Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Economics Examples
Economics Examples
Uploaded by
Zehaan Singh SuriOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Economics Examples
Economics Examples
Uploaded by
Zehaan Singh SuriCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIT/SUBUNIT EXAMPLES
CH 32 - Public goods face the free rider problem, when
Efficiency & Market consumers benefit from goods or services that were
Failure & not purchased.
CH 35 Different - Missing markets, where demand and supply cannot
Market Structures determine the allocation of resources for the
- Public Goods quantity required.
- For E.g, to reduce landfill waste one person
assumes that the trash produced is less than a
collective of people, this is an incentive to free-ride
on other people's efforts of recycling.
- Tragedy of the - Assumes that when consumers make decisions
commons people only take decisions that maximise their own
utility.
- If a consumer seeks to do so this may deplete
resources and damages overall social welfare.
- For E.g overfishing, many fishermen have the
motive to fish as much as they can, quicker than
they are replenished.
- Fishermen don't have the incentive to hold back as
their impact may be futile.
- Monopolies - Google holds up to 60% of advertising revenue and
holds the main and major market share of the tech
industry.
- Google has all data of consumers online activity,
which provides asymmetric information.
- Google can assess which ads are appropriate
based on search activity, and promote goods and
services to consumers.
- Oligopolies - In August 2015, Pfizer and Flynn Pharma were
found to have colluded to charge unfair and
excessive prices on anti-epilepsy drugs inflating the
NHS’ expenditure for the drug.
- In the 1960s, before regulations were in place
General Motors, Ford and Chrysler were collusive
oligopolies.
- As Chrysler increased its price, General Motors
increased its price lower than Chrysler's.
- This then led to Chrysler pushing its price down to
General Motors as Chrysler was losing consumers
due to the relatively cheaper price. (Form of a
formal oligopoly)
- In order to increase joint profits a collusive price is
1 Economics Examples By Siya N & Deeksha P
UNIT/SUBUNIT EXAMPLES
set and followed above marginal costs at this
quantity.
- This leads to a loss in total welfare and consumer
surplus, and increased producer surplus.
- Due to General Motor being the market leader Ford
set a similar price as a form of tacit collusion.
- Oligopolies - OPEC is responsible for 80% of crude oil
production, 12 countries manipulate supply and
price of crude oil.
- The cartel can easily influence the prices of oil.
- In early 2020, Saudi Arabia, had decreased its
production of crude oil which resulted in a price war
between Russia and Saudi Arabia as a decrease in
production leads to an increase in the price of crude
oil in hopes of increasing profits.
- This could lead to cheating as other member
countries in the OPEC would cheat on the
production quota in order to make a profit.
- Monopolistic - Zara & H&M produce heterogeneous products.
- This focuses on non price factors in order to
differentiate products, H&M produces clothes that
are environmentally sustainable and could
contribute to promoting toward sustainable
consumers.
- The Body Shop and Bath and Body Works
produce heterogeneous products such as shower
gels, candles etc. However, The Body Shop focuses
more on using more ‘clean’ ingredients in their
products and use sustainable packaging
- Burger King and Mcdonalds sell burgers, although
they are similar products, but the differentiation of
products is done by establishing a brand.
- Monopsony - Supermarkets have monopsony power when
market buying from farms. If they don't sell to big
supermarkets, they have very few alternatives. This
has led to protests about milk prices
- Books are one of Amazon.com’s biggest
purchases and if publishers don’t sell it to them at
discounted prices, they miss out on selling the
books on one of the largest distributor sites.
CH33
Externalities
2 Economics Examples By Siya N & Deeksha P
UNIT/SUBUNIT EXAMPLES
- Negative - Pigou on externalities, industrialists are not
Production concerned with any external costs to others in
Externalities society.
- Pollution from manufacturing chemical goods, this
can lead to contaminated water and this leads to
fishermen not being able to catch fish, which leads
to a loss of income.
- Producing beef is an extensive process that impacts
the environment as the amazon rainforest is
deforested for production.
- Negative
Consumption - Pigou stated that the consumption of alcohol can
Externalities lead to an increased demand for police and
healthcare.
- The consumption of cigarettes can lead to passive
smoking that affects a third party.
- Positive - Pfizer produced the Covid-19 vaccines in a short
Production amount of time despite the high cost of production.
Externalities - Encouraging firms by subsidising production of
housing will encourage firms to build houses in slum
areas, this allows people to afford good housing and
may reduce social problems.
- Positive - Encouraging consumers to invest in education can
Consumption improve skills and productivity and can benefit the
Externalities rest of society.
