Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electric Drive Systems: AC Machine (DC Sinamics)
Electric Drive Systems: AC Machine (DC Sinamics)
Uploaded by
Ahmed IshaqOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electric Drive Systems: AC Machine (DC Sinamics)
Electric Drive Systems: AC Machine (DC Sinamics)
Uploaded by
Ahmed IshaqCopyright:
Available Formats
Practical Presentation SS 2022
Electric Drive Systems
AC Machine (DC Sinamics)
Prepared By:
Fahad Jamshaid
A K MD Bodiuzzaman
Syed Khizar Hayat
Accompanying Course Information 1
Contents
Goal / Tasks
Introduction
Parts & Components
Circuit & Operation
Safety Measures
Commissioning
Accompanying Course Information 2
Goal / Tasks
❑ Operate Three Phase AC fan.
❑ Operate Three Phase AC Machine.
(Make sure Machine will run only when Fan is operating).
❑ Measure Rotational Speed of Machine.
❑ Control Speed using Frequency Converter.
❑ Rotation of Motor in both directions.
(Clock-wise and Anti clock wise direction).
❑ Stop Machine in case of Emergency.
Accompanying Course Information 3
Introduction
AC Machine with DC Sinamics
❑ Three Phase AC Machine
❑ DC Input
❑ AC Output (Three Phase with 50Hz Frequency)
Three Phase AC Supply
DC Supply
3 Phase Inverter, Control
Unit, Electric Components,
Speed Control Unit etc.
Accompanying Course Information 4
Parts & Components
AC Machine with DC Sinamics
❑ Rectifier
❑ Inverter
❑ Three Phase AC Motor
❑ Tachogenerator
❑ Temperature sensor
❑ Potentiometer
❑ Circuit Breakers
❑ Push Buttons, Switches
❑ Relays
❑ Fuses
❑ Control Unit
Accompanying Course Information 5
DC Supply via Rectifier
Grid is supplying with AC power and no DC source.
3 phase Rectifier is used to convert 3 phase AC Supply into DC to feed
the DC Sinamics.
Smoothing Capacitor (Filter) can be used to Three Phase Rectifier
remove the ripples from rectifier output.
Accompanying Course Information 6
Frequency Inverter
❑ Inverter is used to convert DC voltage from rectifier to three phase AC
voltage to run the 3 Phase AC motor.
❑ Harmonics such as 3rd, 5th and so on…
❑ Specially designed filter used to remove the harmonics.
Three Phase Inverter
Accompanying Course Information 7
3 Phase AC Motor
Parts of AC Motor
Three Phase Motor has mainly two parts:
❑ Stator Windings
❑ Stationary part placed in stator of
motor.
❑ Stator Frame, outer part (covering, Stator of 3 Phase AC Motor
protection and mechanical strength)
❑ Stator core (reduce eddy current &
Hysteresis loss)
❑ Stator or field windings (3 windings,
120 degree apart, wound on the stator
of AC machine. Produces three phase
magnetic field.
Accompanying Course Information 8
3 Phase AC Motor
❑ Rotor
❑ Rotating Part of Motor.
❑ Contains conductors in the form of Aluminum or copper bars connected
to form a circuit.
❑ The rotor surrounds the motor shaft and is the motor component that
rotates to produce the mechanical energy output of the motor.
❑ The spinning fan draws ambient air from outside across the stator and
rotor for cooling.
Rotor of 3 phase AC Machine
Accompanying Course Information 9
Operation of 3 Phase AC Motor
Accompanying Course Information 10
Operation of 3 Phase AC Motor
❑ Three Phase AC Supply in given to the Stator windings.
❑ AC currents are phase-shifted by 120o, the magnetic polarity of the
three coils are not all identical at the same instant of time.
❑ Produces three phase changing magnetic field, known as Rotating
Magnetic field.
❑ Changing magnetic field from the stator induces a current in the
rotor coils by EMF (Faraday’s Law).
❑ Rotor induced current results in opposing magnetic field by rotor.
(Lenz’s Law)
❑ The rotor seeks to align its polarity against that of the stator field,
the result being a net torque is applied to the shaft
Accompanying Course Information 11
Components
Tachogenerator
❑ Electrical generator used to detect the speed of electrical machines or
other drives.
