Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Oral Recitation
Oral Recitation
Uploaded by
Teresa Marie Cordero0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageThe brain is the control center of the nervous system. DNA is a double helix structure made of nucleotides. The thyroid gland located at the base of the neck regulates calcium levels and biological clocks. Semen contains sugars from seminal vesicles added to sperm.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe brain is the control center of the nervous system. DNA is a double helix structure made of nucleotides. The thyroid gland located at the base of the neck regulates calcium levels and biological clocks. Semen contains sugars from seminal vesicles added to sperm.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageOral Recitation
Oral Recitation
Uploaded by
Teresa Marie CorderoThe brain is the control center of the nervous system. DNA is a double helix structure made of nucleotides. The thyroid gland located at the base of the neck regulates calcium levels and biological clocks. Semen contains sugars from seminal vesicles added to sperm.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
The organ which is considered to be the control center of the nervous system.
A double helix structure molecule that has a long chain of nucleotides.
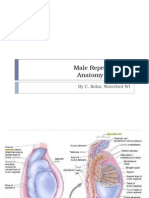
An organ which is found in both males and females. It is usually longer in males than that of females.
A white or grayish fluid secreted by the penis.
A hormone that is secreted by the pituitary gland and that is involved in tissue growth.
A “fight or flight” hormone.
Is the term used to describe the sequence of events that occur in your body as it prepares for the possibility of pregnancy.
Refers to the female sex cells.
A component of the peripheral nervous system that regulates involuntary physiologic processes of our body.
A sac of skin that holds the testes.
An erectile organ that contains the urethra.
A disorder that happens during childhood when there is an abnormal increase in height associated with too much secretion of
growth hormones.
A butterfly-shaped endocrine gland located at the base of the front of the neck.
A type of RNA that transfers amino acids to the ribosome.
A part of a nucleotide that forms phosphodiester bonds with the pentose sugars to create the sides of the nucleotide “ladder”.
A type of sugar is produced from the seminal vesicles and is added to the semen.
A pea-sized gland located below the brain and sometimes called as the “MASTER GLAND”.
A part of the neuron that contains the nucleus.
Refers to the monthly bleeding of females’ vagina.
Refers to two days before ovulation and two days after ovulation.
A process which refers to the release of egg from the ovary.
A single-stranded molecule which has a shorter chain of nucleotides.
A class of molecules composed of one or more long chains of amino acids.
Refers to the passing of traits from parents to offspring.
Refers to the female gonads where egg cells are being produced.
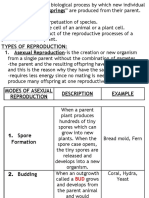
A process by which organisms make more organisms like themselves.
It is where the egg is fertilized by the sperm cell.
A type of gland which are ductless and release the substances that they make (hormones) directly into the bloodstream.
Refers to the process through which the level of one substance influences the level of one substance.
An organ which connects the brain and the body.
A hormone that is produced by the thyroid gland and that is involved in calcium homeostasis by decreasing the calcium level in
the blood.
A gland that produces a hormone which regulates the biological clock in some animals.
A nerve which sends electrical signals between your brain, face, neck and torso.
A part of the neuron that carries the impulses away from the cell body.
A type of gland that do not produce hormones and they release their product through a duct.
A phase of the menstrual cycle wherein endometrium sheds.
A system that includes the brain, spinal cord, and a complex network of nerves.
These are bundles of nerve fibers connected to the spinal cord that carry information to and away from the spinal cord.
These are building blocks of proteins.
The process by which a double-stranded DNA molecule is copied to produce two identical DNA molecules.
An organ that receives the penis of the male during mating.
It is a system composed of glands that secrete different types of hormones that affect almost every cell, organ, and function of
our body.
A part of the brain which is responsible for maintaining our posture, balance and coordination.
A type of neuron which carry impulses from the sense organs to the brain and spinal cord.
A hollow organ in a woman’s pelvis in which an embryo can grow and develop.
A long, coiled tube that stores sperm and transports them from the testes into the vas deferens.
Are chemical messengers that travel throughout an organism’s body, usually in the blood.
A hormone your pituitary gland releases that triggers your adrenal glands to release cortisol.
