Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Laboratory Investigation Report: Haematology
Laboratory Investigation Report: Haematology
Uploaded by
HarshitCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Mrs Anar DeviDocument14 pagesMrs Anar DeviM.DNo ratings yet
- Xdue6378 2Document2 pagesXdue6378 2S Abedi50% (2)
- Essentials of Medical Laboratory Practice - Lieseke, Constance L. (SRG)Document564 pagesEssentials of Medical Laboratory Practice - Lieseke, Constance L. (SRG)Kaan Halici89% (36)
- Test Report: Complete Blood Count (CBC)Document3 pagesTest Report: Complete Blood Count (CBC)WSC ALMANo ratings yet
- 1-Dengue IgG & IgM - PO2709736085-377Document12 pages1-Dengue IgG & IgM - PO2709736085-377TV UNITNo ratings yet
- 1-Complete Blood Count - PO1106326185-399Document8 pages1-Complete Blood Count - PO1106326185-399Arup KumarNo ratings yet
- Department of Hematology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. IntervalDocument3 pagesDepartment of Hematology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Intervalaf dNo ratings yet
- Design and Spatial BehaviorDocument24 pagesDesign and Spatial BehaviorHuiyiChang100% (1)
- Kinesiotape Durante El EmbarazoDocument3 pagesKinesiotape Durante El EmbarazoNostrum Sport100% (2)
- Medical Laboratory Report: Haemoglobin Total Leucocyte Count Total Erythrocyte Count Platelet Count MPV PCT PDWDocument4 pagesMedical Laboratory Report: Haemoglobin Total Leucocyte Count Total Erythrocyte Count Platelet Count MPV PCT PDWdhavalNo ratings yet
- Saniya Fathima (7G28Jy) :::: Patient Age / Sex 26 Y / Female BranchDocument3 pagesSaniya Fathima (7G28Jy) :::: Patient Age / Sex 26 Y / Female BranchShah FaisalNo ratings yet
- Kidney FunctionDocument19 pagesKidney FunctionFarooq Bin MahfoozNo ratings yet
- Medical Laboratory Report: Haemoglobin Total Leucocyte Count Total Erythrocyte Count Platelet Count MPV PCT PDWDocument4 pagesMedical Laboratory Report: Haemoglobin Total Leucocyte Count Total Erythrocyte Count Platelet Count MPV PCT PDWdhavalNo ratings yet
- Report 0bd39992Document8 pagesReport 0bd39992NEETFIXNo ratings yet
- Report 3f90266bDocument18 pagesReport 3f90266bSK TacNo ratings yet
- Ssumangarg@gmail - Com 20220825193722Document13 pagesSsumangarg@gmail - Com 20220825193722Suman GargNo ratings yet
- PRAVEEN Y (ID - 8167522) :::: Patient Age / Sex 32 Y / MaleDocument5 pagesPRAVEEN Y (ID - 8167522) :::: Patient Age / Sex 32 Y / Malepraveen yNo ratings yet
- 1-Senior Citizen Basic Package - PO3248534977-432Document16 pages1-Senior Citizen Basic Package - PO3248534977-432Krishna Nand RaiNo ratings yet
- Department of Hematology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. IntervalDocument3 pagesDepartment of Hematology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Intervalaf dNo ratings yet
- Report of Mr. RAJA PDFDocument3 pagesReport of Mr. RAJA PDFraja.tyagi2125No ratings yet
- Method: Calculated: Page 1 of 9 07-Sep-2022 08:54 PMDocument10 pagesMethod: Calculated: Page 1 of 9 07-Sep-2022 08:54 PMburela_naveenNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument2 pagesReportIshikaNo ratings yet
- Don't Know Love - 1004584Document14 pagesDon't Know Love - 1004584baapj39No ratings yet
- Haematology: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Reference IntervalDocument5 pagesHaematology: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Reference Intervalshivanand.n ShivanandNo ratings yet
- LabTest 03jul2023Document5 pagesLabTest 03jul2023jkgupta0003No ratings yet
- Mirza Kayesh Begg - 250274290 - CompleteReportDocument12 pagesMirza Kayesh Begg - 250274290 - CompleteReportSYEDA MYSHA ALINo ratings yet
- Department of Hematology Comprehensive Full Body Checkup Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. IntervalDocument11 pagesDepartment of Hematology Comprehensive Full Body Checkup Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. IntervalshyamNo ratings yet
