Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
Justin Domingo GuerreroOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Untitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
Justin Domingo GuerreroCopyright:
Available Formats
THE NOTRE DAME OF ESPERANZA, INC.
Saliao, Esperanza, Sultan Kudarat
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL DEPARTMENT
Academic Year 2022-2023, 2nd Semester
CONCEPT NOTE #1
Basic Calculus
ACTIVITY TITLE: The Unit Circle
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Illustrate the unit circle and the relationship between the linear and angular
measures of the central angle in a unit circle.
2. Convert angle measures from degrees to radians and vice versa.
3. Illustrate angles in standard position and find coterminal angles.
REFERENCE: Pre-Calculus With Software Applications for Senior High School, Revised Edition
AUTHORS: De Guzman and Quintana
PAGES: 136-146
CONCEPT NOTES:
THE UNIT CIRCLE
Definitions:
1. An angle is formed by two lines or rays intersecting at a common point called vertex. One ray or line
determines the initial side, and the other ray determines the terminal side.
2. Angle measure is the amount of rotation done by a terminal side away from the initial side. A 1 0 degree
angle is equal to 1/360 of a complete revolution of the terminal side. Note that one revolution is
equivalent to 3600.
3. Degrees and radians are the two basic units of angle measures.
The unit circle is a circle whose center is at the origin and whose radius has a length of one unit or r=1.
BASIC CALCULUS | CONCEPT NOTES | P a g e | 1
NOTE: Each of the terminal sides corresponds to the hypotenuse of a right triangle inside the unit circle. Using
the coordinates in the figures above, we can prove that the radius of a unit circle is indeed 1 unit.
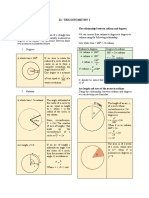
RADIAN MEASURE
Radian measure is also known as the ratio between the length of the arc intercepted by the central angle
and the length of the radius. Note that a central angle is an angle whose vertex lies on the center of the
circle.
s
Formula for the radian measure: θ=
r
Where s is the length of the subtended arc, l = length of the radius and θ = radian measure (measured in
radians).
CONVERSION FACTORS FOR ANGLE MEASURES FROM DEGREE TO RADIANS AND VICE VERSA
180
1 rad=
π
π
1 °=
180
1 revolution=2 πrad=360 °
1 °=60' (60 minutes)
'
1 =60 (60 seconds
ANGLES IN STANDARD POSITION
BASIC CALCULUS | CONCEPT NOTES | P a g e | 2
An angle is considered in standard position if the vertex is located at the origin and the initial side is on the
positive x-axis.
By determining the amount of the rotation from the initial side to the terminal side, the angle can be
measured. If the rotation is counterclockwise, the measurement is positive. If the rotation is clockwise,
the measurement is negative.
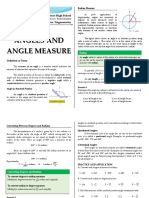
COTERMINAL ANGLES
Coterminal angles are angles in standard position having the same terminal side.
To get coterminal angles, simply add or subtract 360 0 from any given angles measured in degrees or add or
subtract 2 π from any given angle measured in radians.
BASIC CALCULUS | CONCEPT NOTES | P a g e | 3
You might also like
- Lab 5 - Parallax and Distance To The MoonDocument6 pagesLab 5 - Parallax and Distance To The MoonJose AlvarezNo ratings yet
- 3D, 4D, and 5D ModelsDocument5 pages3D, 4D, and 5D ModelsMohammed Al-DhafeeriNo ratings yet
- Circular MeasurementsDocument15 pagesCircular Measurementsmihlemgoduka22No ratings yet
- 5 PDFDocument56 pages5 PDFdNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions: A Mathematician Knows How To Solve A Problem, He Can Not Solve It. - MILNEDocument37 pagesTrigonometric Functions: A Mathematician Knows How To Solve A Problem, He Can Not Solve It. - MILNEnizam17100% (1)
- Learning Module in Pre CalculusDocument13 pagesLearning Module in Pre CalculusChristian Anthony SerquiñaNo ratings yet
- PRE CALCULUS 2ndQ SLMDocument45 pagesPRE CALCULUS 2ndQ SLMWilmar RonioNo ratings yet
- 3 TrigonometryDocument52 pages3 Trigonometryธนเสฐฐ์ กิตติวรรธโนทัยNo ratings yet
- Unit CircleDocument23 pagesUnit CircleRayezeus Jaiden Del Rosario100% (1)
- SMILE Learner S Packet Q2 Week 1Document9 pagesSMILE Learner S Packet Q2 Week 1Leizel TicoyNo ratings yet
- Stationary Ray Terminal Side:, When The Rotation Is Counterclockwise, AndDocument3 pagesStationary Ray Terminal Side:, When The Rotation Is Counterclockwise, AndSheila BaluyosNo ratings yet
