Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antidepressants
Antidepressants
Uploaded by
Christel Mariz Santella0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageTriCyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) work by increasing serotonin, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. They are considered stimulants and require monitoring of heart rate and potential side effects like cardiotoxicity and liver toxicity. Management of TCAs includes promoting sleep by administering them before bed to reduce insomnia, and monitoring cardiac function, liver function, eye pressure, and urinary patterns. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) work by decreasing serotonin, epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine levels by inhibiting their breakdown. They are contraindicated with tyramine-containing foods which can cause hypertensive crisis and require calcium channel blockers treatment. Electroconv
Original Description:
Original Title
(3) ANTIDEPRESSANTS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTriCyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) work by increasing serotonin, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. They are considered stimulants and require monitoring of heart rate and potential side effects like cardiotoxicity and liver toxicity. Management of TCAs includes promoting sleep by administering them before bed to reduce insomnia, and monitoring cardiac function, liver function, eye pressure, and urinary patterns. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) work by decreasing serotonin, epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine levels by inhibiting their breakdown. They are contraindicated with tyramine-containing foods which can cause hypertensive crisis and require calcium channel blockers treatment. Electroconv
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageAntidepressants
Antidepressants
Uploaded by
Christel Mariz SantellaTriCyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) work by increasing serotonin, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. They are considered stimulants and require monitoring of heart rate and potential side effects like cardiotoxicity and liver toxicity. Management of TCAs includes promoting sleep by administering them before bed to reduce insomnia, and monitoring cardiac function, liver function, eye pressure, and urinary patterns. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) work by decreasing serotonin, epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine levels by inhibiting their breakdown. They are contraindicated with tyramine-containing foods which can cause hypertensive crisis and require calcium channel blockers treatment. Electroconv
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
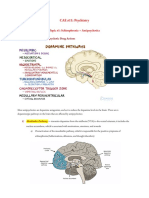
NCM 117 LEC
PSYCHIATRIC NURSING
L E C / PROF. ACUAR
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________
MIDTERMS
OUTLINE TriCyclic Antidepressants (TCA medications)
Antidepressants / Mood Elevators ● Most effective
I. Different Medications under Antidepressants ● MOA: increases serotonin and norepinephrine (epinephrine
A. SSRI may be elevated with norepinephrine)
B. TCA ● thats why its called TRI – it elevates 3 neurotransmitters
C. MAOI (serotonin, norepinephrine, and epinephrine)
● considered as stimulants so MONITOR HEART RATE
ANTIDEPRESSANTS / MOOD ELEVATORS ● may have more side effects
● Normal Mood - balance out the feelings of happiness and
sadness NOTE: uunahin iadminister ang SSRI because safety muna
● MANIA - exaggerated feeling of happiness
● MAJOR DEPRESSION - exaggerated feeling of sadness Medication takes effect after 2 to 4 weeks
→ If not corrected by normal activities, take medications
(antidepressants) PRAMINE/TRIPTYLLINE
● Bipolar Disorder – combination of both mania and major 1. Clomipramine (Anafranil) → for OCPD
depression (alternating) 2. Imipramine (Tofranil) → Bedwetting (enuresis)
3. Desipramine (Norpramine)
A. DIFFERENT MEDICATIONS UNDER 4. Amitriptyline
ANTIDEPRESSANTS 5. Nortriptyline
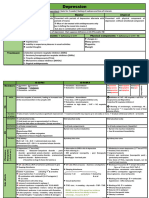
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRI) MANAGEMENT:
● Not the most effective medication, but the safest type of ● Promote Insomnia or Drowsiness (more evident) → given at
medication hours of sleep
