Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Instructional Material Development (Imade) Mathematics in The Modern World
Instructional Material Development (Imade) Mathematics in The Modern World
Uploaded by
cosmic0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views24 pagesThis document provides an overview of the mathematical language and symbols module. It discusses how mathematics has its own precise language to communicate ideas with symbols and rules. The objectives are to discuss mathematical language, symbols, and conventions. It covers topics like mathematical expressions, variables, sentences, and logical connections between statements using operators like negation, conjunction, disjunction, implication, and biconditional. Truth tables are presented as a way to understand truth values of propositions under different conditions. Activities include exercises on order of operations and logical connectives, while an online quiz is listed for assessment.
Original Description:
Original Title
Untitled
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of the mathematical language and symbols module. It discusses how mathematics has its own precise language to communicate ideas with symbols and rules. The objectives are to discuss mathematical language, symbols, and conventions. It covers topics like mathematical expressions, variables, sentences, and logical connections between statements using operators like negation, conjunction, disjunction, implication, and biconditional. Truth tables are presented as a way to understand truth values of propositions under different conditions. Activities include exercises on order of operations and logical connectives, while an online quiz is listed for assessment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views24 pagesInstructional Material Development (Imade) Mathematics in The Modern World
Instructional Material Development (Imade) Mathematics in The Modern World
Uploaded by
cosmicThis document provides an overview of the mathematical language and symbols module. It discusses how mathematics has its own precise language to communicate ideas with symbols and rules. The objectives are to discuss mathematical language, symbols, and conventions. It covers topics like mathematical expressions, variables, sentences, and logical connections between statements using operators like negation, conjunction, disjunction, implication, and biconditional. Truth tables are presented as a way to understand truth values of propositions under different conditions. Activities include exercises on order of operations and logical connectives, while an online quiz is listed for assessment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 24
Instructional Material Development
(IMADE)
Mathematics in the Modern World
Created by: Stefhany G. David , LPT
Section 1. The Nature of Mathematics
II. Mathematical Language and Symbols
Overview
Objectives
Course Materials
Activities/Assessments
Overview
Like any language , Mathematics has its own
symbols , syntax and rules. The language of
Mathematics was designed so that we could write
about things like numbers, sets ,functions , etc.
The language of mathematics is the system used by
mathematicians to communicate mathematical
ideas among themselves, and is distinct from
natural languages in that it aims to communicate
abstract, logical ideas with precision and
unambiguity.
Objectives:
After successful completion of this module, you
should be able to:
Discuss the language, symbols and conventions of
Mathematics
Explain the nature of Mathematics as a language
Perform operations on mathematical expressions
correctly
Acknowledge that Mathematics is a useful
language
Course Materials
1.Mathematical Language and Symbols
1.1 Mathematical Language
- is the system used to communicate mathematical
ideas
1.1.1 Characteristics of Mathematical Language
* It is non- temporal. There is no past future in
Math
* It is devoid of emotional content and it is
always precise.
Course Materials
1.1.1.1 Precise
-able to make very fine distinction
Ex. The use of mathematical symbols is only base on
its meaning and purpose like
+ means add
- means subtract
x means multiply
÷ means divide
1.1.1.2 Concise
Course Materials
1.1.1.2 Concise
say things briefly
Ex. The long English sentence can be shortened using
mathematical symbols like Eight plus two equals ten
which means 8+2 = 10
1.1.1.3Powerful
able to express complex thoughts with relative ease
Ex. The application of critical thinking and problem
solving skills requires the comprehension, analysis and
reason simple obtain the correct solutions.
Course Materials
1.2 Operational Terms and Symbols
1.2.1 Mathematics Symbols
Course Materials
ORDER IN OPERATIONS
Course Materials
1.2.2.Mathematical Expressions
- consists of terms. This terms of mathematical
expressions is separated from other terms with
mathematics symbols.
Ex. 3 , -6 , 2x , 5y
1.2.3. Variables
- also called literal coefficient , represents the
unknown and make use of letters.