- precalSLHT - Week1Document10 pagesprecalSLHT - Week1Mikaela Sai ReynesNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 Trigonometry (Angles)Document5 pagesUNIT 3 Trigonometry (Angles)Billy Jasper DomingoNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Lesson 1 - Angle MeasureDocument50 pagesModule 3 - Lesson 1 - Angle MeasureGavriel Tristan Vital100% (1)
- 2 - Angles and Their MeasurementsDocument47 pages2 - Angles and Their MeasurementsKristine Dorado100% (1)
- Unit Circle: (Angle, Radian Measure, Degree Measure and Coterminal Angle)Document16 pagesUnit Circle: (Angle, Radian Measure, Degree Measure and Coterminal Angle)Charry DawnNo ratings yet
- MATH 1330 - Section 4.2 - Radians, Arc Length, and Area of A SectorDocument6 pagesMATH 1330 - Section 4.2 - Radians, Arc Length, and Area of A Sectoranon_864905075No ratings yet
- Q2 Mathematics 10 AS Week 4Document8 pagesQ2 Mathematics 10 AS Week 4Ljoy Vlog SurvivedNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument18 pagesTrigonometryCaitlyn GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Group 1 KheimDocument4 pagesGroup 1 KheimWriznym SampangNo ratings yet
- 12.trigonometry IDocument10 pages12.trigonometry IWhatyoudoingNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument84 pagesTrigonometryAmber MontesNo ratings yet
- Math 04 Pre-Calculus: Course Outcome 1Document49 pagesMath 04 Pre-Calculus: Course Outcome 1Michaela Princess Gutierrez100% (1)
- KS4 Pre Cal Q2 SY2122 Print Validated 2Document40 pagesKS4 Pre Cal Q2 SY2122 Print Validated 2Matt MarquiciasNo ratings yet
- Radian and Degree MeasureDocument22 pagesRadian and Degree Measureapi-285179261100% (1)
- TrigonometryDocument84 pagesTrigonometryMARYBETH DIABORDONo ratings yet
- Lesson 5. Angle Measurement Unit Circle Circular FunctionsDocument10 pagesLesson 5. Angle Measurement Unit Circle Circular FunctionsDiane MorosNo ratings yet
- Angles and Their MeasureDocument32 pagesAngles and Their MeasureHazel Clemente Carreon100% (2)
- q2 Lesson 2 Angle MeasurementDocument15 pagesq2 Lesson 2 Angle MeasurementalexalorchaNo ratings yet
- MMW10 TrigoDocument4 pagesMMW10 TrigoCarjane Ubalubao Acuyong DyoNo ratings yet
- STM 001 Reviewer 1Document10 pagesSTM 001 Reviewer 1Armhay Loraine DuavezNo ratings yet
- Plane Trigonometry: Math 2Document7 pagesPlane Trigonometry: Math 2Lovely Amor CatipayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Pre-CalculusDocument13 pagesChapter 3 Pre-CalculusaiNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Angles and Angle MeasureDocument19 pages4.1 Angles and Angle Measurevincentmanimtim03No ratings yet
- MAT122 - Lesson 1 (2022-2023 Sem 2)Document25 pagesMAT122 - Lesson 1 (2022-2023 Sem 2)Lesley SimonNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Book FinalDocument109 pagesTrigonometry Book FinaldhruvNo ratings yet
- (Stem - Pc11T-Iia-1) (Stem - Pc11T-Iia-2) : Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) 1Document9 pages(Stem - Pc11T-Iia-1) (Stem - Pc11T-Iia-2) : Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) 1Naddy RetxedNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus Week VIII - Unit CircleDocument32 pagesPre-Calculus Week VIII - Unit CircleSam MNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Trigonometry: 5.1 Introduction of Trigonometry FunctionDocument21 pagesChapter 5: Trigonometry: 5.1 Introduction of Trigonometry FunctionMWPNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Formula Final VDocument15 pagesTrigonometry Formula Final VAjay Chaudhary100% (1)
- Lecture Notes - Angles and Angle MeasureDocument2 pagesLecture Notes - Angles and Angle MeasureabercrombieNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document19 pagesLesson 1Frencelaurence ListonNo ratings yet
- 12: Trigonometry I: Measure of AnglesDocument10 pages12: Trigonometry I: Measure of AnglesInspire The PeopleNo ratings yet
- Dsec1 2Document8 pagesDsec1 2Nour KhaledNo ratings yet
- Angles and Angular MeasuresDocument9 pagesAngles and Angular MeasuresLNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry ReviewDocument13 pagesTrigonometry ReviewAntonio DionisioNo ratings yet
- MTH 103 AnglesDocument3 pagesMTH 103 AnglesWapaya JacobNo ratings yet
- Circular Function: Unit CircleDocument4 pagesCircular Function: Unit CircleKreshia KC IledanNo ratings yet
- Angle Measurement 3Document15 pagesAngle Measurement 3shaynemichaellaniog2020No ratings yet
- Page 0041Document1 pagePage 0041Hùng MạnhNo ratings yet