● Effect: Slowly increase serotonin → promotes episodes or ● Monitor the following:
feelings of happiness → (priority) Cardiac function - Cardiotoxic
● Lesser neurotransmitters targeted, lesser side effects → Liver Function - hepatotoxicity
→ Eye function - increases Intraocular pressure(IOP) →
S - Safest – targets only one neurotransmitter (low side effect) glaucoma (Normal IOP level: 10-21 mmHG)
S - Stimulant – promotes elevation of serotonin → Bladder function/Urinary patterns - possibly promote
Common side effect is insomnia; Suppression of urinary retention
appetite → weight loss
Medication is best administered at the morning MonoAmine Oxidase Inhibitor (MAOI)
after meal ● Amines - SNS Neurotransmitters
R - Reproductive Impairment – commonly male individuals → DECREASE
I - Impotence / Delayed Ejaculation → erection problems ▪ S - Serotonin
(erectile dysfunction); decreased libido ▪ E - Epinephrine
▪ N - Norepinephrine
● Serotonin Crisis – adverse effect of the medication ▪ D - Dopamine
→ may be due to exaggerated administration of SSRI ● Oxidase - Enzymes that destroys amines
→ may be due to SSRI was accidentally administered in ● Oxidase destroys amines → all neurotransmitters (SEND)
combination with other antidepressants (such as will elevate
mono-amine oxidase inhibitors)
→ ALWAYS MONITOR FOR HEART RATE Examples of Medications
→ worst possible effect is arrhythmia ● Parnate
▪ check for the the HR first before checking in ECG ● Marplan
● Nardil
COMMON SSRI (ends in -xetine / -xamine) ● Emsam (selegiline) – newest type of MAO
1. Luvox (Fluvoxamine)
2. Paxil (Paroxetine) ● CONTRAINDICATED TO TYRAMINE-CONTAINING
3. Prozac (Fluoxetine) → Priapism - painful contraction of the PRODUCTS
penis which leads to prolonged erection → (monitor increasing blood pressure - hypertensive crisis
4. Zoloft (Sertraline) → can lead to seizure attacks → stroke)
5. Citalopram (Celexa) / Desyrel (Trazodone) - newest SSRI → Examples of tyramine-containing product: processed,
found in the market. fermented, and overripe products (Tyramine)
6. Vestaril (Reboxetine) → MOC antihypertensive: Calcium Channel Blockers
SSRI should not be given together with other Electroconvulsive therapy
antidepressants and alcohol ● Electroconvulsive therapy/shock therapy - last resort for
treating depression
St. John’s wort - herbal remedy for depression
You might also like
- Classroom Management: PD: Kevin M. Reeves January 20, 2016Document16 pagesClassroom Management: PD: Kevin M. Reeves January 20, 2016Samiullah Durrani100% (2)
- Motorized Treadmill: Owner'S ManualDocument46 pagesMotorized Treadmill: Owner'S ManualMohammed ShabanNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic Drugs: Bryan Mae H. DegorioDocument65 pagesPsychotropic Drugs: Bryan Mae H. DegorioBryan Mae H. Degorio100% (2)
- Pharmacology (All Lectures)Document283 pagesPharmacology (All Lectures)Youssef ElzataryNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic Drugs: Western Mindanao State UniversityDocument41 pagesPsychotropic Drugs: Western Mindanao State UniversityAmie CuevasNo ratings yet
- AntidepressantsDocument4 pagesAntidepressantsGrace CabilloNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 DepressionDocument26 pagesLecture 2 Depressionammarr44776No ratings yet
- PsychopharmacologyDocument8 pagesPsychopharmacologyzashileighNo ratings yet
- Anti Depresan1Document39 pagesAnti Depresan1Akmal SafwanNo ratings yet
- Clinical ToxicologyDocument6 pagesClinical ToxicologyGrace MarinoNo ratings yet
- AntideprresentDocument54 pagesAntideprresentHadiqa KhanNo ratings yet
- Anti Depressant DrugsDocument31 pagesAnti Depressant DrugsR A H U LNo ratings yet
- Depression PDFDocument10 pagesDepression PDFLyadelou FortuNo ratings yet
- NeuropharmacologyDocument30 pagesNeuropharmacologytracy_lau_8No ratings yet
- Anti DepressentsDocument2 pagesAnti DepressentsAch Ri Fa INo ratings yet
- Anti Psychotic CNS EacDocument33 pagesAnti Psychotic CNS EacPavan chowdaryNo ratings yet
- AnxiolyticsDocument2 pagesAnxiolyticsChristel Mariz SantellaNo ratings yet
- CAE #11 - PsychiatryDocument51 pagesCAE #11 - PsychiatryMariam ShenoudaNo ratings yet
- A.Psikosis Tipikal/ Neuroleptik/Major Tranquilizer A.Depresi/Thymoleptic A.ManiaDocument10 pagesA.Psikosis Tipikal/ Neuroleptik/Major Tranquilizer A.Depresi/Thymoleptic A.ManiajejezzNo ratings yet
- Overview of Psychotropic DrugsDocument7 pagesOverview of Psychotropic Drugsnad101No ratings yet
