Professional Documents
Culture Documents
More Colour Research
More Colour Research
Uploaded by
api-652525025Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
More Colour Research
More Colour Research
Uploaded by
api-652525025Copyright:
Available Formats
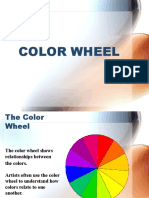
Hue, Tint, Shade and Tone
The hue of a colour refers to a family of colours on the colour wheel.
The Tint of a colour is the amount of white added to make a colour lighter.
The Shade is the amount of black added to make a colour darker.
The Tone is when grey is added to make a colour softer.
Monochrome Colour
Monochrome is where only one colour is used or is used as a base colour.
This is useful for creating simple designs and is usually easy to use and understand.
Achromatic Colour
Achromatic colours aren’t colours at all and only use greyscale. An achromatic colour
scheme only uses black and white shades but is still an effective colour choice.
Analogous Colours
These are colours that are very similar to each other and usually adjacent in the colour
wheel. For example, red, orange and yellow.
Complementary Colours
These are colours that are opposite to each other on the colour wheel and look good when
put together. For example, red and blue.
Triadic Colours
A colour scheme where there are 3 evenly spaced colours on the wheel put together.
Orange, blue and green together is an example of this.
Split Complementary Colours
A colour scheme made using a base colour and two secondary colours. If blue was chosen
for example, the split complementary colours would be pink and orange.
You might also like
- Color TheoryDocument21 pagesColor TheoryRemya71% (7)
- Prang Color TheoryDocument15 pagesPrang Color TheoryRemya86% (7)
- Color WheelDocument16 pagesColor WheelZarsha NaveedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Color TheoryDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Color Theoryis gueNo ratings yet
- Color Theory For Floral DesignDocument26 pagesColor Theory For Floral Design82031142100% (1)
- Black Etc. Color Derives From The Spectrum of Light (Distribution of Light Energy VersusDocument11 pagesBlack Etc. Color Derives From The Spectrum of Light (Distribution of Light Energy VersusRemyaNo ratings yet
- Dyad Triad and TetradDocument3 pagesDyad Triad and TetradFarhan SuraniNo ratings yet
- Color TheoryDocument12 pagesColor TheoryheygirlheyNo ratings yet
- Color TheoryDocument37 pagesColor TheoryBurhan PashaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 2 - Hiran Wijesekara Design AcademyDocument7 pagesLecture Notes 2 - Hiran Wijesekara Design Academydraping pattern sloperNo ratings yet
- Ethiopian Institute of Textile and Fashion Technology (Eitex) Bahir Dar UniversityDocument36 pagesEthiopian Institute of Textile and Fashion Technology (Eitex) Bahir Dar UniversityNati TsedekeNo ratings yet
- Complementary Colors That Are Opposite Each Other On The ColorDocument1 pageComplementary Colors That Are Opposite Each Other On The ColorLevin Claire VinoyaNo ratings yet
- Color Harmonies PDFDocument3 pagesColor Harmonies PDFSamudra GuptaNo ratings yet
- Color Theory 101Document11 pagesColor Theory 101Rui Jorge100% (2)
- Minimalist Quote PosterDocument4 pagesMinimalist Quote PosterSyruz Mortega BanquilayNo ratings yet
- March GoalsDocument3 pagesMarch Goalsapi-295142988No ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Color PsychologyDocument52 pagesLecture 9 Color Psychologymusamach295No ratings yet
- Electrical Installation MaintenanceDocument7 pagesElectrical Installation MaintenanceAlken KentNo ratings yet
- Monochromatic HarmonyDocument2 pagesMonochromatic HarmonyLith EspinNo ratings yet
- Colors DocDocument12 pagesColors DocTeorija PajaclukaNo ratings yet
- 2art First Grading Educ Lesson 2 - Value and ColorDocument102 pages2art First Grading Educ Lesson 2 - Value and Colorapi-288938459100% (1)
- Color SchemeDocument4 pagesColor SchemeinteriorsignetNo ratings yet
- Colour DetailDocument52 pagesColour DetailRadhika Rajeev100% (2)
- D 2Document6 pagesD 2Kimberly Etulle CelonaNo ratings yet
- Colour: Element of Design: Color TerminologyDocument25 pagesColour: Element of Design: Color Terminologymanmohansinghlotey100% (1)
- Colour in Design and GraphicsDocument8 pagesColour in Design and GraphicsGlorious GullyNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Interior Design: Name: Yew Jing Hui Student ID: 2014050061 Prepared For: Ms. CherylDocument16 pagesDiploma in Interior Design: Name: Yew Jing Hui Student ID: 2014050061 Prepared For: Ms. CherylSrishti JainNo ratings yet
