Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsContemp
Contemp
Uploaded by
Irold SanchezEconomic globalization refers to the increasing interdependence of world economies through cross-border trade, capital flows, and spread of technologies. While globalization is not new, having occurred throughout history, the current level of global economic integration is unprecedented. Convergence describes trends moving together, while divergence describes trends moving apart. International monetary systems establish rules for payments, exchange rates, and capital movement and have evolved from the gold standard to the Bretton Woods system to today's floating currencies. Trade policies and agreements, whether unilateral or multilateral, influence the flow of goods between nations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- NF - Apple EUADocument2 pagesNF - Apple EUAgustavogko01100% (1)
- 02 Worksheet 1 TCWDocument2 pages02 Worksheet 1 TCWJericho FajardoNo ratings yet
- Activities For Lesson 2Document7 pagesActivities For Lesson 2KATHLEEN BALBOANo ratings yet
- INDIVIDUALASSIGNMENT3Document2 pagesINDIVIDUALASSIGNMENT3Lee Louise Andrew E. CaoNo ratings yet
- The Contemporary World: 02 Worksheet 1Document3 pagesThe Contemporary World: 02 Worksheet 1Ashley AcuñaNo ratings yet
- International Financial SystemDocument75 pagesInternational Financial SystemRaghu PrasadNo ratings yet
- International Finance: THE GOLD STANDARD (1876-1913)Document20 pagesInternational Finance: THE GOLD STANDARD (1876-1913)sujata11No ratings yet
- Bus 420 International Monetary SystemDocument7 pagesBus 420 International Monetary SystemYomi BrainNo ratings yet
- The International Monetary System: Exchange Rate RegimeDocument4 pagesThe International Monetary System: Exchange Rate RegimeAyeshasaddique turkNo ratings yet
- International Monetary SystemDocument7 pagesInternational Monetary SystemAmethyst NocelladoNo ratings yet
- Internal FinanceDocument7 pagesInternal Financeakhlaqur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Evolution of IMSDocument8 pagesEvolution of IMSpayalmulchandani15No ratings yet
- Review CLC.T5.2024Document7 pagesReview CLC.T5.2024Nguyễn Duy ĐạtNo ratings yet
- Global Economy NotesDocument4 pagesGlobal Economy Notes2022-201417No ratings yet
- Monetary System Chapter 3 (WWW - Bustudymate.in (BUStudymate - In)Document18 pagesMonetary System Chapter 3 (WWW - Bustudymate.in (BUStudymate - In)aitshailajamlNo ratings yet
- Evolution of International MonetaryDocument7 pagesEvolution of International MonetaryManish KumarNo ratings yet
- WK 3 ContempDocument34 pagesWK 3 Contempaprilstamaria0427No ratings yet
- The Global Economy ReportDocument11 pagesThe Global Economy ReportAlvin BautistaNo ratings yet
- Magbanua, Christian Mod.7 QuizdocxDocument2 pagesMagbanua, Christian Mod.7 QuizdocxChristian MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- International Finance Ass 2Document5 pagesInternational Finance Ass 2Sugen RajNo ratings yet
- Ibt 8Document10 pagesIbt 8tenyente gimoNo ratings yet
- International Monetary SystemsDocument19 pagesInternational Monetary SystemsIdrees BharatNo ratings yet
- International Monetary System and The Balance of Payments: Week 4 Abdul Halim, BSM, MBADocument22 pagesInternational Monetary System and The Balance of Payments: Week 4 Abdul Halim, BSM, MBApardamaianNo ratings yet
- Socsci Mod1 To 6Document34 pagesSocsci Mod1 To 6VILLARANTE, CHRESSYLE ANNE FABIALANo ratings yet
- Unit 2.1 2020-2021Document36 pagesUnit 2.1 2020-2021Chinkee LorzanoNo ratings yet
- International FinanceDocument3 pagesInternational FinanceRiyaNo ratings yet
- Mohamad Hafiz Bin Ahmad RadziDocument9 pagesMohamad Hafiz Bin Ahmad RadziMohd HafizNo ratings yet
- A General Introduction To International Economic LawDocument20 pagesA General Introduction To International Economic LawОля КозакNo ratings yet
- Assignment of IfDocument7 pagesAssignment of IfAnand SinghNo ratings yet
- The Global EconomyDocument8 pagesThe Global EconomyRaven Evangelista CanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document31 pagesUnit 1PSBALARAMNo ratings yet
- GE4 Discussion Task - Module 2Document2 pagesGE4 Discussion Task - Module 2Junielle AutajayNo ratings yet
