Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gaussian Surface A
Gaussian Surface A
Uploaded by
sumit kumarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gaussian Surface A
Gaussian Surface A
Uploaded by
sumit kumarCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
Total electric flux coming out of a unit positive charge put in air is
ok;q esa fLFkr bdkbZ /ku vkos'k ls fudyus okys lEiw.kZ fo|qr ¶yDl dk eku gS
(a) 0 (b) 0−1 (c) (4 p 0 ) −1 (d) 4 0
2. Eight dipoles of charges of magnitude e are placed inside a cube. The total electric flux coming out of the cube will
be
,d ?ku ds vUnj e ifjek.k ds vkos'k okys 8 f}/kzqo j[ks gSaA ?ku ls fuxZr dqy fo|qr ¶yDl dk eku gksxk
8e 16 e e
(a) (b) (c) (d) Zero
0 0 0
3. According to Gauss’ Theorem, electric field of an infinitely long straight wire is proportional to
xkWl izes; ds vuqlkj vuUr yEckbZ ds lh/ks rkj ds dkj.k fo|qr {ks= vuqØekuqikrh gksrk gS
1 1 1
(a) r (b) 2
(c) (d)
r r3 r
4. A point charge +q is placed at the centre of a cube of side L . The electric flux emerging from the cube is
,d ?ku ds dsUæ ij ftldh izR;sd Hkqtk dh yEckbZ L gS ,d vkos’k q j[kk gSA ?ku ls fuxZr fo|qr ¶yDl gksxk
q 6 qL 2 q
(a) (b) Zero (c) (d)
0 0 6 L2 0
5. The S.I. unit of electric flux is
fo|qr ¶yDl dk SI ek=d gS
(a) Weber (b) Newton per coulomb (c) Volt metre (d) Joule per coulomb
6. A charge q is placed at the centre of a cube. Then the flux passing through one face of cube will be
,d vkos’k q dks ?ku ds dsUnz ij j[kk x;k gSA ?ku ds izR;sd i`"B ls xqtjus okyk ¶yDl gS
q q q q
(a) (b) (c) (d)
0 2 0 40 6 0
7. A sphere of radius R has a uniform distribution of electric charge in its volume. At a distance x from its centre, for
x R , the electric field is directly proportional to
f=T;k R ds xksys ds vk;ru esa fo|qr vkos'k dk leku forj.k gSA blds dsUæ ls x nwjh ij x R ds fy,] fo|qr {ks= ds vuqØekuqikrh gksxk
1 1
(a) 2
(b) (c) x (d) x2
x x
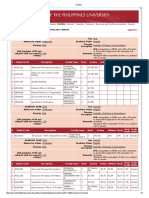
8. The electric flux for Gaussian surface A that enclose the charged particles in free space is (given q1 = –14 nC, q2 = 78.85
nC, q3 = – 56 nC)
fuEu fp= esa xkWfl;u lrg A }kjk ?ksjs x;s vkos'kksa ds dkj.k blls fuxZr ¶yDl gksxk (fn;k gS q1 = –14 nC, q2 = 78.85 nC, q3 = – 56