CH33 - Encouraging consumers to consume a healthy diet
Externalities will lower the pressure faced by the healthcare
- Positive industry; through educational campaigns and nudge
consumption theory.
externalities - Nudge theory can occur in schools where a
healthier option of fruits rather than sweets can be
placed at eye level for students to immediately
choose the fruit.
CH34
Economies of scale - Car production has many processes that require
- Specialisation division of labour and specialising in producing a
certain part. Specialised workers require less
training of workers and a more efficient production
process.
- Supermarkets benefit from bulk buying where the
- Bulk Buying marginal cost of delivering more products is quite
low, and only requires one driver, and less fuel
3 Economics Examples By Siya N & Deeksha P
UNIT/SUBUNIT EXAMPLES
costs, as the average cost of transporting 100 is
more than 10,000.
- Large companies with an established brand image
- Marketing can lead to lower average costs as the cost of
marketing is spread across a larger output and the
cost is insignificant.
- For e.g, redbull collaborates with athletes all year
round to promote the product, the costs may be
insignificant as the revenue gained is substantial.
- To develop new technology or drugs only larger
- Risk Bearing firms can bear the risk as the investment can be
funded by the several products sold by the firm
UNIT/SUBUNIT EXAMPLES
CH37
Differing objectives
and policies of
firms Groupon, a global American e-commerce business that
- Sales revenue connects people to different activities such as theme parks,
maximisation concerts and so on. Their logic is that sales will increase to
W.J. Baumol the point they will make a profit by investing heavily on
advertising.
CSR - environmental Lego
objectives/ - Aiming to reduce their CO2 impact by 37% by 2032
sustainable - Installing renewable energy in their stores, offices
and factories
- Using more sustainable packaging and materials for
the products
SDG goal 12 - Ensure sustainable production and
consumption patterns
UNIT/SUBUNIT EXAMPLES
CH40
Labour markets
- Wage - Comparing wages of lawyers and McDonald’s
determination workers.
- Lawyers get paid higher as their supply is inelastic
4 Economics Examples By Siya N & Deeksha P
due to qualifications and MRPL is higher as if they
are successful they can generate more revenue.
- McDonald’s workers have an elastic demand since
qualifications are not high and MRPL is lower as
limited profits generated from selling Big Macs.
CH?
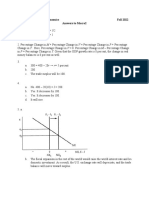
Price discrimination - 3rd degree pricing
- Broadband charges consumers a higher
price at renewal than at original purchase
due to default bias, where consumers
assume that there are no other substitutes
available, therefore providing a lower
coefficient of PED.
- 3 graphs of ped
- Pharma in the US uses price discrimination
to charge high prices for insulin as demand
for these goods are price inelastic, ‘
- Monopoly power could reduce prices to
discourage new entrants or to force firms out
of the market.
- Eval:
- Financial regulations have banned the use of
such price strategies that broadband
companies, BT, and Sky Media have
implemented, and are expected to provide
households on income support with a
cheaper deal, through cross subsidisation.
- Monopolies could reinvest the supernormal
profits gained in order to improve dynamic
efficiency, Astra-zeneca, researching more
effective covid vaccines, and prices it at
P=MC where it is allocatively efficient for
astrazeneca to produce.
2nd degree price discrimination
- Costco uses second-degree price discrimination as
it offers discounts on bulk purchases
- This is done through loyalty cards or BOGOF
- Sam’s Club uses a similar concept
Third degree PD
- Travel tourism industry
CH46 - Macro Economic growth and BOP
problems and their - Growth in a country can be export-led
inter-relatedness - Countries such as China,Hong Kong, South
Korea, Vietnam (Southeast Asian countries)
5 Economics Examples By Siya N & Deeksha P
heavily rely on exporting goods and services
- Exports have a significant value in the real GDP
CH47.2 - QE in the UK
Effectiveness of - UK adopted quantitative easing during the Great
monetary policy Recession in 2009, reducing interest rates to 0.5%
(QE) failed
- This occurred due to low credit, low animal spirits
and lack of willingness of banks to lend.
CH? The EU’s Common Fisheries Policy (CFP)
Government - Set of rules through which European fishing fleets
failures and fish stocks are managed
- To ensure that fisheries and aquaculture are
ecologically, economically and socially sustainable.
- The quota system favours big industrial trawlers
while penalising small, sustainable inshore fishing
communities who are denied quotas.
Trade unions have a monopoly over workers with a
CH40 specific skill.
Labour markets and - Production has switched from France and Germany
government to other low cost European countries, such as
intervention Poland, Czech republic, where labour costs are
cheaper, and trade unions have little to no influence
over firms.
CH? - Eli and Lilly
Market failure - Insulin is a lucrative business venture in the USA,
Maximum price as big pharmaceutical companies take part in
charging high prices for a necessary good where
demand is relatively inelastic.
