Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quiz 1 (Fluid Machineries1)
Quiz 1 (Fluid Machineries1)
Uploaded by
SiN X0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pages1. This document appears to be a test or quiz about fluid machinery and pumps. It contains 27 multiple choice questions testing knowledge of different types of pumps, components, properties, and applications.
2. The questions cover topics like positive displacement pumps, centrifugal pumps, deep well pumps, compressor applications and properties, pump efficiency definitions, and fluid properties like pressure, velocity head, specific gravity.
3. The document is formatted as a test for students to complete by selecting the correct multiple choice answer for each question. It provides a high-level assessment of knowledge across various fluid machinery and pump topics.
Original Description:
Original Title
Quiz 1 (fluid machineries1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. This document appears to be a test or quiz about fluid machinery and pumps. It contains 27 multiple choice questions testing knowledge of different types of pumps, components, properties, and applications.
2. The questions cover topics like positive displacement pumps, centrifugal pumps, deep well pumps, compressor applications and properties, pump efficiency definitions, and fluid properties like pressure, velocity head, specific gravity.
3. The document is formatted as a test for students to complete by selecting the correct multiple choice answer for each question. It provides a high-level assessment of knowledge across various fluid machinery and pump topics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pagesQuiz 1 (Fluid Machineries1)
Quiz 1 (Fluid Machineries1)
Uploaded by
SiN X1. This document appears to be a test or quiz about fluid machinery and pumps. It contains 27 multiple choice questions testing knowledge of different types of pumps, components, properties, and applications.
2. The questions cover topics like positive displacement pumps, centrifugal pumps, deep well pumps, compressor applications and properties, pump efficiency definitions, and fluid properties like pressure, velocity head, specific gravity.
3. The document is formatted as a test for students to complete by selecting the correct multiple choice answer for each question. It provides a high-level assessment of knowledge across various fluid machinery and pump topics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Name: __________________________ Score: _________
Date: _________________ Fluid Machineries
BSME-3
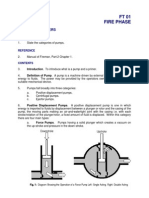
Test I. Identification nozzle on the opposite side of the casing from
______________1. Amount of fluid displaced by the stuffing box and having the face of the
the piston as it moves from top dead center to suction nozzle perpendicular to the
the bottom dead center. longitudinal axis of the shaft.
______________2. A machine used to increase A. Centrifugal pump
the pressure of a gas by decreasing its volume. B. End suction pump
______________3. Ratio of actual gas drawn in C. In line pump
at intake condition to displacement volume. D. Horizontal pump
______________4. Ratio of compressor power 6. Imparts velocity to the liquid,
to brake power. resulting from centrifugal force as the
______________5. Product of the mean impeller is rotated.
effective pressure and displacement volume A. Impeller
______________6. A positive-displacement B. Casing
machine that uses a piston to compress a gas C. Stuffing box
and deliver it at high pressure. D. Shaft sleeve
______________7. These are substances 7. The power of portable air compressors
capable of flowing. used for construction, mining, road
______________8. Pressure exerted by the building, and painting ranges from:
atmosphere on every surface with which it A. 1 hp to 500 hp
comes contact and is measured by barometer. B. ½ hp to 500 hp
______________9. Is the volume per unit mass C. 1 hp to 1000 hp
of a substance. It is reciprocal of the mass D. ½ hp to 1000 hp
density. 8. Pump used to increase air pressure
_____________10. Also known as “Relative above normal, air is then used as a
Density” is the ratio of the density or specific motive power.
weight of a substance to the density or specific A. Air cooled engine
weight of some other standard substance. B. Air compressor
C. Air condenser
Test II. Elements D. Air injection
1. The vertical difference between the 9. When a pump is opening at a vacuum
pumping water level and the static of 4 in Hg, which of the following is not
water level. correct?
A. Static water level A. The pressure is 25.92 in Hg
B. Pumping water level B. The pressure is 10.721 psia
C. Suction head C. The pressure is 158.4 torr
D. Drawdown D. The pressure is 0.8663 atm
2. A type reciprocating pump having a 10. Primary purpose of a pump in a fluid
steam cylinder with no lap on valves, a loop is to
water cylinder and a common piston rod. A. Add energy to the flow
A. Direct acting steam pump B. Add mass to the flow
B. Crank and flywheel reciprocating pump C. Extract energy from the flow
C. Power driven pump D. None of the above
D. Piston pump 11. The isentropic efficiency of a pump is
3. In order to avoid cavitation the NPSH of given by the
an installation should be: A. Ratio of actual to ideal energy extracted
A. At least equal or greater than the NPSH B. Ratio of ideal to actual energy supplied
of the pump C. Ratio of ideal to actual energy extracted
B. At least equal or less than the NPSH of D. Ratio of actual to ideal energy supplied
the pump 12. Centrifugal blowers can supply.