❑ Develops DC voltage proportional to the speed of the connected motor.
Temperature Sensor
❑ Used to measure the temperature of motor in order to prevent it from
over heating and to keep the motor within extreme limits.
Potentiometer
❑ It is used to control the speed of motor.
❑ It has three terminal, one with maximum, one with minimum value and
other is sliding terminal.
Accompanying Course Information 12
Components
Relay
❑ The Relay is a switching device which gives a signal to the circuit breaker
as soon as the fault occurs in the power system.
Circuit Breaker
❑ Electrical safety device
❑ Received signal from the relay.
❑ Protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by an overcurrent or
short circuit.
Example:
Motor has installed a relay of 30A.
Current increased from 30A.
Relay give signal to circuit breaker
Circuit breaker interrupts the current.
Accompanying Course Information 13
Industrial Motor Controls
Figure: control unit [9]
• Power Management control: short circuit protection ,Overvoltage protection
• Speed Control for efficient use of the motor
• Temperature Control : overheating
• Emergency safety control
Accompanying Course Information 14
Consideration for circuit development
soft-start
▪ Induction motors can have inrush currents seven to ten times that of the
operational current. Starting torques can be 3 times higher to overcome
the starting conditions, causing mechanical stress on the components in
the motor.
▪ Reduce the load on the self-starting motor and the current surge of the
motor during start-up.
▪ This reduces the mechanical stress on the motor and shaft, as well as the
electrodynamics' stresses on the attached power cables and electrical
distribution network, extending the lifespan of the system.
Parameter to monitor:
A digital soft-starter controller continuously monitors the voltage during
start-up, adjusting to the load of the motor to provide a smooth
acceleration and the speed control.
Accompanying Course Information 15
Speed monitor :
The synchronous speed ns of the motor is calculated by:
120∗𝑓𝑠
ns = [rpm]
𝑃
where ,fs is the synchronous stator frequency in Hz, p is the number of stator poles.
The load torque is produced by slip frequency. The motor speed is characterized by a slip sr
(ns −nr ) nsl
Sr = =
ns ns
Where, nr is the rotor mechanical speed and nsl is the slip speed, both in rpm.
The motor speed is controlled by variation of a stator frequency with the influence of the
load torque.
Accompanying Course Information 16
Figure: Torque-Speed Characteristic at Constant Voltage and Frequency [9]
Accompanying Course Information 17
Speed Closed-Loop System
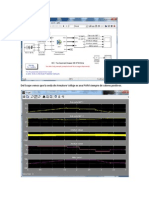
Figure: Closed Loop Control System [9]
To improve system performance, a closed-loop Volts per Hertz control was
introduced. In this method, a speed sensor measures the actual motor
speed and the system takes this input into consideration.
Accompanying Course Information 18
Connecting the fan
▪ The motor has to be operated with fan
▪ If the motor is operated without fan it will overheat because the heat
that is generated cannot be dissipated.
▪ Destruction of the motor is the consequence.
▪ Provide a protective circuit that prevents the main motor from being
switched on when the fan unit is not in operation.
Parameter to Monitor: Temperature
Accompanying Course Information 19
Stopping
▪ There are three forms of stopping: coasting, braking or a deceleration ramp.
▪ When power is removed from a motor, it begins to coast to a stop and is time dependent
upon the inertia and the load. Coasting is impractical in some applications because the
motor
would take too long to stop.
▪ Brake can be used to stop the motor quickly. Mechanical brake: magnetic clutch
▪ Electric brake : Dynamic DC braking and regenerative brakes
self-holding
When the relay is triggered, the state is retained by a function called a self-
holding circuit. A self-holding circuit enables a control range to be set and
also prevents the relay from switching rapidly due to ripples of power supply.
Accompanying Course Information 20
Overview of electrical faults
Figure: Electrical faults[10]
Accompanying Course Information 21
Wiring diagram
Figure: Wiring diagram
Accompanying Course Information 22
Safety Measures
1. Personal Health Safety
❑ Avoid working alone in the lab. Perform the lab in the presence of instructor
because the procedures being conducted are hazardous.