Is the hormone of the thymus, and it stimulates the development of disease-fighting T cells.
A hormone given to people who have low glucose level in their blood.
A type of neuron which carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles.
You might also like
- Unit 3 Module 1Document6 pagesUnit 3 Module 1heide100% (1)
- Physique Zero 8 Minute WorkoutsDocument4 pagesPhysique Zero 8 Minute WorkoutsShuvajoyyy100% (1)
- Grade 10 3rd Quarter Science ReviewerDocument5 pagesGrade 10 3rd Quarter Science ReviewerZayin DelMundoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands - Definition Examples Function Biology DictionaryDocument7 pagesEndocrine Glands - Definition Examples Function Biology Dictionaryrania khanNo ratings yet
- 3-1 Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive SystemDocument61 pages3-1 Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive SystemKim CyrilNo ratings yet
- ReproducytiveDocument13 pagesReproducytivePosionous SubstancesNo ratings yet
- Science Notes BruhDocument7 pagesScience Notes BruhIsaac JTNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesEndocrine Systemkevin maheshNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesEndocrine SystemRishu SinghNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument3 pagesSCIENCEAngelica PoblacionNo ratings yet
- What Is The Endocrine System?Document4 pagesWhat Is The Endocrine System?JR MamelocoNo ratings yet
- General Physiology: Samina AhmadDocument41 pagesGeneral Physiology: Samina AhmadMuhammad bilalNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument14 pagesEndocrine Systemjon AtlunaNo ratings yet
- (Reading 6) The Reproductive SystemDocument22 pages(Reading 6) The Reproductive SystemPhú LêNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 3Rd QuarterDocument7 pagesScience Reviewer 3Rd Quartermikykyla08No ratings yet
- BIOLOGICAL BASIS OF BEHAVIOUR-Mbundire (2023) 2Document9 pagesBIOLOGICAL BASIS OF BEHAVIOUR-Mbundire (2023) 2Emmanuel MulengaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4.5Document4 pagesTutorial 4.5Rosa FinizioNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument55 pagesNervous SystemRhesa SesucaNo ratings yet
- Guiruela JelianDocument3 pagesGuiruela JelianLyra LingcoranNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive AnatomyDocument28 pagesMale Reproductive AnatomyOyedotun TundeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Par.1 and 2Document2 pagesChapter 5 Par.1 and 2Anouar el OuakiliNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument14 pagesEndocrine SystemGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument14 pagesEndocrine SystemALYSSA MAE DAPADAPNo ratings yet
- What Does The Endocrine System Do?Document10 pagesWhat Does The Endocrine System Do?hadiqa azizNo ratings yet
- Control Coordination NotesDocument6 pagesControl Coordination NotesRaman ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument17 pagesScience ReviewerankaaNo ratings yet
- BibliographyDocument9 pagesBibliographySam SamNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviourDocument25 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviourSarfraz Ahmad MayoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Unit 3 Science Grade 10Document6 pagesLecture Unit 3 Science Grade 10Krizt Theodore Colico100% (7)
- 002 Male-Structures-And-Internal-Functions-Of-ErectionDocument5 pages002 Male-Structures-And-Internal-Functions-Of-ErectionMiguelito JeromeNo ratings yet
- Male Reproduction Anat and PhysioDocument36 pagesMale Reproduction Anat and PhysioDeny ShajiniNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Endocrine System HypothalamusDocument27 pagesAnatomy of The Endocrine System Hypothalamusdaphnereeze100% (1)
- Reproductive and Endocrine SystemsDocument38 pagesReproductive and Endocrine SystemsDebbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemsDocument30 pagesReproductive SystemsMARIAM AVILANo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemZander Ragasa GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Sci NotesDocument6 pagesSci NotesJabez Edwin SivaNo ratings yet
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Document8 pagesStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Ayush KumarNo ratings yet
- Big Book Science HGHDocument16 pagesBig Book Science HGHjackie lou mulaNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Exocrine GlandsDocument5 pagesThe Endocrine System: Exocrine GlandsahmedfikryNo ratings yet
