Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answers 1
Answers 1
Uploaded by
J DopeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answers 1
Answers 1
Uploaded by
J DopeCopyright:
Available Formats
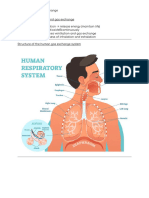
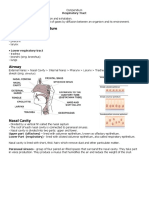
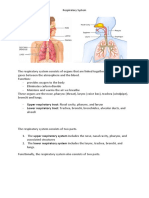
larynx - known as the voice box
asthma - bronchial tubes contract quickly causing shortness of breath, coughing, and wheezing
bronchitis - when bronchial tubes are irritated
letter d - which structure shown in the diagram below contracts, causing a pressure change…
trachea - a tube about 12cm long
lung cancer - caused by inhaling tar in cigarette smoke
lungs - made up of spongy, elastic tissue that stretches as you breathe
nasal cavity - passage way that moistens the air
diaphragm - muscular structure that helps to expand and contract the lungs, forcing air in and out
to remove carbon dioxide and supply oxygen to the body - main function of gas exchange
cilia and mucous membranes - which structures filter and moisten air as it passes through the
bronchioles - smaller tubes within the lungs
pharynx - tube-like passage used for food, liquid, and air
trachea - organ label #6
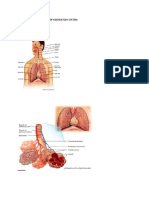
more O2 and CO2 to exchange - alveoli increase the surface area in the lungs to allow
capillaries - the thin, moist membranes of the alveoli
respiration - a process that allows the body to get oxygen to burn food
emphysema - disease is linked to smoking and results in a reduction in the number
larynx - the airway that has two pairs of vocal chords
bronchi - two main branches from the trachea
trachea - after air moves through the pharynx it continues downward
bronchi - two short tubes that carry air into the lungs
take in O2 and remove CO2 - the function of the respiratory system
alveoli - clusters of tiny air sacs that allow the exchange
two CO2 - diagram that illustrates the function of an alveolus
trachea - respiratory structure supported by rings of cartilage
oxygen - the gas known to stay alive
trachea - the windpipe is also called the..
cellular respiration - the cellular process which uses oxygen and sugar
rib cage - main bone structure that protects the lungs
pneumonia - illness of the lungs where the alveoli become inflamed
carbon dioxide - breathed out from our mouth and nose
trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli - sequence
they permit exchange between the external atmosphere and the circulatory system - which
statement best describes the function of the respiratory passageways of a human
You might also like
- Respiratory System (Anatomy and Physiology)Document71 pagesRespiratory System (Anatomy and Physiology)Butch Dumdum100% (11)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory System (Handouts)Document5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory System (Handouts)bluecindy87No ratings yet
- Res (Iratory SystemDocument2 pagesRes (Iratory SystemJosielyn ValladolidNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System For PowelDocument41 pagesRespiratory System For PowelNikko Bondoc ManaloNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument3 pagesScienceVaughn Siegfried FuertezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document3 pagesChapter 6api-304486052No ratings yet
- LEC - Week 9 (Respiratory)Document42 pagesLEC - Week 9 (Respiratory)Al SerenosoNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange II: The Structure of The Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesGas Exchange II: The Structure of The Respiratory SystemScribd UserNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Biology IgcseDocument6 pagesChapter 11 Biology Igcsemeri zanniniNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in HumansDocument23 pagesGas Exchange in HumansVNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesRespiratory Systemmuskaan.kukrejaNo ratings yet
- Breathing, Ventilation and Gas ExchangeDocument5 pagesBreathing, Ventilation and Gas Exchangeonlooker.eternityNo ratings yet
- RespiratorychempowerpointDocument10 pagesRespiratorychempowerpointapi-252255196No ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 11 Notes (Grade 11)Document8 pagesBio Chapter 11 Notes (Grade 11)Tammy Lam100% (2)
- PhysicallyDocument10 pagesPhysicallysanjay9555926973No ratings yet
- Respiratory Tract Structure: Alveolus)Document5 pagesRespiratory Tract Structure: Alveolus)MarekGojtowskiNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System: ASTIKA NUR ROHMAH, S.Kep., NS., M.BiomedDocument43 pagesThe Respiratory System: ASTIKA NUR ROHMAH, S.Kep., NS., M.BiomedAdek KhazeliaNo ratings yet