- 8 International Monetary System PDFDocument22 pages8 International Monetary System PDFdevesh_mendiratta_61No ratings yet
- Economic Project Praveen Patil 1Document38 pagesEconomic Project Praveen Patil 1Rahul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of The International Monetary SystemDocument12 pagesThe Evolution of The International Monetary SystemAbhijeet Gupta 1513No ratings yet
- Contemporary World 3Document62 pagesContemporary World 3Adrian AndalNo ratings yet
- International Monetary SystemDocument6 pagesInternational Monetary SystemPragya KasanaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Finance Markets Investments and Financial Management 15th Edition Melicher Solutions ManualDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Finance Markets Investments and Financial Management 15th Edition Melicher Solutions Manualquandiendjv100% (24)
- Floating A CurrencyDocument3 pagesFloating A Currencykorum8urraNo ratings yet
- Welcome To: International Finance: by Amit Kumar Harsh Kumar Balkar SinghDocument32 pagesWelcome To: International Finance: by Amit Kumar Harsh Kumar Balkar Singhbally_bNo ratings yet
- International Business and TradeDocument3 pagesInternational Business and Tradejntvtn7pc9No ratings yet
- The International Institution The Bretton Wood System General Agreement On GATT and The World Trade OrganizationDocument20 pagesThe International Institution The Bretton Wood System General Agreement On GATT and The World Trade OrganizationShanlane CoronelNo ratings yet
- Assignment On International Monetary System: Prepared ForDocument6 pagesAssignment On International Monetary System: Prepared ForMd Nazmus SakibNo ratings yet
- International Monetary SystemDocument4 pagesInternational Monetary SystemHassani AllyNo ratings yet
- Understanding The International Monetary SystemDocument7 pagesUnderstanding The International Monetary SystemSteve BaronNo ratings yet
- International BankingDocument62 pagesInternational BankingDjSunil SkyNo ratings yet
- Evaluating The International Monetary System and The Availability To Move Towards One Single Global CurrencyDocument25 pagesEvaluating The International Monetary System and The Availability To Move Towards One Single Global Currencyboomfox17No ratings yet
- Week 4 EC 304Document9 pagesWeek 4 EC 304Mustafa KhanNo ratings yet
- Evolution of The International Monetary Systems: Unit 5 SectionDocument4 pagesEvolution of The International Monetary Systems: Unit 5 SectionBabamu Kalmoni JaatoNo ratings yet
- Internation FinanceDocument9 pagesInternation FinancemanishaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 World Financial EnvironmentDocument6 pagesUnit 4 World Financial EnvironmentTharun VelammalNo ratings yet
- FinanceDocument9 pagesFinanceck124881No ratings yet
- F31 Foreign Exchange: 1. What Is The Importance of The Field You Have Chosen?Document4 pagesF31 Foreign Exchange: 1. What Is The Importance of The Field You Have Chosen?Holy BunkersNo ratings yet
- Forex ManagementDocument57 pagesForex ManagementKriti VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Navigation Search International Monetary Systems LTDDocument6 pagesNavigation Search International Monetary Systems LTDInnovative AkibNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rate SystemsDocument27 pagesExchange Rate SystemsmaurishkaNo ratings yet
- Review QuestionsDocument2 pagesReview QuestionsHads LunaNo ratings yet
- Module 9 - Foreign Exchange MarketsDocument9 pagesModule 9 - Foreign Exchange MarketsChris tine Mae MendozaNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Factors Affecting TradeDocument36 pagesMacroeconomic Factors Affecting TradeErika Bermas MedenillaNo ratings yet