C. Equal to the NPSH of the pump only A. Large volumes of air at low pressures
D. Greater than the NPSH of the pump only B. Small volumes of air at high pressures
4. Find the velocity head for a velocity C. Large volumes of air at high pressures
of 18 m/s. D. Small volumes of air at low pressures
A. 33.0 m 13. For a six compression of air set, the
B. 0.92 m minimum work conditions are:
C. 1.8 m A. Pressure rise per stage will be equal
D. 16.5 m B. Work done in successive stages will be in
5. A single suction pump having its suction geometrical progression
C. Cylinder volumes will be same B. Turbine pump
D. Temperature rise in the cylinders will be C. Ejector centrifugal pump
the same D. Air lift
14. A vertical turbine pump with the pump 21. A type of deep well pump that represent the
and motor closed coupled and design to application of vertical centrifugal pump to
be installed underground, as in the case deep well service and are built for heads up to
of a deep well pump. A. Horizontal split case 305 meters and for capacities up to 28,495
pump liters per minute.
B. Submersible pump A. Plunger pump
C. Booster pump B. Turbine pump
D. Vertical shaft turbine pump C. Ejector centrifugal pump
15. A timber, concrete or masonry D. Air lift
enclosure having a screened inlet kept 22. A type of reciprocating pump that receives
partially filled with water by an open its forward and backward motion of the piston
body of water such as pond, lake, or and plunger from the rotary motion of a
steams. revolving crankshaft by means of a crank and
A. Aquifer connecting rod.
B. Wet pit A. Direct acting steam pump
C. Ground water B. Crank and flywheel reciprocating pump
D. Well water C. Power driven pump
16. Water which is available from a D. Piston pump
well, driven into water bearing 23. A type reciprocating pump having a
subsurface strata (aquifer) steam cylinder with no lap on valves, a
A. Aquifer water cylinder and a common piston rod.
B. Wet pit A. Direct acting steam pump
C. Ground water B. Crank and flywheel reciprocating pump
D. Well water C. Power driven pump
17. The level with respect to the pump, D. Piston pump
of the body of water from which it 24. A type of rotary pump consists of an
takes suction when the pump is not in eccentrically bored cam rotated by a shaft
operation. concentric in a cylindrically bored casing, with
A. Static water level an aburment or follower so arranged that with
B. Pumping water level each rotation of the drive shaft a positive
C. Suction head quantity of liquid is displaced from the space
D. Discharge head between the cam and the pump casing.
18. The level with respect to the pump, A. Cam and piston pump
of the body of water from which it B. Gear pump
takes suction when the pump is in C. Screw pump
operation. D. Vane pump
A. Static water level 25. A type of rotary pump consists of two or
B. Pumping water level more gears, operating in closely fitted casing so
C. Suction head arranged that when the gear teeth unmesh on
D. Drawdown one side liquid fills the space between the gear
19. A type of deep well pump wherein teeth and is carried around in the tooth space to
compressed air is admitted to the well to lift the opposite side and displaced as the teeth
water to the surface, for successful operation mesh again.
of the system, the discharge pipe must have its A. Cam and piston pump
lower end submerged in the well water. B. Gear pump
A. Plunger pump C. Screw pump
B. Turbine pump D. Vane pump
C. Ejector centrifugal pump 26. A positive displacement unit wherein
D. Air lift the pumping action is accomplished by
20. A type of deep well pump which are the forward and backward movement of
refinement of the old hand pump that a piston or plunger inside a cylinder
have played such an important role in usually provided with valves.