- Anjali Khapare - 23071171Document3 pagesAnjali Khapare - 23071171dr.menganeNo ratings yet
- Archana Lab ReportDocument10 pagesArchana Lab Reportprabalsoni125No ratings yet
- Lab ResultDocument7 pagesLab ResultAanshika RaizadaNo ratings yet
- Fully Automated Lab Accurate Reports Reports Verified by PathologistDocument11 pagesFully Automated Lab Accurate Reports Reports Verified by PathologistBathri NathanNo ratings yet
- Test Results Units Biological Reference Range Hematology:::::: Ms. Farha MemonDocument5 pagesTest Results Units Biological Reference Range Hematology:::::: Ms. Farha MemonKM GASTRO CENTERNo ratings yet
- Report 89594e5fDocument10 pagesReport 89594e5fNaresh SrikakolapuNo ratings yet
- 1-Senior Citizen Advanced Package - PO3427386675-856Document18 pages1-Senior Citizen Advanced Package - PO3427386675-856Ravi PrakashNo ratings yet
- Test Reports 2Document2 pagesTest Reports 2Chandrasekhara Reddy TNo ratings yet
- 8000000936: Patient ID 80001350 Sid No Nehru Nagar Branch Mr. Vasanth NDocument3 pages8000000936: Patient ID 80001350 Sid No Nehru Nagar Branch Mr. Vasanth NSudha SaravananNo ratings yet
- Medical Laboratory Report: Haemoglobin Total Leucocyte Count Total Erythrocyte Count Platelet Count MPV PCT PDWDocument4 pagesMedical Laboratory Report: Haemoglobin Total Leucocyte Count Total Erythrocyte Count Platelet Count MPV PCT PDWdhavalNo ratings yet
- Sunita NepalDocument5 pagesSunita NepalPrajay NepalNo ratings yet
- Aman CBCDocument1 pageAman CBCAman RathoreNo ratings yet
- Department of Hematology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. IntervalDocument5 pagesDepartment of Hematology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. IntervalHarishNo ratings yet
- Haematology: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Reference IntervalDocument2 pagesHaematology: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Reference IntervalVivek RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- MR Shashidhar Kulkarni 29 04 2023 02 35 25 PMDocument2 pagesMR Shashidhar Kulkarni 29 04 2023 02 35 25 PMagaymashashi2906No ratings yet
- Report 28340c20Document10 pagesReport 28340c20Rahul ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Labreportnew - 2023-02-17T141822.094Document8 pagesLabreportnew - 2023-02-17T141822.094pavanimatteguntaNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument18 pagesBloodPriyanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Labreportnew - 2023-10-17T102750.286Document2 pagesLabreportnew - 2023-10-17T102750.286sidlab202No ratings yet
- 1-Good Health Premium Package - PO1065281239-651Document19 pages1-Good Health Premium Package - PO1065281239-651Renu ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Haematology Haematology Haematology HaematologyDocument3 pagesHaematology Haematology Haematology HaematologyGopinandan PandeyNo ratings yet
- Jyoti Singh ReportsDocument5 pagesJyoti Singh ReportsRaghujyotisNo ratings yet
- Department of Hematology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. IntervalDocument6 pagesDepartment of Hematology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. IntervalHarishNo ratings yet
- Haematology: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Reference IntervalDocument6 pagesHaematology: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Reference IntervalumeshlpsNo ratings yet
- R Selvi:::: Patient Age / Sex 56 Y / Female BranchDocument7 pagesR Selvi:::: Patient Age / Sex 56 Y / Female Branchop nNo ratings yet
- LabReportNew - 2024-03-22T202901.640Document8 pagesLabReportNew - 2024-03-22T202901.640alex taylorNo ratings yet
- Department of Laboratory Sciences: Clinical Biochemistry/ Immuno AsssayDocument3 pagesDepartment of Laboratory Sciences: Clinical Biochemistry/ Immuno AsssayKavyaleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Fully Automated Lab Accurate Reports Reports Verified by PathologistDocument14 pagesFully Automated Lab Accurate Reports Reports Verified by PathologistRavindranatha AnNo ratings yet
