Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calcium-Vitamin D-Thyroid Disorders
Calcium-Vitamin D-Thyroid Disorders
Uploaded by
simranCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Assure Model Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesAssure Model Lesson PlanNicole Hernandez71% (17)
- Glycine As A Lixiviant For The Leaching of Low Grade Copper Gold Ores Bennson Chemuta TandaDocument306 pagesGlycine As A Lixiviant For The Leaching of Low Grade Copper Gold Ores Bennson Chemuta TandaJavierAntonioGuardiolaEsparzaNo ratings yet
- XIAOMIDocument10 pagesXIAOMISrinath Saravanan75% (4)
- Vitamin D Research Paper - PDocument9 pagesVitamin D Research Paper - Papi-720438286No ratings yet
- 7 PDFDocument4 pages7 PDFAyu Putri Leciyuni TadEsNo ratings yet
- Asds 07 169Document5 pagesAsds 07 169Jpraveen SundarNo ratings yet
- Lec2/ Epidemiology of Dental CariesDocument7 pagesLec2/ Epidemiology of Dental Cariesمحمد العراقيNo ratings yet
- Lec2/ Epidemiology of Dental CariesDocument7 pagesLec2/ Epidemiology of Dental Cariesمحمد العراقيNo ratings yet
- Singh BrijendraDocument5 pagesSingh BrijendraAfianti SulastriNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Health Sciences and Research: Caries Prevention: Vitamin Way - A Novel ApproachDocument5 pagesInternational Journal of Health Sciences and Research: Caries Prevention: Vitamin Way - A Novel Approachmaryam.saadNo ratings yet
- Gingivitis A Silent Disease PDFDocument4 pagesGingivitis A Silent Disease PDFPragita Ayu SaputriNo ratings yet
- Vitamin D Deficiency & Early Implant Failure - DentaMedicaDocument2 pagesVitamin D Deficiency & Early Implant Failure - DentaMedicaOromax OhmRajani0% (1)
- 7 Oral Health of Geriatric People Modified Copy or ReferenceDocument15 pages7 Oral Health of Geriatric People Modified Copy or ReferenceNitya KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & MetabolismDocument7 pagesBest Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolismarber mulolliNo ratings yet
- Periodontal DiseaseDocument2 pagesPeriodontal Diseasekiki119100% (1)
- Periodontal Changes in Ortho Treatment / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument81 pagesPeriodontal Changes in Ortho Treatment / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- P Dye Vit D PPDocument22 pagesP Dye Vit D PPapi-720438286No ratings yet
- Bucal Alteration in DMDocument11 pagesBucal Alteration in DMradityardtNo ratings yet
- 1nutrition and Oral Health 5th YearDocument11 pages1nutrition and Oral Health 5th Yeardr_masamaraNo ratings yet
- Etiology of Dental CariesDocument35 pagesEtiology of Dental Cariesayshil mary sajiNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Bone DiseaseDocument9 pagesAssignment On Bone DiseaseShamaNo ratings yet
- Periodontal Diseases in Children PedoDocument34 pagesPeriodontal Diseases in Children Pedoarpita7dr9693No ratings yet
- Nutrition ArticleDocument5 pagesNutrition ArticleAafiah IfadaNo ratings yet
- Dental Alterations in Sickle Cell Disease: April 2016Document6 pagesDental Alterations in Sickle Cell Disease: April 2016Laura Mejia VergaraNo ratings yet
- Let's Celebrate National Brush Day! by SlidesgoDocument25 pagesLet's Celebrate National Brush Day! by SlidesgoALFEARA YUNIARNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Bone DiseaseDocument9 pagesAssignment On Bone DiseaseNoor-E-Khadiza ShamaNo ratings yet
- By Dr. Smitha B K Post Graduate Student Department of Preventive and Community DentistryDocument58 pagesBy Dr. Smitha B K Post Graduate Student Department of Preventive and Community DentistryAnnupriya KhannaNo ratings yet
- OSTEOMALACIADocument3 pagesOSTEOMALACIASandraNo ratings yet
