Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Os Class1
Os Class1
Uploaded by
prasantabinuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Os Class1
Os Class1
Uploaded by
prasantabinuCopyright:
Available Formats
Operating system
Definition :
An operating system acts as an intermediary between the user of a computer
and computer hardware. The purpose of an operating system is to provide an
environment in which a user can execute programs conveniently and
efficiently.
An operating system is a software that manages computer hardware. The
hardware must provide appropriate mechanisms to ensure the correct operation
of the computer system and to prevent user programs from interfering with the
proper operation of the system.
An operating system is concerned with the allocation of resources and services,
such as memory, processors, devices, and information. The operating system
correspondingly includes programs to manage these resources, such as a
traffic controller, a scheduler, a memory management module, I/O programs,
and a file system.
Goal of os-
1. Convenience: An OS makes a computer more convenient to use.
2. Efficiency: An OS allows the computer system resources to be used
efficiently.
3.Throughput: An OS should be constructed so that It can give
maximum throughput(Number of tasks per unit time).
Important functions of an operating System:
1. Security –
The operating system uses password protection to protect user data and
similar other techniques. it also prevents unauthorized access to programs
and user data.
2. Control over system performance –
Monitors overall system health to help improve performance. records the
response time between service requests and system response to having a
complete view of the system health. This can help improve performance by
providing important information needed to troubleshoot problems.
3. Job accounting –
Operating system Keeps track of time and resources used by various tasks
and users, this information can be used to track resource usage for a
particular user or group of users.
4. Error detecting aids –
The operating system constantly monitors the system to detect errors and
avoid the malfunctioning of a computer system.
5. Coordination between other software and users –
Operating systems also coordinate and assign interpreters, compilers,
assemblers, and other software to the various users of the computer
systems.
6. Memory Management –
The operating system manages the Primary Memory or Main Memory. Main
memory is made up of a large array of bytes or words where each byte or
word is assigned a certain address. Main memory is fast storage and it can
be accessed directly by the CPU. For a program to be executed, it should be
first loaded in the main memory. An Operating System performs the
following activities for memory management:
It keeps track of primary memory, i.e., which bytes of memory are used by
which user program. The memory addresses that have already been
allocated and the memory addresses of the memory that has not yet been
used. In multiprogramming, the OS decides the order in which processes are
granted access to memory, and for how long. It Allocates the memory to a
process when the process requests it and deallocates the memory when the
process has terminated or is performing an I/O operation.
7. Processor Management –
In a multi-programming environment, the OS decides the order in which
processes have access to the processor, and how much processing time
each process has. This function of OS is called process scheduling. An
Operating System performs the following activities for processor
management.
Keeps track of the status of processes. The program which performs this
task is known as a traffic controller. Allocates the CPU that is a processor to
a process. De-allocates processor when a process is no more required.
8. Device Management –
An OS manages device communication via their respective drivers. It
performs the following activities for device management. Keeps track of all
devices connected to the system. designates a program responsible for
every device known as the Input/Output controller. Decides which process
gets access to a certain device and for how long. Allocates devices in an
effective and efficient way. Deallocates devices when they are no longer
required.
9. File Management –
A file system is organized into directories for efficient or easy navigation and
usage. These directories may contain other directories and other files. An
Operating System carries out the following file management activities. It
keeps track of where information is stored, user access settings and status
of every file, and more… These facilities are collectively known as the file
system.
