Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 4 Tense
Unit 4 Tense
Uploaded by
Dr. KafleOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 4 Tense
Unit 4 Tense
Uploaded by
Dr. KafleCopyright:
Available Formats
Bridge Course (After SEE)
Unit 4
Tense
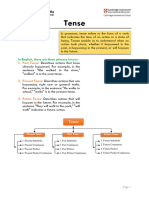
The use of tense forms and their changes into passive forms
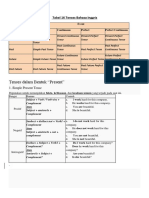
I. Present Tense
1. Simple present tense
It is used for habitual actions, universal truths, present actions, future time table.
Formula: Subject + V1/V5 + Object
Example: Dayananda reads the Bible.
He teases us.
Simple present tense (passive)
It is used to emphasize the object, and the object is brought as subject in passive
sentence.
Formula: Obj (as subject)+is/am/are + V3 + by + agent
Example: The Bible is read by Daynanda.
We are teased by him.
2. Present continuous tense
It is used for long present actions, future actions.
Formula: Subject + is/am/are + V4 (ing) + obj
Singular sub. takes 'is' whereas plural sub. takes are'
Example: She is chopping onions.
They are playing Chess
Present continuous tense (passive)
Formula: Obj + is/am/are + being + V3 + by + agent
Example: Onions are being chopped by her.
Chess is being played.
3. Present perfect tense
It is used for an action that occurred in the past/recent past and still its effect is there.
Formula: Sub + has/have + V3+ obi
Example: I have loved a girl.
You have persuaded them.
She has written a poem.
Present perfect tense (passive)
Formula: Obj + has/have + been + V3 + by + agent
Downloaded From: Study Notes Nepal Join Group
Bridge Course (After SEE)
Example: A girl has been loved by me.
They have been persuaded by you.
A poem has been written by her.
Present perfect continuous tense
It is used for an action that begins in the past and continues into
the present and it is still unknown when it ends.
Formula: Sub + has/have + been + V4(ing) + obj
Singular sub. takes ‘has' whereas plural sub. takes 'have'
Example: I've been teaching in a school for five years.
They have been publishing books since 1999.
She has been working as a receptionist in Newton Academy.
- No passive form.
Il. Past Tense
1. Simple past tense
It is used for the completed actions that occurred at a particular past time.
Formula: Sub + V2+ obj
Example: Nirmala ate rice pudding.
They bought new clothes.
Simple past tense (passive)
Formula: Obj + was/were + V3 + by + sub(agent)
Example: Rice pudding was eaten by Nirmala.
New clothes were brought.
2. Past continuous tense
It is used for occurring simultaneous past actions and also for the action occurring in
the past and was interrupted by another past action.
Formula: Sub + was/were + V4 (ing) + obj
Singular sub. takes 'was' whereas plural sub. takes 'were'
Example: She was wearing red dress.
They were demanding her banishment.
They were presenting papers.
Downloaded From: Study Notes Nepal Join Group
Bridge Course (After SEE)
Past continuous tense (passive)
Formula: Obj + was/were + being + V3 + by + agent
Example: Red dress was being worn by her.
Her banishment was being demanded.
Papers were being presented.
3. Past perfect tense
It is used for something that happened in the past and is not continued into the present
for some reason or the other.
Formula: sub+had+V3+obj
Example: They had met their relatives.
He had visited museum last year.
Past perfect tense (passive)
Formula: Obj + had been + V3 + by + agent
Example: Their relatives had been met by them.
Museum had been visited by him last year.
4. Past perfect continuous tense
Formula: Sub + had been + V4 (ing) + obj
Example: They had been living in the USA.
He had been waiting for Yamuna.
- No passive form
III. Future Tense
1. Simple future tense
It is used for definite planned action.
Formula: Sub + shall/will + V1 + obj
Example: I shall love her.
He will meet me tomorrow
Simple future tense (passive)
Formula: Obj + shall/will + be + V3 + by + agent
Example: She will be loved by me.
I shall be met tomorrow by him.
2. Future continuous tense
It is used for an action that will be taking place at a specific time in the future.
Downloaded From: Study Notes Nepal Join Group
Bridge Course (After SEE)
Formula: Sub + shall/will + be + V4(ing) + obj
Example: We will be having an exam in September.
I shall be calling you tomorrow.
They will be enjoying a party at 10 p.m.
- No passive form.
3. Future perfect tense
It is used for the action that began in the past, and is still continued in the present and
will finish at a specific time in the future.