- Patho PneumoniaDocument26 pagesPatho PneumoniaRenz Ivan FuntilonNo ratings yet
- Handout On GAS EXCHANGEDocument4 pagesHandout On GAS EXCHANGEEli Joshua EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes For IGCSE BiologyDocument3 pagesSummary Notes For IGCSE BiologyStudy GuyNo ratings yet
- Animalphysio2nd 180428184330Document28 pagesAnimalphysio2nd 180428184330environmentalgyanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System s2 2019Document56 pagesRespiratory System s2 2019noviantyramadhani12No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Case StudyDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Case StudyRj MagpayoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 46: The Circulatory and Respiratory SystemDocument18 pagesChapter 46: The Circulatory and Respiratory Systemapi-520057338No ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Structure and FunctionDocument18 pagesRespiratory System: Structure and FunctionEdmon Garett ValentinoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Respiratory SystemCarlos Alfonso Borromeo AmoresNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory SystemElle MateoNo ratings yet
- DescriptionDocument2 pagesDescriptionGliane, Adrie Ann C.No ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesThe Respiratory SystemmvslikavNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - Answer KeyDocument2 pagesRespiratory System - Answer Keyapi-25002257750% (2)
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesHuman Respiratory SystemintelligentkaranNo ratings yet
- Respiratory 2Document2 pagesRespiratory 2Naka LimutNo ratings yet
- Notes On Respiratory System, Gaseous ExchangeDocument4 pagesNotes On Respiratory System, Gaseous Exchangeshelter musasaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesAnaphy Respiratory SystemAngelika SanchezNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesRespiratory SystemShivani Sriram100% (1)
- The Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesThe Respiratory Systempaulo_camuaNo ratings yet
- Bio 101 Respitatory Test Study GuideDocument11 pagesBio 101 Respitatory Test Study Guideamorris0906No ratings yet
- ReproductiveDocument5 pagesReproductiveJason Vinluan CarinanNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in HumansDocument8 pagesGas Exchange in Humanstawana nyikaNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory Systemkakai0.0No ratings yet
- Respiratory AnatomyDocument35 pagesRespiratory Anatomyapi-217919217No ratings yet
- Respiration CompressedDocument63 pagesRespiration Compressed5000epcbbNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of Respiratory SystemDocument18 pagesParts and Functions of Respiratory Systemjosephabram051590No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemNesra de PeraltaNo ratings yet
- A New BookDocument8 pagesA New Bookapi-327183872No ratings yet
- Chapter II - Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesChapter II - Respiratory SystemIndranil SinhaNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System: Carolina Rancier Horacio Vicioso Patricia Otero Dessirée Reyes Ana CarolinaDocument8 pagesThe Respiratory System: Carolina Rancier Horacio Vicioso Patricia Otero Dessirée Reyes Ana CarolinapattsoteroNo ratings yet
- 17 1 - Print VersionDocument28 pages17 1 - Print Versionapi-239353579No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The LungsDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The LungsMayownski TejeroNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY SYSTEMDocument15 pagesRESPIRATORY SYSTEMx22bqp9wtgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 BIODocument4 pagesChapter 11 BIODakshitaNo ratings yet
- Science Senior 2Document4 pagesScience Senior 2ajichristianbaniadamNo ratings yet
- Why Do You Need To BreatheDocument4 pagesWhy Do You Need To BreatheNur Hidayah MahaliNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Reported By: C.M. HerreraDocument19 pagesRespiratory System: Reported By: C.M. HerreraTsume ShoutaroNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System OkDocument36 pagesRespiratory System Okakselerasi10No ratings yet
- Respiratory System 8Document32 pagesRespiratory System 8Naanmatha PuspanathanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument53 pagesRespiratory SystemRotan CirebonNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System 1Document33 pagesRespiratory System 1Arianne Jen Genotiva100% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyKelly Camero ÜNo ratings yet
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet