Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Con Rod Crank Pin
Con Rod Crank Pin
Uploaded by
naveenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Con Rod Crank Pin
Con Rod Crank Pin
Uploaded by
naveenCopyright:
Available Formats
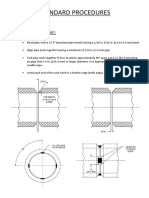
CONNECTING RODS AND BOTTOM END BOLTS
(a) causes of bottom end bolt failures
Stress concentration in way of change of section, damaged fillet and damaged surface
finish
Over stretching / tightening causing permanent damage due to plastic deformation
Uneven tightening causing overloading of some bolt
Inadequate pretension causing high fluctuation of stress in bolts and consequently fatigue
failure
Improper seating of bolt head and nut resulting in bending stress in bolts
Corrosive attack due contaminated lube oil
(b) methods used to tighten the bottom end bolts
Hydraulic device (measure stretch)
During tightening measurements of extension are essential for correct stress
All hydraulic equipments to be checked and pressure gauge to be calibrated
Tightening must be done in stages
Tightening to be done in sequence as per maker’s requirement
Torque spanner
First do calibration of torque spanner and adjust the required torque
Torque should be applied in more than one stage
During final torque applied all work to done by one person and slowly done
Hand tightening
Place one mark on bolt head
Place two marks for angle for final tightening as per maker’s instruction
Do that in more than one stage
Angular accuracy is essential for correct tightening load
(c) Modern design of bottom end bolt
Shank diameter is 10% less than core diameter
Fillet is provided between shank and bolt head to prevent stress concentration
3 to 4 threads remain free below contact face of the nut
High degree of surface finish to prevent stress concentration
Cold rolling of threads to improve fatigue strength
Bolt stiffness to be less than bearing housing less dynamic load on bolt
High UTS alloy steel with long thin elastic bolts for higher fatigue strength
Fitted portion to keep as short as possible to prevent stress concentration and to obtain
greatest resilience
(d) The inspection and maintenance of bottom end bolts
Sound testing to detect internal flaws and cracks
Bolt threads
Surface finish of bolts
Satinath Ghosh – Marine Fisheries Academy – 25th Batch Page 1
Fillet area
Cracks
Measuring elongation of bolts
Checking pretension of bolts
Checking locking device, if any
Satinath Ghosh – Marine Fisheries Academy – 25th Batch Page 2
You might also like
- Saudi Aramco Piping QC Inspector Sample Interview QuestionsDocument6 pagesSaudi Aramco Piping QC Inspector Sample Interview QuestionsRichard Periyanayagam83% (6)
- E-Assessment QuestionsDocument189 pagesE-Assessment Questionsnaveen100% (1)
- Singapore Polytechnic: MPA E-Assessment Guide For MEO COC 1/2Document76 pagesSingapore Polytechnic: MPA E-Assessment Guide For MEO COC 1/2naveen100% (1)
- Contractor's Guide for Installation of Gasketed PVC Pipe for Water / for SewerFrom EverandContractor's Guide for Installation of Gasketed PVC Pipe for Water / for SewerRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Vibration of Cooling Tower Fans 2015Document37 pagesVibration of Cooling Tower Fans 2015fazzlie100% (1)
- Design and Optimization of Weld Neck Flange For Pressure VesselDocument5 pagesDesign and Optimization of Weld Neck Flange For Pressure Vesselcat arroNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Compressor Valve DesignDocument15 pagesReciprocating Compressor Valve Designsaikatchoudhuri100% (1)
- All-in-One Manual of Industrial Piping Practice and MaintenanceFrom EverandAll-in-One Manual of Industrial Piping Practice and MaintenanceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Weld Like a Pro: Beginning to Advanced TechniquesFrom EverandWeld Like a Pro: Beginning to Advanced TechniquesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Composite StructuresDocument25 pagesComposite StructuresVivek Premji100% (1)
- Plastic Part DesignDocument10 pagesPlastic Part Designalidani_1No ratings yet
- Molding Design GuideDocument11 pagesMolding Design GuideMichael ZhangNo ratings yet
- Connection Design Standards: Document No: Cds-1 Second Edition Date: December 9, 2005Document47 pagesConnection Design Standards: Document No: Cds-1 Second Edition Date: December 9, 2005Rajesh Jellelu100% (6)
- Connection TypeDocument9 pagesConnection Typesmelihates100% (1)
- D&F DesignPrinciple TypesofWeldedJoints MechJoints&ReinforcementDocument63 pagesD&F DesignPrinciple TypesofWeldedJoints MechJoints&ReinforcementFaiz IshakNo ratings yet
- 6.design of Connections in Steel Building ConstructionDocument50 pages6.design of Connections in Steel Building ConstructionNovember RainNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel Training ModuleDocument40 pagesPressure Vessel Training ModuleIdil Fitri100% (1)
- Introduction-Design-Guide 2Document16 pagesIntroduction-Design-Guide 2Sutha100% (1)
- Section 19 - Appendix C - FormsDocument52 pagesSection 19 - Appendix C - Formsfivehours5No ratings yet
- MD PV Asme v0.1Document35 pagesMD PV Asme v0.1Kamlesh LuharNo ratings yet
- Connection Design - Its Role in Steel DetailingDocument9 pagesConnection Design - Its Role in Steel DetailingEduardo De Castro Cruz Jr.No ratings yet
- Plastic Design GuidelineDocument8 pagesPlastic Design GuidelineDebarpanNagNo ratings yet
- Soal Soal CSWIP 3.2Document9 pagesSoal Soal CSWIP 3.2handriyantoNo ratings yet
- Section 3 Notes On Structural Design and Design RequirementsDocument6 pagesSection 3 Notes On Structural Design and Design Requirementsel_hasbiNo ratings yet
- Fabrication Inspection ProcedureDocument11 pagesFabrication Inspection Procedurewill_herry100% (6)
- NMDOT Bridge ProceduresDocument11 pagesNMDOT Bridge Proceduressiva_civil4051No ratings yet
- Standard ProceduresDocument15 pagesStandard ProceduresViraci100% (1)
- Case Study For Structural Beam FailureDocument7 pagesCase Study For Structural Beam FailureRakesh RanjanNo ratings yet
- A Subsea Housing Design Checklist PDFDocument8 pagesA Subsea Housing Design Checklist PDFmimi_chan_17100% (1)
- CSWIP Welding Inspection Notes and Questions PDFDocument115 pagesCSWIP Welding Inspection Notes and Questions PDFrahim_335162856100% (3)
- Flange and Gasket Details: Boltright Results Summary Tightening ProcedureDocument2 pagesFlange and Gasket Details: Boltright Results Summary Tightening ProcedureSofyan TaibNo ratings yet
- Procedures For Drill String Design Engineering EssayDocument16 pagesProcedures For Drill String Design Engineering EssayGerardy Cantuta AruniNo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Trắc Nghiệm CSTKMHH File AvDocument56 pagesBài Tập Trắc Nghiệm CSTKMHH File Avtienpr0809No ratings yet
- Water Pump ReportDocument15 pagesWater Pump ReportMohammed BashierNo ratings yet
- One MarksDocument27 pagesOne MarksDeepak PooranachandranNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Positioning Committee: Thrusters and Pod-SealsDocument45 pagesDynamic Positioning Committee: Thrusters and Pod-SealsXa MauNo ratings yet
- Flanges and Its DescriptionDocument5 pagesFlanges and Its Descriptionjoh aseerkNo ratings yet
- 484 Welding Guidelines For Design EngineersDocument4 pages484 Welding Guidelines For Design EngineersPham Song Hong100% (1)
- Saudi Aramco Piping QC Inspector Sample Interview Questions & Answers..Document5 pagesSaudi Aramco Piping QC Inspector Sample Interview Questions & Answers..Ch SIB100% (1)
- Cost Effective ConnectionsDocument14 pagesCost Effective ConnectionsMarakan MaranNo ratings yet
- Aramco Interview QuestionsDocument38 pagesAramco Interview QuestionsMd Sharique86% (7)
- API RP 572 QuizDocument17 pagesAPI RP 572 Quizamalhaj2013No ratings yet
- Technical MemorandumDocument16 pagesTechnical MemorandumRazlan SaidunNo ratings yet
- BS 1881 - 109-1983 Testing ConcreteDocument10 pagesBS 1881 - 109-1983 Testing ConcreteAlsonChinNo ratings yet
- ASME PCC 1 HugoJulien Eng ModDocument2 pagesASME PCC 1 HugoJulien Eng ModTarunNo ratings yet
- NCPWBBulletin 2010-07 Flange AssemblyDocument4 pagesNCPWBBulletin 2010-07 Flange AssemblyPramod AthiyarathuNo ratings yet
- Theory Application of Roll Forming (2010) - WebDocument21 pagesTheory Application of Roll Forming (2010) - WebVenugopalan Manaladikalam100% (1)
- Equipment DesignDocument88 pagesEquipment DesignbigbossNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Failure of an Idle Gear Shaft of a GearboxDocument9 pagesFatigue Failure of an Idle Gear Shaft of a GearboxGuilherme BandeiraNo ratings yet
- Piping QuestionnaireDocument10 pagesPiping QuestionnaireRahman100% (2)
- Rev00-Gasket Installation & Bolt Torquing ProcedureDocument24 pagesRev00-Gasket Installation & Bolt Torquing ProcedureHansel FrancisNo ratings yet
- Volume-II, Technical SpecificationsDocument116 pagesVolume-II, Technical SpecificationsNaveen NagisettiNo ratings yet
- How to prepare Welding Procedures for Oil & Gas PipelinesFrom EverandHow to prepare Welding Procedures for Oil & Gas PipelinesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Spot Welding Interview Success: An Introduction to Spot WeldingFrom EverandSpot Welding Interview Success: An Introduction to Spot WeldingNo ratings yet
- Advanced Processing and Manufacturing Technologies for Nanostructured and Multifunctional Materials IIFrom EverandAdvanced Processing and Manufacturing Technologies for Nanostructured and Multifunctional Materials IITatsuki OhjiNo ratings yet
- Joining of Polymer-Metal Hybrid Structures: Principles and ApplicationsFrom EverandJoining of Polymer-Metal Hybrid Structures: Principles and ApplicationsSergio T. Amancio FilhoNo ratings yet
- Welding Terminology: A Guide to MIG, TIG, Stick, Gas, and Spot Welding TermsFrom EverandWelding Terminology: A Guide to MIG, TIG, Stick, Gas, and Spot Welding TermsNo ratings yet
- Metal Stitching or MetalockingDocument1 pageMetal Stitching or MetalockingnaveenNo ratings yet
- ME Expansion Tank Level Going LowDocument4 pagesME Expansion Tank Level Going LownaveenNo ratings yet
- Marine Growth Preventive SystemDocument3 pagesMarine Growth Preventive SystemnaveenNo ratings yet
- Battery Room: ConstructionalDocument1 pageBattery Room: ConstructionalnaveenNo ratings yet
- ECA CO ProcedureDocument2 pagesECA CO ProcedurenaveenNo ratings yet
- EKG Final QuestionsDocument4 pagesEKG Final QuestionsnaveenNo ratings yet
- Naval Architect & Ship Construction: Non Destructive TestDocument109 pagesNaval Architect & Ship Construction: Non Destructive TestnaveenNo ratings yet
- Mpa Questions 2022Document2 pagesMpa Questions 2022naveenNo ratings yet
- Refrigerent Compressor Stopping ProcedureDocument1 pageRefrigerent Compressor Stopping ProcedurenaveenNo ratings yet
- Ref Comp Manual StartDocument2 pagesRef Comp Manual StartnaveenNo ratings yet
- Ref Comp Auto StartDocument2 pagesRef Comp Auto StartnaveenNo ratings yet
- Cargo Comp Starting ProcedureDocument2 pagesCargo Comp Starting ProcedurenaveenNo ratings yet