country home and small town water A. Rotary pumps
supply from wells. B. Reciprocating pumps
A. Plunger pump C. Deep well pumps
D. Centrifugal pumps 27. Provides a mechanical A. –32.02 kW C. 50.01 kW
sealing B. 33.02 kW D. –50.01 kW
arrangement that takes the place of 5. An air compressor takes air at 90 kPa and
the packing. discharges to 700 kPa. If the volume flow of
A. Packing discharge is 1.3 m3/s, compute the capacity of
B. Gland the air compressor. Assume isentropic
C. Seal gage compression.
D. Mechanical seal A. 5.63 m3/s C. 5.98 m3/s
28. Provides passage to distribute the B. 4.63 m3/s D. 4.9H8 m3/s
sealing medium uniformly around the 6. A single-acting, single-stage reciprocating
portion of the shaft that passes through compressor is required to deliver 50 kg per hour
the stuffing box. Also known as water seal from 100 kPa and 250C conditions to 900 kPa
of lantern ring. delivery pressure. The compression is expected
A. Packing to follow PV1.25 = C. Determine the required
B. Gland power of the compressor under ideal
C. Seal gage conditions.
D. Mechanical seal A. 3.28 kW C. 3.75 kW
29. Which of the following is a safety device B. 4.28 kW D. 4.75 kW
on a compressor? 7. An air compressor consumed 1200 kw-hr per
A. Relief valve day of energy. The electric motor driving the
B. Strainer compressor has an efficiency of 80%. If
C. Over speed shut down indicated power of the compressor is 34 kW,
D. Over pressure shut down find the mechanical efficiency of the
30. Which of the following is a displacement compressor.
compressor? A. 57 % C. 87%
A. Reciprocating air compressor B. 85% D. 95%
B. Vane blower 8. A single acting air compressor has a
C. Centrifugal blower volumetric efficiency of 87 % operates at 500
D. Axial flow compressors rpm. It takes in air at 100 kPa and 300C and
discharges it at 600 kPa. The air handled is 6
Test III. Problem Solving m3/min measured at discharge condition. If
1. An air compressor has a power of 40 kW at compression is isentropic, find the mean
4% clearance. If clearance will increase to 7%, effective pressure in kPa.
what is the new power? A. 203.59 kPa C. 253.64 kPa
A. 70 kW C. 53 kW B. 303.59 kPa D. 353.64 kPa
B. 40 kW D. 60 kW 9. A 5kW motor is used to drive an air
2. A single stage air compressor handles 0.454 compressor. Determine the compressor work if
m3/s of atmospheric pressure,270C air, and the compressor efficiency is 82%.
delivers it to a receiver at 652.75 kPa. Its A. 3.6 kW C. 6.09 kW
volumetric efficiency is 0.72, its compression B. 4.1 kW D. 4.3 kW
efficiency on an isothermal basis is 0.85 and its 10. The bore and stroke of an air compressor
mechanical efficiency is 0.90. If it rotates at 350 are 276mm and 164mm respectively. Running at
rpm, what power in kW is required to drive it? 20rad/sec. If the capacity of the compressor is
A. 95 C. 120 0.02436m3/s. What is the compressor
B. 112 D. 100 volumetric efficiency?
3. An ideal single stage air compressor without A. 0.80 C. 0.84
clearance takes in air at 100 kPa with a B. 0.78 D. 0.94
temperature of 160C and delivered it at 413 kPa
after isentropic compression. What is the
discharge work done by the compressor in
kJ/kg?
A. –59.22 C. –72.5
B. –118.44 D. –145
4. A rotary compressor receives 8 m3/min. of a
gas ( R = 0.410 kJ/kg-K, Cp =1.03 kJ/kg-K) at 108
kPa, 270C and delivers it at 650 kPa. Find the
work if compression is polytropic with PV1.3 =
C.