❑ High voltages dangerous for health
❑ Avoid using loose dress, or tie while operating the machine
❑ Don’t make changes to the pin configuration (add/remove the pins) while the
machine operating
❑ Know the Emergency Exit routes, first Aid box (1st floor), fire extinguisher and
Emergency contact (I.C.E Call 999,0112)
Accompanying Course Information 23
Safety Measures
2. Safety for Machinery/Circuit
❑ Emergency Stop Button : The red round button placed in the panel is
Emergency Stop button. Press the button in case of emergency to avoid any bad
things.
Fig : Emergency Stop Button
❑ Wires: Place correct wires at correct positions.
❑ Fuse: The fuse is used to protect the controller in case of over current. we use
F11 here in the circuit. The fuse cannot be repaired once damaged.
❑ Circuit Breaker: The circuit breaker is used to protect the Fan. we use Q1 in the
circuit. The circuit braker is tripped but not damaged.
Accompanying Course Information 24
Safety Measure
❑ Here in this circuit, for the safety we introduce a topology that when the motor
rotates (as explained previously) it produce heat losses. The heat losses is
proportional to the square of the current.
❑ To counter this effect, a cooling system (Fan) needs to be operate in parallel
with the motor operation all the time.
❑ For further safety, the motor will works only when the Fan is working properly.
❑ For inverter safety, it is necessary to ensure that same leg switches will conduct
in the same time, otherwise it produce the short circuit between the input
supply.
Accompanying Course Information 25
Wires Color Coding
❑ Black Wire : Used for Live phase
❑ Blue Wire: Used for Neutral
Black and Blue wires are used for single phase AC Supply (220 V)
❑ Red Wire: Used for positive DC
❑ Blue Wire: Used for negative DC / Gnd
❑ Red and Blue wires are used for DC supply
❑ Black, Grey, Brown is used for three phase AC supply
❑ Yellow: used for potential Earth
Accompanying Course Information 26
Commissioning
▪ Hardware
– Three Phase Rectifiers
– Circuit Breaker
– Fuses
– Relay
– Switches
– Wires
▪ Software
– PWM Generation for inverter switches
– Speed control
– Position control
Accompanying Course Information 27
Thank You for the Attention ☺
Accompanying Course Information 28
References
[1] https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.electronics-tutorials.ws%2Fpower%2Fthree-phase-
rectification.html&psig=AOvVaw2F8GxsDQN-
7zX_NyOq88ok&ust=1650756747774000&source=images&cd=vfe&ved=0CAwQjRxqFwoTCPjDh57qqPcCFQAAAAAdAAAAABAD
[2] https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.electricalvolt.com%2F2019%2F06%2Frotating-magnetic-field-in-
three-phase-induction-
motor%2F&psig=AOvVaw0lOYFgxzaKt23DEikPhhMS&ust=1650761197736000&source=images&cd=vfe&ved=0CAwQjRxqFwoTCKCD
4Ib7qPcCFQAAAAAdAAAAABBD
[3] Construction of Three Phase Induction Motor _ Electrical4U
[4] https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.flaktgroup.com%2Fen%2Fnews%2Fnews-
archive%2F2020%2Fjuly%2Fbasic-principles-of-ac-induction-
motors%2F&psig=AOvVaw2YH2N13OlzEMaxpDIA_NM_&ust=1650762740156000&source=images&cd=vfe&ved=0CAwQjRxqFwoTC
ODgtseAqfcCFQAAAAAdAAAAABAS
[5] What is a 3-Phase Motor and How Does it Work_
[6] 3 Phase Induction Motor Definition And Working Principle
[7] https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/uploads/articles/ezgif.com-gif-maker_(1)_.gif
[8] https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.researchgate.net%2Ffigure%2Fthree-phase-inverter-output-
voltage-and-current-waveforms-cut-diode-7-The-
difference_fig5_303331885&psig=AOvVaw0JPblOYnbEC8RSM6TEzLLi&ust=1650899162113000&source=images&cd=vfe&ved=0CAw
QjRxqFwoTCOi-3OL8rPcCFQAAAAAdAAAAABAb