- SurveyDocument2 pagesSurveyIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Info ManagemtntDocument1 pageInfo ManagemtntIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Info ManagemtntDocument1 pageInfo ManagemtntIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Chapter 1 5 BodyDocument28 pagesPart 2 Chapter 1 5 BodyIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- NSTPDocument2 pagesNSTPIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Preliminaries - To PrintDocument17 pagesPreliminaries - To PrintIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Zamora BiodataDocument1 pageZamora BiodataIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- TatanDocument3 pagesTatanIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- SE 411 - Deliverable - Part 2Document3 pagesSE 411 - Deliverable - Part 2Irold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Putanginang ResearchDocument14 pagesPutanginang ResearchIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Reflection: Irold Jerald A. Sanchez Bsit-1BDocument1 pageReflection: Irold Jerald A. Sanchez Bsit-1BIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- 04 Readings 1Document2 pages04 Readings 1Irold SanchezNo ratings yet
- BalanaDocument17 pagesBalanaIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- SE 411 - Deliverable - Part 1Document10 pagesSE 411 - Deliverable - Part 1Irold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Summary of cs495 - 01Document3 pagesSummary of cs495 - 01Irold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Chapteer 2Document2 pagesChapteer 2Irold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Eye Lab 7Document1 pageEye Lab 7Irold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument8 pagesCase StudyIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Dlori KenkenDocument3 pagesDlori KenkenIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Answers Midterm ActDocument3 pagesAnswers Midterm ActIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Job InterviewDocument1 pageJob InterviewIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- 02 Assignment 1Document1 page02 Assignment 1Irold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Midterm Activity 01Document6 pagesMidterm Activity 01Irold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise 1Document1 pageLaboratory Exercise 1Irold SanchezNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Answers-Midterm ActDocument8 pagesAnswers-Midterm ActIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- ERP BattlecardDocument1 pageERP BattlecardAdrian BohorquezNo ratings yet
- Growth of Online Marketing in India-A StudyDocument6 pagesGrowth of Online Marketing in India-A StudyNeha TajveNo ratings yet
- Users Manual 4215923Document7 pagesUsers Manual 4215923smallhausenNo ratings yet
- Banking Products and Sevices FinalDocument17 pagesBanking Products and Sevices Finaljevesh9No ratings yet
- NAZ 3RD Exam Form Payment Receipt - 100317Document2 pagesNAZ 3RD Exam Form Payment Receipt - 100317Pulakesh TahbildarNo ratings yet
- NAVOne NewDocument19 pagesNAVOne Newamit.kumarNo ratings yet
- Cbmec 1 New Module 1Document22 pagesCbmec 1 New Module 1Calabia, Angelica MerelosNo ratings yet
- Recorrido Del Proceso de Cierre ContableDocument15 pagesRecorrido Del Proceso de Cierre ContableHenrry Valle GuerreroNo ratings yet
- OJT CertificateDocument11 pagesOJT CertificatePriela DanielNo ratings yet
- Isdn Bri Back UpDocument47 pagesIsdn Bri Back UpSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- TPK Database May 2009Document1,544 pagesTPK Database May 2009api-17236257No ratings yet
- ACT502 Assignment - Sem 2 - 2018Document5 pagesACT502 Assignment - Sem 2 - 2018tgmn4kssd2No ratings yet
- Insurance QuestionsDocument2 pagesInsurance Questionsmarkobare2019No ratings yet
- Dimerco Logistics Overview Presentation LMTDocument27 pagesDimerco Logistics Overview Presentation LMTDuska VuletaNo ratings yet
- Accounting ReviewerDocument15 pagesAccounting ReviewerDeryll MacanasNo ratings yet
- Case Study - ECOMART - Local - WithquestionsDocument3 pagesCase Study - ECOMART - Local - Withquestionsrizza mae agujaNo ratings yet
- IV Internet of Things IOTDocument19 pagesIV Internet of Things IOTJaquias Calelao AlfredNo ratings yet
- Week1 - CLO1 - Routing Concepts - SRWE - Module - 14Document42 pagesWeek1 - CLO1 - Routing Concepts - SRWE - Module - 14shahad 112No ratings yet
- DeKalb County Commissioners Chief of Staff Morris Williams P-Card ActivityDocument37 pagesDeKalb County Commissioners Chief of Staff Morris Williams P-Card ActivityViola DavisNo ratings yet
- 2022 Reyee Backpack-V1.03-0303Document30 pages2022 Reyee Backpack-V1.03-0303almi syarif ChaniagoNo ratings yet
- CV Deva DharmapuspaDocument3 pagesCV Deva Dharmapuspadevie.iklanNo ratings yet