Formula: sub + shall/will + have + V3 + obj
Example: You will have loved him.
They will have finished it by tomorrow
Future perfect tense (passive)
Formula: Obj+shall/will+have+been+V3+by+agent
Example: He will have been loved by you.
It will have been finished by tomorrow
4. Future perfect continuous tense
It is used to emphasize the length of time that will have occurred before a specific
time in the future.
Formula: Sub+will/shall+have+been +V4(ing)tobj
Example: He will have been working for the institute for ten years.
I shall have been living here for fifteen years.
- No passive form.
Notes:
❖ If the active sentence is given in model+be verb then we change it into the following
way;
○ He should complete his homework before the light goes off.
⇒His homework should be completed before the light goes off.
● She could join the army.
⇒ The army could be joined by her.
❖ If the active sentence is in model+have+ V3 then we change this sentence into passive
in the following way;
➢ Govinda could have finished the work this morning
⇒ The work could have been finished this morning.
Downloaded From: Study Notes Nepal Join Group
Bridge Course (After SEE)
❖ If the active sentence is in imperative structure, then we change the active sentence
into passive in the following way;
➢ Open the door.
⇒Let the door be opened.
● Drive the car.
⇒Let the car be driven.
➢ Give the order.
⇒Let the order be given.
❖ When two objects are used in the active sentence, then either of the objects can be
used as the subject in the passive, and if the active structure is in interrogative
(question) form, the passive also must be in the same structure.
➢ Who taught you English grammar?
⇒By whom was English grammar taught to you?
⇒By whom were you taught English grammar?
➢ Why does the principal praise the students?
⇒Why are the students praised by the principal?
➢ Is someone making the tea for me?
⇒Is the tea being made for me?
➢ I have given a pen to her.
⇒A pen has been given to her by me.
⇒She has been given a pen by me.
Downloaded From: Study Notes Nepal Join Group
You might also like
- Newenterprise b2 SB SampleDocument14 pagesNewenterprise b2 SB Sampleavril printemps100% (2)
- Taste of Salt CurriculumDocument67 pagesTaste of Salt CurriculumAnn Marie DoleyNo ratings yet
- The Passive: Form: Tense/Form Passive Pattern Example: Passive Example: ActiveDocument6 pagesThe Passive: Form: Tense/Form Passive Pattern Example: Passive Example: ActiveОксанаNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument5 pagesTensesCharan Teja AdepuNo ratings yet
- Tenses English by Kami ShahDocument4 pagesTenses English by Kami Shahkami5185No ratings yet
- Gram SpeakingDocument37 pagesGram SpeakingDikshya BhandariNo ratings yet
- Chytia Nurhalizah - P17320121410 - TK 1 STDocument8 pagesChytia Nurhalizah - P17320121410 - TK 1 STCHYTIA NURHALIZAHNo ratings yet
- English Grammar NotesDocument32 pagesEnglish Grammar NotesYash PatelNo ratings yet
- Tenses Notes DocumentDocument16 pagesTenses Notes DocumentA BhavyaNo ratings yet
- 16 Tenses PDFDocument37 pages16 Tenses PDFFatih100% (1)
- Uses of TensesDocument17 pagesUses of TensesMsPushpanjali PatilNo ratings yet
- Grammar HandoutDocument10 pagesGrammar Handoutstonegrave68No ratings yet
- Tense SlideDocument15 pagesTense SlideAshe AlexNo ratings yet
- Makalah: Politeknik Piksi Ganesha Bandung 2017Document7 pagesMakalah: Politeknik Piksi Ganesha Bandung 2017Putri RahmadaniNo ratings yet
- Tense Indefinite Continuous Perfect Perfect Continuous: Presen TDocument2 pagesTense Indefinite Continuous Perfect Perfect Continuous: Presen TBilal BhattiNo ratings yet
- Format Makalah B. InggrisDocument9 pagesFormat Makalah B. InggrisNely VeronichaNo ratings yet
- Adverbs:: Yrian Irtual NiversityDocument16 pagesAdverbs:: Yrian Irtual Niversityyazan khwiesNo ratings yet
- Lesson - TenseDocument31 pagesLesson - Tenseneel_103No ratings yet
- Tenses ReviewDocument8 pagesTenses Reviewjeff jaberNo ratings yet