[9]. 3-Phase AC Motor Control with V/Hz Speed Closed Loop Using the 56F800/E
https://www.nxp.com/docs/en/application-note/AN1958.pdf
[10].https://cache.industry.siemens.com/dl/files/231/34682231/att_80493/v1/1PL628_BE_0308_en.pdf
Accompanying Course Information 29
You might also like
- A Beginners Guide To Motorcycle WiringDocument73 pagesA Beginners Guide To Motorcycle WiringSimon Shakespeare89% (9)
- Exp. 3 - Load Test and Equivalent Circuit Determination On Three Phase Squirrel Cage Induction Motor andDocument9 pagesExp. 3 - Load Test and Equivalent Circuit Determination On Three Phase Squirrel Cage Induction Motor andSanjay MeenaNo ratings yet
- Maintenance of GateDocument20 pagesMaintenance of GateMyles OliverNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of Three Phase Induction Motor UsingDocument9 pagesSpeed Control of Three Phase Induction Motor UsingPantech ElectricalNo ratings yet
- ENEL280 AC Motor Control LabDocument5 pagesENEL280 AC Motor Control LabPatrick LustyNo ratings yet
- ElecDocument31 pagesElecdeepanshumehalawat07No ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Iduction Motor Drive Using Slip Power RecoveryDocument6 pagesExperiment 2 - Iduction Motor Drive Using Slip Power RecoveryDeepak BansalNo ratings yet
- Dcservo NewkitDocument11 pagesDcservo NewkitNikita MalikNo ratings yet
- Induction MachineDocument20 pagesInduction MachineUsama RaoNo ratings yet
- Question No 1: Speed Control of DC MotorDocument10 pagesQuestion No 1: Speed Control of DC MotorProxima YusNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processor Based Vbyf Control of Speed of Induction MotorDocument24 pagesDigital Signal Processor Based Vbyf Control of Speed of Induction MotorManu JainNo ratings yet
- Variable Speed DeriveDocument18 pagesVariable Speed DeriveEngr. Naveed MazharNo ratings yet
- DC Drive ExplainationDocument17 pagesDC Drive ExplainationTabassum BanoNo ratings yet
- Part II - AC MotorsDocument30 pagesPart II - AC MotorsYan Liang HaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document31 pagesLecture 6amanuel abrehaNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Report DLW VaranasiDocument84 pagesSummer Training Report DLW VaranasiHemant MeenaNo ratings yet
- CNC MachinesDocument52 pagesCNC Machinespranav sharmaNo ratings yet
- 8-mg-400-motor-generator-trainer (Data Sheet)Document5 pages8-mg-400-motor-generator-trainer (Data Sheet)rajaalidadkayani.rockNo ratings yet
- Computer Numeric ControlDocument48 pagesComputer Numeric Controlabdifatah.nadir.snu.eduNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Reporting1Document158 pagesGroup 3 Reporting1skylerr.jordanNo ratings yet
- Emergency Supply: Ain Shams UniversityDocument28 pagesEmergency Supply: Ain Shams UniversityHossam MagedNo ratings yet
- Angular Accuracy Back EMFDocument8 pagesAngular Accuracy Back EMFSoudamini HansdahNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Induction Motor Drives: SyllabusDocument8 pagesModule 3: Induction Motor Drives: SyllabusManoj SkNo ratings yet
- DC Shunt Motor Speed ControlDocument7 pagesDC Shunt Motor Speed Controleric wahomeNo ratings yet
- Dynanometer AND Power Measurement: Member: Noble, A. Ocularis, J. Pamplona, J.P. Rallos, T. Tabar, K.C.B. Tamba, KDocument6 pagesDynanometer AND Power Measurement: Member: Noble, A. Ocularis, J. Pamplona, J.P. Rallos, T. Tabar, K.C.B. Tamba, Kkeith tambaNo ratings yet
- Spa 2Document4 pagesSpa 2millionNo ratings yet
- Computer Numeric Control: Prof. J. Ramkumar Department of Mechanical Engineering IIT KanpurDocument48 pagesComputer Numeric Control: Prof. J. Ramkumar Department of Mechanical Engineering IIT KanpurAjay VermaNo ratings yet