- KN-2111 Stable 3.09.C.8.0-0 Router Startup-ConfigDocument11 pagesKN-2111 Stable 3.09.C.8.0-0 Router Startup-ConfigŞevki SağlamNo ratings yet
- Account Statement: Transactions ListDocument3 pagesAccount Statement: Transactions Listtawhide_islamicNo ratings yet
- Account Closure RequestDocument1 pageAccount Closure Requestanilmourya5No ratings yet
- MPSG 2-0 InfographicDocument1 pageMPSG 2-0 InfographicNorzaherawati Aryani Md TahirNo ratings yet
- PlacementsDocument1 pagePlacementsAafiNo ratings yet
- PART - II TO Be Filled in by The Doctor / Hospital in Utmost Good FaithDocument2 pagesPART - II TO Be Filled in by The Doctor / Hospital in Utmost Good FaithArvind BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Macatangay Bsn-g4b - Business Model CanvasDocument3 pagesMacatangay Bsn-g4b - Business Model CanvasGaea Angela MACATANGAYNo ratings yet
- Accounting Basics, Part 1: Accrual, Double-Entry Accounting, Debits & Credits, Chart of Accounts Journals And, LedgerDocument147 pagesAccounting Basics, Part 1: Accrual, Double-Entry Accounting, Debits & Credits, Chart of Accounts Journals And, LedgerThe Three Queens100% (1)
Contemp
Contemp
Uploaded by
Irold Sanchez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesEconomic globalization refers to the increasing interdependence of world economies through cross-border trade, capital flows, and spread of technologies. While globalization is not new, having occurred throughout history, the current level of global economic integration is unprecedented. Convergence describes trends moving together, while divergence describes trends moving apart. International monetary systems establish rules for payments, exchange rates, and capital movement and have evolved from the gold standard to the Bretton Woods system to today's floating currencies. Trade policies and agreements, whether unilateral or multilateral, influence the flow of goods between nations.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEconomic globalization refers to the increasing interdependence of world economies through cross-border trade, capital flows, and spread of technologies. While globalization is not new, having occurred throughout history, the current level of global economic integration is unprecedented. Convergence describes trends moving together, while divergence describes trends moving apart. International monetary systems establish rules for payments, exchange rates, and capital movement and have evolved from the gold standard to the Bretton Woods system to today's floating currencies. Trade policies and agreements, whether unilateral or multilateral, influence the flow of goods between nations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesContemp
Contemp
Uploaded by
Irold SanchezEconomic globalization refers to the increasing interdependence of world economies through cross-border trade, capital flows, and spread of technologies. While globalization is not new, having occurred throughout history, the current level of global economic integration is unprecedented. Convergence describes trends moving together, while divergence describes trends moving apart. International monetary systems establish rules for payments, exchange rates, and capital movement and have evolved from the gold standard to the Bretton Woods system to today's floating currencies. Trade policies and agreements, whether unilateral or multilateral, influence the flow of goods between nations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
For every group, summarize and explain the following after reading 02 Readings 1-2:
1. What is economic globalization?
2. Is economic globalization a new phenomenon?
3. What are the differences and similarities between convergence and divergence?
4. What does International Monetary Systems do?
5. What is The Gold Standard?
6. What are the roles of The Bretton Woods System and Its Dissolution?
7. What does European Monetary Integration do?
8. What are International Trade and Trade Policies?
9. What is Unilateral Trade Order?
1. Economic globalization refers to the increasing interdependence of world economies as a
result of the growing scale of cross-border trade of commodities and services, flow of
international capital and wide and rapid spread of technologies.