- Two Neglected Biologic Risk Factors in Bone Grafting and Implantology PDFDocument5 pagesTwo Neglected Biologic Risk Factors in Bone Grafting and Implantology PDFMatheus FalkenbachNo ratings yet
- Nutrition For Geriatric Complete Denture Wearing Patients 888Document20 pagesNutrition For Geriatric Complete Denture Wearing Patients 888Dhanu DhanushreeNo ratings yet
- Ism 2 Research 2Document2 pagesIsm 2 Research 2api-269819101No ratings yet
- Molecules: Development and Characterization of An Orodispersible Film For Vitamin D3 SupplementationDocument14 pagesMolecules: Development and Characterization of An Orodispersible Film For Vitamin D3 Supplementationheristiana pratiwiNo ratings yet
- Caries DentalDocument9 pagesCaries DentalGaby Araya AlvarezNo ratings yet
- 4 - Classification of Periodontal DiseasesDocument29 pages4 - Classification of Periodontal DiseasesReda IsmaeelNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Status and Its Effect On Dental HealthDocument5 pagesNutritional Status and Its Effect On Dental HealthMemex papNo ratings yet
- 8.diet, Nutrition, and Sugar SubstitutesDocument29 pages8.diet, Nutrition, and Sugar Substituteskhush sidhuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DentistryDocument52 pagesIntroduction To DentistryMaryam KardoustNo ratings yet
- Awareness of Oral Manifestations Related To Systemic DiseasesDocument5 pagesAwareness of Oral Manifestations Related To Systemic DiseasesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 8 Tooth Ankylosis Andits Orthodontic ImplicationDocument6 pages8 Tooth Ankylosis Andits Orthodontic ImplicationPretty HiaNo ratings yet
- Orh Fact SheetDocument2 pagesOrh Fact SheetAliantz MosesNo ratings yet
- Oral Deasease and Dental HealthDocument2 pagesOral Deasease and Dental HealthAgam KgNo ratings yet
- Oral Health and NutritionDocument36 pagesOral Health and NutritionShabeel PnNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Lecture 6 (CH. 11-13) 2Document21 pagesNutrition Lecture 6 (CH. 11-13) 2Parizad NaseriNo ratings yet
- Articulo Cientifico 2, MartesDocument7 pagesArticulo Cientifico 2, MartesValeryNo ratings yet
- Ijpi 3 2 75 79Document5 pagesIjpi 3 2 75 79Rabiatul AdawiyahNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology of Periodontal DiseaseDocument24 pagesEpidemiology of Periodontal DiseaseAsad Khan5556No ratings yet
- Folic Acid and Periodontal Disease PDFDocument8 pagesFolic Acid and Periodontal Disease PDFAnonymous 8raPGW1tLNo ratings yet
- محاضرة 9Document11 pagesمحاضرة 9mkomyu088No ratings yet
- Diet, Nutrition, and Prevention of Dental DiseaseDocument26 pagesDiet, Nutrition, and Prevention of Dental DiseaseMuhammad Benny SetiyadiNo ratings yet
- Highlights Symptoms of Periodontal DiseaseDocument12 pagesHighlights Symptoms of Periodontal DiseaseTriana Wahyu SaputriNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors For Periodontal Diseases 2022Document13 pagesRisk Factors For Periodontal Diseases 2022SnowNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Teeth and Supporting StructuresDocument45 pagesPathology of Teeth and Supporting StructuresIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Resto Geriatric DentDocument50 pagesResto Geriatric DentJen de Luna50% (2)
- Chronic and Aggressive PeriodontitisDocument46 pagesChronic and Aggressive PeriodontitisMoola Bharath ReddyNo ratings yet
- OsteomalaciaDocument8 pagesOsteomalaciaRudhira KatragaddaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Etentulous PatientsDocument23 pagesNutrition in Etentulous PatientsKartik R. MorjariaNo ratings yet
- Food & Nutrition Update: Prevention of Dental CariesDocument4 pagesFood & Nutrition Update: Prevention of Dental CariessitapuNo ratings yet