You might also like
- UTILITIES Quiz 3Document3 pagesUTILITIES Quiz 3Amiel TayagNo ratings yet
- Elements in Power Plant and Industrial Plant EngineeringDocument19 pagesElements in Power Plant and Industrial Plant EngineeringRc Tuppal75% (8)
- Jugo Chapter 12Document21 pagesJugo Chapter 12Reinzo Gallego100% (2)
- Pump & PrimerDocument16 pagesPump & Primerrmaffireschool100% (12)
- NPCDocument32 pagesNPCKhristine Lerie PascualNo ratings yet
- 325F Diagrama Hidraulico PDFDocument2 pages325F Diagrama Hidraulico PDFRICHARD100% (1)
- Pump DrawingDocument1 pagePump DrawingOcta RioNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Calculation For FFDocument2 pagesHydraulic Calculation For FFAnsari1918No ratings yet
- A) Mechanical Energy: 4.impulse Turbine Requires A. High Head and Low DischargeDocument5 pagesA) Mechanical Energy: 4.impulse Turbine Requires A. High Head and Low DischargeGautam GunjanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Fluid MachineriesDocument98 pagesChapter 12 - Fluid MachineriesWaw0% (1)
- (123doc) - Tai-Lieu-Thi-Tuyen-Loc-Dau-Nghi-Son-Pumps-Sumary1 PDFDocument12 pages(123doc) - Tai-Lieu-Thi-Tuyen-Loc-Dau-Nghi-Son-Pumps-Sumary1 PDFTrường Tùng LýNo ratings yet
- B. Open: Hydraulic Machines McqsDocument9 pagesB. Open: Hydraulic Machines McqsSharaz AliNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic MachinesDocument11 pagesHydraulic MachinesmaivizhiNo ratings yet
- Sme MCQDocument41 pagesSme MCQTejas ManeNo ratings yet
- Hydroelectric PlantDocument14 pagesHydroelectric PlantLisa Valois PedrigalNo ratings yet
- Series 1Document2 pagesSeries 1Alexia VargasNo ratings yet
- Building Utilities Test ACCDocument13 pagesBuilding Utilities Test ACCAlfred Theodore BandojoNo ratings yet
- Pump MaintenanceDocument6 pagesPump Maintenancejomar negropradoNo ratings yet
- Ppe / Ipe: Final CoachingDocument331 pagesPpe / Ipe: Final CoachingMark Joseph Nambio NievaNo ratings yet
- Utilities Pugeda Quiz 3Document1 pageUtilities Pugeda Quiz 3corazon philNo ratings yet
- Pumps Pump Is A Machine Used To Add Energy To A Liquid To Transfer The Liquid From AnotherDocument21 pagesPumps Pump Is A Machine Used To Add Energy To A Liquid To Transfer The Liquid From AnotherNygel CanamanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 LectureDocument50 pagesChapter 14 LectureOngNo ratings yet
- Pipe CNS 1 6Document239 pagesPipe CNS 1 6John LuisNo ratings yet
- Pipe CNS 01Document37 pagesPipe CNS 01maria katherine pantojaNo ratings yet
- Objective Questions - 2Document3 pagesObjective Questions - 2Gunjan KumarNo ratings yet
- Compressors, Gas Dynamics and Gas Turbines MCQDocument11 pagesCompressors, Gas Dynamics and Gas Turbines MCQمحمد عابدينNo ratings yet
- Cns1 and Cns2Document89 pagesCns1 and Cns2Richel MendozaNo ratings yet
- MCQ's of Industrial Hydraulics & Pneumatics Laboratory: B. One DirectionDocument3 pagesMCQ's of Industrial Hydraulics & Pneumatics Laboratory: B. One Directionyuvarajballal100% (4)
- PPE-IPE (Edited) Final CoachingDocument13 pagesPPE-IPE (Edited) Final CoachingNelson Naval CabingasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Lecture 1Document36 pagesChapter 4 - Lecture 1Muhd HarithNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Pumps 1) A Centrifugal Pump Is Superior To A Reciprocating Pump BecauseDocument3 pagesReciprocating Pumps 1) A Centrifugal Pump Is Superior To A Reciprocating Pump BecauseRavinth KumarNo ratings yet
- Steam Nozzles and Turbines: A - B. C. DDocument8 pagesSteam Nozzles and Turbines: A - B. C. DRavi TarunNo ratings yet
- MCQ 1Document5 pagesMCQ 1SMIT CHRISTIANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document140 pagesChapter 1Syed YousufuddinNo ratings yet
- Jet, Submersible and Rotary PumpsDocument15 pagesJet, Submersible and Rotary Pumpsmssant100% (1)
- Steam Nozzles and Turbines PDFDocument31 pagesSteam Nozzles and Turbines PDFpaulaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Steam Power PlantDocument123 pagesChapter 5 - Steam Power PlantOnline EducatorNo ratings yet
- D Genral Final With New QuestionsDocument80 pagesD Genral Final With New QuestionsAnonymous NzUA3hNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics (ECH3113) - Chapter 5 TurbomachineryDocument122 pagesFluid Mechanics (ECH3113) - Chapter 5 Turbomachinerysam19961No ratings yet
- Competence 1-5Document14 pagesCompetence 1-5KookieNo ratings yet
- Synergy Question 2019Document5 pagesSynergy Question 2019Glysarien GlysarienNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument23 pagesReviewerAriel Mark PilotinNo ratings yet
- Pipe Terms With AnswerDocument23 pagesPipe Terms With AnswerTIKTOK COMPILATIONNo ratings yet
- Fluid MachineriesDocument94 pagesFluid Machineriesvan querubinNo ratings yet
- Steam Boilers and EnginesDocument71 pagesSteam Boilers and EnginesChristian ArgonzaNo ratings yet
- FM and HHM Objective Type QuestionsDocument15 pagesFM and HHM Objective Type QuestionsAchyutha AnilNo ratings yet
- PPD 06 Mech ReviewDocument37 pagesPPD 06 Mech ReviewCyron Elden Senarillos-Talita Bangis-BodegasNo ratings yet
- MCQ of IFPDocument27 pagesMCQ of IFPYuvraj Ballal83% (6)
- Pumps Notes: H Q PowerDocument12 pagesPumps Notes: H Q PowerahmedaboshadyNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Pump With Air VesselDocument19 pagesReciprocating Pump With Air VesselKrunal Patil93% (15)
- Fluid Mechanics Multiple Choice Questions For EngineersDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics Multiple Choice Questions For EngineersGerry Lou Quiles80% (5)
- PIPE ElementsDocument99 pagesPIPE ElementsJustin MercadoNo ratings yet
- Turbo-Machinery Model ExamDocument2 pagesTurbo-Machinery Model ExamKaleab AndualemNo ratings yet
- QuizDocument30 pagesQuizkkp_28787No ratings yet
- PumpsDocument122 pagesPumpsFour AyesNo ratings yet
- FM 2e SI Chap14 LectureDocument123 pagesFM 2e SI Chap14 LectureJavinKhongNo ratings yet
- Fluid Machinery Part 4Document19 pagesFluid Machinery Part 4s75957xxktNo ratings yet
- H and P Unit I II III MQCDocument36 pagesH and P Unit I II III MQCSuryakant LadNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engineering Exam: I. Encircle The Letter Corresponding To The Nearest AnswerDocument3 pagesPower Plant Engineering Exam: I. Encircle The Letter Corresponding To The Nearest AnswerHectorCabz100% (1)
- Meo Class 4Document55 pagesMeo Class 4adam shaneNo ratings yet
- 1714992440Document1 page1714992440Kendrick RomeroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document32 pagesChapter 2Uzair MaswanNo ratings yet
- 11 Mep Final SolvedDocument64 pages11 Mep Final SolvedAnurag Pandey100% (1)
- ScriptDocument1 pageScriptSiN XNo ratings yet
- Https Onlineservices - Dmw.gov - PH OnlineServices Main PrintResume - AspxDocument1 pageHttps Onlineservices - Dmw.gov - PH OnlineServices Main PrintResume - AspxSiN XNo ratings yet
- Script ZapantaDocument2 pagesScript ZapantaSiN XNo ratings yet
- System Unit Disassembly and AssemblyDocument2 pagesSystem Unit Disassembly and AssemblySiN XNo ratings yet
- Algebra - CDocument64 pagesAlgebra - CSiN XNo ratings yet
- Yo Ma - John'Ro: IncorporatedDocument2 pagesYo Ma - John'Ro: IncorporatedSiN XNo ratings yet
- MD2 Exam PDFDocument319 pagesMD2 Exam PDFSiN XNo ratings yet
- Analytic GeometryDocument111 pagesAnalytic GeometrySiN XNo ratings yet
- MD 01Document100 pagesMD 01SiN XNo ratings yet
- MD 09Document100 pagesMD 09SiN XNo ratings yet
- Effects of TV Commercials in The Lifestyle of A TeenagerDocument1 pageEffects of TV Commercials in The Lifestyle of A TeenagerSiN XNo ratings yet
- Writing A Quantitative Research ThesisDocument14 pagesWriting A Quantitative Research ThesisAldhabby100% (1)
- Cooling Load CapacityDocument77 pagesCooling Load CapacitySiN XNo ratings yet
- Title Proposal Project StudyDocument7 pagesTitle Proposal Project StudySiN XNo ratings yet
- OJT Narrative OutlineDocument5 pagesOJT Narrative OutlineSiN XNo ratings yet
- Thesis in Fluid MachineriesDocument71 pagesThesis in Fluid MachineriesSiN XNo ratings yet
- Citation Mustang HydraulicsDocument6 pagesCitation Mustang HydraulicsDVSNo ratings yet
- Spec Piping Material PDFDocument18 pagesSpec Piping Material PDFMuchamad FaizNo ratings yet
- Preface To The First EditionDocument2 pagesPreface To The First EditionTưMãNo ratings yet
- 2 Cylinder Part No.930764 1 4 Solenoide Valve 5/2part No.938693 1Document3 pages2 Cylinder Part No.930764 1 4 Solenoide Valve 5/2part No.938693 1haleshNo ratings yet
- U2 Exercises AquiferDocument18 pagesU2 Exercises AquifersubxaanalahNo ratings yet
- 2015 0526 DWG Plumbing DDSetDocument24 pages2015 0526 DWG Plumbing DDSetMae AromazNo ratings yet
- Aurum Price List July 2023Document119 pagesAurum Price List July 2023Hem NathNo ratings yet
- 00006.15 M3New - TM - 09 - MaintenanceWork - E - Rev. 0Document5 pages00006.15 M3New - TM - 09 - MaintenanceWork - E - Rev. 0Andreea DanielaNo ratings yet
- RE213144 John Deere Sensor - AVS - PartsDocument9 pagesRE213144 John Deere Sensor - AVS - PartsthaisswiestNo ratings yet
- BÜCHI Pump Unit C-605/C-615 Prelim. SM 96080, Chapter 5 Service ManualDocument36 pagesBÜCHI Pump Unit C-605/C-615 Prelim. SM 96080, Chapter 5 Service ManualSebastián Saldarriaga RingwelskiNo ratings yet
- 300f Overview eDocument3 pages300f Overview eEng-Mohammed SalemNo ratings yet
- 'ROMA' Fig. 160-2 Pressure Relief Valve With CapDocument2 pages'ROMA' Fig. 160-2 Pressure Relief Valve With CapPhilNo ratings yet
- Brochure Full Glenfield Dams Reservoirs and Hydropwer Services Mar 17Document20 pagesBrochure Full Glenfield Dams Reservoirs and Hydropwer Services Mar 17Mai SharafNo ratings yet
- Per KG Rate Rs.-270.00 VAT 13%: 0.00 270.00Document84 pagesPer KG Rate Rs.-270.00 VAT 13%: 0.00 270.00Sunil YadavNo ratings yet
- Wilo Booster Set Helix Pump Manual 16Document1 pageWilo Booster Set Helix Pump Manual 16Luke ClareNo ratings yet
- Shapotools Brief O&M InstructionsDocument2 pagesShapotools Brief O&M InstructionsJay PatelNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Materials and Hardware SDocument216 pagesModule 6 - Materials and Hardware SMustafa KarakayaNo ratings yet
- LT Gate Globe Check Valves Api 602Document12 pagesLT Gate Globe Check Valves Api 602Krunal MahidadiaNo ratings yet
- Master Plumbing Reviewer 2Document24 pagesMaster Plumbing Reviewer 2mcpayodNo ratings yet
- Ductile Iron Fittings, Dismantling Joints and XR Reducers - 0Document30 pagesDuctile Iron Fittings, Dismantling Joints and XR Reducers - 0Mahmoud AwadNo ratings yet
- Ductile Iron Piping Shall Be in Accordance With American Water Works AssociationDocument2 pagesDuctile Iron Piping Shall Be in Accordance With American Water Works AssociationKasuni LiyanageNo ratings yet
- Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageSchematic Diagramamr elzeinyNo ratings yet
- l3070 e 0 0 PDFDocument128 pagesl3070 e 0 0 PDFAdhita MeryantoNo ratings yet
- Sequence TestDocument2 pagesSequence Testmaswil99No ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Leaky Aquifers: Analysis and Evaluation of Pumping Test Data, Revised Second EditionDocument26 pagesChapter 4-Leaky Aquifers: Analysis and Evaluation of Pumping Test Data, Revised Second EditionJerryNo ratings yet
- 2.7 Valve Block Oil: 567802 Ref Part No Description - 08 NotesDocument2 pages2.7 Valve Block Oil: 567802 Ref Part No Description - 08 NotesPrinceSadhotraNo ratings yet