2 Globalization is not new. Since the start of civilization, people have traded goods with their
neighbors. As cultures advanced, they were able to travel farther afield to trade their own goods
for desirable products found elsewhere
3 Divergence generally means two things are moving apart while convergence implies
that two forces are moving together. In the world of economics, finance, and trading,
divergence and convergence are terms used to describe the directional relationship of two
trends, prices, or indicators
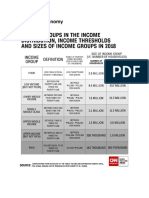
4 The international monetary system provides the institutional framework for determining
the rules and procedures for international payments, determination of exchange rates,
and movement of capital. The major stages of the evolution of the international monetary
system can be categorized into the following stages.
5 The gold standard is a monetary system where a country's currency or paper money has
a value directly linked to gold. With the gold standard, countries agreed to convert paper
money into a fixed amount of gold. A country that uses the gold standard sets a fixed price for
gold and buys and sells gold at that price.
6 The Bretton Woods System required a currency peg to the U.S. dollar which was in turn
pegged to the price of gold. The Bretton Woods System collapsed in the 1970s but created a
lasting influence on international currency exchange and trade through its development
of the IMF and World Bank
7 European monetary integration refers to a 30-year long process that began at the end of the
1960s as a form of monetary cooperation intended to reduce the excessive influence of the
US dollar on domestic exchange rates, and led, through various attempts, to the creation of a
Monetary Union and a common currency.
8 Trade policy is a government's stance on international trade, or a combination of laws
and practices that affects imports and exports. Trade policies can include regulations, tariffs,
and quotas
9 Unilateral trade agreements are one-sided, non-reciprocal trade preferences granted by
developed countries to developing ones, with the goal of helping them to increase exports
and spur economic development
You might also like
- NF - Apple EUADocument2 pagesNF - Apple EUAgustavogko01100% (1)
- 02 Worksheet 1 TCWDocument2 pages02 Worksheet 1 TCWJericho FajardoNo ratings yet
- Activities For Lesson 2Document7 pagesActivities For Lesson 2KATHLEEN BALBOANo ratings yet
- INDIVIDUALASSIGNMENT3Document2 pagesINDIVIDUALASSIGNMENT3Lee Louise Andrew E. CaoNo ratings yet
- The Contemporary World: 02 Worksheet 1Document3 pagesThe Contemporary World: 02 Worksheet 1Ashley AcuñaNo ratings yet
- International Financial SystemDocument75 pagesInternational Financial SystemRaghu PrasadNo ratings yet
- International Finance: THE GOLD STANDARD (1876-1913)Document20 pagesInternational Finance: THE GOLD STANDARD (1876-1913)sujata11No ratings yet
- Bus 420 International Monetary SystemDocument7 pagesBus 420 International Monetary SystemYomi BrainNo ratings yet
- The International Monetary System: Exchange Rate RegimeDocument4 pagesThe International Monetary System: Exchange Rate RegimeAyeshasaddique turkNo ratings yet
- International Monetary SystemDocument7 pagesInternational Monetary SystemAmethyst NocelladoNo ratings yet
- Internal FinanceDocument7 pagesInternal Financeakhlaqur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Evolution of IMSDocument8 pagesEvolution of IMSpayalmulchandani15No ratings yet
- Review CLC.T5.2024Document7 pagesReview CLC.T5.2024Nguyễn Duy ĐạtNo ratings yet
- Global Economy NotesDocument4 pagesGlobal Economy Notes2022-201417No ratings yet
- Monetary System Chapter 3 (WWW - Bustudymate.in (BUStudymate - In)Document18 pagesMonetary System Chapter 3 (WWW - Bustudymate.in (BUStudymate - In)aitshailajamlNo ratings yet