- Periodontal Diseases in Children PedoDocument34 pagesPeriodontal Diseases in Children PedoFourthMolar.comNo ratings yet
- 2008 2 D Aiuto Massi Benedetti enDocument4 pages2008 2 D Aiuto Massi Benedetti enMaría Jesús EspínolaNo ratings yet
- Preliminary A. BackgroundDocument7 pagesPreliminary A. BackgroundDonny NasutionNo ratings yet
- Understanding Periodontitis: A Comprehensive Guide to Periodontal Disease for Dentists, Dental Hygienists and Dental PatientsFrom EverandUnderstanding Periodontitis: A Comprehensive Guide to Periodontal Disease for Dentists, Dental Hygienists and Dental PatientsNo ratings yet
- 1612126325PTE Writing Practice Paper 3Document3 pages1612126325PTE Writing Practice Paper 3simranNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument16 pagesUntitledsimranNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia and Resuscitation - 1Document44 pagesAnesthesia and Resuscitation - 1simranNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1,034 pagesUntitledsimranNo ratings yet
- Old-The Examination Consists of A Total of 320 Questions AcrossDocument9 pagesOld-The Examination Consists of A Total of 320 Questions AcrosssimranNo ratings yet
- RECESSIONDocument16 pagesRECESSIONsimranNo ratings yet
- 12 Composite ResinsDocument20 pages12 Composite ResinssimranNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis Wallchart 2018Document1 pageAnaphylaxis Wallchart 2018simranNo ratings yet
- 19 Choosing Between Restoration ModalitiesDocument10 pages19 Choosing Between Restoration ModalitiessimranNo ratings yet
- Florid Cemento-Osseous DysplasiaDocument3 pagesFlorid Cemento-Osseous DysplasiasimranNo ratings yet
- PERICORONITISDocument4 pagesPERICORONITISsimranNo ratings yet
- OrthoDocument64 pagesOrthosimranNo ratings yet
- Gce Chemistry ReviewDocument41 pagesGce Chemistry Review7a4374 hisNo ratings yet
- (Lines - of - Thought - ) Robert - C. - Stalnaker-Our - Knowledge - of - The - Internal - World - (Lines - of - Thought) - Oxford - University - Press, - USA (2008) (1) by Stalnaker PDFDocument20 pages(Lines - of - Thought - ) Robert - C. - Stalnaker-Our - Knowledge - of - The - Internal - World - (Lines - of - Thought) - Oxford - University - Press, - USA (2008) (1) by Stalnaker PDFPriyanka DeNo ratings yet
- PKM Full C.V. Sept 2021Document11 pagesPKM Full C.V. Sept 2021aopera87No ratings yet
- Influence of Nieghbors On Japan Student NotebookDocument9 pagesInfluence of Nieghbors On Japan Student Notebookapi-233464494No ratings yet
- Journal Entry Posting QuizDocument4 pagesJournal Entry Posting QuizLiwliwa BrunoNo ratings yet
- Ob2 Sas 14Document5 pagesOb2 Sas 14Ralph Louie ManagoNo ratings yet
- Sociology Exploring The Architecture of Everyday Life Readings 10th Edition Newman Test BankDocument11 pagesSociology Exploring The Architecture of Everyday Life Readings 10th Edition Newman Test Bankdoctorsantalumu9coab100% (27)
- FinAcc MCQ Sem2 PDFDocument11 pagesFinAcc MCQ Sem2 PDFBhavesh Rathod100% (2)
- Weaning Meal Plan 7 9 MonthsDocument1 pageWeaning Meal Plan 7 9 MonthsDeborah EvangelineNo ratings yet
- How Is Paper MadeDocument9 pagesHow Is Paper MadeDeo WarrenNo ratings yet
- Holiday Assignment - GR12 EnglishDocument3 pagesHoliday Assignment - GR12 Englishabhishektatu2007No ratings yet
- Nandan CoffeeDocument18 pagesNandan CoffeegautamNo ratings yet
- Edu Portfolio Project 7Document2 pagesEdu Portfolio Project 7api-609449697No ratings yet
- Issues and Challenges Implementation of Basic Education and VocationalDocument10 pagesIssues and Challenges Implementation of Basic Education and VocationalfaridahmarianiNo ratings yet
- Overtime in NursingDocument5 pagesOvertime in NursingallisonNo ratings yet
- BF Necromancer Supplement r11Document13 pagesBF Necromancer Supplement r11Michael KirchnerNo ratings yet