- Color TheoryDocument19 pagesColor Theorysmitharao100% (1)
- 7 ColorsDocument39 pages7 Colorspratima1823100% (1)
- Color Presentation PDFDocument186 pagesColor Presentation PDFYoe Putra Paddong100% (2)
- Psychology of ColorsDocument28 pagesPsychology of ColorsLaira LicudineNo ratings yet
- Psychology of ColorDocument32 pagesPsychology of ColorRICHARD BLANDININo ratings yet
- Colors and Color MixingDocument10 pagesColors and Color MixingCydryck OlivaNo ratings yet
- Color HarmoniesDocument6 pagesColor Harmoniesmark aley solimanNo ratings yet
- Color TheoryDocument18 pagesColor TheoryReniel MarkNo ratings yet
- Color WheelDocument30 pagesColor WheelJasmin Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Grade 9, Color TheoryDocument35 pagesGrade 9, Color TheoryLily Riddle MalfoyNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Part IIDocument20 pagesModule 3 Part IIKanchan ManhasNo ratings yet
- Color Theory: Reference Book For The Serious Art Student: "An Introduction To Art Techniques"Document23 pagesColor Theory: Reference Book For The Serious Art Student: "An Introduction To Art Techniques"pacifistlightNo ratings yet
- Color Harmonies: Basic Techniques For Combining ColorsDocument5 pagesColor Harmonies: Basic Techniques For Combining ColorsRhea Blny MñgNo ratings yet
- Color TheoriesDocument10 pagesColor TheoriesmanmohansinghloteyNo ratings yet
- Creating Color Harmony 2021Document24 pagesCreating Color Harmony 2021Omkar LagadNo ratings yet
- Color WheelDocument2 pagesColor Wheelsardonidos Fidel Jr.No ratings yet
- ColorDocument10 pagesColorMUHAMMAD Al rayanNo ratings yet
- Color TheoryDocument38 pagesColor TheorySajid Holy83% (6)
- Color TheoryDocument29 pagesColor TheoryAnshul RaskarNo ratings yet
- Psychology of Color2Document33 pagesPsychology of Color2abdikani abdilaahiNo ratings yet
- Colors Colors: Ar. Diane A. JoseDocument65 pagesColors Colors: Ar. Diane A. JoseTrisha LlamesNo ratings yet
- ColorTheory DONEDocument5 pagesColorTheory DONEErika Joy TacordaNo ratings yet
- Basic Color Schemes Introduction To Color TheoryDocument5 pagesBasic Color Schemes Introduction To Color TheoryRei Gaius LacanariaNo ratings yet
- A Color Wheel Consisting of Primary - ZahraDocument12 pagesA Color Wheel Consisting of Primary - Zahrazahrabncdxb100% (1)
- Color TheoryDocument16 pagesColor TheoryNursana AbdurajaNo ratings yet
- 10.1 Color FundamentalsDocument11 pages10.1 Color FundamentalsCarlo RosaioNo ratings yet
- Color TheoryDocument20 pagesColor TheoryEarl Quinn VarillaNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To Color TypesDocument10 pages1.introduction To Color TypesAmrita TomarNo ratings yet
- Color WheelDocument15 pagesColor WheelHayna SoldeNo ratings yet
- Color WheelDocument15 pagesColor WheelSelle AbayanNo ratings yet
- Color Wheel & Schemes With Window DisplaysDocument34 pagesColor Wheel & Schemes With Window DisplaysChanchal bathamNo ratings yet
- Q2 Week 5-6 TLE 7Document2 pagesQ2 Week 5-6 TLE 7sardonidos Fidel Jr.No ratings yet
- Special Subjects: Basic Color Theory: An Introduction to Color for Beginning ArtistsFrom EverandSpecial Subjects: Basic Color Theory: An Introduction to Color for Beginning ArtistsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Script ExampleDocument1 pageScript Exampleapi-652525025No ratings yet
- FMP Statement of Aims - OriginalDocument5 pagesFMP Statement of Aims - Originalapi-652525025No ratings yet
- FMP Risk AssesmentDocument3 pagesFMP Risk Assesmentapi-652525025No ratings yet
- FMP Location RecDocument2 pagesFMP Location Recapi-652525025No ratings yet
- Movement ResearchDocument1 pageMovement Researchapi-652525025No ratings yet
- Call Sheet 2022 1Document1 pageCall Sheet 2022 1api-652525025No ratings yet
- Colour Research Page 1Document2 pagesColour Research Page 1api-652525025No ratings yet
- Production ScheduleDocument1 pageProduction Scheduleapi-652525025No ratings yet
- Primary Research - FinalDocument2 pagesPrimary Research - Finalapi-652525025No ratings yet
- TV Ad Evaluation FinalDocument2 pagesTV Ad Evaluation Finalapi-652525025No ratings yet
- Exploring Sound Worksheet FinalDocument3 pagesExploring Sound Worksheet Finalapi-652525025No ratings yet
- Secondary Research - FinalDocument2 pagesSecondary Research - Finalapi-652525025No ratings yet
- Exploring Research WorksheetDocument3 pagesExploring Research Worksheetapi-652525025No ratings yet