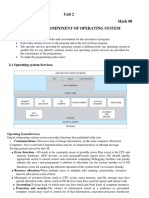
Conceptual view of a computer system
1. User
2. System and application programs
3. Operating system
4. Hardware
You might also like
- Mori Seiki SL Series Service ManualDocument16 pagesMori Seiki SL Series Service ManualMerauke 1No ratings yet
- IGNOU Mini Project Report MCADocument68 pagesIGNOU Mini Project Report MCAAshim Ranjan Bora80% (5)
- Onenote: Quick Reference GuideDocument3 pagesOnenote: Quick Reference GuideCarlos F. MendozaNo ratings yet
- TRB Study Materials Operating System: WWW - Governmentexams.co - in 1Document9 pagesTRB Study Materials Operating System: WWW - Governmentexams.co - in 1Jeyaraman DhanarajNo ratings yet
- Functions of Operating SystemDocument5 pagesFunctions of Operating SystemDEBLAIR MAKEOVER100% (5)
- COIT 403 Course Contents in Integrative Programming Technologies PDFDocument3 pagesCOIT 403 Course Contents in Integrative Programming Technologies PDFAaron Jude PaelNo ratings yet
- Custom Signature FieldsDocument7 pagesCustom Signature FieldsAbs1981No ratings yet
- Fipy Manual: Release 3.4.2.1Document617 pagesFipy Manual: Release 3.4.2.1Jun Obam'doNo ratings yet
- Important Functions of An Operating SystemDocument1 pageImportant Functions of An Operating SystemItech AnandNo ratings yet
- Functions of Operating SystemDocument2 pagesFunctions of Operating SystemSafeer Ullah khanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operating SystemDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Operating SystemVinars PatelNo ratings yet
- FocusTask2 Reading2Document6 pagesFocusTask2 Reading2pascalotieno1No ratings yet
- Unit - 1Document28 pagesUnit - 1Mahendra ChennareddyNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems - Unit-1Document28 pagesOperating Systems - Unit-1Srija GNo ratings yet
- 1.what Is An Operating SystemDocument18 pages1.what Is An Operating SystemComputer DepartmentNo ratings yet
- Os R19 - Unit-1Document26 pagesOs R19 - Unit-1Ranadheer BjskNo ratings yet
- Notes of Unit - II Comp FundamentalDocument29 pagesNotes of Unit - II Comp Fundamentaluserdumb709No ratings yet
- Operating System Lecture Note Module-1Document32 pagesOperating System Lecture Note Module-1Kefelegn GulintNo ratings yet
- Os NotesDocument31 pagesOs NotesAvinash YeshwanthpurNo ratings yet
- Functions of Operating SystemDocument5 pagesFunctions of Operating SystemHurain Zahid100% (2)
- Operating SystemDocument35 pagesOperating SystemVasudevNo ratings yet
- Chapter-01 (Operating Systems Fundamentals) Dr. Sheeraz Arif (Assoc. Professor) Operating SystemDocument9 pagesChapter-01 (Operating Systems Fundamentals) Dr. Sheeraz Arif (Assoc. Professor) Operating SystemSheeraz ArifNo ratings yet
- Function of OSDocument2 pagesFunction of OSShrimp MantisNo ratings yet
- An Operating SystemDocument27 pagesAn Operating Systemlandry NowaruhangaNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument14 pagesOperating SystemPrajwal NiroulaNo ratings yet
- Unit OneDocument13 pagesUnit OneAkshat JainNo ratings yet
- Operating System Module 1 For 1st Year MCADocument34 pagesOperating System Module 1 For 1st Year MCAsuhasmattmsNo ratings yet
- Ict ProjectDocument16 pagesIct Projectpshantanu123No ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument19 pagesOperating Systemvaddi srivallideviNo ratings yet
- OS OverviewDocument3 pagesOS OverviewCường WINDNo ratings yet
- OS NOTEDocument83 pagesOS NOTEsurajgvgmNo ratings yet
- Functions of Operating SystemDocument2 pagesFunctions of Operating Systemfelicitygaming8No ratings yet