nC) Gaussian
q3 surface A
(a) 103 Nm2 C–1 (b) 103 CN-1 m–2 q1
q2 Gaussian
(c) 6.32 103 Nm2 C–1 (d) 6.32 103 CN-1 m–2 surface B
9. Two infinite plane parallel sheets separated by a distance d have equal and opposite uniform charge densities .
Electric field at a point between the sheets is
nks vuUr lery vkSj lekUrj pknjksa ds chp dh nwjh d gSA mu ij cjkcj ,oa foijhr vkos'k dk i`"B ?kuRo gSA pknjksa ds chp esa fdlh
fcUnq ij oS|qr {ks= dh rhozrk gksxh
(a) Zero (b) (c) (d) Depends upon the location of the point
0 2 0
10. The inward and outward electric flux for a closed surface in units of N - m 2 / C are respectively 8 10 3
and 4 10 3. Then the total charge inside the surface is [where 0 = permittivity constant]
fdlh cUn i`"B ls vUnj dh vksj rFkk ckgj dh vksj fo|qr ¶yDl N −m2 /C bdkbZ;ksa esa Øe’k% 8 10 3 o 4 10 3 gS rks i`"B ds vUnj dqy
vkos’k gksxk [tgk¡ 0 = fo|qr'khyrk gS]
(−4 10 3 )
(a) 4 10 3 C (b) − 4 10 3 C (c) C (d) − 4 10 3 0 C
You might also like
- Introductory Statistics 8th Edition Mann Solutions ManualDocument29 pagesIntroductory Statistics 8th Edition Mann Solutions ManualJohnWhitextnzm100% (13)
- CUET Physics ChapterwiseDocument273 pagesCUET Physics ChapterwiseNafeesNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument21 pagesElectrostaticsIrmin HasanNo ratings yet
- SSC JE Previous Paper Electrical 2011 PDFDocument15 pagesSSC JE Previous Paper Electrical 2011 PDFprathap kumarNo ratings yet
- Bseh Practice Paper (March 2024) : PhysicsDocument11 pagesBseh Practice Paper (March 2024) : Physicsathy14052006No ratings yet
- SSC JE Previous Paper Electrical 2010Document13 pagesSSC JE Previous Paper Electrical 2010InstalatiiGeneraleNo ratings yet
- 2024 Model 4Document13 pages2024 Model 4Pradeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Fo"K &HKKSFRD Fokku@: Class - Xii Sub-Physics IDocument16 pagesFo"K &HKKSFRD Fokku@: Class - Xii Sub-Physics IAlok DevNo ratings yet
- PhysicsforAIEEE CET2009 10 PDFDocument224 pagesPhysicsforAIEEE CET2009 10 PDFPraveen KumarpillaiNo ratings yet
- NK C SI R: Electrostatics, Home Work Sheet-6Document2 pagesNK C SI R: Electrostatics, Home Work Sheet-6AishwaryNo ratings yet
- Ouat 2016 PCBDocument12 pagesOuat 2016 PCBAswini Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- DPP-4 (Electric Flux and Gauss' Law)Document8 pagesDPP-4 (Electric Flux and Gauss' Law)Youtuber RSNo ratings yet
- 14 ElectrostaticsDocument38 pages14 ElectrostaticskumarNo ratings yet
- 13 - ElectrostaticsDocument8 pages13 - Electrostaticsp_k_soni_iit_physics78% (9)
- Electrostatic Assignment RPSC FinalDocument22 pagesElectrostatic Assignment RPSC Finalstudiesj184No ratings yet
- 2012Document15 pages2012Subramoniam AyyappanNo ratings yet
- CUET 2022 Chapterwise Physics PYQsDocument156 pagesCUET 2022 Chapterwise Physics PYQsbro96793No ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument14 pagesElectrostaticsmoxits76No ratings yet
- Assignment 2 ElectrostaticsDocument6 pagesAssignment 2 ElectrostaticsVijay Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- JEE - Physics - Electrostatics - SolutionsDocument15 pagesJEE - Physics - Electrostatics - SolutionsSanjana KumariNo ratings yet
- DPP-2 (Coulomb's Law and Principle of Superposition)Document6 pagesDPP-2 (Coulomb's Law and Principle of Superposition)Youtuber RSNo ratings yet
- Eklavyats-2023-Part Test 1 (Physics) : QuestionsDocument34 pagesEklavyats-2023-Part Test 1 (Physics) : QuestionsSaptarshiNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics ExerciseDocument10 pagesElectrostatics ExerciseRohit SahuNo ratings yet
- Coulomb's Law, Electric Field & Potential (05!05!2024)Document6 pagesCoulomb's Law, Electric Field & Potential (05!05!2024)raman451982No ratings yet
- Sample Test Paper 2015 Acme PDFDocument16 pagesSample Test Paper 2015 Acme PDFDr-Bini Das AshishNo ratings yet
- +4 For Correct,-1 For Wrong 2 HRDocument8 pages+4 For Correct,-1 For Wrong 2 HRRajan TakiarNo ratings yet