- RULE - Sub +v1+s/es+object: Example - DoesDocument19 pagesRULE - Sub +v1+s/es+object: Example - Does꧁༒•Ѵιཌཇའ•MAx•༒꧂No ratings yet
- Response Paper: 1. Present SimpleDocument4 pagesResponse Paper: 1. Present SimpleMayhana DwiNo ratings yet
- English Buku KompilasiDocument45 pagesEnglish Buku KompilasiDanis lutfiNo ratings yet
- Nesti Puji Astuti - 5117011 - Perbaikan NilaiDocument24 pagesNesti Puji Astuti - 5117011 - Perbaikan NilaiNesti PujiaNo ratings yet
- Definition:: Action That Will Occur or Happen in The Future. Sub+ (1 Form of Verb) +objDocument4 pagesDefinition:: Action That Will Occur or Happen in The Future. Sub+ (1 Form of Verb) +objLiam JuddNo ratings yet
- English Grammar NotesDocument53 pagesEnglish Grammar NotesHemangini SomaniNo ratings yet
- Aspects of VerbsDocument77 pagesAspects of VerbsnonNo ratings yet
- English Learners All Tenses With ExamplesDocument3 pagesEnglish Learners All Tenses With ExamplesJudy Ann Jude AdornaNo ratings yet
- Diktat Bahasa Inggris Xii Sem 2 2015Document22 pagesDiktat Bahasa Inggris Xii Sem 2 2015Kiki SurjantoNo ratings yet
- English Assignment 16 Tenses in English Arya Damar 14 XI IPA 6Document4 pagesEnglish Assignment 16 Tenses in English Arya Damar 14 XI IPA 6Arya DamarNo ratings yet
- Exploring Descriptive English Grammar Exploring Descriptive English GrammarDocument20 pagesExploring Descriptive English Grammar Exploring Descriptive English GrammarLayla ZalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Ratha's Course OutlineDocument9 pagesRatha's Course OutlineVitiadaro RinNo ratings yet
- 16 English TensesDocument14 pages16 English Tensesdinaanggraeni023No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Cdi5Document6 pagesLesson 2 Cdi5catherinemarquez1029No ratings yet
- Grammar 3 Syllabus 1 Pages 1 6 CompressedDocument6 pagesGrammar 3 Syllabus 1 Pages 1 6 CompressedIinpuspitaa sariiNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 6 Bahasa InggrisDocument7 pagesKelompok 6 Bahasa Inggrisrahmad fitriansyahNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Voice Worksheet and NotesDocument7 pagesActive and Passive Voice Worksheet and NotesMartha MendozaNo ratings yet
- Tenses NewDocument15 pagesTenses NewKaviya RaviNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Notes JRDocument57 pagesEnglish Grammar Notes JRshahhiya2006No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 UASDocument3 pagesChapter 8 UASZul KarnaenNo ratings yet
- Hello 2Document12 pagesHello 2Tan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple - Grammar Guide Part 1 of 3Document5 pagesPresent Perfect Simple - Grammar Guide Part 1 of 3Igor NircaNo ratings yet
- Simple Present TenseDocument5 pagesSimple Present TenseAlgam RumfotNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument19 pagesPassive VoicealisinaalipoorNo ratings yet
- English Grammar LessonsDocument9 pagesEnglish Grammar LessonsRangothri Sreenivasa SubramanyamNo ratings yet
- PEL 130 Lecture 4Document23 pagesPEL 130 Lecture 4Roshan PoudhyalNo ratings yet
- Principal Parts and Tenses of The VerbsDocument35 pagesPrincipal Parts and Tenses of The Verbs1900248No ratings yet
- Name: Laiba Amer Roll Number: 20011511-080Document12 pagesName: Laiba Amer Roll Number: 20011511-080Butt ButtNo ratings yet
- Class 11 English Core by Raghav...Document80 pagesClass 11 English Core by Raghav...Raghav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Course6 Grammar 2Document3 pagesCourse6 Grammar 2Yahya BouslimiNo ratings yet
- Tense (All 12 Types)Document6 pagesTense (All 12 Types)Ahans GamerNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document1 pagePresentation 1aishariaz342No ratings yet
- AnGLais s2Document4 pagesAnGLais s2SAHRA YOUNo ratings yet
- TENSEDocument12 pagesTENSEButt ButtNo ratings yet
- Back II 20211 Grammar PointDocument17 pagesBack II 20211 Grammar Pointhis schoolNo ratings yet
- Sometimes Often: Verb in Infinitive Read ForgetsDocument15 pagesSometimes Often: Verb in Infinitive Read ForgetsromNo ratings yet
