Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 viewsOpRes Reviewer
OpRes Reviewer
Uploaded by
Feane LamasanThis document discusses forecasting, which involves making predictions about future values of variables to help with planning and decision making. It outlines the forecasting process, which includes determining the purpose, time horizon, technique, data analysis, forecast, and monitoring. Common forecast types are judgmental, time series, and associative models. Time series forecasts use historical data patterns to predict the future, while judgmental forecasts incorporate subjective inputs. The document also covers elements of a good forecast, forecast variations, naive forecasts, and averaging techniques like moving averages.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Chapter 4 Airworthiness LimitationsDocument3 pagesChapter 4 Airworthiness LimitationsHrishikesh NarasimhanNo ratings yet
- McDonalds Franchise Disclosure DocumentDocument2 pagesMcDonalds Franchise Disclosure DocumentPrabjot Singh0% (1)
- Forecasting Techniques: Production and Operations in ManagementDocument71 pagesForecasting Techniques: Production and Operations in Managementsiddhartha chpeuriNo ratings yet
- Risk Based Internal Audit Plan PDFDocument40 pagesRisk Based Internal Audit Plan PDFDjay'hFrost100% (1)
- Forecasting Demand: Lesson 4Document13 pagesForecasting Demand: Lesson 4HerondaleNo ratings yet
- OM1 Chapter 3: ForecastingDocument1 pageOM1 Chapter 3: ForecastingRoseanne Binayao LontianNo ratings yet
- Forecasting: Chapter Three Operations Management William J. StevensonDocument13 pagesForecasting: Chapter Three Operations Management William J. StevensonJahirul Islam ShovonNo ratings yet
- Forecasting: Types of Forecasting ModelsDocument8 pagesForecasting: Types of Forecasting Modelslovely abinalNo ratings yet
- Forecasting: Chapter Three Operations Management William J. StevensonDocument20 pagesForecasting: Chapter Three Operations Management William J. StevensonFarhat IshaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2: Demand ForecastingDocument5 pagesMODULE 2: Demand Forecastingkristel lei diamanteNo ratings yet
- Operational Management POMG2710: Chapter OutlineDocument17 pagesOperational Management POMG2710: Chapter OutlineلبليايلاNo ratings yet
- Forecasting Part 1Document83 pagesForecasting Part 1Gela SorianoNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2: Demand ForecastingDocument4 pagesMODULE 2: Demand Forecastingkristel lei diamanteNo ratings yet
- SCM - Group 5Document4 pagesSCM - Group 5aainaa aqilahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Forecasting - 1st PartDocument34 pagesChapter 3 - Forecasting - 1st PartSam ElmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Heizer S2Document20 pagesChapter-3 Heizer S2Maxene Joi PigtainNo ratings yet
- ForecastingDocument10 pagesForecastingkiiadizonNo ratings yet
- Forecasting: I See That You Will Get An A From This CourseDocument60 pagesForecasting: I See That You Will Get An A From This CourseTalemaNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Forecasting Part 1Document16 pages3.2 Forecasting Part 1MBA LOGISTICS & SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENTNo ratings yet
- Forecasting: I See That You Will Get An A From This CourseDocument70 pagesForecasting: I See That You Will Get An A From This CourseTalemaNo ratings yet
- Week 1-5Document10 pagesWeek 1-5Yinshuang WangNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 ForecastingDocument23 pagesChapter-2 ForecastingsrikantushaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Forecasting(s)Document96 pagesLecture 3 - Forecasting(s)Vicaria McDowellNo ratings yet
- Forecasting Written ReportDocument7 pagesForecasting Written ReportCrestina Chu BagsitNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Rev (Introduction To Demand and Revenue Management)Document81 pagesWeek 1 Rev (Introduction To Demand and Revenue Management)wahyunidaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - ForecastingDocument39 pagesLesson 3 - ForecastingTomoyo AdachiNo ratings yet