- 11.BMD 308 - Adrenergic PharmacologyDocument29 pages11.BMD 308 - Adrenergic PharmacologyMega XtericsNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Neuromuscular DisordersDocument4 pagesPharmacology Neuromuscular Disorders8dxf5bqv6gNo ratings yet
- PsychopharmacologyDocument160 pagesPsychopharmacologyInah Sarita100% (1)
- 12.2.4 - Antidepressants (2008-Fev2013)Document40 pages12.2.4 - Antidepressants (2008-Fev2013)Gabrielle NnomoNo ratings yet
- Antidepresive Sedative ActivatoareDocument2 pagesAntidepresive Sedative ActivatoareDrima EdiNo ratings yet
- CNS 12 - Class Notes.pdfDocument44 pagesCNS 12 - Class Notes.pdfSaurav ShawNo ratings yet
- NEURO FINAlDocument44 pagesNEURO FINAlUswa MehmoodNo ratings yet
- AnxietyDocument6 pagesAnxietyMasa MasaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting CNSDocument30 pagesDrugs Affecting CNSGwen De CastroNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Central Nervous System CnsDocument35 pagesLecture 8 Central Nervous System CnsakramuddaulaNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic Drugs.Document15 pagesPsychotropic Drugs.Xiaoqing SongNo ratings yet
- PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGYDocument2 pagesPSYCHOPHARMACOLOGYJulia Rae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- An Tide Prees AntDocument38 pagesAn Tide Prees Antnamah odatNo ratings yet
- AntidepressantsDocument4 pagesAntidepressantsAhmed MansourNo ratings yet
- Pharma 2 BookDocument168 pagesPharma 2 BookSuhaib KasabraNo ratings yet
- CNS Depressants - Anxiolytics & Sedative HypnoticsDocument4 pagesCNS Depressants - Anxiolytics & Sedative HypnoticsJustin HulinNo ratings yet
- Antidepressant DrugsDocument47 pagesAntidepressant DrugsOjambo Flavia75% (4)
- PharmacologReview File Important (AutoRecovered)Document29 pagesPharmacologReview File Important (AutoRecovered)sami khanNo ratings yet
- Pharm Chem 3.14.22Document45 pagesPharm Chem 3.14.22Morrigan DearmanNo ratings yet
- Types of Antidepressants and How They WorkDocument1 pageTypes of Antidepressants and How They WorkSadiq AchakzaiNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants AntianxietyDocument95 pagesAntidepressants AntianxietyCharles YiuNo ratings yet
- Share BioPsychDocument5 pagesShare BioPsychmaryjanevaldezvillacampa08No ratings yet
- Lecture 11 Sedative-Hypnotic and Anti-Anxiety AgentsDocument32 pagesLecture 11 Sedative-Hypnotic and Anti-Anxiety AgentsHafsa ShakilNo ratings yet
- PsychopharmacologyDocument98 pagesPsychopharmacologyMontero, Ma. Cecilia - BSN 3-B100% (1)
- Antidepressants DrugsDocument2 pagesAntidepressants DrugsSony Montaño CañeteNo ratings yet
- HW 2 Na 3Document7 pagesHW 2 Na 3Araw GabiNo ratings yet
- Stereotypical Behavior: Rate Dependence EffectsDocument2 pagesStereotypical Behavior: Rate Dependence EffectsJustin HulinNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants ChristianDocument37 pagesAntidepressants ChristianciaranNo ratings yet
- Psychopharma 1Document7 pagesPsychopharma 1Mitchee Zialcita100% (1)
- Anti-Depressant Drugs: Presented by L.Nithish Shankar Ii Year Mbbs KGMCDocument17 pagesAnti-Depressant Drugs: Presented by L.Nithish Shankar Ii Year Mbbs KGMCÑiťhišh Śhankąŕ LóganáthánNo ratings yet
- Norepinephrine - Released From Postganglionic: Autonomic Nervous System MedicationsDocument7 pagesNorepinephrine - Released From Postganglionic: Autonomic Nervous System MedicationsJohn denver FloresNo ratings yet
- CNS DrugsDocument57 pagesCNS DrugsHussein Al-jmrawiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology in PsychiatryDocument33 pagesPharmacology in PsychiatryKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- The PSYCH MAP ColoredDocument2 pagesThe PSYCH MAP Coloredcentrino17No ratings yet
- Drugs HandoutDocument9 pagesDrugs Handoutekwamboka956No ratings yet
- Antidepressants UOLDocument85 pagesAntidepressants UOLYahya AhmedNo ratings yet
- Week 11 - Psychotherapeutic DrugsDocument20 pagesWeek 11 - Psychotherapeutic DrugsuserherwwweNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitter Pathway in PsychiatryDocument22 pagesNeurotransmitter Pathway in PsychiatryameerNo ratings yet
- Obat Pada SSPDocument21 pagesObat Pada SSPNirina Wulan HapsariNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric DrugsDocument16 pagesPsychiatric Drugsqaid.yazdeen98No ratings yet