* the number with the variable is the numerical coefficient
Ex. 2x ,-5y ,10b , -4ac
1.2.4 Constant
- any single number
Ex. -1 ,0 ,1
Course Materials
1.2.4. Mathematical Sentence
-combines two mathematical expressions using a
comparison operator
Ex. Equation : x + y =1
Inequality : 15x – 5 y < 3y
1.2.4.1 Open Sentence
-it uses variables, meaning that is not know
whether or not the mathematical sentence is true or false
Ex. 4 -3 = v , 23xy <3y
1.2.4.1 Close Sentence
it is a mathematical sentence which is known to
be true or false
Ex. 18(32) > 1655 , 25-25 =1
Course Materials
1.3 Comparison of English Language to
Mathematical Language
English Language Mathematical Language
Noun Expression
Peter , Binan , Car 8x , 4+3 , -6y
Sentence Sentence
She is pretty. 4+5=9
Sentential Form Expression Form
The sum of four and six is 10. 4 + 6 = 10
Course Materials
1.4 Logical Connections
Logic – study of the methods and principles used to distinguish good from bad.
Logical Operator – symbols or words used to connect two or more sentences
1.4.1 Proposition
A proposition is a declarative statement which is either true or false. It is a
technique of knowledge representation in logical and mathematical form.
*Propositional logic (PL) is the simplest form of logic where all the statements are
made by propositions.
Ex. a) It is Sunday.
b) The Sun rises from West (False proposition)
c) 3+3= 7(False proposition)
d) 5 is a prime number.
Course Materials
1.4.1 Proposition
Following are some basic facts about propositional logic:
Propositional logic is also called Boolean logic as it works on 0 and 1.
In propositional logic, we use symbolic variables to represent the logic, and we
can use any symbol for a representing a proposition, such A, B, C, P, Q, R, etc.
Propositions can be either true or false, but it cannot be both.
Propositional logic consists of an object, relations or function, and logical
connectives.
These connectives are also called logical operators.
The propositions and connectives are the basic elements of the propositional
logic.
Connectives can be said as a logical operator which connects two sentences.
A proposition formula which is always true is called tautology, and it is also called
a valid sentence.
Course Materials
1.4.1 Proposition
Following are some basic facts about propositional logic:
A proposition formula which is always false is called Contradiction.
A proposition formula which has both true and false values is called
Statements which are questions, commands, or opinions are not propositions such
as "Where is Robin", "How are you", "What is your name", are not propositions.
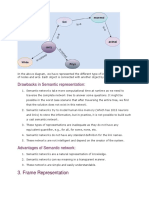
1.4.1.1 Syntax of propositional logic
The syntax of propositional logic defines the allowable sentences for the
knowledge representation.
1.4.1.2 Types of Propositions:
1.4.1.2.1Atomic Proposition
Atomic propositions are the simple propositions. It consists of a single
proposition symbol. These are the sentences which must be either true or
false.
Course Materials
1.4.1.2.1Atomic Proposition
Ex. a) 2+2 is 4, it is an atomic proposition as it is a true fact.
b) "The Sun is cold" is also a proposition as it is a false fact.
1.4.1.2.2 Compound proposition
Compound propositions are constructed by combining simpler or atomic
propositions, using parenthesis and logical connectives.
Ex. a) "It is raining today, and street is wet."
b) "Ankit is a doctor, and his clinic is in Mumbai.“
1.4.2 Logical Connectives
Logical connectives are used to connect two simpler propositions or representing a
sentence logically. We can create compound propositions with the help of logical
connectives. There are mainly five connectives, which are given as follows:
1.4.2.1 Negation
A sentence such as ¬ P is called negation of P. A literal can be either Positive
literal or negative literal.
Course Materials
1.4.2.2 Conjunction
A sentence which has ∧ connective such as, P ∧ Q is called a conjunction.
Example: Rohan is intelligent and hardworking. It can be written as,
P= Rohan is intelligent,
Q= Rohan is hardworking.
→ P∧ Q.
1.4.2.3 Disjunction
A sentence which has ∨ connective, such as P ∨ Q. is called disjunction, where P
and Q are the propositions.
Example: "Ritika is a doctor or Engineer",
Here P= Ritika is Doctor. Q= Ritika is Doctor,
so we can write it as P ∨ Q.
Course Materials
1.4.2.4 Implication
A sentence such as P → Q, is called an implication. Implications are also known
as if-then rules. It can be represented as
Ex. If it is raining, then the street is wet.