- ForecastingDocument52 pagesForecastingVfhhdfvhhNo ratings yet
- ForecastingDocument19 pagesForecastingarelNo ratings yet
- Chapter II: Forecasting: ForecastDocument3 pagesChapter II: Forecasting: ForecastCJ De LunaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - OM NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 3 - OM NoteswejdazoNo ratings yet
- Man SciDocument4 pagesMan SciRIANE PADIERNOSNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Ops&SCMDocument67 pagesUnit 3 - Ops&SCMsumitsingh95345No ratings yet
- 2nd Year - CBMEDocument13 pages2nd Year - CBMEHo Sol JungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document93 pagesChapter 24zfq8g84rkNo ratings yet
- Ba ReviewerDocument7 pagesBa ReviewerJamielyn Dy DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2.1 ForecastingDocument33 pagesLecture 2.1 ForecastingMd. Mahbub KhanNo ratings yet
- Forecasting FundamentalszDocument2 pagesForecasting FundamentalszSatish KhullarNo ratings yet
- TQM Presentatio 55805079 3Document21 pagesTQM Presentatio 55805079 3Edi WowNo ratings yet
- ForecastingDocument2 pagesForecastingMiranda, Aliana Jasmine M.No ratings yet
- Sales ForecastingDocument32 pagesSales ForecastingtanyaNo ratings yet
- LOGI 3477 - Week 2 3Document134 pagesLOGI 3477 - Week 2 3krnkilincNo ratings yet
- Forecasting OMTQMDocument39 pagesForecasting OMTQMMicaella TimpugNo ratings yet
- CH 3 ForecastingDocument20 pagesCH 3 Forecastingkebaman1986No ratings yet
- Management Science ReviewerDocument16 pagesManagement Science ReviewerMc RamosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Planning: To Set DirectionDocument39 pagesChapter 3-Planning: To Set Directioneric labordoNo ratings yet
- POM 343 Chapter 8 TermsDocument1 pagePOM 343 Chapter 8 TermsjordanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document17 pagesChapter 2Eyob AberaNo ratings yet
- Mansci FinalsDocument4 pagesMansci FinalsLee Ann FermilNo ratings yet
- ForecastingDocument5 pagesForecastingPatrizia Nicole GozeNo ratings yet
- Forecasting BatulanbonifacioDocument34 pagesForecasting Batulanbonifaciocherish.jorge.patalNo ratings yet
- Forecasting TechniquesDocument9 pagesForecasting TechniquesJohn Jay NalicatNo ratings yet
- Operations DossierDocument81 pagesOperations DossierMudit FauzdarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ForecastingDocument102 pagesChapter 3 ForecastingJanak KarkiNo ratings yet
- Kayne Marquez - BME 1 - Activity 3.1Document5 pagesKayne Marquez - BME 1 - Activity 3.1Colline MarquezNo ratings yet
- Removal P2Document7 pagesRemoval P2hmvhNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 OM EditedDocument23 pagesUnit 5 OM EditedermiasnasirtaleginNo ratings yet
- SCMchap 2Document9 pagesSCMchap 2NguyenNo ratings yet
- What Is Forecasting: (Not Sure If Need Pa Isama Ung Decoupling Points)Document6 pagesWhat Is Forecasting: (Not Sure If Need Pa Isama Ung Decoupling Points)Angel Jasmin TupazNo ratings yet
- Day 4 - ForecastingDocument5 pagesDay 4 - ForecastingNate Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- CHAP 3-5 OMT BooksDocument16 pagesCHAP 3-5 OMT Booksbae joohyunNo ratings yet
- Operation Management FinalDocument7 pagesOperation Management FinalmonteverdevinNo ratings yet
- P501: Managing Operations & Supply Chain: Lecture - 7Document33 pagesP501: Managing Operations & Supply Chain: Lecture - 7halaku duttaNo ratings yet
- MODULE5Document10 pagesMODULE5Feane LamasanNo ratings yet
- PEDocument1 pagePEFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Economic DevelopmentDocument25 pagesReviewer in Economic DevelopmentFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- MicroeconDocument1 pageMicroeconFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document6 pagesChapter 1Feane LamasanNo ratings yet