- PathkindDocument5 pagesPathkindgovt.job4692No ratings yet
- Hematology: KongamdanaDocument1 pageHematology: KongamdanaShariqNo ratings yet
- Hematology: KongamdanaDocument1 pageHematology: KongamdanaShariqNo ratings yet
- IT217236 Report 1Document2 pagesIT217236 Report 1NamithaNo ratings yet
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) : Department of Haematology and Clinical PathologyDocument2 pagesComplete Blood Count (CBC) : Department of Haematology and Clinical PathologyNamithaNo ratings yet
- SR8188385Document2 pagesSR8188385mohanchowdhury1948No ratings yet
- MrsSANGEETASAHU 45Y FemaleDocument6 pagesMrsSANGEETASAHU 45Y FemalesayyedatfatmaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Biochemistry Diageasy All Health Check-Up: End of ReportDocument11 pagesClinical Biochemistry Diageasy All Health Check-Up: End of ReportHarshitNo ratings yet
- Final Report: ArsenazoDocument2 pagesFinal Report: ArsenazoHarshitNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Investigation Report: Clinical BiochemistryDocument4 pagesLaboratory Investigation Report: Clinical BiochemistryHarshitNo ratings yet
- This Is An Electronically Authorized Prescription, Hence Does Not Require A Signature. Reference Number: MH279307Document1 pageThis Is An Electronically Authorized Prescription, Hence Does Not Require A Signature. Reference Number: MH279307HarshitNo ratings yet
- N1 Soil ReportDocument20 pagesN1 Soil ReportMunjedNo ratings yet
- Test BillDocument6 pagesTest BillWaseem AhmadNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae Kelly WaltersDocument8 pagesCurriculum Vitae Kelly Waltersapi-311907685No ratings yet
- Cell Culture Media - A ReviewDocument29 pagesCell Culture Media - A ReviewFarhana Anuar100% (1)
- The Organic Nature of The StateDocument15 pagesThe Organic Nature of The Statedivyanshu sharmaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Parasitology #1Document11 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology #1Judy BaguiwenNo ratings yet
- Energy Flow in Ecosystems PDFDocument34 pagesEnergy Flow in Ecosystems PDFMARTINA MENIENo ratings yet
- Types of Plant DiseasesDocument14 pagesTypes of Plant DiseasesMuqadas NoorNo ratings yet
- Science - Levels of OrganizationDocument4 pagesScience - Levels of OrganizationAlexNo ratings yet
- Radiation Protection Bushong Study GuideDocument6 pagesRadiation Protection Bushong Study GuideAsha6842100% (1)
- The Biomedical Engineering Handbook: Second EditionDocument13 pagesThe Biomedical Engineering Handbook: Second EditionEng-Mugahed AlmansorNo ratings yet
- Pharm - Common Lab Values For NCLEX Kaplan 2013Document2 pagesPharm - Common Lab Values For NCLEX Kaplan 2013sarahpierre10No ratings yet
- Australian Birdkeeper October-November 2018Document60 pagesAustralian Birdkeeper October-November 2018Gábor Deák100% (1)
- OCR AS-Level Biology June 2023 Mark Scheme 1Document23 pagesOCR AS-Level Biology June 2023 Mark Scheme 1FatimaNo ratings yet
- 211 Mitosis LabDocument5 pages211 Mitosis LabadekNo ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Conservation Biology by Bradley J. Cardinale All ChapterDocument43 pagesFull Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Conservation Biology by Bradley J. Cardinale All Chapteryadielnasraa100% (4)
- Jaka Index6 PDFDocument85 pagesJaka Index6 PDFFábio Origuela de LiraNo ratings yet
- Brain Myths ExposedDocument10 pagesBrain Myths ExposedSiva Nesh100% (1)
- Polish - English TaskDocument5 pagesPolish - English TaskdaranNo ratings yet
- DLP-L01.1 - Introduction To Personal DevelopmentDocument2 pagesDLP-L01.1 - Introduction To Personal DevelopmentDenise Nicole T. LopezNo ratings yet
- Bitw ProductdirectoryDocument89 pagesBitw ProductdirectorySHIVANINo ratings yet
- Science: BiologyDocument22 pagesScience: BiologyMike RollideNo ratings yet
