences Ist SemleartaNo ratings yet
- 3 CellsDocument6 pages3 CellsEly FructuosoNo ratings yet
- February 27, 2012 - Chapter 7: Inside The CellDocument4 pagesFebruary 27, 2012 - Chapter 7: Inside The CellVincent Troy SantosNo ratings yet
- The Cytoskeleton Is A Network of Filament and Tubules That Extends Throughout A CellDocument9 pagesThe Cytoskeleton Is A Network of Filament and Tubules That Extends Throughout A CellHania GulNo ratings yet
- Centro, MF. Module - 6.Document9 pagesCentro, MF. Module - 6.jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Question Sheet+ Notes All TopicsDocument19 pagesQuestion Sheet+ Notes All TopicsSidraNo ratings yet
- 8 Cell - The Unit of Life-NotesDocument6 pages8 Cell - The Unit of Life-NotesBhavanya RavichandrenNo ratings yet
- 8 Cell - The Unit of Life-NotesDocument6 pages8 Cell - The Unit of Life-NotesdeveshjayakumaryadavNo ratings yet
- 3011 Doc 20240327 Wa0021.Document24 pages3011 Doc 20240327 Wa0021.vavc720No ratings yet
- MODULE 2.2 Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument11 pagesMODULE 2.2 Cellular Level of OrganizationKate Andrea PanizalesNo ratings yet
- M PRtpbo Fxo F46 YBll E9 HDocument5 pagesM PRtpbo Fxo F46 YBll E9 Hrudrakumbhar2005No ratings yet
- The CytoskeletonDocument9 pagesThe CytoskeletonElena OlmedoNo ratings yet
- The CytoskeletonDocument63 pagesThe CytoskeletonAmara TargaryenNo ratings yet
- The CytoskeletonDocument31 pagesThe CytoskeletonSanthoshsv 143No ratings yet
- Connective Tissue (CT)Document37 pagesConnective Tissue (CT)Fady FadyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document153 pagesLecture 3Miya GordNo ratings yet
- 2.4 - Eukaryotic Cell StructureDocument12 pages2.4 - Eukaryotic Cell Structurejpvnym85gdNo ratings yet
- 6.1-How Are Cells Studied?: Magnification Resolution Contrast Electron Microscope (EM)Document7 pages6.1-How Are Cells Studied?: Magnification Resolution Contrast Electron Microscope (EM)Sadasivarao GaddeNo ratings yet
- Thecytoskeleton PPTDocument11 pagesThecytoskeleton PPTseenu mohapatra100% (1)
- Module 2.2 Cellular Basis of LifeDocument10 pagesModule 2.2 Cellular Basis of LifechellesuguitanNo ratings yet
- IkatDocument38 pagesIkatReenha TrisnawatiNo ratings yet
- Summary NotesDocument14 pagesSummary NotesNo-Face. PersonaNo ratings yet
- Cell The Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesCell The Unit of LifeRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Unit 2 - Cell Structure and FunctionDocument12 pagesAP Biology Unit 2 - Cell Structure and FunctionSam SankarNo ratings yet
- From Tubulin to Thought: The Nexus of Cytoskeleton Microtubules and Brain Complexity.From EverandFrom Tubulin to Thought: The Nexus of Cytoskeleton Microtubules and Brain Complexity.No ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- ParaphrasingDocument12 pagesParaphrasingdhwiwdhNo ratings yet
- To CommunicationDocument63 pagesTo CommunicationdhwiwdhNo ratings yet
- 5 Minute Self Introduction Speech TemplateDocument2 pages5 Minute Self Introduction Speech TemplatedhwiwdhNo ratings yet
- Glutamato Deamination by Oxidation Is Readily ReversibleDocument9 pagesGlutamato Deamination by Oxidation Is Readily ReversibledhwiwdhNo ratings yet
- Valid and Invalid Arguments: CS 202 Epp Section 1.3 Aaron BloomfieldDocument17 pagesValid and Invalid Arguments: CS 202 Epp Section 1.3 Aaron BloomfielddhwiwdhNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitleddhwiwdhNo ratings yet
- Biology Depth Study - Cystic FibrosisDocument7 pagesBiology Depth Study - Cystic FibrosisDog DogNo ratings yet