- Recently, Eli and Lilly implemented a $35 cap on
the production of insulin, a 70% price cut, making it
more affordable for diabetics to afford insulin, this
reduces the deadweight loss of market inefficiency,
where there is over-charge of necessary products.
CH? - The common agricultural policy
Government - Aims to increase productivity, ensure fair standards
intervention - of living for farmers, stabilise markets, secure
minimum prices supplies and ensure fair prices.
- Provides vocational education, and research
coordination
- Chatgpt: Ensure a stable supply of affordable food
for EU consumers
- Ensure a fair income for farmers
6 Economics Examples By Siya N & Deeksha P
- Promote sustainable agriculture and protect the
environment
- Foster rural development
- The direct payments are designed to support
farmers' income and compensate them for the public
goods they provide, such as the preservation of
landscapes and biodiversity.
- The market support measures are aimed at
stabilising prices and ensuring a fair income for
farmers.
- Rural development programs are designed to
promote economic growth, social inclusion, and
environmental protection in rural areas.
- The EU has implemented several reforms to address
these criticisms, including the introduction of more
environmentally friendly policies and the reduction of
direct payments to larger farmers.
CH?
Privatisation
- The 2020 Indian Agricultural act
- This act allows farmers to sell their produce outside
government regulated markets.
- This act permits farmers to enter into agreements
with private companies, exporters, and retailers for
the sale of their produce at a pre-agreed price.
- deregulate the production, supply, and distribution of
essential commodities such as cereals, pulses,
oilseeds, edible oils, onions, and potatoes. The
amendment removes stock holding limits on these
commodities.
- encourage private investment in the agricultural
sector, and reduce the role of middlemen. They also
claim that the acts will benefit consumers by
increasing competition and reducing prices.
- weaken the bargaining power of small farmers. They
fear that the new system will benefit large
corporations at the expense of small farmers and
lead to the exploitation of farmers by private
companies. (monopsony power from private firms)
- farmers are demanding the repeal of these acts and
the guarantee of a minimum support price for their
crops
7 Economics Examples By Siya N & Deeksha P
CH53 -
Globalisation
One of the limitations of globalisation is tax avoidance
- Companies like Amazon and Google set up offices
in countries like Bermuda and Luxembourg w/ very
low rates of corporation tax
- It can be considered unfair competition for
domestic firms who don’t use tax avoidance
measures
Reducing
unemployment
through Apple recently opened a 300-acre factory in Karnataka to
globalisation create 100,000 jobs which involve building iPhones
CH44
Money & Banking
2008 Financial crisis:
- Easy credit and low interest rates that led to
excessive borrowing and lending.
- Banks and financial institutions taking on too much
risk and making risky investments, such as subprime
mortgages. (Providing mortgages to individuals with
below-average credit scores.)
- Inadequate regulation and oversight of the financial
industry.
- Financial innovation and the use of complex
financial products that were poorly understood.
Mortgage-backed securities (MBS): These were
securities that were backed by subprime mortgages
(high risk of default) sold to investors to diversify
their portfolios.
- A housing bubble (sudden rise in housing prices
due to speculation and excessive demand, when it
bursts there is a sudden decrease in housing
prices) that bursts, leading to a sharp decline in
home prices and mortgage defaults.
- The interconnectedness of the global financial
system, which meant that problems in one area
could quickly spread to other areas.
8 Economics Examples By Siya N & Deeksha P
- Panic and loss of confidence among investors and
consumers, leading to a sharp contraction in credit
and a severe economic downturn.
Monetary policy 2008 financial crisis
- The attempt to try and solve the financial crisis was
to increase the monetary base through quantitative
easing.
- Therefore implementing an expansionary monetary
supply,
- This did not lead to an increase in economic growth
as the velocity of money has decreased to the lack
of consumer confidence to spend money.