- Electric Drives ControlDocument29 pagesElectric Drives ControlNebyou DanielNo ratings yet
- 19 Speed PDFDocument8 pages19 Speed PDFNur Muhammad DzikriNo ratings yet
- Ch8 - DC DrivesDocument55 pagesCh8 - DC DrivesAli HasanyNo ratings yet
- DC ServomotorDocument16 pagesDC ServomotorNSS18EE048 BILINE KCNo ratings yet
- Etd Lab3Document10 pagesEtd Lab3Isaya KawanaNo ratings yet
- DynamoDocument9 pagesDynamostart201169201169No ratings yet
- Speed Control of Three Phase Induction MotorDocument25 pagesSpeed Control of Three Phase Induction MotorTrios TECHNOLOGIESNo ratings yet
- Hartono 2019 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1381 012053Document9 pagesHartono 2019 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1381 012053NithyashriNo ratings yet
- EEE 4766 Lab 3Document7 pagesEEE 4766 Lab 3Muhammad Adnan, 180021217No ratings yet
- Generator TroubleshootingDocument22 pagesGenerator TroubleshootingMichael Cabrera Rabino100% (2)
- Electrical Drives (ARG)Document24 pagesElectrical Drives (ARG)alu bhindiNo ratings yet
- Control System Lab ManualDocument52 pagesControl System Lab ManualMohammad Umar RehmanNo ratings yet
- Purpose of Variable Frequency DrivesDocument25 pagesPurpose of Variable Frequency DrivesGaurav MobarNo ratings yet
- 1.2 LABSHEET1 - DC Part 2Document25 pages1.2 LABSHEET1 - DC Part 2Zainuddin BusuNo ratings yet
- No Load Test of IMDocument2 pagesNo Load Test of IM2K20/CEEE/23 Nishi Kant kumarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine Trainer PDFDocument4 pagesElectrical Machine Trainer PDFaswardiNo ratings yet
- MC CGPTDocument12 pagesMC CGPTMostafa HamdyNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Control LabDocument5 pagesDC Motor Control Labdks697bvhcNo ratings yet
- Mott Chapter 21Document29 pagesMott Chapter 21kundayi shavaNo ratings yet
- Control and Operation of A Vertical Axis Wind Turbine: SCADA Systems For Wind FarmsDocument7 pagesControl and Operation of A Vertical Axis Wind Turbine: SCADA Systems For Wind FarmsSalem SobhyNo ratings yet
- Different Methods of Speed Control of Three-Phase PDFDocument7 pagesDifferent Methods of Speed Control of Three-Phase PDFRicardo BerizzoNo ratings yet
- Association Induction Motors To ConvertersDocument16 pagesAssociation Induction Motors To ConvertersConspiracy BaapNo ratings yet
- DC6 - Two-Quadrant Chopper 200 HP DC DriveDocument3 pagesDC6 - Two-Quadrant Chopper 200 HP DC Drivebryan eduardo villegas carrascoNo ratings yet
- 2 Lva1 App6891Document13 pages2 Lva1 App6891gouravNo ratings yet
- Ac Servo MotorDocument14 pagesAc Servo MotorJeyanthNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of 3Ø AC Induction Motor Using VSI & MicrocontrollerDocument32 pagesSpeed Control of 3Ø AC Induction Motor Using VSI & MicrocontrollerVijay PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2: Dynamic Behavior of Electric DrivesDocument43 pagesChapter-2: Dynamic Behavior of Electric DrivesMuket AgmasNo ratings yet
- Computer Numeric Control: Prof. J. Ramkumar Department of Mechanical Engineering IIT KanpurDocument48 pagesComputer Numeric Control: Prof. J. Ramkumar Department of Mechanical Engineering IIT KanpurHassnain MohdNo ratings yet
- The Voltech Handbook of PWM Motor DrivesDocument53 pagesThe Voltech Handbook of PWM Motor DrivesPovaS100% (1)
- Servo Motor - Diagram, Definition, Types, Working & ApplicationsDocument31 pagesServo Motor - Diagram, Definition, Types, Working & ApplicationsTanmay MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Motor Control CenterDocument81 pagesMotor Control CenterMohamed Mohamed100% (2)
- Lesson 5Document5 pagesLesson 5Phạm Thanh TùngNo ratings yet