- PRECAL Final Module 1 4Document41 pagesPRECAL Final Module 1 4Glen MillarNo ratings yet
- 01 Unit Circle and Circular FunctionsDocument21 pages01 Unit Circle and Circular FunctionsJoseph Christopher ButaslacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - TrigonometryDocument18 pagesChapter 4 - TrigonometryDamon LeongNo ratings yet
- Precalculus Q2 SLM WK1 084052Document10 pagesPrecalculus Q2 SLM WK1 084052Jenifer FloresNo ratings yet
- Algebra 12 AnglesDocument44 pagesAlgebra 12 AnglesTrixie Agustin100% (1)
- 4 2 Trig FNDocument18 pages4 2 Trig FNAudrey LeeNo ratings yet
- All LESSON Handouts - Chapter 6 RevisedDocument19 pagesAll LESSON Handouts - Chapter 6 Revisedvexiox900No ratings yet
- Maths Module 8: TrigonometryDocument19 pagesMaths Module 8: TrigonometryDie A MuslimahNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus ReviewerDocument21 pagesPre Calculus ReviewerAndrei SamaritaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Book by PJ SirDocument109 pagesTrigonometry Book by PJ SirSARFARAZ 2343No ratings yet
- Trignometry Complete AssignmentDocument44 pagesTrignometry Complete Assignmentroyalcamp2005No ratings yet
- GCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Elementary Statics and DynamicsDocument15 pagesElementary Statics and DynamicsPooja Bk0% (1)
- Physics HomeworkDocument8 pagesPhysics HomeworkCarlos Javier De la Paz LunaNo ratings yet
- Physics 22Document20 pagesPhysics 22Kazuto ShibaNo ratings yet
- Vectors in Two Dimensions: Read Chapter 1.6-1.9Document31 pagesVectors in Two Dimensions: Read Chapter 1.6-1.9Scarlet VillamorNo ratings yet
- MOTION IN 1 D AND 2DDocument58 pagesMOTION IN 1 D AND 2DSomya RamanNo ratings yet
- Math PosterDocument1 pageMath PosterMuhammad Amirul Haziq Bin ZawawiNo ratings yet
- Motion in Two and Three Dimensions: R X I y J Z KDocument11 pagesMotion in Two and Three Dimensions: R X I y J Z KWahyu SipahutarNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Technology A Two Year Course PDFDocument573 pagesMechanical Technology A Two Year Course PDFNurul LatifahNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Test MC ID 1 Law of Sines Law of Cosines and Area ID 1Document3 pagesUnit 3 Test MC ID 1 Law of Sines Law of Cosines and Area ID 1Edward Raymund CuizonNo ratings yet
- Chapter III The Right Triangle 1Document23 pagesChapter III The Right Triangle 1RonjayNo ratings yet
- Uniform Circular MotionDocument23 pagesUniform Circular MotionAbdul Ahad SajjadNo ratings yet
- MATH 259 - Review Sheet (Prerequisite Topics) : (This Is NOT A Comprehensive List!)Document4 pagesMATH 259 - Review Sheet (Prerequisite Topics) : (This Is NOT A Comprehensive List!)Celal KermangilNo ratings yet
- CE 214 Quiz 2 Answer KeyDocument2 pagesCE 214 Quiz 2 Answer KeyJerome M JaldoNo ratings yet
- Forces in Space Noncoplanar System of ForcesDocument58 pagesForces in Space Noncoplanar System of ForcesNicolás TovarNo ratings yet
- Area of ShapesDocument9 pagesArea of ShapesUmesh Chikhlikar100% (1)
- Special Theory of Relativity 1.1 Introduction (II)Document32 pagesSpecial Theory of Relativity 1.1 Introduction (II)Nur Munirah100% (1)
- List of Formulas For Mathematics CFS IIUMDocument2 pagesList of Formulas For Mathematics CFS IIUMAmin HashimNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Introduction To Trigonometry Study NotesDocument9 pagesCBSE Class 10 Introduction To Trigonometry Study Notesramniwaschak08No ratings yet
- Triangles Measurements (A) : Calculate The Missing Measurements For Each Triangle. 1. 2Document2 pagesTriangles Measurements (A) : Calculate The Missing Measurements For Each Triangle. 1. 2Rondinelli RamonNo ratings yet
- CH 16Document30 pagesCH 16Adeel AsgharNo ratings yet
- 3trigonometric FormulaeDocument2 pages3trigonometric FormulaeMahek IrfanNo ratings yet
- MECH 1302 Dynamics SEM 2, 19/20: Kinematics of A ParticlesDocument29 pagesMECH 1302 Dynamics SEM 2, 19/20: Kinematics of A ParticlesOsob MohamudNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry To Find Angle MeasuresDocument4 pagesTrigonometry To Find Angle MeasuresAndreana McQueenNo ratings yet
- Surveying TRAVERSE ExplianationsDocument10 pagesSurveying TRAVERSE Explianationstaha15No ratings yet
- Rational KinematicsDocument27 pagesRational KinematicsStephen AbadinasNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document27 pagesCH 6math magicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09Document49 pagesChapter 09bella100% (2)
- Identify Right Triangle 1Document2 pagesIdentify Right Triangle 1MittalNo ratings yet