- Evolution of International MonetaryDocument7 pagesEvolution of International MonetaryManish KumarNo ratings yet
- WK 3 ContempDocument34 pagesWK 3 Contempaprilstamaria0427No ratings yet
- The Global Economy ReportDocument11 pagesThe Global Economy ReportAlvin BautistaNo ratings yet
- Magbanua, Christian Mod.7 QuizdocxDocument2 pagesMagbanua, Christian Mod.7 QuizdocxChristian MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- International Finance Ass 2Document5 pagesInternational Finance Ass 2Sugen RajNo ratings yet
- Ibt 8Document10 pagesIbt 8tenyente gimoNo ratings yet
- International Monetary SystemsDocument19 pagesInternational Monetary SystemsIdrees BharatNo ratings yet
- International Monetary System and The Balance of Payments: Week 4 Abdul Halim, BSM, MBADocument22 pagesInternational Monetary System and The Balance of Payments: Week 4 Abdul Halim, BSM, MBApardamaianNo ratings yet
- Socsci Mod1 To 6Document34 pagesSocsci Mod1 To 6VILLARANTE, CHRESSYLE ANNE FABIALANo ratings yet
- Unit 2.1 2020-2021Document36 pagesUnit 2.1 2020-2021Chinkee LorzanoNo ratings yet
- International FinanceDocument3 pagesInternational FinanceRiyaNo ratings yet
- Mohamad Hafiz Bin Ahmad RadziDocument9 pagesMohamad Hafiz Bin Ahmad RadziMohd HafizNo ratings yet
- A General Introduction To International Economic LawDocument20 pagesA General Introduction To International Economic LawОля КозакNo ratings yet
- Assignment of IfDocument7 pagesAssignment of IfAnand SinghNo ratings yet
- The Global EconomyDocument8 pagesThe Global EconomyRaven Evangelista CanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document31 pagesUnit 1PSBALARAMNo ratings yet
- GE4 Discussion Task - Module 2Document2 pagesGE4 Discussion Task - Module 2Junielle AutajayNo ratings yet
- 8 International Monetary System PDFDocument22 pages8 International Monetary System PDFdevesh_mendiratta_61No ratings yet
- Economic Project Praveen Patil 1Document38 pagesEconomic Project Praveen Patil 1Rahul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of The International Monetary SystemDocument12 pagesThe Evolution of The International Monetary SystemAbhijeet Gupta 1513No ratings yet
- Contemporary World 3Document62 pagesContemporary World 3Adrian AndalNo ratings yet
- International Monetary SystemDocument6 pagesInternational Monetary SystemPragya KasanaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Finance Markets Investments and Financial Management 15th Edition Melicher Solutions ManualDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Finance Markets Investments and Financial Management 15th Edition Melicher Solutions Manualquandiendjv100% (24)
- Floating A CurrencyDocument3 pagesFloating A Currencykorum8urraNo ratings yet
- Welcome To: International Finance: by Amit Kumar Harsh Kumar Balkar SinghDocument32 pagesWelcome To: International Finance: by Amit Kumar Harsh Kumar Balkar Singhbally_bNo ratings yet
- International Business and TradeDocument3 pagesInternational Business and Tradejntvtn7pc9No ratings yet
- The International Institution The Bretton Wood System General Agreement On GATT and The World Trade OrganizationDocument20 pagesThe International Institution The Bretton Wood System General Agreement On GATT and The World Trade OrganizationShanlane CoronelNo ratings yet
- Assignment On International Monetary System: Prepared ForDocument6 pagesAssignment On International Monetary System: Prepared ForMd Nazmus SakibNo ratings yet
- International Monetary SystemDocument4 pagesInternational Monetary SystemHassani AllyNo ratings yet
- Understanding The International Monetary SystemDocument7 pagesUnderstanding The International Monetary SystemSteve BaronNo ratings yet
- International BankingDocument62 pagesInternational BankingDjSunil SkyNo ratings yet