- Theory DC ServoMDocument3 pagesTheory DC ServoMKaustubh DesaiNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Ac Motor Control With VHZ Speed Closed Loop Using The 56f800eDocument36 pages3 Phase Ac Motor Control With VHZ Speed Closed Loop Using The 56f800ePrabhu RajNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Large Hydro Generators Operation and Maintenance by Glenn Mottershead, Stefano Bomben, Isidor Kerszenbaum, Geoff KlempnerDocument661 pagesHandbook of Large Hydro Generators Operation and Maintenance by Glenn Mottershead, Stefano Bomben, Isidor Kerszenbaum, Geoff Klempnersubhamay sarkarNo ratings yet
- Eco Marathon Axial FluxDocument35 pagesEco Marathon Axial Fluxphysics802No ratings yet
- Trans Flux MotorDocument46 pagesTrans Flux MotorkoppulabroNo ratings yet
- Chiller Final SopDocument20 pagesChiller Final SopKrishnan Natarajan0% (1)
- TD4-2 TDZ4WSDocument1 pageTD4-2 TDZ4WSinna husnaNo ratings yet
- Ongc Training ReportDocument73 pagesOngc Training ReportKUNAL0% (1)
- Supplementary Specification To IEC 60034-1 High Voltage Three-Phase Cage Induction MotorsDocument39 pagesSupplementary Specification To IEC 60034-1 High Voltage Three-Phase Cage Induction MotorsIrwanNo ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument9 pagesDC MachinesRishan AkalankaNo ratings yet
- AK351 - Technical Data SheetDocument8 pagesAK351 - Technical Data SheetCris_eu09No ratings yet
- DSG and DIG Range of Low, Medium and High Voltage AlternatorsDocument20 pagesDSG and DIG Range of Low, Medium and High Voltage AlternatorsPutri Nur Ayu AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Electrical DrivesDocument102 pagesElectrical DrivesDeepanshu Saxena100% (1)
- Synchronous Non Excited Reluctance MotorDocument14 pagesSynchronous Non Excited Reluctance Motorcamming soonNo ratings yet
- Thesis - Design, Control and Simulation of PMSG Based Stand-AloneDocument68 pagesThesis - Design, Control and Simulation of PMSG Based Stand-AloneMAZHAR ALAM MALLICKNo ratings yet
- GATE EE 2011 With SolutionsDocument52 pagesGATE EE 2011 With SolutionsAbhishek MohanNo ratings yet
- EE Assignment 23-24 Sem 1Document7 pagesEE Assignment 23-24 Sem 1Triggered CreatorNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines 1Document14 pagesElectrical Machines 1WolfNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Induction Motor: Instructional ObjectivesDocument33 pagesThree-Phase Induction Motor: Instructional Objectiveskricks92No ratings yet
- SSC JE 2016 Electrical Set-1 With KeyDocument16 pagesSSC JE 2016 Electrical Set-1 With KeyJitesh EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Electric Vehicle 4th ModuleDocument13 pagesElectric Vehicle 4th ModuleAmruth DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Troubleshooting in Seven StepsDocument9 pagesElectrical Troubleshooting in Seven StepspetarurosNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficient MotorsDocument6 pagesEnergy Efficient MotorsS Bharadwaj ReddyNo ratings yet
- ELK Motor - Katalog - 2018 - EN PDFDocument48 pagesELK Motor - Katalog - 2018 - EN PDFyounes100% (1)
- Three phaseInductionMotorTypesandStructureDocument12 pagesThree phaseInductionMotorTypesandStructureShivam ShindeNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Induction Motor Starting Parameters Using MatlabDocument6 pagesCalculation of Induction Motor Starting Parameters Using MatlabДејан ПејовскиNo ratings yet
- As - Chapter 6 - Synchronous MachineDocument28 pagesAs - Chapter 6 - Synchronous Machinechibssa alemayehuNo ratings yet
- DaaDocument83 pagesDaavenkyn88No ratings yet
- Brushless-DC Motor Driver Considerations and Selection GuideDocument12 pagesBrushless-DC Motor Driver Considerations and Selection GuideJohn XaviNo ratings yet