- Self and Brain - What Is Self-Related Processing PDFDocument2 pagesSelf and Brain - What Is Self-Related Processing PDFhimkeraditya100% (1)
- Middle AdulthoodDocument27 pagesMiddle AdulthoodgopikaNo ratings yet
- Notes: Huberman Lab Podcast: Episode 1: How Your Nervous System Works & ChangesDocument5 pagesNotes: Huberman Lab Podcast: Episode 1: How Your Nervous System Works & ChangesMihaela CenușeNo ratings yet
- 230 - Respiratory Physiology) External Respiration - Ventilation Perfusion CouplingDocument4 pages230 - Respiratory Physiology) External Respiration - Ventilation Perfusion Couplingyoussef magdyNo ratings yet
- Biology Form4 Chapter9Document8 pagesBiology Form4 Chapter9Wei EnNo ratings yet
Laboratory Investigation Report: Haematology
Laboratory Investigation Report: Haematology
Uploaded by
HarshitOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Laboratory Investigation Report: Haematology
Laboratory Investigation Report: Haematology
Uploaded by
HarshitCopyright:
Available Formats
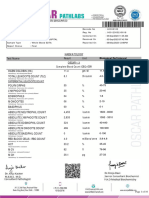
Laboratory Investigation Report
P4830492
Name : Mrs. SOUMYA SRIVASTAVA Sample No. : PMC220618005
DOB : Collected : 18/06/2022 11:02
Age / Gender : 22 Y / Female Registered : 18/06/2022 10:42
Referred by : SELF Reported : 18/06/2022 13:12
HAEMATOLOGY
Test Result Flag Unit Reference Range Methodology
ERYTHROCYTE SEDIMENTATION RATE (ESR) 38 H mm in 1st hr 0 - 15 Wintrobe
WINTROBE
Interpretation Notes :
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR or sed rate) is a relatively simple, inexpensive, non-specific test that has been used for many years to help detect
inflammation associated with conditions such as infections, cancers, and autoimmune diseases.Since ESR is a non-specific marker of inflammation and is
affected by other factors, the results must be used along with other clinical findings, the individual's health history, and results from other laboratory tests.A
single elevated ESR, without any symptoms of a specific disease, will usually not give enough information to make a medical decision. Furthermore, a normal
result does not rule out inflammation or disease.Moderately elevated ESR occurs with inflammation but also with anemia, infection, pregnancy, and with
aging.A very high ESR usually has an obvious cause, such as a severe infection, marked by an increase in globulins, polymyalgia rheumatica or temporal
arteritis. When monitoring a condition over time, rising ESRs may indicate increasing inflammation or a poor response to a therapy; normal or decreasing
ESRs may indicate an appropriate response to treatment.
Sample Type : Whole Blood-EDTA
End of Report
Dr. Anushree Rai
M.D. Pathology
Page 1 of 3 Consultant Pathologist
This is an electronically authenticated report
Final Report
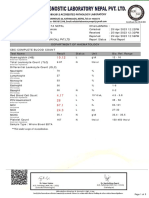
Laboratory Investigation Report
P4830492
Name : Mrs. SOUMYA SRIVASTAVA Sample No. : PMC220618005
DOB : Collected : 18/06/2022 11:02
Age / Gender : 22 Y / Female Registered : 18/06/2022 10:42
Referred by : SELF Reported : 18/06/2022 12:59
HAEMATOLOGY
Test Result Flag Unit Reference Range Methodology
COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT
HAEMOGLOBIN 6.6 L g/dl 12 - 15 Colorimetric
RED BLOOD CELL COUNT (RBC) 3.07 L millions/mm³ 3.8 - 4.8 Electrical Impedence
PACKED CELL VOLUME/HEMATOCRIT (PCV) 24.4 L % Vol 33 - 45 Calculated
MEAN CORPUSCULAR VOLUME (MCV) 79.5 L fL 83 - 101 Calculated
MEAN CORPUSCULAR HAEMOGLOBIN (MCH) 21.5 L pg 27 - 33 Calculated
MEAN CORPUSCULAR HAEMOGLOBIN 27 L g/dl 31.5 - 36.5 Calculated
CONCENTRATION (MCHC)
RED CELL DISTRIBUTION WIDTH (RDW-CV) 23.6 H % 11 - 16 Automated-Cell Counter
RED CELL DISTRIBUTION WIDTH (RDW-SD) 65.2 H fL 35 - 56 Automated-Cell Counter
TOTAL LEUCOCYTE COUNT 6.1 10^3/µL 4 - 11 Electrical Impedence
DIFFERENTIAL COUNT (DC)
NEUTROPHILS 53 % 40 - 75
LYMPHOCYTES 38 % 20 - 45
EOSINOPHILS 05 % 0-6
MONOCYTES 04 % 0 - 10
BASOPHILS 00 % 0-1