Let P= It is raining, and Q= Street is wet,
so it is represented as P → Q
1.4.2.5 Biconditional
A sentence such as P⇔ Q is a Biconditional sentence
Ex. If I am breathing, then I am alive.
P= I am breathing, Q= I am alive,
it can be represented as P ⇔ Q.
Course Materials
Following is the summarized table for Propositional Logic Connectives:
1.4.3 Truth Table
In propositional logic, we need to know the truth values of propositions in all
possible scenarios. We can combine all the possible combination with logical
connectives, and the representation of these combinations in a tabular format is
called Truth table. Following are the truth table for all logical connectives:
Course Materials
Course Materials
Course Materials
References for reading References for videos
The Language of Mathematics https://www.youtube.com/watch?
(from One Mathematics Cat , v=hwkns-pyPJ8
Please! By Carol Burns Fisher)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?
(ii) The Language and Grammar of v=M7xYj7cAzog
Mathematics
https://www.youtube.com/watch?
v=PCpS3i-T2wc
https://www.youtube.com/watch?
v=BouqkWYlfzg&t=3s
Activities /Assessments
Individual Activities:
1. Exercises about PEMDAS/BOMDAS (see the last slide)
2. Exercises about Logical Connectives
*Make your own 3 samples for each kinds of Logical
Connectives
Assessment
Online Quiz
You might also like
- Chapter 2 Lesson 2.1Document6 pagesChapter 2 Lesson 2.1Shereen MendizabalNo ratings yet
- Math in The Modern World Week 3-4Document9 pagesMath in The Modern World Week 3-4Michael LabayoNo ratings yet
- Unit3 &4Document17 pagesUnit3 &4gogaNo ratings yet
- GE 4 Chapter 2 NotesDocument6 pagesGE 4 Chapter 2 NotesRonnie Francisco ToribioNo ratings yet
- Colegio de San Gabriel Arcangel of Caloocan, Inc.: Module I: Mathematics As A LanguageDocument15 pagesColegio de San Gabriel Arcangel of Caloocan, Inc.: Module I: Mathematics As A LanguageKIRITO SALINASNo ratings yet
- A Self-Instructional Module On Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument29 pagesA Self-Instructional Module On Mathematics in The Modern WorldGeorge Vincent SismarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 LM 2Document6 pagesChapter 2 LM 2Liandysan23No ratings yet
- Introduction To Logic Module 1Document3 pagesIntroduction To Logic Module 1LUCAS, PATRICK JOHNNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document39 pagesLec 2احمد نصارNo ratings yet
- Discrete MathematicsDocument10 pagesDiscrete MathematicsDr-Muhammad Ijaz Khan100% (1)
- Chapter 2 - Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument32 pagesChapter 2 - Mathematical Language and SymbolsAlthea Faye Rabanal100% (1)
- Math21 - Chapter 2Document40 pagesMath21 - Chapter 2Jessica SergioNo ratings yet
- MATH 101 MODULE 2 Mathematical Language and SymbolDocument6 pagesMATH 101 MODULE 2 Mathematical Language and SymbolMaria Izabelle QuemiNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 StudentsDocument40 pagesChap 2 Studentsmauvegreige8No ratings yet
- Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument72 pagesMathematical Language and SymbolsJurren Valderama Pigao100% (1)
- Lesson 2 - Mathematical Language & Symbols - Part 1Document37 pagesLesson 2 - Mathematical Language & Symbols - Part 1ENGR. ADRIEL MARASIGANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Mathematecal LanguageDocument25 pagesChapter 2 Mathematecal LanguageririricelNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern World-Lesson4Document27 pagesMathematics in The Modern World-Lesson4LharvaeNo ratings yet
- Sir Leo John G. Hinayas: Southern Philippines Baptist Theological Seminary IncDocument3 pagesSir Leo John G. Hinayas: Southern Philippines Baptist Theological Seminary IncLeo John HinayasNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument18 pagesMathematical Language and SymbolsMaricel CarreonNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of AI Unit-3 NotesDocument15 pagesFundamentals of AI Unit-3 NotesChauhan NakulNo ratings yet