- Evaluating The International Monetary System and The Availability To Move Towards One Single Global CurrencyDocument25 pagesEvaluating The International Monetary System and The Availability To Move Towards One Single Global Currencyboomfox17No ratings yet
- Week 4 EC 304Document9 pagesWeek 4 EC 304Mustafa KhanNo ratings yet
- Evolution of The International Monetary Systems: Unit 5 SectionDocument4 pagesEvolution of The International Monetary Systems: Unit 5 SectionBabamu Kalmoni JaatoNo ratings yet
- Internation FinanceDocument9 pagesInternation FinancemanishaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 World Financial EnvironmentDocument6 pagesUnit 4 World Financial EnvironmentTharun VelammalNo ratings yet
- FinanceDocument9 pagesFinanceck124881No ratings yet
- F31 Foreign Exchange: 1. What Is The Importance of The Field You Have Chosen?Document4 pagesF31 Foreign Exchange: 1. What Is The Importance of The Field You Have Chosen?Holy BunkersNo ratings yet
- Forex ManagementDocument57 pagesForex ManagementKriti VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Navigation Search International Monetary Systems LTDDocument6 pagesNavigation Search International Monetary Systems LTDInnovative AkibNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rate SystemsDocument27 pagesExchange Rate SystemsmaurishkaNo ratings yet
- Review QuestionsDocument2 pagesReview QuestionsHads LunaNo ratings yet
- Module 9 - Foreign Exchange MarketsDocument9 pagesModule 9 - Foreign Exchange MarketsChris tine Mae MendozaNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Factors Affecting TradeDocument36 pagesMacroeconomic Factors Affecting TradeErika Bermas MedenillaNo ratings yet
- SurveyDocument2 pagesSurveyIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Info ManagemtntDocument1 pageInfo ManagemtntIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Info ManagemtntDocument1 pageInfo ManagemtntIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Chapter 1 5 BodyDocument28 pagesPart 2 Chapter 1 5 BodyIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- NSTPDocument2 pagesNSTPIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Preliminaries - To PrintDocument17 pagesPreliminaries - To PrintIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Zamora BiodataDocument1 pageZamora BiodataIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- TatanDocument3 pagesTatanIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- SE 411 - Deliverable - Part 2Document3 pagesSE 411 - Deliverable - Part 2Irold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Putanginang ResearchDocument14 pagesPutanginang ResearchIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Reflection: Irold Jerald A. Sanchez Bsit-1BDocument1 pageReflection: Irold Jerald A. Sanchez Bsit-1BIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- 04 Readings 1Document2 pages04 Readings 1Irold SanchezNo ratings yet
- BalanaDocument17 pagesBalanaIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- SE 411 - Deliverable - Part 1Document10 pagesSE 411 - Deliverable - Part 1Irold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Summary of cs495 - 01Document3 pagesSummary of cs495 - 01Irold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Chapteer 2Document2 pagesChapteer 2Irold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Eye Lab 7Document1 pageEye Lab 7Irold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument8 pagesCase StudyIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Dlori KenkenDocument3 pagesDlori KenkenIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Answers Midterm ActDocument3 pagesAnswers Midterm ActIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Job InterviewDocument1 pageJob InterviewIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- 02 Assignment 1Document1 page02 Assignment 1Irold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Midterm Activity 01Document6 pagesMidterm Activity 01Irold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise 1Document1 pageLaboratory Exercise 1Irold SanchezNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- Answers-Midterm ActDocument8 pagesAnswers-Midterm ActIrold SanchezNo ratings yet