- All Living Things ReproduceDocument4 pagesAll Living Things ReproduceMelinde BarluadoNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System - Integral PartsDocument3 pagesThe Endocrine System - Integral PartsDavid TanNo ratings yet
- ReproductiveDocument3 pagesReproductiveJanKennette MangaccatNo ratings yet
- Mikroteaching MateriDocument21 pagesMikroteaching MateriNopia DewiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document9 pagesLesson 4Eden Mae PerezNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument20 pagesEndocrine SystemJasmine faith casasNo ratings yet
- GROUP 9 Edocrine System ReportDocument52 pagesGROUP 9 Edocrine System Reportroyeth montezaNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System!Document11 pagesThe Endocrine System!Adrian 'Aj' AllenNo ratings yet
- Add A SubheadingDocument11 pagesAdd A SubheadingLexyn Rhaine InfanteNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Group 1Document26 pagesEndocrine System Group 1Jayson Kier AquinoNo ratings yet
- 12a. Final Notes On Male ReproductionDocument8 pages12a. Final Notes On Male ReproductionNishant ShahNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy - Module 1 & 2 - Final TermDocument46 pagesHuman Anatomy - Module 1 & 2 - Final TermwelpNo ratings yet
- 3-Coordination in AnimalsDocument23 pages3-Coordination in AnimalsDerrick MNo ratings yet
- Ms Word Notes - Template (May 2022)Document5 pagesMs Word Notes - Template (May 2022)Aries SungaNo ratings yet
- HAPL4 - HUMAN ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY - MODULE 4 & 5Document47 pagesHAPL4 - HUMAN ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY - MODULE 4 & 5welpNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL AND NERVOUS CONTROL (Autosaved)Document34 pagesCHEMICAL AND NERVOUS CONTROL (Autosaved)Anonymous Xg7hIOAzNo ratings yet
- Coordinated Functions of Endocrine and Reproductive SystemsDocument22 pagesCoordinated Functions of Endocrine and Reproductive SystemsMindi May AguilarNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsDocument29 pagesEndocrine System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsAlyssum Marie50% (2)
- Endocrine SystemDocument14 pagesEndocrine SystemWhyL NificentNo ratings yet
- Objective: Third Quarter Notes in Grade 10 Science Biology The Male Reproductive SystemDocument45 pagesObjective: Third Quarter Notes in Grade 10 Science Biology The Male Reproductive Systemmarife gupaalNo ratings yet
- Plant: Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesPlant: Reproductive Systemchan_1016No ratings yet
- Deciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineFrom EverandDeciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Examination in Science 9Document2 pagesSecond Quarter Examination in Science 9Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Naming CompoundsDocument2 pagesNaming CompoundsTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Final Exam in Chem 1Document2 pagesFinal Exam in Chem 1Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- First Final Examination in Science 7Document8 pagesFirst Final Examination in Science 7Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Pretest in Physical Science 12Document3 pagesPretest in Physical Science 12Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Examination in Physical Science 12 (2019-2020)Document2 pages2nd Quarter Examination in Physical Science 12 (2019-2020)Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- SECOND QUARTERLY EXAMINATION IN SCIENCE 8 (Simplicity)Document2 pagesSECOND QUARTERLY EXAMINATION IN SCIENCE 8 (Simplicity)Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- First Quarterly Examination in Science 10Document2 pagesFirst Quarterly Examination in Science 10Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- First Quarterly Examination in Science 7 (2019-2020)Document2 pagesFirst Quarterly Examination in Science 7 (2019-2020)Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Long Test in Science 7Document1 pageLong Test in Science 7Teresa Marie Cordero100% (1)