- The state of the economy: high unemployment did
not encourage increases in prices and wages (lack
of demand)
9 Economics Examples By Siya N & Deeksha P
You might also like
- ABM-APPLIED ECONOMICS 12 - Q1 - W5 - Mod5Document18 pagesABM-APPLIED ECONOMICS 12 - Q1 - W5 - Mod5Carmilleah Freyjah86% (51)
- Explain Why Oligopolistic Firms Are Affected by Both Interdependence and UncertaintyDocument2 pagesExplain Why Oligopolistic Firms Are Affected by Both Interdependence and UncertaintySMEBtheWizard50% (2)
- Eco515 - Managerial EconomicsDocument14 pagesEco515 - Managerial EconomicsBryan ShieldsNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in International MarketingDocument9 pagesReviewer in International MarketingBianca Jane GomezNo ratings yet
- FODADocument1 pageFODAMaria PaulaNo ratings yet
- Law, Ethics & CSRDocument31 pagesLaw, Ethics & CSRElly TanNo ratings yet
- Vegan Cosmetic Cocoon: Group 3Document26 pagesVegan Cosmetic Cocoon: Group 3Lê Nguyễn Linh Đan100% (1)
- Market Failure: by Varghese T JohnDocument35 pagesMarket Failure: by Varghese T Johnvachutty100% (3)
- Essentials of Economics 9th Edition Schiller Solution Manual 1Document12 pagesEssentials of Economics 9th Edition Schiller Solution Manual 1brenda100% (43)
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Think Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsDocument20 pagesThink Big Go Small: Adapting Business Models To Incorporate Smallholders Into Supply ChainsOxfamNo ratings yet
- IMT Covid19Document6 pagesIMT Covid19Kashish PuriNo ratings yet
- AP Microeconomics Practice Exam1 AnswerkeyDocument27 pagesAP Microeconomics Practice Exam1 Answerkey예서No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Market StructureDocument87 pagesCHAPTER 7 Market StructureRia Athirah100% (1)
- Merger:: BusinessDocument4 pagesMerger:: BusinessShIva Leela ChoUdaryNo ratings yet
- Walmart Chicken Price Fixing ComplaintDocument98 pagesWalmart Chicken Price Fixing ComplaintmglennonexaminerNo ratings yet
- Solutions - Summer Exam 2019 PDFDocument56 pagesSolutions - Summer Exam 2019 PDFaliakhtar02No ratings yet
- Full Download Ebook Ebook PDF Microeconomics 10th Edition by David C Colander PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Ebook Ebook PDF Microeconomics 10th Edition by David C Colander PDFdanny.wainer321100% (43)
- Oligopoly (Research)Document5 pagesOligopoly (Research)Caramel SundaeNo ratings yet
- Mini Project Hazordous ManagementDocument54 pagesMini Project Hazordous ManagementEr. Hebin RajNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 - Pure CompetitionDocument32 pagesTopic 5 - Pure Competitionvinh96698No ratings yet
- B5 Nabm4Document4 pagesB5 Nabm4Flonie DensingNo ratings yet
- Course Outline: International Islamic University MalaysiaDocument5 pagesCourse Outline: International Islamic University MalaysiaatenhyunaeNo ratings yet
- Oligopoly-Intermediate MicroeconomicsDocument16 pagesOligopoly-Intermediate MicroeconomicsBayarjargal Ariun-ErdeneNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 - MergedDocument43 pagesProblem Set 2 - MergedSamantha Marie RebolledoNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument2 pagesEconomicsIrish Mae T. EspallardoNo ratings yet
- Presentation VivesDocument19 pagesPresentation VivesShashwat JainNo ratings yet
- Introduction 6Document8 pagesIntroduction 6Study BuddyNo ratings yet
- Business Development and Sales Strategy of UnibicDocument14 pagesBusiness Development and Sales Strategy of UnibicAarya KhedekarNo ratings yet
- Mba Regulations Student Copy 2010-2011Document94 pagesMba Regulations Student Copy 2010-2011vamsibrilliantNo ratings yet
- Mulyiple Choice Questions On EcnomicsDocument4 pagesMulyiple Choice Questions On EcnomicssandeeproseNo ratings yet
- Dubai Retail Review 2017 PDFDocument11 pagesDubai Retail Review 2017 PDFSantosh DsouzaNo ratings yet
- 06 Pricing in Theory and Practice 2021Document54 pages06 Pricing in Theory and Practice 2021Mad MuxNo ratings yet
- CAPE Economics 2007 U1 P1Document10 pagesCAPE Economics 2007 U1 P1aliciaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Abdul Quadir: Ms. Jyoti Biswal Jyotib@xlri - Ac.inDocument7 pagesManagerial Economics Abdul Quadir: Ms. Jyoti Biswal Jyotib@xlri - Ac.inAditi GoyalNo ratings yet
- Mock 21 HL Paper 3 EconomicsDocument12 pagesMock 21 HL Paper 3 EconomicsiafraserNo ratings yet
- Implicit Cartels: 14.12 Game Theory Muhamet YildizDocument11 pagesImplicit Cartels: 14.12 Game Theory Muhamet YildizmunchkaNo ratings yet
- Applied Economic Quarter 1 Module 5 Week5 1Document9 pagesApplied Economic Quarter 1 Module 5 Week5 1CHAPEL JUN PACIENTE75% (4)
- Kodak СompanyDocument5 pagesKodak СompanyLiên HạNo ratings yet