- UU BBA SEM 1 Fundamentals of Computing Unit 5Document24 pagesUU BBA SEM 1 Fundamentals of Computing Unit 5gunjikagupta098No ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument4 pagesOperating Systemshazebkhann100% (1)
- DocumentsDocument18 pagesDocumentslamiaz7888No ratings yet
- Important Question Operating System 1Document26 pagesImportant Question Operating System 1bihirof259No ratings yet
- OS Unit-1 NotesDocument31 pagesOS Unit-1 Notesamulya.bcaNo ratings yet
- An Operating SystemDocument3 pagesAn Operating SystemUmme FarwaNo ratings yet
- OSY Unit IDocument15 pagesOSY Unit IRenuka KeneNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument11 pagesOperating SystemDamber ThapaNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems Concepts: Lecture 1 - IntroductionDocument18 pagesOperating Systems Concepts: Lecture 1 - IntroductionRashda KhanzadaNo ratings yet
- Goals:: Unit-1 Introducation To O/SDocument34 pagesGoals:: Unit-1 Introducation To O/SJanabhawana CampusNo ratings yet
- Lynda Vimbai Gonese Nd3 - Part-TimeDocument6 pagesLynda Vimbai Gonese Nd3 - Part-TimeLynda Vimbai GoneseNo ratings yet
- Unit1 - Introduction To OSDocument7 pagesUnit1 - Introduction To OSAdarsh PandeyNo ratings yet
- 1 2 Operating System Question BankDocument32 pages1 2 Operating System Question BankShivraj Patil100% (1)
- Operating SystemsDocument26 pagesOperating Systemsmahima yadavNo ratings yet
- An Operating SystemDocument3 pagesAn Operating SystemTapash SunjunuNo ratings yet
- OS Module 5Document22 pagesOS Module 5shekhawatharsh54No ratings yet
- An Operating SystemDocument3 pagesAn Operating SystemMuhammad Adnan KhalidNo ratings yet
- Computer Application - PCC-CM-PHD103 - Computer - Application Class Assignment:1Document3 pagesComputer Application - PCC-CM-PHD103 - Computer - Application Class Assignment:1Rakesh JhaNo ratings yet
- Bca Ii Sem Operating SystemsDocument78 pagesBca Ii Sem Operating SystemsSiva KumarNo ratings yet
- UNIT-I (B) Working Knowledge of Computer System: Hat Is Perating YstemDocument13 pagesUNIT-I (B) Working Knowledge of Computer System: Hat Is Perating YstemsurendarNo ratings yet
- Intro To OSDocument9 pagesIntro To OSdesignography02No ratings yet
- Operating System (English) PDFDocument5 pagesOperating System (English) PDFdeepika100% (2)
- Services and Component of Operating System1Document6 pagesServices and Component of Operating System1Nisarg GugaleNo ratings yet
- OS Unit 1 NotesDocument48 pagesOS Unit 1 NotesHARSHA VINAY KOTNI HU21CSEN0100574No ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument9 pagesOperating SystemappleNo ratings yet
- An Operating SystemDocument97 pagesAn Operating SystemBaptist GHNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 OS Notes - Part 1Document30 pagesUnit 1 OS Notes - Part 1dedali8086No ratings yet
- Role of Operating System As Resource ManagerDocument4 pagesRole of Operating System As Resource ManagerdeeNo ratings yet
- Overview of Operating System: HardwareDocument13 pagesOverview of Operating System: Hardware33GKandekar AshishNo ratings yet
- Suggest Question and AnswersDocument8 pagesSuggest Question and AnswersOMKAR KUMARNo ratings yet
- Os Unit-1 (Bca)Document54 pagesOs Unit-1 (Bca)Bot IdNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems: Concepts to Save Money, Time, and FrustrationFrom EverandOperating Systems: Concepts to Save Money, Time, and FrustrationNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandOperating Systems Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- SORTING (Bubble Sort) Aim of The Experiment: Write A C Program That Implement Bubble Sort Method To Sort A GivenDocument12 pagesSORTING (Bubble Sort) Aim of The Experiment: Write A C Program That Implement Bubble Sort Method To Sort A GivenprasantabinuNo ratings yet