- Third Merit List FY BMS 2021-2022 Christian Minority: Form No Denomination Name Gender Stream 12th %Document8 pagesThird Merit List FY BMS 2021-2022 Christian Minority: Form No Denomination Name Gender Stream 12th %Albin JohnNo ratings yet
- HealthcareStudentWorkbook XIIDocument130 pagesHealthcareStudentWorkbook XIIRobin McLarenNo ratings yet
- Cini Manual PDF FreeDocument536 pagesCini Manual PDF FreeJaeIlLee100% (1)
- Reaction Paper by Gapoy, FrednixenDocument5 pagesReaction Paper by Gapoy, FrednixenFrednixen Bustamante GapoyNo ratings yet
- EZD6 Advantages RulesV1Document2 pagesEZD6 Advantages RulesV1Vinícius Braceloti100% (1)
- Reactor Clarifier Brochure 0619Document8 pagesReactor Clarifier Brochure 0619ABDUL MUZAMMILNo ratings yet
- Online Class Student GuidelinesDocument12 pagesOnline Class Student GuidelinesElaine Fiona Villafuerte100% (1)
- In-Depth Interviews & EthnographyDocument29 pagesIn-Depth Interviews & EthnographyJin ZuanNo ratings yet
- CME Applique TutorialDocument20 pagesCME Applique TutorialMarittaKarmaNo ratings yet
- The Beacon - April 11, 2013Document14 pagesThe Beacon - April 11, 2013Catawba SecurityNo ratings yet
- Persuasive Essay Examples College LevelDocument9 pagesPersuasive Essay Examples College Levelafibaixzyhpqmc100% (2)
Calcium-Vitamin D-Thyroid Disorders
Calcium-Vitamin D-Thyroid Disorders
Uploaded by
simranOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Calcium-Vitamin D-Thyroid Disorders
Calcium-Vitamin D-Thyroid Disorders
Uploaded by
simranCopyright:
Available Formats
CALCIUM-
Proper calcium intake is important for tooth health for several reasons.
First, a lack of proper calcium intake can lead to a health problem called
osteoporosis, which is a bone condition characterized by a loss of bone
density and bone weakening. When osteoporosis affects the jawbone, it
can make the jaw too weak to support the roots of teeth properly, which
can lead to tooth loss.
A calcium deficiency, also called hypocalcemia, can also increase your risk
of tooth decay and general tooth brittleness.
VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY-
Effects on dental treatment-
Infection—It is well known that vitamin D deficiency can impair the immune
response to oral microbial infections, increasing the risk of oral infections
and periodontitis. The antimicrobial protein synthesis by immune and
epithelial cells as well as nonspecific immune responses are activated by
vitamin D.Vitamin D also takes part in the specific immune response and
suppresses the destructive effects of chronic periodontitis.
Bone metabolism—Vitamin D plays an important role in the metabolism of
bone. In the bone, vitamin D stimulates the activity of osteoclasts and
increases the production of extracellular matrix proteins by osteoblasts.
Deficient vitamin D levels have been correlated with low bone density,
pathologic fracture, and poor bone healing after dental surgery. In addition,
case reports have suggested that low vitamin D levels can be correlated
with failure of bone grafts and regenerative materials.
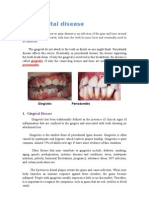
Periodontium—Because vitamin D has antimicrobial and anti-
inflammatory effects, it has been shown that patients with low levels are
more susceptible to developing gingival and periodontal disease. Because
of the vitamin’s positive influence on bone metabolism, periodontal patients
with low levels of vitamin D have also demonstrated poor responses to
periodontal surgery. Studies have shown that patients with a vitamin D
deficiency in blood plasma have worse results (i.e., lower tissue attachment
level and probing depth change) after periodontal surgery.