- Class 9Document23 pagesClass 9Vandana SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electro Statics - 25-08-2020 PDFDocument10 pagesElectro Statics - 25-08-2020 PDFPonharish kumar.JNo ratings yet
- Asm 11Document27 pagesAsm 11BHAVYA KUSHWAHANo ratings yet
- Class 12th Physics Sample PaperDocument5 pagesClass 12th Physics Sample PaperAashika DhareNo ratings yet
- Entry Test - 2 (JEE Eklavya 2023-Earlybird)Document45 pagesEntry Test - 2 (JEE Eklavya 2023-Earlybird)vwxyz technologyNo ratings yet
- BITSAT 2018 Question Paper With SolutionsDocument16 pagesBITSAT 2018 Question Paper With Solutionsaryanarone123No ratings yet
- Bseh Practice Paper (March 2024) : PhysicsDocument13 pagesBseh Practice Paper (March 2024) : Physicsathy14052006No ratings yet
- Tejas: Practice Sheet JEE PhysicsDocument5 pagesTejas: Practice Sheet JEE Physicsallenpw402No ratings yet
- Physics Jee Neet DPP A 01Document3 pagesPhysics Jee Neet DPP A 01Swapna BhupalNo ratings yet
- Physics (Question Paper)Document7 pagesPhysics (Question Paper)Jay Doshi ShashikantNo ratings yet
- By Himanshu Chauhan Xii-Daily Practice Test ElectrostaticsDocument3 pagesBy Himanshu Chauhan Xii-Daily Practice Test ElectrostaticsAarzoo malraNo ratings yet
- Test On Gauss LawDocument3 pagesTest On Gauss Lawsangita07071980No ratings yet
- Åtkz CS.M: Section (A) : Energy BandDocument45 pagesÅtkz CS.M: Section (A) : Energy BandAnanya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Tifr - 2017Document10 pagesTifr - 2017sampannkumarNo ratings yet
- Elec Assign 2Document5 pagesElec Assign 2paulaNo ratings yet
- Section A: Multiple Choice TypeDocument10 pagesSection A: Multiple Choice TypeMahendra PandaNo ratings yet
- Class XI Sample PaperDocument10 pagesClass XI Sample PaperRamanujam SinghNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics - Day 2Document4 pagesElectrostatics - Day 2Sunita Manocha Girdhar100% (1)
- Assignment 3 Ques Electric ChargesDocument12 pagesAssignment 3 Ques Electric Chargeswarrior techNo ratings yet
- 2022 Question PaperDocument15 pages2022 Question PaperlafaNo ratings yet
- October 1, 2010: PhysicsDocument7 pagesOctober 1, 2010: PhysicssaikatstatsNo ratings yet
- Ultrix15 Questions - Class 12th PhysicsDocument145 pagesUltrix15 Questions - Class 12th Physicssinhatanvi40No ratings yet
- Physics 12.set 1Document7 pagesPhysics 12.set 1Alok RanjanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Forces)Document7 pagesChapter 1 (Forces)Chandrika AnchanNo ratings yet
- DPP - 02 - Electrostatics - Electric FieldDocument4 pagesDPP - 02 - Electrostatics - Electric FieldAnshul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Physics 222 - Test 2 - Spring 2012Document2 pagesPhysics 222 - Test 2 - Spring 2012eltytanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For High School Science/Physics/DPMT2005: QuestionsDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank For High School Science/Physics/DPMT2005: QuestionsDhika PutraNo ratings yet
- ILQ Chapter23Document35 pagesILQ Chapter23Drakey JavierNo ratings yet
- 110-Electric Charges & FieldsDocument11 pages110-Electric Charges & FieldsHanzalaNo ratings yet
- 100 MCQSDocument11 pages100 MCQSshiviNo ratings yet
- 1-Electric Charge and FieldDocument5 pages1-Electric Charge and FieldpragyanpithagroupofeducationNo ratings yet
- Chap1 Phy3 SampleProblems PDFDocument39 pagesChap1 Phy3 SampleProblems PDFAmmar-Ul-Haq Ammar-Ul-HaqNo ratings yet
- Gate 2003 PHDocument12 pagesGate 2003 PHPasupuleti AnilNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Data Types in Ms-AccessDocument3 pagesData Types in Ms-AccessUmeshSharmaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Protection in Outer SpaceDocument13 pagesEnvironmental Protection in Outer SpaceHarman SainiNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Organization Theory and Design Canadian 3rd Edition Daft Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Organization Theory and Design Canadian 3rd Edition Daft Test Bank PDFliamhe2qr8100% (9)