- C Pointers: Declaring A PointerDocument9 pagesC Pointers: Declaring A PointerprasantabinuNo ratings yet
- Nalanda Institute of Technology (Nit)Document1 pageNalanda Institute of Technology (Nit)prasantabinuNo ratings yet
- Nalanda Institute of Technology (Nit)Document1 pageNalanda Institute of Technology (Nit)prasantabinuNo ratings yet
- Declaration of Two Dimensional Array in CDocument8 pagesDeclaration of Two Dimensional Array in CprasantabinuNo ratings yet
- Week 1: Assignment 1 (Cloud Computing) : A. B. C. DDocument4 pagesWeek 1: Assignment 1 (Cloud Computing) : A. B. C. DprasantabinuNo ratings yet
- Rumana BaharDocument3 pagesRumana BaharprasantabinuNo ratings yet
- Lantek Sharp Cut Cutting SoftwareDocument17 pagesLantek Sharp Cut Cutting SoftwareandonialbizulantekNo ratings yet
- Sweetercalc Documentation: Updated: 27.04.2016Document38 pagesSweetercalc Documentation: Updated: 27.04.2016Javer RivasNo ratings yet
- MJJ Query ASPNETDocument186 pagesMJJ Query ASPNETMichelle JonesNo ratings yet
- MOD09 UserGuide v1 3Document40 pagesMOD09 UserGuide v1 3Argemiro Lucena AraujoNo ratings yet
- GOES-R Ground Segment Project NSOF Lunchtime Seminar: 17 September 2009Document34 pagesGOES-R Ground Segment Project NSOF Lunchtime Seminar: 17 September 2009Santosh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Data Link: Systems OperationDocument6 pagesData Link: Systems OperationGabriel Paco LunaNo ratings yet
- Overall - Scan-My HD Receiver PDFDocument5 pagesOverall - Scan-My HD Receiver PDFsaif22sNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument709 pagesDocumentfaiyaz432No ratings yet
- Mentor Graphics Corporation, Designing With Xilinx's Embedded Processors in HDL Designer, AppNote 10005Document34 pagesMentor Graphics Corporation, Designing With Xilinx's Embedded Processors in HDL Designer, AppNote 10005dupipiNo ratings yet
- Cwna (Wi Fi Administration) : CWNA - Certified Wireless Network AdministratorDocument1 pageCwna (Wi Fi Administration) : CWNA - Certified Wireless Network AdministratorBayu Andrianto0% (1)
- 2018 OOAD AnswersDocument9 pages2018 OOAD AnswersArun HarrishNo ratings yet
- Ekosistem Bisnis Iot Di Indonesia: Fita Indah MaulaniDocument13 pagesEkosistem Bisnis Iot Di Indonesia: Fita Indah MaulaniAgung Kus SugihartoNo ratings yet
- ADV7511 Programming GuideDocument203 pagesADV7511 Programming GuidemikeisivanNo ratings yet
- MultiZone Limitations and HintsDocument2 pagesMultiZone Limitations and HintsRubén Darío Becerra GalindoNo ratings yet
- Module 10Document3 pagesModule 10Trevor BornsteinNo ratings yet
- Java Programs - Image EditorDocument1 pageJava Programs - Image EditorNameNo ratings yet
- ERP NotesDocument16 pagesERP NoteslavinNo ratings yet
- 2021 Bece User GuideDocument26 pages2021 Bece User Guideangus ogwucheNo ratings yet
- Create A Wallet Account: Etherflyer Exchange TutorialDocument7 pagesCreate A Wallet Account: Etherflyer Exchange TutorialBodasNo ratings yet
- OneExpert CATV ONX630 DatasheetDocument20 pagesOneExpert CATV ONX630 DatasheetJhon Jairo CaicedoNo ratings yet
- Weka - Architectural - WhitePaper-W02R6WP201812-1Document25 pagesWeka - Architectural - WhitePaper-W02R6WP201812-1Wilson OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Python Scientific IntroDocument335 pagesPython Scientific IntrosuperbuchNo ratings yet
- Services ProcurementDocument17 pagesServices ProcurementlarisaschiopuNo ratings yet