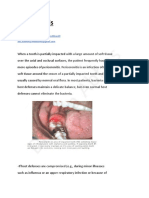
Dental implants—Since osseointegration of dental implants depends on
bone metabolism, there is a possibility that low levels of vitamin D in the
blood can negatively affect healing processes and new bone formation on
the implant surface. The relationship between serum levels of vitamin D
and osseointegration of dental implants is controversial and has been
evaluated in a few case reports and animal studies. Most studies suggest
that adequate serum levels of vitamin D can enhance the healing of peri-
implant bone tissue.VDD is highly implicated with oral diseases and has
been linked with a higher risk of tooth defects, caries, periodontitis and oral
treatments failure.
Numerous studies have shown that vitamin D deficiency also increases the
risk of dental decay. This is because vitamin D helps the body absorb
calcium and phosphate — both of which are crucial for building and
keeping strong tooth enamel. Without an adequate intake of vitamin D, our
teeth are at risk for weakening and developing cavities.
Teeth are mineralized organs, surrounded by alveolar bone, and formed by
three distinctive hard tissues: enamel, dentin, and cementum. The tooth
mineralization process occurs parallel to skeletal mineralization, yet if
mineral metabolism is disturbed then failures will occur similarly to those
that occur in bone tissue. Vitamin D plays a key role in bone and tooth
mineralization, and when levels are unregulated it can lead to the “rachitic
tooth”, which is a defective and hypomineralized organ highly susceptible to
fracture and decay.
HYPOTHYROIDISM-
Hemostasis - Patients with long standing hypothyroidism may have
increased subcutaneous mucopolysaccharides due to decrease in the
degradation of these substances. The presence of excess subcutaneous
mucopolysaccharides may decrease the ability of small blood vessels to
constrict when cut and may result in increased bleeding from infiltrated
tissues, including mucosa and skin. Local pressure for an extended time
will probably control the bleeding from the small vessels adequately.
Susceptibility to infection - Patient with hypothyroidism may have
delayed wound healing due to decreased metabolic activity in fibroblasts.
Delayed wound healing may be associated with an increased risk for
infection because of the longer exposure of the unhealed tissue to
pathogenic organisms. Hypothyroid patients are not considered to be
immunocompromised.
Patients who have hypothyroidism are susceptible to cardiovascular
disease from arteriosclerosis and elevated LDL. Before treating such
patients, consult with their primary care providers who can provide
information on their cardiovascular statuses. Patients who have atrial
fibrillation can be on anticoagulation therapy and might require antibiotic
prophylaxis before invasive procedures, depending on the severity of the
arrhythmia.If valvular pathology is present, the need for antibiotic
prophylaxis must be assessed.
You might also like
- Assure Model Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesAssure Model Lesson PlanNicole Hernandez71% (17)
- Glycine As A Lixiviant For The Leaching of Low Grade Copper Gold Ores Bennson Chemuta TandaDocument306 pagesGlycine As A Lixiviant For The Leaching of Low Grade Copper Gold Ores Bennson Chemuta TandaJavierAntonioGuardiolaEsparzaNo ratings yet
- XIAOMIDocument10 pagesXIAOMISrinath Saravanan75% (4)
- Vitamin D Research Paper - PDocument9 pagesVitamin D Research Paper - Papi-720438286No ratings yet
- 7 PDFDocument4 pages7 PDFAyu Putri Leciyuni TadEsNo ratings yet
- Asds 07 169Document5 pagesAsds 07 169Jpraveen SundarNo ratings yet
- Lec2/ Epidemiology of Dental CariesDocument7 pagesLec2/ Epidemiology of Dental Cariesمحمد العراقيNo ratings yet
- Lec2/ Epidemiology of Dental CariesDocument7 pagesLec2/ Epidemiology of Dental Cariesمحمد العراقيNo ratings yet
- Singh BrijendraDocument5 pagesSingh BrijendraAfianti SulastriNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Health Sciences and Research: Caries Prevention: Vitamin Way - A Novel ApproachDocument5 pagesInternational Journal of Health Sciences and Research: Caries Prevention: Vitamin Way - A Novel Approachmaryam.saadNo ratings yet
- Gingivitis A Silent Disease PDFDocument4 pagesGingivitis A Silent Disease PDFPragita Ayu SaputriNo ratings yet
- Vitamin D Deficiency & Early Implant Failure - DentaMedicaDocument2 pagesVitamin D Deficiency & Early Implant Failure - DentaMedicaOromax OhmRajani0% (1)
- 7 Oral Health of Geriatric People Modified Copy or ReferenceDocument15 pages7 Oral Health of Geriatric People Modified Copy or ReferenceNitya KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & MetabolismDocument7 pagesBest Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolismarber mulolliNo ratings yet
- Periodontal DiseaseDocument2 pagesPeriodontal Diseasekiki119100% (1)
- Periodontal Changes in Ortho Treatment / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument81 pagesPeriodontal Changes in Ortho Treatment / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- P Dye Vit D PPDocument22 pagesP Dye Vit D PPapi-720438286No ratings yet
- Bucal Alteration in DMDocument11 pagesBucal Alteration in DMradityardtNo ratings yet
- 1nutrition and Oral Health 5th YearDocument11 pages1nutrition and Oral Health 5th Yeardr_masamaraNo ratings yet
- Etiology of Dental CariesDocument35 pagesEtiology of Dental Cariesayshil mary sajiNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Bone DiseaseDocument9 pagesAssignment On Bone DiseaseShamaNo ratings yet
- Periodontal Diseases in Children PedoDocument34 pagesPeriodontal Diseases in Children Pedoarpita7dr9693No ratings yet
- Nutrition ArticleDocument5 pagesNutrition ArticleAafiah IfadaNo ratings yet
- Dental Alterations in Sickle Cell Disease: April 2016Document6 pagesDental Alterations in Sickle Cell Disease: April 2016Laura Mejia VergaraNo ratings yet
- Let's Celebrate National Brush Day! by SlidesgoDocument25 pagesLet's Celebrate National Brush Day! by SlidesgoALFEARA YUNIARNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Bone DiseaseDocument9 pagesAssignment On Bone DiseaseNoor-E-Khadiza ShamaNo ratings yet
- By Dr. Smitha B K Post Graduate Student Department of Preventive and Community DentistryDocument58 pagesBy Dr. Smitha B K Post Graduate Student Department of Preventive and Community DentistryAnnupriya KhannaNo ratings yet
- OSTEOMALACIADocument3 pagesOSTEOMALACIASandraNo ratings yet
- Two Neglected Biologic Risk Factors in Bone Grafting and Implantology PDFDocument5 pagesTwo Neglected Biologic Risk Factors in Bone Grafting and Implantology PDFMatheus FalkenbachNo ratings yet
- Nutrition For Geriatric Complete Denture Wearing Patients 888Document20 pagesNutrition For Geriatric Complete Denture Wearing Patients 888Dhanu DhanushreeNo ratings yet
- Ism 2 Research 2Document2 pagesIsm 2 Research 2api-269819101No ratings yet
- Molecules: Development and Characterization of An Orodispersible Film For Vitamin D3 SupplementationDocument14 pagesMolecules: Development and Characterization of An Orodispersible Film For Vitamin D3 Supplementationheristiana pratiwiNo ratings yet
- Caries DentalDocument9 pagesCaries DentalGaby Araya AlvarezNo ratings yet
- 4 - Classification of Periodontal DiseasesDocument29 pages4 - Classification of Periodontal DiseasesReda IsmaeelNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Status and Its Effect On Dental HealthDocument5 pagesNutritional Status and Its Effect On Dental HealthMemex papNo ratings yet
- 8.diet, Nutrition, and Sugar SubstitutesDocument29 pages8.diet, Nutrition, and Sugar Substituteskhush sidhuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DentistryDocument52 pagesIntroduction To DentistryMaryam KardoustNo ratings yet
- Awareness of Oral Manifestations Related To Systemic DiseasesDocument5 pagesAwareness of Oral Manifestations Related To Systemic DiseasesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 8 Tooth Ankylosis Andits Orthodontic ImplicationDocument6 pages8 Tooth Ankylosis Andits Orthodontic ImplicationPretty HiaNo ratings yet
- Orh Fact SheetDocument2 pagesOrh Fact SheetAliantz MosesNo ratings yet
- Oral Deasease and Dental HealthDocument2 pagesOral Deasease and Dental HealthAgam KgNo ratings yet
- Oral Health and NutritionDocument36 pagesOral Health and NutritionShabeel PnNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Lecture 6 (CH. 11-13) 2Document21 pagesNutrition Lecture 6 (CH. 11-13) 2Parizad NaseriNo ratings yet
- Articulo Cientifico 2, MartesDocument7 pagesArticulo Cientifico 2, MartesValeryNo ratings yet
- Ijpi 3 2 75 79Document5 pagesIjpi 3 2 75 79Rabiatul AdawiyahNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology of Periodontal DiseaseDocument24 pagesEpidemiology of Periodontal DiseaseAsad Khan5556No ratings yet
- Folic Acid and Periodontal Disease PDFDocument8 pagesFolic Acid and Periodontal Disease PDFAnonymous 8raPGW1tLNo ratings yet
- محاضرة 9Document11 pagesمحاضرة 9mkomyu088No ratings yet
- Diet, Nutrition, and Prevention of Dental DiseaseDocument26 pagesDiet, Nutrition, and Prevention of Dental DiseaseMuhammad Benny SetiyadiNo ratings yet
- Highlights Symptoms of Periodontal DiseaseDocument12 pagesHighlights Symptoms of Periodontal DiseaseTriana Wahyu SaputriNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors For Periodontal Diseases 2022Document13 pagesRisk Factors For Periodontal Diseases 2022SnowNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Teeth and Supporting StructuresDocument45 pagesPathology of Teeth and Supporting StructuresIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Resto Geriatric DentDocument50 pagesResto Geriatric DentJen de Luna50% (2)
- Chronic and Aggressive PeriodontitisDocument46 pagesChronic and Aggressive PeriodontitisMoola Bharath ReddyNo ratings yet
- OsteomalaciaDocument8 pagesOsteomalaciaRudhira KatragaddaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Etentulous PatientsDocument23 pagesNutrition in Etentulous PatientsKartik R. MorjariaNo ratings yet
- Food & Nutrition Update: Prevention of Dental CariesDocument4 pagesFood & Nutrition Update: Prevention of Dental CariessitapuNo ratings yet
- Periodontal Diseases in Children PedoDocument34 pagesPeriodontal Diseases in Children PedoFourthMolar.comNo ratings yet
- 2008 2 D Aiuto Massi Benedetti enDocument4 pages2008 2 D Aiuto Massi Benedetti enMaría Jesús EspínolaNo ratings yet
- Preliminary A. BackgroundDocument7 pagesPreliminary A. BackgroundDonny NasutionNo ratings yet
- Understanding Periodontitis: A Comprehensive Guide to Periodontal Disease for Dentists, Dental Hygienists and Dental PatientsFrom EverandUnderstanding Periodontitis: A Comprehensive Guide to Periodontal Disease for Dentists, Dental Hygienists and Dental PatientsNo ratings yet
- 1612126325PTE Writing Practice Paper 3Document3 pages1612126325PTE Writing Practice Paper 3simranNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument16 pagesUntitledsimranNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia and Resuscitation - 1Document44 pagesAnesthesia and Resuscitation - 1simranNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1,034 pagesUntitledsimranNo ratings yet
- Old-The Examination Consists of A Total of 320 Questions AcrossDocument9 pagesOld-The Examination Consists of A Total of 320 Questions AcrosssimranNo ratings yet
- RECESSIONDocument16 pagesRECESSIONsimranNo ratings yet
- 12 Composite ResinsDocument20 pages12 Composite ResinssimranNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis Wallchart 2018Document1 pageAnaphylaxis Wallchart 2018simranNo ratings yet
- 19 Choosing Between Restoration ModalitiesDocument10 pages19 Choosing Between Restoration ModalitiessimranNo ratings yet
- Florid Cemento-Osseous DysplasiaDocument3 pagesFlorid Cemento-Osseous DysplasiasimranNo ratings yet
- PERICORONITISDocument4 pagesPERICORONITISsimranNo ratings yet
- OrthoDocument64 pagesOrthosimranNo ratings yet
- Gce Chemistry ReviewDocument41 pagesGce Chemistry Review7a4374 hisNo ratings yet
- (Lines - of - Thought - ) Robert - C. - Stalnaker-Our - Knowledge - of - The - Internal - World - (Lines - of - Thought) - Oxford - University - Press, - USA (2008) (1) by Stalnaker PDFDocument20 pages(Lines - of - Thought - ) Robert - C. - Stalnaker-Our - Knowledge - of - The - Internal - World - (Lines - of - Thought) - Oxford - University - Press, - USA (2008) (1) by Stalnaker PDFPriyanka DeNo ratings yet
- PKM Full C.V. Sept 2021Document11 pagesPKM Full C.V. Sept 2021aopera87No ratings yet
- Influence of Nieghbors On Japan Student NotebookDocument9 pagesInfluence of Nieghbors On Japan Student Notebookapi-233464494No ratings yet
- Journal Entry Posting QuizDocument4 pagesJournal Entry Posting QuizLiwliwa BrunoNo ratings yet
- Ob2 Sas 14Document5 pagesOb2 Sas 14Ralph Louie ManagoNo ratings yet
- Sociology Exploring The Architecture of Everyday Life Readings 10th Edition Newman Test BankDocument11 pagesSociology Exploring The Architecture of Everyday Life Readings 10th Edition Newman Test Bankdoctorsantalumu9coab100% (27)
- FinAcc MCQ Sem2 PDFDocument11 pagesFinAcc MCQ Sem2 PDFBhavesh Rathod100% (2)
- Weaning Meal Plan 7 9 MonthsDocument1 pageWeaning Meal Plan 7 9 MonthsDeborah EvangelineNo ratings yet
- How Is Paper MadeDocument9 pagesHow Is Paper MadeDeo WarrenNo ratings yet
- Holiday Assignment - GR12 EnglishDocument3 pagesHoliday Assignment - GR12 Englishabhishektatu2007No ratings yet
- Nandan CoffeeDocument18 pagesNandan CoffeegautamNo ratings yet
- Edu Portfolio Project 7Document2 pagesEdu Portfolio Project 7api-609449697No ratings yet
- Issues and Challenges Implementation of Basic Education and VocationalDocument10 pagesIssues and Challenges Implementation of Basic Education and VocationalfaridahmarianiNo ratings yet
- Overtime in NursingDocument5 pagesOvertime in NursingallisonNo ratings yet
- BF Necromancer Supplement r11Document13 pagesBF Necromancer Supplement r11Michael KirchnerNo ratings yet
- Third Merit List FY BMS 2021-2022 Christian Minority: Form No Denomination Name Gender Stream 12th %Document8 pagesThird Merit List FY BMS 2021-2022 Christian Minority: Form No Denomination Name Gender Stream 12th %Albin JohnNo ratings yet
- HealthcareStudentWorkbook XIIDocument130 pagesHealthcareStudentWorkbook XIIRobin McLarenNo ratings yet
- Cini Manual PDF FreeDocument536 pagesCini Manual PDF FreeJaeIlLee100% (1)
- Reaction Paper by Gapoy, FrednixenDocument5 pagesReaction Paper by Gapoy, FrednixenFrednixen Bustamante GapoyNo ratings yet
- EZD6 Advantages RulesV1Document2 pagesEZD6 Advantages RulesV1Vinícius Braceloti100% (1)
- Reactor Clarifier Brochure 0619Document8 pagesReactor Clarifier Brochure 0619ABDUL MUZAMMILNo ratings yet
- Online Class Student GuidelinesDocument12 pagesOnline Class Student GuidelinesElaine Fiona Villafuerte100% (1)
- In-Depth Interviews & EthnographyDocument29 pagesIn-Depth Interviews & EthnographyJin ZuanNo ratings yet
- CME Applique TutorialDocument20 pagesCME Applique TutorialMarittaKarmaNo ratings yet
- The Beacon - April 11, 2013Document14 pagesThe Beacon - April 11, 2013Catawba SecurityNo ratings yet
- Persuasive Essay Examples College LevelDocument9 pagesPersuasive Essay Examples College Levelafibaixzyhpqmc100% (2)