- Solutions: Answers Are Marked in Bold and UnderlineDocument4 pagesSolutions: Answers Are Marked in Bold and Underlinemanvi mahipalNo ratings yet
- Friction and WearpdfDocument25 pagesFriction and WearpdfLupillo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Adder and SubtractorDocument17 pagesAdder and SubtractorVELURU RANJITH URK18CS020No ratings yet
- Common Computer Connector TypesDocument36 pagesCommon Computer Connector TypesDaisy Mangahas BaleriteNo ratings yet
- La Haine Scene EssayDocument3 pagesLa Haine Scene Essaycampaigne04sb4688No ratings yet
- IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics Volume issue 2018 [doi 10.1109_TIE.2018.2866115] Mohapatra, Soumya Ranjan; Agarwal, Vivek -- Model Predictive Controller with Reduced Complexity for Grid .pdfDocument5 pagesIEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics Volume issue 2018 [doi 10.1109_TIE.2018.2866115] Mohapatra, Soumya Ranjan; Agarwal, Vivek -- Model Predictive Controller with Reduced Complexity for Grid .pdfElahe Hoseini NasabNo ratings yet
- Presenting Your Research in The ConferenceDocument43 pagesPresenting Your Research in The ConferenceAhmad HuseinNo ratings yet
- Supervision What HowDocument7 pagesSupervision What HowBilla GillasNo ratings yet
- OperatorsDocument30 pagesOperatorsMinnakanti Sai Venkata PavanNo ratings yet
- Unapplied RecieptsDocument2 pagesUnapplied RecieptsDavies ChristopherNo ratings yet
- 2019 Conference Program v6 WEBDocument158 pages2019 Conference Program v6 WEBOlusayo100% (1)
- Philosophy CH 1Document18 pagesPhilosophy CH 1Ali YilmazNo ratings yet
- D3711Document5 pagesD3711rimi7alNo ratings yet
- Tesol Observation Report 3Document5 pagesTesol Observation Report 3api-286635247No ratings yet
- Union University'S Lesson Plan Format (Template Available at HTTP://WWW - Uu.edu/programs/tep)Document4 pagesUnion University'S Lesson Plan Format (Template Available at HTTP://WWW - Uu.edu/programs/tep)api-199791774No ratings yet
- Competitor ECommerce DWDesignDocument3 pagesCompetitor ECommerce DWDesignAradana MishraNo ratings yet
- ASME Flange Loading CalculationDocument1 pageASME Flange Loading CalculationssjunedNo ratings yet
- CTR Tti Misc YukselDocument99 pagesCTR Tti Misc YukselMahnooranjumNo ratings yet
- GradesDocument4 pagesGradesJericho PedragosaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Remote Sensing and Gis Ce 333 Unit - 1 Remote SensingDocument13 pagesBasics of Remote Sensing and Gis Ce 333 Unit - 1 Remote SensingShanmuga SundaramNo ratings yet
- Exe File Cutepdf Writer Print WindowsDocument2 pagesExe File Cutepdf Writer Print WindowsRobertNo ratings yet
- 2A - Lean Six Sigma Airplane Simulation PDFDocument8 pages2A - Lean Six Sigma Airplane Simulation PDFBalaji SNo ratings yet
- M20 Operatives Dossier (Final Download)Document102 pagesM20 Operatives Dossier (Final Download)Michael SearleNo ratings yet
- Deontological Ethics SummaryDocument5 pagesDeontological Ethics SummarynikkeesNo ratings yet
- TT - Revit Structure - Working With Structural Components PDFDocument34 pagesTT - Revit Structure - Working With Structural Components PDFAshutosh AnandNo ratings yet
- United States Court of Appeals, Third CircuitDocument15 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals, Third CircuitScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet





































































![IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics Volume issue 2018 [doi 10.1109_TIE.2018.2866115] Mohapatra, Soumya Ranjan; Agarwal, Vivek -- Model Predictive Controller with Reduced Complexity for Grid .pdf](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/442862669/149x198/015e35b7eb/1578984110?v=1)