- Lung AssessmentDocument4 pagesLung AssessmentChristel Mariz SantellaNo ratings yet
- NCM 116 RLE Week 3Document32 pagesNCM 116 RLE Week 3Christel Mariz SantellaNo ratings yet
- OSTEOSARCOMA SisonDocument14 pagesOSTEOSARCOMA SisonChristel Mariz SantellaNo ratings yet
- NCM 116 RLE Week 4Document28 pagesNCM 116 RLE Week 4Christel Mariz SantellaNo ratings yet
- ArthritisDocument6 pagesArthritisChristel Mariz SantellaNo ratings yet
- Neuroses VS PsychosisDocument23 pagesNeuroses VS PsychosisChristel Mariz SantellaNo ratings yet
- AnxiolyticsDocument2 pagesAnxiolyticsChristel Mariz SantellaNo ratings yet
- Bipolar DisorderDocument2 pagesBipolar DisorderChristel Mariz SantellaNo ratings yet
- Vice-Principals Job Description PDFDocument2 pagesVice-Principals Job Description PDFapi-532410048No ratings yet
- Intelligent ConstructionDocument4 pagesIntelligent ConstructionRikesh SapkotaNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id2460891Document38 pagesSSRN Id2460891swayamprava routNo ratings yet
- Infusion Pump HX-801E Operator Manual: Please Read This Manual Completely Prior To Using The Device!Document32 pagesInfusion Pump HX-801E Operator Manual: Please Read This Manual Completely Prior To Using The Device!Roberto RamírezNo ratings yet
- Polifur Acrylic Clearcoat v1 - 1Document5 pagesPolifur Acrylic Clearcoat v1 - 1victorzy06No ratings yet
- The Dynamics of Public Policy by Adrian Kay PDFDocument158 pagesThe Dynamics of Public Policy by Adrian Kay PDFSadam Lashari100% (1)
- How To Choose Needle Hole DiameterDocument3 pagesHow To Choose Needle Hole DiameterAri CleciusNo ratings yet
- What Is DelusionDocument10 pagesWhat Is Delusionvw8620440No ratings yet
- Information Systems For Healthcare Management Eighth Edition 8Th Edition Full ChapterDocument41 pagesInformation Systems For Healthcare Management Eighth Edition 8Th Edition Full Chapterarnold.kluge705100% (24)
- Pencegahan Dan Penanganan StuntingDocument30 pagesPencegahan Dan Penanganan Stuntinghusnul khotimahNo ratings yet
- How To Give An Im Injection Portfolio Track ChangesDocument4 pagesHow To Give An Im Injection Portfolio Track Changesapi-582970027No ratings yet
- Pol - COVID VACCINE DETOX THREAD - Politically Incorrect - 4chanDocument1 pagePol - COVID VACCINE DETOX THREAD - Politically Incorrect - 4chanAndrija NaglicNo ratings yet
- Shell Omala S2 G 320: Performance, Features & BenefitsDocument3 pagesShell Omala S2 G 320: Performance, Features & BenefitsMohd FaidzalNo ratings yet
- Neurology: CindyDocument32 pagesNeurology: CindyTaschiro YuliarthaNo ratings yet
- RPP Science Unit 1 - Organ System NFDocument8 pagesRPP Science Unit 1 - Organ System NFMs SinarNo ratings yet
- GEHC Site Planning Final Drawing Diamond System PDFDocument6 pagesGEHC Site Planning Final Drawing Diamond System PDFIrinel BuscaNo ratings yet
- Skin Disease in DogsDocument18 pagesSkin Disease in DogsBibek SutradharNo ratings yet
- Medgluv - Gloves - Certifications - OpulentDocument35 pagesMedgluv - Gloves - Certifications - Opulentsaisridhar99100% (1)
- Mcgill, Programa de VeranoDocument18 pagesMcgill, Programa de VeranoXosé María André RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of CyclingDocument82 pagesAnatomy of Cyclingclaudia Torres100% (1)
- WHH Vacancy Announcement - WASH Field OfficerDocument2 pagesWHH Vacancy Announcement - WASH Field OfficerAwes SewsaNo ratings yet
- PedoDocument14 pagesPedoHarjotBrarNo ratings yet
- Periodontal Disease As A Specific, Albeit Chronic, Infection: Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument26 pagesPeriodontal Disease As A Specific, Albeit Chronic, Infection: Diagnosis and TreatmentGali Alfaro ZagalNo ratings yet
- (The Oily Press Lipid Library) Frank Gunstone - Lipids For Functional Foods and Nutraceuticals-Woodhead Publishing (2003) PDFDocument341 pages(The Oily Press Lipid Library) Frank Gunstone - Lipids For Functional Foods and Nutraceuticals-Woodhead Publishing (2003) PDFCamilo Andrés CastroNo ratings yet
- Menopause: Hormones, Lifestyle, and Optimizing AgingDocument15 pagesMenopause: Hormones, Lifestyle, and Optimizing Agingsetya riniNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document38 pagesUnit 5Vy YenNo ratings yet
- Krok 2 Medicine 2014 1Document545 pagesKrok 2 Medicine 2014 1Amrut LovesmusicNo ratings yet
- 5K 30 - 40 MILES: September 4Document5 pages5K 30 - 40 MILES: September 4joogNo ratings yet