- OPMAN ReviewerDocument2 pagesOPMAN ReviewerFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- BROCHUREDocument2 pagesBROCHUREFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - STSDocument3 pagesChapter 7 - STSFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- Chameleon 'S Tail: LinkDocument1 pageChameleon 'S Tail: LinkFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- WR Group3Document22 pagesWR Group3Feane LamasanNo ratings yet
- Market StructuresDocument2 pagesMarket StructuresFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Culminating ProjectDocument5 pagesModule 7 Culminating Projectapi-650742146100% (1)
- Manufacturing Manager Generic JD1Document4 pagesManufacturing Manager Generic JD1Bishal PandaNo ratings yet
- POM C12 Inventory ManagementDocument10 pagesPOM C12 Inventory ManagementLouis PatNo ratings yet
- Project Management - AhujaDocument518 pagesProject Management - AhujaChristian GarciaNo ratings yet
- Six Strategies For Competing Through Service An AgDocument5 pagesSix Strategies For Competing Through Service An Agmehdi achourNo ratings yet
- Protecting Legacy The Value of A Family OfficeDocument25 pagesProtecting Legacy The Value of A Family OfficeRavi BabuNo ratings yet
- Esmail PDFDocument12 pagesEsmail PDFMirela-Elena PopaNo ratings yet
- Noc18 mg42 Assignment4Document4 pagesNoc18 mg42 Assignment4Karan PatelNo ratings yet
- Job Description in ExcelDocument8 pagesJob Description in ExcelMuhammad ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Course Outline - Corporate Governance - 2021 - MBA 13th BatchDocument6 pagesCourse Outline - Corporate Governance - 2021 - MBA 13th BatchElma UmmatiNo ratings yet
- Lovepreet's, Cover Letter and Resume.Document4 pagesLovepreet's, Cover Letter and Resume.lovepreetsk0465No ratings yet
- Developing Performance Indicators For Managing Maintenance - 0 IntroductionDocument26 pagesDeveloping Performance Indicators For Managing Maintenance - 0 IntroductionSandro GastanagaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document58 pagesChapter 4Mohit PariharNo ratings yet
- Price Adjustment Guidance Note On ProcurementDocument40 pagesPrice Adjustment Guidance Note On ProcurementMintesnot BogaleNo ratings yet
- Tugas Pra Uas HehehehehDocument2 pagesTugas Pra Uas HehehehehrereskippersNo ratings yet
- Sample Chapter 3 MethodologyDocument3 pagesSample Chapter 3 Methodologykyla deguzmanNo ratings yet
- Improving Overall Equipment Effectiveness OEE of Extrusion Machine Using Lean Manufacturing ApproachManufacturing TechnologyDocument9 pagesImproving Overall Equipment Effectiveness OEE of Extrusion Machine Using Lean Manufacturing ApproachManufacturing TechnologyLuis Ulloa De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Learning Journal Unit 5 AdvertisingDocument4 pagesLearning Journal Unit 5 AdvertisingDominga SilvaNo ratings yet
- Service Operations ManagementDocument68 pagesService Operations ManagementAnushka KanaujiaNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting 1: (Prepared by MS. ARMI K. BUYCO, CPA, MBA)Document3 pagesManagement Accounting 1: (Prepared by MS. ARMI K. BUYCO, CPA, MBA)Gilner PomarNo ratings yet
- Procedure Transportaton & DeliveryDocument1 pageProcedure Transportaton & DeliveryDanishAnwerNo ratings yet
- Plantillas MarketingDocument26 pagesPlantillas MarketingAntelmoNo ratings yet
- MGT 301 Fall 2023 Final Term Question Paper (Online Exam)Document1 pageMGT 301 Fall 2023 Final Term Question Paper (Online Exam)tasnia nishatNo ratings yet
- Ey Iif Global Risk Survey V FinalDocument52 pagesEy Iif Global Risk Survey V Finalbildyosta sapparNo ratings yet
- Job Cost Sheet - Job J-832-LMDocument2 pagesJob Cost Sheet - Job J-832-LMAbrar Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document22 pagesLecture 3Dr Waheed AsgharNo ratings yet
- Charu Gupta 4 Years March'2023 CVDocument3 pagesCharu Gupta 4 Years March'2023 CVJapLangNo ratings yet
OpRes Reviewer
OpRes Reviewer
Uploaded by
Feane Lamasan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesThis document discusses forecasting, which involves making predictions about future values of variables to help with planning and decision making. It outlines the forecasting process, which includes determining the purpose, time horizon, technique, data analysis, forecast, and monitoring. Common forecast types are judgmental, time series, and associative models. Time series forecasts use historical data patterns to predict the future, while judgmental forecasts incorporate subjective inputs. The document also covers elements of a good forecast, forecast variations, naive forecasts, and averaging techniques like moving averages.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses forecasting, which involves making predictions about future values of variables to help with planning and decision making. It outlines the forecasting process, which includes determining the purpose, time horizon, technique, data analysis, forecast, and monitoring. Common forecast types are judgmental, time series, and associative models. Time series forecasts use historical data patterns to predict the future, while judgmental forecasts incorporate subjective inputs. The document also covers elements of a good forecast, forecast variations, naive forecasts, and averaging techniques like moving averages.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesOpRes Reviewer
OpRes Reviewer
Uploaded by
Feane LamasanThis document discusses forecasting, which involves making predictions about future values of variables to help with planning and decision making. It outlines the forecasting process, which includes determining the purpose, time horizon, technique, data analysis, forecast, and monitoring. Common forecast types are judgmental, time series, and associative models. Time series forecasts use historical data patterns to predict the future, while judgmental forecasts incorporate subjective inputs. The document also covers elements of a good forecast, forecast variations, naive forecasts, and averaging techniques like moving averages.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
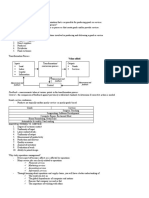
Forecasting: 3.
Select a forecasting technique
4. Obtain, clean and analyze data
Forecast:
5. Make the forecast
- Statement about the future value 6. Monitor the forecast
of a variable of interest, demand
Types of Forecast:
- Used to make informed decisions
- Long-range or Short-range Judgmental – uses
- Affect decisions and activities subjective inputs
throughout an organization - executive options
Accounting – cost/ profit - sales force opinions
estimates - consumer surveys
Finance – cash flow and - outside opinion
funding - delphi method (opinions of
Human Resources – hiring/ managers and staff, achieves
recruiting/ training a consensus forecast)
Marketing – pricing, Time series – uses historical
promotion, strategy data assuming the future will
MIS – ITAS systems, services be like the past
Operations – schedules, - trend – long-term movement
MRP, workloads in data
Product/ service design – new - seasonality – short-term
products and services regular variations in data
- Assumes causal system (past => - cycle – wavelike variations
future) of more than one year’s
- Rarely perfect because of duration
randomness - irregular variations – by
- More accurate for groups vs. unusual circumstances
individuals - random variations – by
- Accuracy decreases as time chance
horizon increases Associative models – uses
explanatory variables to
Elements of a Good Forecast: predict the future
Timely Forecast Variations:
Reliable
Accurate Trend
Meaningful Cycles
Written Seasonal variations
Easy to use Naïve Forecasts – forecast of
Steps in Forecasting Process: any period equals the previous
period’s actual value
1. Determine purpose of forecast
2. Establish a time horizon - simple to use
- virtually no cost
- quick and easy to prepare
- data analysis is nonexistent
- easily understandable
- cannot provide high accuracy
- can be a standard for accuracy
Techniques for Averaging:
Moving average – technique
that averages a number of
recent actual values, updated
as new values become
available.
Weighted moving average –
more recent values in a series
are given more weight in
computing the forecast
Exponential smoothing
You might also like
- Chapter 4 Airworthiness LimitationsDocument3 pagesChapter 4 Airworthiness LimitationsHrishikesh NarasimhanNo ratings yet
- McDonalds Franchise Disclosure DocumentDocument2 pagesMcDonalds Franchise Disclosure DocumentPrabjot Singh0% (1)
- Forecasting Techniques: Production and Operations in ManagementDocument71 pagesForecasting Techniques: Production and Operations in Managementsiddhartha chpeuriNo ratings yet
- Risk Based Internal Audit Plan PDFDocument40 pagesRisk Based Internal Audit Plan PDFDjay'hFrost100% (1)
- Forecasting Demand: Lesson 4Document13 pagesForecasting Demand: Lesson 4HerondaleNo ratings yet
- OM1 Chapter 3: ForecastingDocument1 pageOM1 Chapter 3: ForecastingRoseanne Binayao LontianNo ratings yet
- Forecasting: Chapter Three Operations Management William J. StevensonDocument13 pagesForecasting: Chapter Three Operations Management William J. StevensonJahirul Islam ShovonNo ratings yet
- Forecasting: Types of Forecasting ModelsDocument8 pagesForecasting: Types of Forecasting Modelslovely abinalNo ratings yet
- Forecasting: Chapter Three Operations Management William J. StevensonDocument20 pagesForecasting: Chapter Three Operations Management William J. StevensonFarhat IshaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2: Demand ForecastingDocument5 pagesMODULE 2: Demand Forecastingkristel lei diamanteNo ratings yet
- Operational Management POMG2710: Chapter OutlineDocument17 pagesOperational Management POMG2710: Chapter OutlineلبليايلاNo ratings yet
- Forecasting Part 1Document83 pagesForecasting Part 1Gela SorianoNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2: Demand ForecastingDocument4 pagesMODULE 2: Demand Forecastingkristel lei diamanteNo ratings yet
- SCM - Group 5Document4 pagesSCM - Group 5aainaa aqilahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Forecasting - 1st PartDocument34 pagesChapter 3 - Forecasting - 1st PartSam ElmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Heizer S2Document20 pagesChapter-3 Heizer S2Maxene Joi PigtainNo ratings yet
- ForecastingDocument10 pagesForecastingkiiadizonNo ratings yet
- Forecasting: I See That You Will Get An A From This CourseDocument60 pagesForecasting: I See That You Will Get An A From This CourseTalemaNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Forecasting Part 1Document16 pages3.2 Forecasting Part 1MBA LOGISTICS & SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENTNo ratings yet
- Forecasting: I See That You Will Get An A From This CourseDocument70 pagesForecasting: I See That You Will Get An A From This CourseTalemaNo ratings yet
- Week 1-5Document10 pagesWeek 1-5Yinshuang WangNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 ForecastingDocument23 pagesChapter-2 ForecastingsrikantushaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Forecasting(s)Document96 pagesLecture 3 - Forecasting(s)Vicaria McDowellNo ratings yet
- Forecasting Written ReportDocument7 pagesForecasting Written ReportCrestina Chu BagsitNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Rev (Introduction To Demand and Revenue Management)Document81 pagesWeek 1 Rev (Introduction To Demand and Revenue Management)wahyunidaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - ForecastingDocument39 pagesLesson 3 - ForecastingTomoyo AdachiNo ratings yet
- ForecastingDocument52 pagesForecastingVfhhdfvhhNo ratings yet
- ForecastingDocument19 pagesForecastingarelNo ratings yet
- Chapter II: Forecasting: ForecastDocument3 pagesChapter II: Forecasting: ForecastCJ De LunaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - OM NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 3 - OM NoteswejdazoNo ratings yet