ATYPICAL CELLS 00 % 0-2
PLATELET COUNT 201 10^3/µL 150 - 450 Electrical Impedence
MEAN PLATELET VOLUME (MPV) ---.- fL 7 - 12 Electrical Impedence
PLATELET DISTRIBUTION WIDTH (PDW) ---.- fL 9 - 17 Calculated
Sample Type : Whole Blood-EDTA
End of Report
Dr. Anushree Rai
M.D. Pathology
Page 2 of 3 Consultant Pathologist
This is an electronically authenticated report
Final Report
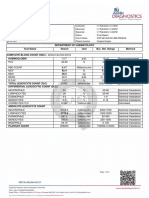
Laboratory Investigation Report
P4830492
Name : Mrs. SOUMYA SRIVASTAVA Sample No. : PMC220618005
DOB : Collected : 18/06/2022 11:02
Age / Gender : 22 Y / Female Registered : 18/06/2022 10:42
Referred by : SELF Reported : 18/06/2022 12:59
CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY
Test Result Flag Unit Reference Range Methodology
SERUM CREATININE 0.54 mg/dL 0.50-1.10 Jaffe Kinetic
Interpretation Notes :
Creatinine is a waste product that forms when creatine, which is found in your muscle, breaks down. The kidneys maintain the blood creatinine in a normal
range. Creatinine has been found to be a fairly reliable indicator of kidney function. Elevated creatinine level signifies impaired kidney function or kidney
disease.
CRP QUANTITATIVE 1.04 mg/L <5 Turbidimetric
Interpretation Notes :
C-reactive protein (CRP) is one of the most sensitive acute-phase reactants for inflammation. CRP is synthesized by the liver. Elevated serum CRP levels are
nonspecific and may be useful for the detection of systemic inflammatory processes; to assess treatment of bacterial infections with antibiotics; to detect
intrauterine infections with concomitant premature amniorrhexis; to differentiate between active and inactive forms of disease with concurrent infection, eg, in
patients suffering from systemic lupus erythematosus or colitis ulcerosa; to therapeutically monitor rheumatic disease and assess anti-inflammatory therapy; to
determine the presence of postoperative complications at an early stage, such as infected wounds, thrombosis, and pneumonia; and to distinguish between
infection and bone marrow rejection. Postoperative monitoring of CRP levels of patients can aid in the recognition of unexpected complications (persisting high
or increasing levels). Measuring changes in the concentration of CRP provides useful diagnostic information about the level of acuity and severity of a disease.
It also allows judgments about the disease genesis. Persistence of a high serum CRP concentration is usually a grave prognostic sign that generally indicates
the presence of an uncontrolled infection.
* C-reactive protein (CRP) response may be less pronounced in patients suffering from liver disease.
SGPT/ALT 16.1 U/L 4 - 45 IFCC
Interpretation Notes : The alanine aminotransferase (ALT) test is typically used to detect liver injury. It is often ordered in conjunction with aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
as part of a liver panel or comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP) to screen for and/or help diagnose liver disease.ALT is an enzyme found mostly in the cells of the liver and
kidney. When the liver is damaged, ALT is released into the blood. This makes ALT a useful test for early detection of liver damage.AST and ALT are considered to be two of
the most important tests to detect liver injury, although ALT is more specific to the liver than is AST. Sometimes AST is compared directly to ALT and an AST/ALT ratio is
calculated. This ratio may be used to distinguish between different causes of liver damage and to help recognize heart or muscle injury.ALT values are often compared to the
results of other tests such as alkaline phosphatase (ALP), total protein, and bilirubin to help determine which form of liver disease is present.ALT is often used to monitor the
treatment of persons who have liver disease, to see if the treatment is working, and may be ordered either by itself or along with other tests for this purpose.