- Math 101 Module Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument5 pagesMath 101 Module Mathematics in The Modern WorldArianne Rose FangonNo ratings yet
- Sir Leo John G. Hinayas: Southern Philippines Baptist Theological Seminary IncDocument3 pagesSir Leo John G. Hinayas: Southern Philippines Baptist Theological Seminary IncLeo John HinayasNo ratings yet
- Logic ProgrammingDocument11 pagesLogic ProgrammingSagarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Knowledge and ReasoningDocument10 pagesChapter 4-Knowledge and ReasoningSeyo KasayeNo ratings yet
- MMW Worksheet 2.5-The Laguage of LogicDocument6 pagesMMW Worksheet 2.5-The Laguage of LogicZoren Divina BorretaNo ratings yet
- Notes Real AnalysisDocument91 pagesNotes Real AnalysisCarlos MartinezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Proof in AnalysisDocument113 pagesIntroduction To Proof in AnalysisAndreas DewantoNo ratings yet
- MMW Module 2b FDDocument17 pagesMMW Module 2b FDelmer.platiljrNo ratings yet
- CSA 2001 (Module-3)Document108 pagesCSA 2001 (Module-3)Roop KishorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument54 pagesChapter 2 Mathematical Language and SymbolsComputer ACCNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern World BSE English 1: Prepared By: Mrs. Elsie A. Vibares Math Instructor 1Document49 pagesMathematics in The Modern World BSE English 1: Prepared By: Mrs. Elsie A. Vibares Math Instructor 1Vinny BitchNo ratings yet
- MMW Module 2 - MATHEMATICAL LANGUAGE AND SYMBOLSDocument12 pagesMMW Module 2 - MATHEMATICAL LANGUAGE AND SYMBOLSSandreiAngelFloresDuralNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Knowledge RepresentationDocument13 pagesUnit 4 Knowledge Representationjskri3399No ratings yet
- Week 1 - Introduction To Discrete Structures-MergedDocument21 pagesWeek 1 - Introduction To Discrete Structures-MergedEmmanuel GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Communicating MathematicsDocument17 pagesCommunicating Mathematicsfotini81729No ratings yet
- Wop Logic-FinalDocument4 pagesWop Logic-FinalMihir VahanwalaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document12 pagesLesson 2Erica ComendadorNo ratings yet
- MMW Module 2.1Document5 pagesMMW Module 2.1ROJE DANNELL GALVANNo ratings yet
- Aug Lesson Plan.Document6 pagesAug Lesson Plan.Shaun ThembaNo ratings yet
- Propositional Logic: Logic and Problem SolvingDocument57 pagesPropositional Logic: Logic and Problem SolvingAshish GhishingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document14 pagesChapter 2LIGAWAD, MELODY P.No ratings yet
- The Nature of Mathematics: Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument51 pagesThe Nature of Mathematics: Mathematical Language and SymbolsSofia NadineNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log: TeacherDocument4 pagesDaily Lesson Log: TeacherJoan Ramirez RongaleriosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Ged 102Document3 pagesLesson 2 Ged 102Chloe RosalesNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Ge 114Document11 pagesModule 4 Ge 114frederick liponNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Language and SymbolsDocument36 pagesMathematics Language and Symbolssantillan.arnaldo.duranNo ratings yet
- MMW E Worktext Chapter 2 OnlyDocument6 pagesMMW E Worktext Chapter 2 OnlyAmber SnowNo ratings yet
- Copy Lecture Guide GEC004 PDFDocument35 pagesCopy Lecture Guide GEC004 PDFRachel Peters0% (1)
- WGN2Document6 pagesWGN2Stephanie ViarNo ratings yet
- UNIT-3 KB Part1Document67 pagesUNIT-3 KB Part1Roop KishorNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1Quennie Kent Rosal DaguilNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Illustrating Polynomial EquationsDocument14 pagesMathematics: Illustrating Polynomial EquationsAira MatoNo ratings yet
- The Language of Mathematics: Instructor's ManualDocument45 pagesThe Language of Mathematics: Instructor's ManualNel BorniaNo ratings yet
- GEC 3 Moduls Week 13 FINALDocument9 pagesGEC 3 Moduls Week 13 FINALJayson Aquino SantiagoNo ratings yet
- AI Notes Part-4Document20 pagesAI Notes Part-4Divyanshu PatwalNo ratings yet