- Man SciDocument4 pagesMan SciRIANE PADIERNOSNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Ops&SCMDocument67 pagesUnit 3 - Ops&SCMsumitsingh95345No ratings yet
- 2nd Year - CBMEDocument13 pages2nd Year - CBMEHo Sol JungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document93 pagesChapter 24zfq8g84rkNo ratings yet
- Ba ReviewerDocument7 pagesBa ReviewerJamielyn Dy DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2.1 ForecastingDocument33 pagesLecture 2.1 ForecastingMd. Mahbub KhanNo ratings yet
- Forecasting FundamentalszDocument2 pagesForecasting FundamentalszSatish KhullarNo ratings yet
- TQM Presentatio 55805079 3Document21 pagesTQM Presentatio 55805079 3Edi WowNo ratings yet
- ForecastingDocument2 pagesForecastingMiranda, Aliana Jasmine M.No ratings yet
- Sales ForecastingDocument32 pagesSales ForecastingtanyaNo ratings yet
- LOGI 3477 - Week 2 3Document134 pagesLOGI 3477 - Week 2 3krnkilincNo ratings yet
- Forecasting OMTQMDocument39 pagesForecasting OMTQMMicaella TimpugNo ratings yet
- CH 3 ForecastingDocument20 pagesCH 3 Forecastingkebaman1986No ratings yet
- Management Science ReviewerDocument16 pagesManagement Science ReviewerMc RamosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Planning: To Set DirectionDocument39 pagesChapter 3-Planning: To Set Directioneric labordoNo ratings yet
- POM 343 Chapter 8 TermsDocument1 pagePOM 343 Chapter 8 TermsjordanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document17 pagesChapter 2Eyob AberaNo ratings yet
- Mansci FinalsDocument4 pagesMansci FinalsLee Ann FermilNo ratings yet
- ForecastingDocument5 pagesForecastingPatrizia Nicole GozeNo ratings yet
- Forecasting BatulanbonifacioDocument34 pagesForecasting Batulanbonifaciocherish.jorge.patalNo ratings yet
- Forecasting TechniquesDocument9 pagesForecasting TechniquesJohn Jay NalicatNo ratings yet
- Operations DossierDocument81 pagesOperations DossierMudit FauzdarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ForecastingDocument102 pagesChapter 3 ForecastingJanak KarkiNo ratings yet
- Kayne Marquez - BME 1 - Activity 3.1Document5 pagesKayne Marquez - BME 1 - Activity 3.1Colline MarquezNo ratings yet
- Removal P2Document7 pagesRemoval P2hmvhNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 OM EditedDocument23 pagesUnit 5 OM EditedermiasnasirtaleginNo ratings yet
- SCMchap 2Document9 pagesSCMchap 2NguyenNo ratings yet
- What Is Forecasting: (Not Sure If Need Pa Isama Ung Decoupling Points)Document6 pagesWhat Is Forecasting: (Not Sure If Need Pa Isama Ung Decoupling Points)Angel Jasmin TupazNo ratings yet
- Day 4 - ForecastingDocument5 pagesDay 4 - ForecastingNate Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- CHAP 3-5 OMT BooksDocument16 pagesCHAP 3-5 OMT Booksbae joohyunNo ratings yet
- Operation Management FinalDocument7 pagesOperation Management FinalmonteverdevinNo ratings yet
- P501: Managing Operations & Supply Chain: Lecture - 7Document33 pagesP501: Managing Operations & Supply Chain: Lecture - 7halaku duttaNo ratings yet
- MODULE5Document10 pagesMODULE5Feane LamasanNo ratings yet
- PEDocument1 pagePEFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Economic DevelopmentDocument25 pagesReviewer in Economic DevelopmentFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- MicroeconDocument1 pageMicroeconFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document6 pagesChapter 1Feane LamasanNo ratings yet