- ERP BattlecardDocument1 pageERP BattlecardAdrian BohorquezNo ratings yet
- Growth of Online Marketing in India-A StudyDocument6 pagesGrowth of Online Marketing in India-A StudyNeha TajveNo ratings yet
- Users Manual 4215923Document7 pagesUsers Manual 4215923smallhausenNo ratings yet
- Banking Products and Sevices FinalDocument17 pagesBanking Products and Sevices Finaljevesh9No ratings yet
- NAZ 3RD Exam Form Payment Receipt - 100317Document2 pagesNAZ 3RD Exam Form Payment Receipt - 100317Pulakesh TahbildarNo ratings yet
- NAVOne NewDocument19 pagesNAVOne Newamit.kumarNo ratings yet
- Cbmec 1 New Module 1Document22 pagesCbmec 1 New Module 1Calabia, Angelica MerelosNo ratings yet
- Recorrido Del Proceso de Cierre ContableDocument15 pagesRecorrido Del Proceso de Cierre ContableHenrry Valle GuerreroNo ratings yet
- OJT CertificateDocument11 pagesOJT CertificatePriela DanielNo ratings yet
- Isdn Bri Back UpDocument47 pagesIsdn Bri Back UpSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- TPK Database May 2009Document1,544 pagesTPK Database May 2009api-17236257No ratings yet
- ACT502 Assignment - Sem 2 - 2018Document5 pagesACT502 Assignment - Sem 2 - 2018tgmn4kssd2No ratings yet
- Insurance QuestionsDocument2 pagesInsurance Questionsmarkobare2019No ratings yet
- Dimerco Logistics Overview Presentation LMTDocument27 pagesDimerco Logistics Overview Presentation LMTDuska VuletaNo ratings yet
- Accounting ReviewerDocument15 pagesAccounting ReviewerDeryll MacanasNo ratings yet
- Case Study - ECOMART - Local - WithquestionsDocument3 pagesCase Study - ECOMART - Local - Withquestionsrizza mae agujaNo ratings yet
- IV Internet of Things IOTDocument19 pagesIV Internet of Things IOTJaquias Calelao AlfredNo ratings yet
- Week1 - CLO1 - Routing Concepts - SRWE - Module - 14Document42 pagesWeek1 - CLO1 - Routing Concepts - SRWE - Module - 14shahad 112No ratings yet
- DeKalb County Commissioners Chief of Staff Morris Williams P-Card ActivityDocument37 pagesDeKalb County Commissioners Chief of Staff Morris Williams P-Card ActivityViola DavisNo ratings yet
- 2022 Reyee Backpack-V1.03-0303Document30 pages2022 Reyee Backpack-V1.03-0303almi syarif ChaniagoNo ratings yet
- CV Deva DharmapuspaDocument3 pagesCV Deva Dharmapuspadevie.iklanNo ratings yet
- KN-2111 Stable 3.09.C.8.0-0 Router Startup-ConfigDocument11 pagesKN-2111 Stable 3.09.C.8.0-0 Router Startup-ConfigŞevki SağlamNo ratings yet
- Account Statement: Transactions ListDocument3 pagesAccount Statement: Transactions Listtawhide_islamicNo ratings yet
- Account Closure RequestDocument1 pageAccount Closure Requestanilmourya5No ratings yet
- MPSG 2-0 InfographicDocument1 pageMPSG 2-0 InfographicNorzaherawati Aryani Md TahirNo ratings yet
- PlacementsDocument1 pagePlacementsAafiNo ratings yet
- PART - II TO Be Filled in by The Doctor / Hospital in Utmost Good FaithDocument2 pagesPART - II TO Be Filled in by The Doctor / Hospital in Utmost Good FaithArvind BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Macatangay Bsn-g4b - Business Model CanvasDocument3 pagesMacatangay Bsn-g4b - Business Model CanvasGaea Angela MACATANGAYNo ratings yet
- Accounting Basics, Part 1: Accrual, Double-Entry Accounting, Debits & Credits, Chart of Accounts Journals And, LedgerDocument147 pagesAccounting Basics, Part 1: Accrual, Double-Entry Accounting, Debits & Credits, Chart of Accounts Journals And, LedgerThe Three Queens100% (1)