- Materi Present Continuous TenseDocument12 pagesMateri Present Continuous TenseWahidun HtnNo ratings yet
- AnglesDocument3 pagesAnglesJÚLIA SÁNCHEZ OBRADOR batx1No ratings yet
- Verbs (LNK 22)Document10 pagesVerbs (LNK 22)Karylle BartolayNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple Grammar Guide Part 1 of 3 Grammar Guides - 1235Document5 pagesPresent Perfect Simple Grammar Guide Part 1 of 3 Grammar Guides - 1235tomaNo ratings yet
- Subject + Was/were/v II + Object/ComplementDocument6 pagesSubject + Was/were/v II + Object/ComplementRini TiaraNo ratings yet
- Final English ExamDocument8 pagesFinal English Examms94kh96g2No ratings yet
- UNIT-12: General Use of PrepositionsDocument4 pagesUNIT-12: General Use of PrepositionsDr. KafleNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Single WordDocument6 pagesUnit 7: Single WordDr. KafleNo ratings yet
- UNIT-10: Conditional SentencesDocument1 pageUNIT-10: Conditional SentencesDr. KafleNo ratings yet
- UNIT-6: Speech: Direct and IndirectDocument4 pagesUNIT-6: Speech: Direct and IndirectDr. KafleNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 ArticleDocument4 pagesUnit 3 ArticleDr. KafleNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1: Subject and Verb AgreementDocument3 pagesUnit - 1: Subject and Verb AgreementDr. KafleNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Causative VerbsDocument1 pageUnit 2 Causative VerbsDr. KafleNo ratings yet
- Él Estará TrabajandoDocument2 pagesÉl Estará TrabajandoHelena Prieto GarciaNo ratings yet
- Major Report DummyDocument3 pagesMajor Report Dummyriya sharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 More Practice: VocabularyDocument6 pagesUnit 2 More Practice: Vocabularypol burcet100% (1)
- Belajar TensesDocument17 pagesBelajar TensesBayu PerkasaNo ratings yet
- Fourth Partial, Monitor 1ST SeniorDocument8 pagesFourth Partial, Monitor 1ST Seniorisaac mNo ratings yet
- Gramatica Upper Interm2Document30 pagesGramatica Upper Interm2Azul CieloNo ratings yet
- English Verb TensesDocument5 pagesEnglish Verb TensesNabil El makoudyNo ratings yet
- Жилийн Төлөвлөлт 11r AngiDocument9 pagesЖилийн Төлөвлөлт 11r AngiНандинцэцэг СампилNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Future Perfect Tense A (0) ReDocument2 pagesGrade 4 Future Perfect Tense A (0) Rezkuzainkhan102No ratings yet
- Future Perfect and Perfect ContinuousDocument16 pagesFuture Perfect and Perfect ContinuousChhay KospolNo ratings yet
- Actividad 1 Grammar KatherineDocument7 pagesActividad 1 Grammar KatherineMigdalia GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Presentasi Inggris IDocument21 pagesPresentasi Inggris IMaya KomalaNo ratings yet
- Gold Exp Grammar PPT B2 U3Document9 pagesGold Exp Grammar PPT B2 U3Gulnara0% (1)
- TensesDocument7 pagesTensesisabellavasconcelosmartin15No ratings yet
- 16 TensesDocument17 pages16 TensesSeulraNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa Inggris - Passive VoiceDocument5 pagesMakalah Bahasa Inggris - Passive Voicealhanun100% (1)
- English Verb - To FlyDocument3 pagesEnglish Verb - To FlyCin Dy E PilNo ratings yet
- Fiche Cours AnglaisDocument9 pagesFiche Cours Anglaisliman boukar BoukarNo ratings yet
- 6th Grade Short StoryDocument7 pages6th Grade Short Story『ABN』MARCONo ratings yet
- Tabel 16 Tenses Bahasa InggrisDocument8 pagesTabel 16 Tenses Bahasa InggrisAnonymous xYC2wfV100% (1)
- Verb TenseDocument19 pagesVerb TenseLianneNo ratings yet
- 8 EnglishDocument80 pages8 EnglishvedhavarshiniNo ratings yet
- Shot in The DarkDocument2 pagesShot in The DarkMariaTh16No ratings yet
- Future TensesDocument22 pagesFuture TensesAlexandra EvaNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan in EnglishDocument13 pagesLearning Plan in EnglishGloucille Marie Villacastin67% (3)
- Least Mastered Competencies G9Document1 pageLeast Mastered Competencies G9Renlah HalnerNo ratings yet
- Dosier AlvaroDocument22 pagesDosier AlvaroFernando Muñoz MontesinosNo ratings yet