- OPMAN ReviewerDocument2 pagesOPMAN ReviewerFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- BROCHUREDocument2 pagesBROCHUREFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - STSDocument3 pagesChapter 7 - STSFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- Chameleon 'S Tail: LinkDocument1 pageChameleon 'S Tail: LinkFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- WR Group3Document22 pagesWR Group3Feane LamasanNo ratings yet
- Market StructuresDocument2 pagesMarket StructuresFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Culminating ProjectDocument5 pagesModule 7 Culminating Projectapi-650742146100% (1)
- Manufacturing Manager Generic JD1Document4 pagesManufacturing Manager Generic JD1Bishal PandaNo ratings yet
- POM C12 Inventory ManagementDocument10 pagesPOM C12 Inventory ManagementLouis PatNo ratings yet
- Project Management - AhujaDocument518 pagesProject Management - AhujaChristian GarciaNo ratings yet
- Six Strategies For Competing Through Service An AgDocument5 pagesSix Strategies For Competing Through Service An Agmehdi achourNo ratings yet
- Protecting Legacy The Value of A Family OfficeDocument25 pagesProtecting Legacy The Value of A Family OfficeRavi BabuNo ratings yet
- Esmail PDFDocument12 pagesEsmail PDFMirela-Elena PopaNo ratings yet
- Noc18 mg42 Assignment4Document4 pagesNoc18 mg42 Assignment4Karan PatelNo ratings yet
- Job Description in ExcelDocument8 pagesJob Description in ExcelMuhammad ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Course Outline - Corporate Governance - 2021 - MBA 13th BatchDocument6 pagesCourse Outline - Corporate Governance - 2021 - MBA 13th BatchElma UmmatiNo ratings yet
- Lovepreet's, Cover Letter and Resume.Document4 pagesLovepreet's, Cover Letter and Resume.lovepreetsk0465No ratings yet
- Developing Performance Indicators For Managing Maintenance - 0 IntroductionDocument26 pagesDeveloping Performance Indicators For Managing Maintenance - 0 IntroductionSandro GastanagaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document58 pagesChapter 4Mohit PariharNo ratings yet
- Price Adjustment Guidance Note On ProcurementDocument40 pagesPrice Adjustment Guidance Note On ProcurementMintesnot BogaleNo ratings yet
- Tugas Pra Uas HehehehehDocument2 pagesTugas Pra Uas HehehehehrereskippersNo ratings yet
- Sample Chapter 3 MethodologyDocument3 pagesSample Chapter 3 Methodologykyla deguzmanNo ratings yet
- Improving Overall Equipment Effectiveness OEE of Extrusion Machine Using Lean Manufacturing ApproachManufacturing TechnologyDocument9 pagesImproving Overall Equipment Effectiveness OEE of Extrusion Machine Using Lean Manufacturing ApproachManufacturing TechnologyLuis Ulloa De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Learning Journal Unit 5 AdvertisingDocument4 pagesLearning Journal Unit 5 AdvertisingDominga SilvaNo ratings yet
- Service Operations ManagementDocument68 pagesService Operations ManagementAnushka KanaujiaNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting 1: (Prepared by MS. ARMI K. BUYCO, CPA, MBA)Document3 pagesManagement Accounting 1: (Prepared by MS. ARMI K. BUYCO, CPA, MBA)Gilner PomarNo ratings yet
- Procedure Transportaton & DeliveryDocument1 pageProcedure Transportaton & DeliveryDanishAnwerNo ratings yet
- Plantillas MarketingDocument26 pagesPlantillas MarketingAntelmoNo ratings yet
- MGT 301 Fall 2023 Final Term Question Paper (Online Exam)Document1 pageMGT 301 Fall 2023 Final Term Question Paper (Online Exam)tasnia nishatNo ratings yet
- Ey Iif Global Risk Survey V FinalDocument52 pagesEy Iif Global Risk Survey V Finalbildyosta sapparNo ratings yet
- Job Cost Sheet - Job J-832-LMDocument2 pagesJob Cost Sheet - Job J-832-LMAbrar Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document22 pagesLecture 3Dr Waheed AsgharNo ratings yet
- Charu Gupta 4 Years March'2023 CVDocument3 pagesCharu Gupta 4 Years March'2023 CVJapLangNo ratings yet