- Periodic Table (Chemical Bonding)Document8 pagesPeriodic Table (Chemical Bonding)Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Activity 1Document2 pagesEndocrine Activity 1Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- TOS Grade 10 (1st Quarter 2019-2020)Document3 pagesTOS Grade 10 (1st Quarter 2019-2020)Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Activity in MicroscopeDocument2 pagesActivity in MicroscopeTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument9 pagesCHEMISTRYTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Levels of Biological OrganizationDocument6 pagesLevels of Biological OrganizationTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIONDocument8 pagesREPRODUCTIONTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- CARBONDocument1 pageCARBONTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- CELL OrganellesDocument5 pagesCELL OrganellesTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- MICROSCOPEDocument5 pagesMICROSCOPETeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- WHLP Activity Sheet 1 (Circulatory)Document1 pageWHLP Activity Sheet 1 (Circulatory)Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Concentration of SolutionsDocument30 pagesConcentration of SolutionsTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Ways of Separating MixturesDocument23 pagesWays of Separating MixturesTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument47 pagesAtomic StructureTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- American Fashion Trends Through The DecadesDocument10 pagesAmerican Fashion Trends Through The Decadesdino saurNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodical Test I Science ReviewerDocument7 pages1st Periodical Test I Science Reviewercatherine tamayoNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Human Anatomy 5th Edition by MckinleyDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Human Anatomy 5th Edition by Mckinleydisproof.torquate.vat9100% (50)
- Sim Dump One Cassandra CC ListDocument3 pagesSim Dump One Cassandra CC ListpepitaNo ratings yet
- By Sayyed Nadar ShahDocument9 pagesBy Sayyed Nadar ShahShayan ShayanNo ratings yet
- Arm Diagram Left - Google Search PDFDocument1 pageArm Diagram Left - Google Search PDFjordanNo ratings yet
- PEDH 112 Fourth Quarter ExamDocument4 pagesPEDH 112 Fourth Quarter ExamJoshua Azura50% (2)
- Ethiopian Textile & Garment Industry: S.No. Company Name Telephone FAX E-Mail P.O.BoxDocument7 pagesEthiopian Textile & Garment Industry: S.No. Company Name Telephone FAX E-Mail P.O.BoxMulugeta Kebede100% (1)
- Lab Exercise9 SensesDocument4 pagesLab Exercise9 Sensesian avenNo ratings yet
- Q1 ExamDocument3 pagesQ1 ExamGlenda AstodilloNo ratings yet
- Facts Ideas Learning IssuesDocument4 pagesFacts Ideas Learning IssuesGgg2046No ratings yet
- Anatomy PhysiologyDocument8 pagesAnatomy PhysiologyDOROLA CRIS JANELICA R.No ratings yet
- Mbbs Ist Prof Part I & Part II BooksDocument5 pagesMbbs Ist Prof Part I & Part II Bookssheza_afzaal100% (1)
- DLL - Science 4 - Q2 - W1Document10 pagesDLL - Science 4 - Q2 - W1Jesha Barbara ParohinogNo ratings yet
- Drugs The Straight Facts, Body Enhancement Products OptimizedDocument121 pagesDrugs The Straight Facts, Body Enhancement Products OptimizedDeathbedeli100% (3)
- 3rd Quarter Exam G10Document2 pages3rd Quarter Exam G10Jane Limsan PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Tesda-SwedishDocument53 pagesTesda-SwedishWisdom SeekerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology Part 1Document5 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy and Physiology Part 1Abby Claire SomeraNo ratings yet
- T Par 1636017131 Designers Coco Chanel Ages 7 11 - Ver - 1Document6 pagesT Par 1636017131 Designers Coco Chanel Ages 7 11 - Ver - 1Sofia RementeriaNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Lung CancerDocument50 pagesCase Study On Lung CancerAna Marie Besa Battung-Zalun78% (9)
- StellAmore BeachwearDocument4 pagesStellAmore Beachwearstellamore309No ratings yet
- Terminologi AnatomiaDocument49 pagesTerminologi AnatomiaLuluk QurrataNo ratings yet
- Hair Types and Textures AssignmentDocument3 pagesHair Types and Textures Assignmentapi-320398642No ratings yet
- KharanDocument4 pagesKharansuhaib_wahalaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE ExamDocument4 pagesSCIENCE ExamLesley AntojadoNo ratings yet
- Gold Exp A2P U5 Skills Test ADocument6 pagesGold Exp A2P U5 Skills Test AIrene DibiNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The SkinDocument26 pagesAssessment of The SkinRON PEARL ANGELIE CADORNANo ratings yet
- Botany and Zoology (Grade 12-Biology Reviewer)Document12 pagesBotany and Zoology (Grade 12-Biology Reviewer)Patricia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris Semester 3Document5 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris Semester 3Roby SuhendraNo ratings yet