Sample Type : Serum
End of Report
Dr. Anushree Rai
M.D. Pathology
Page 3 of 3 Consultant Pathologist
This is an electronically authenticated report
Final Report
You might also like
- Mrs Anar DeviDocument14 pagesMrs Anar DeviM.DNo ratings yet
- Xdue6378 2Document2 pagesXdue6378 2S Abedi50% (2)
- Essentials of Medical Laboratory Practice - Lieseke, Constance L. (SRG)Document564 pagesEssentials of Medical Laboratory Practice - Lieseke, Constance L. (SRG)Kaan Halici89% (36)
- Test Report: Complete Blood Count (CBC)Document3 pagesTest Report: Complete Blood Count (CBC)WSC ALMANo ratings yet
- 1-Dengue IgG & IgM - PO2709736085-377Document12 pages1-Dengue IgG & IgM - PO2709736085-377TV UNITNo ratings yet
- 1-Complete Blood Count - PO1106326185-399Document8 pages1-Complete Blood Count - PO1106326185-399Arup KumarNo ratings yet
- Department of Hematology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. IntervalDocument3 pagesDepartment of Hematology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Intervalaf dNo ratings yet
- Design and Spatial BehaviorDocument24 pagesDesign and Spatial BehaviorHuiyiChang100% (1)
- Kinesiotape Durante El EmbarazoDocument3 pagesKinesiotape Durante El EmbarazoNostrum Sport100% (2)
- Medical Laboratory Report: Haemoglobin Total Leucocyte Count Total Erythrocyte Count Platelet Count MPV PCT PDWDocument4 pagesMedical Laboratory Report: Haemoglobin Total Leucocyte Count Total Erythrocyte Count Platelet Count MPV PCT PDWdhavalNo ratings yet
- Saniya Fathima (7G28Jy) :::: Patient Age / Sex 26 Y / Female BranchDocument3 pagesSaniya Fathima (7G28Jy) :::: Patient Age / Sex 26 Y / Female BranchShah FaisalNo ratings yet
- Kidney FunctionDocument19 pagesKidney FunctionFarooq Bin MahfoozNo ratings yet
- Medical Laboratory Report: Haemoglobin Total Leucocyte Count Total Erythrocyte Count Platelet Count MPV PCT PDWDocument4 pagesMedical Laboratory Report: Haemoglobin Total Leucocyte Count Total Erythrocyte Count Platelet Count MPV PCT PDWdhavalNo ratings yet
- Report 0bd39992Document8 pagesReport 0bd39992NEETFIXNo ratings yet
- Report 3f90266bDocument18 pagesReport 3f90266bSK TacNo ratings yet
- Ssumangarg@gmail - Com 20220825193722Document13 pagesSsumangarg@gmail - Com 20220825193722Suman GargNo ratings yet
- PRAVEEN Y (ID - 8167522) :::: Patient Age / Sex 32 Y / MaleDocument5 pagesPRAVEEN Y (ID - 8167522) :::: Patient Age / Sex 32 Y / Malepraveen yNo ratings yet
- 1-Senior Citizen Basic Package - PO3248534977-432Document16 pages1-Senior Citizen Basic Package - PO3248534977-432Krishna Nand RaiNo ratings yet
- Department of Hematology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. IntervalDocument3 pagesDepartment of Hematology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Intervalaf dNo ratings yet
- Report of Mr. RAJA PDFDocument3 pagesReport of Mr. RAJA PDFraja.tyagi2125No ratings yet
- Method: Calculated: Page 1 of 9 07-Sep-2022 08:54 PMDocument10 pagesMethod: Calculated: Page 1 of 9 07-Sep-2022 08:54 PMburela_naveenNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument2 pagesReportIshikaNo ratings yet
- Don't Know Love - 1004584Document14 pagesDon't Know Love - 1004584baapj39No ratings yet
- Haematology: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Reference IntervalDocument5 pagesHaematology: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Reference Intervalshivanand.n ShivanandNo ratings yet
- LabTest 03jul2023Document5 pagesLabTest 03jul2023jkgupta0003No ratings yet
- Mirza Kayesh Begg - 250274290 - CompleteReportDocument12 pagesMirza Kayesh Begg - 250274290 - CompleteReportSYEDA MYSHA ALINo ratings yet
- Department of Hematology Comprehensive Full Body Checkup Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. IntervalDocument11 pagesDepartment of Hematology Comprehensive Full Body Checkup Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. IntervalshyamNo ratings yet
- Anjali Khapare - 23071171Document3 pagesAnjali Khapare - 23071171dr.menganeNo ratings yet
- Archana Lab ReportDocument10 pagesArchana Lab Reportprabalsoni125No ratings yet
- Lab ResultDocument7 pagesLab ResultAanshika RaizadaNo ratings yet