- Neurohealth Properties of Hericium Erinaceus MycelDocument11 pagesNeurohealth Properties of Hericium Erinaceus Myceldokan42No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan PatrickDocument4 pagesLesson Plan PatrickPatrick Jerome SilvanoNo ratings yet
- Cell SignalingDocument87 pagesCell SignalingZaw Linn PhyoNo ratings yet
- Mineralocorticoids: Shajeer. SDocument42 pagesMineralocorticoids: Shajeer. SShajeer SalimNo ratings yet
- Genbio2 Lesson 1 Plant and Animal Nutrition Part 1Document32 pagesGenbio2 Lesson 1 Plant and Animal Nutrition Part 1crystal janr macalisangNo ratings yet
- Biology 9 O Level Test PaperDocument10 pagesBiology 9 O Level Test PaperAllam S/o Mumtaz Ali TunioNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Starch DigestionDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Starch DigestionNikki Ticman100% (1)
- WHLP StemDocument8 pagesWHLP Stemcristina maquintoNo ratings yet
- Physci 111A Lecture 1 XX PDFDocument31 pagesPhysci 111A Lecture 1 XX PDFJASMINE LOUIENo ratings yet
- Introduction To CytogeneticsDocument39 pagesIntroduction To CytogeneticsAnderson AliNo ratings yet
- IBO 2010 Korea Theory Paper 1Document61 pagesIBO 2010 Korea Theory Paper 1Bikash Ranjan RayNo ratings yet
- Biotechnologies: Past History, Present State and Future ProspectsDocument16 pagesBiotechnologies: Past History, Present State and Future ProspectsJuana RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Protocolo Purificacion Desde GelDocument3 pagesProtocolo Purificacion Desde GelAriel ArayaNo ratings yet
- Fisiopatologia Da Dor - Clinical PainDocument8 pagesFisiopatologia Da Dor - Clinical PainEnzoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Basis of Life Organic Compounds: By: Ej R. Agsalda Bsbio-1Document15 pagesChemical Basis of Life Organic Compounds: By: Ej R. Agsalda Bsbio-1Ej AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- BME 553 Exam IDocument12 pagesBME 553 Exam Imgnieves11No ratings yet
- Potent Half-Sandwich Iridium (III) and Ruthenium (II) Anticancer Complexes Containing A P O-Chelated LigandDocument10 pagesPotent Half-Sandwich Iridium (III) and Ruthenium (II) Anticancer Complexes Containing A P O-Chelated LigandFernandaIbarraVázquezNo ratings yet
- Various Expression SystemDocument15 pagesVarious Expression SystemVamsi K KuchibhotlaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Microbiological Methods: SciencedirectDocument7 pagesJournal of Microbiological Methods: Sciencedirectfrancis3ndourNo ratings yet
- 09 Regulation of Gene ExpressionDocument42 pages09 Regulation of Gene ExpressionFirst Anonym877No ratings yet
- General Information On Cancer: Accumulation of Mutations Uncontrolled Cell DivisionDocument24 pagesGeneral Information On Cancer: Accumulation of Mutations Uncontrolled Cell DivisionMario and Krinon MocciaNo ratings yet
- Glutathione FinalDocument33 pagesGlutathione Finalapi-103232543No ratings yet
- Otot 2Document106 pagesOtot 2anita parwatiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2B Guided Notes 2022Document6 pagesUnit 2B Guided Notes 2022Victoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Postharvest Biology and Technology: A A A B C A D DDocument10 pagesPostharvest Biology and Technology: A A A B C A D DRestrepo JuanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Dna Isolation & PurificationDocument10 pagesPrinciples of Dna Isolation & PurificationRatish Singh50% (2)
- Dna Gel Electrophoresis: Gateway To Various Biotechnology InvestigationsDocument16 pagesDna Gel Electrophoresis: Gateway To Various Biotechnology InvestigationsNasrullah RoslanNo ratings yet