- Math 310 BookDocument88 pagesMath 310 BookConcreteRose37No ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument135 pagesArtificial IntelligencesriharinecgNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Logic: 1.1 Understanding ProofsDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Logic: 1.1 Understanding ProofsCarlyne LaneteNo ratings yet
- Set Theory: The Structure of ArithmeticFrom EverandSet Theory: The Structure of ArithmeticRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Proofnets For S5: Sequents and Circuits For Modal LogicDocument21 pagesProofnets For S5: Sequents and Circuits For Modal LogicconsequentlyNo ratings yet
- Q2 Module 7 PLDocument73 pagesQ2 Module 7 PLVianne SaclausaNo ratings yet
- Propositional Logic Notes PDFDocument130 pagesPropositional Logic Notes PDFegeun mankdNo ratings yet
- Section 2.2: Introduction To The Logic of Quantified StatementsDocument5 pagesSection 2.2: Introduction To The Logic of Quantified StatementsTodd ParsnickNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Abstract MathematicsDocument176 pagesAn Introduction To Abstract MathematicsMax Powel100% (1)
- l1 DM Eng 2016Document6 pagesl1 DM Eng 2016morNo ratings yet
- A Note Concerning Criticisms of Ayer's Revised Definition of VerifiabilityDocument7 pagesA Note Concerning Criticisms of Ayer's Revised Definition of Verifiabilityjd watsonNo ratings yet
- Logic Problemset PDFDocument108 pagesLogic Problemset PDFAditya Mishra100% (2)
- DMS ACE Material QuestionsDocument61 pagesDMS ACE Material QuestionsshivamNo ratings yet
- Work Book Unit 1 and 2Document12 pagesWork Book Unit 1 and 2Vivek CHOWDARYNo ratings yet
- By Alone Wolf Group: There Are Five Logical ConnectivesDocument3 pagesBy Alone Wolf Group: There Are Five Logical ConnectivesMuhammad ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Logic and Computer AdditionDocument10 pagesLogic and Computer Additionmarygrace carbonel100% (1)
- Ds 3 ProofDocument55 pagesDs 3 ProofTrinh Quốc BaoNo ratings yet
- Paper - I Discrete MathematicsDocument156 pagesPaper - I Discrete MathematicsAhfrin JNo ratings yet
- 5: Logic: Discrete MathematicsDocument33 pages5: Logic: Discrete MathematicsIra LyanaNo ratings yet
- Finitely Generated Magari AlgebrasDocument24 pagesFinitely Generated Magari AlgebrasLex HendriksNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document10 pagesChapter 12juhii993No ratings yet
- Methods of Inference: Expert Systems: Principles and Programming, Fourth EditionDocument60 pagesMethods of Inference: Expert Systems: Principles and Programming, Fourth EditionEmran AljarrahNo ratings yet
- Predicates & QuantifiersDocument25 pagesPredicates & QuantifiersSean Patrick AlteaNo ratings yet
- Direct ProofDocument6 pagesDirect Proofemilychin113No ratings yet
- CTM A Little Propositional LogicDocument46 pagesCTM A Little Propositional LogicreshmasableNo ratings yet
- Writing ProofsDocument23 pagesWriting ProofsBabelinoBedroGetesJr.0% (1)
- FMSE Lect 06Document64 pagesFMSE Lect 06Izhar HussainNo ratings yet
- The Predicate CalculusDocument71 pagesThe Predicate CalculusArun ManickNo ratings yet
- 1 Mathematical Logic: Statement: A Declarative Sentence Which Is Either True or False But Not Both Is Called ADocument4 pages1 Mathematical Logic: Statement: A Declarative Sentence Which Is Either True or False But Not Both Is Called ADattatray NerkarNo ratings yet
- Neil Falkner - The Fundamentals of Higher Mathematics-XanEdu (2021)Document191 pagesNeil Falkner - The Fundamentals of Higher Mathematics-XanEdu (2021)Mani KamaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Logic: A Brief HistoryDocument21 pagesChapter 3. Logic: A Brief HistoryBusran Salamah TNo ratings yet
- Maths Key Book - PC PDFDocument409 pagesMaths Key Book - PC PDFAliNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - Indirect Proof ActivityDocument4 pagesGroup 1 - Indirect Proof ActivityAscel BabaysonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.4 Logic and ProofsDocument5 pagesLesson 1.4 Logic and ProofsChristel CarantoNo ratings yet