- Fully Automated Lab Accurate Reports Reports Verified by PathologistDocument11 pagesFully Automated Lab Accurate Reports Reports Verified by PathologistBathri NathanNo ratings yet
- Test Results Units Biological Reference Range Hematology:::::: Ms. Farha MemonDocument5 pagesTest Results Units Biological Reference Range Hematology:::::: Ms. Farha MemonKM GASTRO CENTERNo ratings yet
- Report 89594e5fDocument10 pagesReport 89594e5fNaresh SrikakolapuNo ratings yet
- 1-Senior Citizen Advanced Package - PO3427386675-856Document18 pages1-Senior Citizen Advanced Package - PO3427386675-856Ravi PrakashNo ratings yet
- Test Reports 2Document2 pagesTest Reports 2Chandrasekhara Reddy TNo ratings yet
- 8000000936: Patient ID 80001350 Sid No Nehru Nagar Branch Mr. Vasanth NDocument3 pages8000000936: Patient ID 80001350 Sid No Nehru Nagar Branch Mr. Vasanth NSudha SaravananNo ratings yet
- Medical Laboratory Report: Haemoglobin Total Leucocyte Count Total Erythrocyte Count Platelet Count MPV PCT PDWDocument4 pagesMedical Laboratory Report: Haemoglobin Total Leucocyte Count Total Erythrocyte Count Platelet Count MPV PCT PDWdhavalNo ratings yet
- Sunita NepalDocument5 pagesSunita NepalPrajay NepalNo ratings yet
- Aman CBCDocument1 pageAman CBCAman RathoreNo ratings yet
- Department of Hematology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. IntervalDocument5 pagesDepartment of Hematology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. IntervalHarishNo ratings yet
- Haematology: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Reference IntervalDocument2 pagesHaematology: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Reference IntervalVivek RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- MR Shashidhar Kulkarni 29 04 2023 02 35 25 PMDocument2 pagesMR Shashidhar Kulkarni 29 04 2023 02 35 25 PMagaymashashi2906No ratings yet
- Report 28340c20Document10 pagesReport 28340c20Rahul ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Labreportnew - 2023-02-17T141822.094Document8 pagesLabreportnew - 2023-02-17T141822.094pavanimatteguntaNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument18 pagesBloodPriyanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Labreportnew - 2023-10-17T102750.286Document2 pagesLabreportnew - 2023-10-17T102750.286sidlab202No ratings yet
- 1-Good Health Premium Package - PO1065281239-651Document19 pages1-Good Health Premium Package - PO1065281239-651Renu ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Haematology Haematology Haematology HaematologyDocument3 pagesHaematology Haematology Haematology HaematologyGopinandan PandeyNo ratings yet
- Jyoti Singh ReportsDocument5 pagesJyoti Singh ReportsRaghujyotisNo ratings yet
- Department of Hematology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. IntervalDocument6 pagesDepartment of Hematology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. IntervalHarishNo ratings yet
- Haematology: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Reference IntervalDocument6 pagesHaematology: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Reference IntervalumeshlpsNo ratings yet
- R Selvi:::: Patient Age / Sex 56 Y / Female BranchDocument7 pagesR Selvi:::: Patient Age / Sex 56 Y / Female Branchop nNo ratings yet
- LabReportNew - 2024-03-22T202901.640Document8 pagesLabReportNew - 2024-03-22T202901.640alex taylorNo ratings yet
- Department of Laboratory Sciences: Clinical Biochemistry/ Immuno AsssayDocument3 pagesDepartment of Laboratory Sciences: Clinical Biochemistry/ Immuno AsssayKavyaleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Fully Automated Lab Accurate Reports Reports Verified by PathologistDocument14 pagesFully Automated Lab Accurate Reports Reports Verified by PathologistRavindranatha AnNo ratings yet
- PathkindDocument5 pagesPathkindgovt.job4692No ratings yet
- Hematology: KongamdanaDocument1 pageHematology: KongamdanaShariqNo ratings yet
- Hematology: KongamdanaDocument1 pageHematology: KongamdanaShariqNo ratings yet
- IT217236 Report 1Document2 pagesIT217236 Report 1NamithaNo ratings yet
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) : Department of Haematology and Clinical PathologyDocument2 pagesComplete Blood Count (CBC) : Department of Haematology and Clinical PathologyNamithaNo ratings yet
- SR8188385Document2 pagesSR8188385mohanchowdhury1948No ratings yet
- MrsSANGEETASAHU 45Y FemaleDocument6 pagesMrsSANGEETASAHU 45Y FemalesayyedatfatmaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Biochemistry Diageasy All Health Check-Up: End of ReportDocument11 pagesClinical Biochemistry Diageasy All Health Check-Up: End of ReportHarshitNo ratings yet
- Final Report: ArsenazoDocument2 pagesFinal Report: ArsenazoHarshitNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Investigation Report: Clinical BiochemistryDocument4 pagesLaboratory Investigation Report: Clinical BiochemistryHarshitNo ratings yet
- This Is An Electronically Authorized Prescription, Hence Does Not Require A Signature. Reference Number: MH279307Document1 pageThis Is An Electronically Authorized Prescription, Hence Does Not Require A Signature. Reference Number: MH279307HarshitNo ratings yet
- N1 Soil ReportDocument20 pagesN1 Soil ReportMunjedNo ratings yet
- Test BillDocument6 pagesTest BillWaseem AhmadNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae Kelly WaltersDocument8 pagesCurriculum Vitae Kelly Waltersapi-311907685No ratings yet
- Cell Culture Media - A ReviewDocument29 pagesCell Culture Media - A ReviewFarhana Anuar100% (1)
- The Organic Nature of The StateDocument15 pagesThe Organic Nature of The Statedivyanshu sharmaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Parasitology #1Document11 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology #1Judy BaguiwenNo ratings yet
- Energy Flow in Ecosystems PDFDocument34 pagesEnergy Flow in Ecosystems PDFMARTINA MENIENo ratings yet
- Types of Plant DiseasesDocument14 pagesTypes of Plant DiseasesMuqadas NoorNo ratings yet
- Science - Levels of OrganizationDocument4 pagesScience - Levels of OrganizationAlexNo ratings yet
- Radiation Protection Bushong Study GuideDocument6 pagesRadiation Protection Bushong Study GuideAsha6842100% (1)
- The Biomedical Engineering Handbook: Second EditionDocument13 pagesThe Biomedical Engineering Handbook: Second EditionEng-Mugahed AlmansorNo ratings yet
- Pharm - Common Lab Values For NCLEX Kaplan 2013Document2 pagesPharm - Common Lab Values For NCLEX Kaplan 2013sarahpierre10No ratings yet
- Australian Birdkeeper October-November 2018Document60 pagesAustralian Birdkeeper October-November 2018Gábor Deák100% (1)
- OCR AS-Level Biology June 2023 Mark Scheme 1Document23 pagesOCR AS-Level Biology June 2023 Mark Scheme 1FatimaNo ratings yet
- 211 Mitosis LabDocument5 pages211 Mitosis LabadekNo ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Conservation Biology by Bradley J. Cardinale All ChapterDocument43 pagesFull Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Conservation Biology by Bradley J. Cardinale All Chapteryadielnasraa100% (4)
- Jaka Index6 PDFDocument85 pagesJaka Index6 PDFFábio Origuela de LiraNo ratings yet
- Brain Myths ExposedDocument10 pagesBrain Myths ExposedSiva Nesh100% (1)
- Polish - English TaskDocument5 pagesPolish - English TaskdaranNo ratings yet
- DLP-L01.1 - Introduction To Personal DevelopmentDocument2 pagesDLP-L01.1 - Introduction To Personal DevelopmentDenise Nicole T. LopezNo ratings yet
- Bitw ProductdirectoryDocument89 pagesBitw ProductdirectorySHIVANINo ratings yet
- Science: BiologyDocument22 pagesScience: BiologyMike RollideNo ratings yet
- Self and Brain - What Is Self-Related Processing PDFDocument2 pagesSelf and Brain - What Is Self-Related Processing PDFhimkeraditya100% (1)
- Middle AdulthoodDocument27 pagesMiddle AdulthoodgopikaNo ratings yet
- Notes: Huberman Lab Podcast: Episode 1: How Your Nervous System Works & ChangesDocument5 pagesNotes: Huberman Lab Podcast: Episode 1: How Your Nervous System Works & ChangesMihaela CenușeNo ratings yet
- 230 - Respiratory Physiology) External Respiration - Ventilation Perfusion CouplingDocument4 pages230 - Respiratory Physiology) External Respiration - Ventilation Perfusion Couplingyoussef magdyNo ratings yet
- Biology Form4 Chapter9Document8 pagesBiology Form4 Chapter9Wei EnNo ratings yet