Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Supporting Document of How To Choose Empirical Antibiotics in ICU Video Lecture
Supporting Document of How To Choose Empirical Antibiotics in ICU Video Lecture
Uploaded by
Neha AgrawalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Supporting Document of How To Choose Empirical Antibiotics in ICU Video Lecture
Supporting Document of How To Choose Empirical Antibiotics in ICU Video Lecture
Uploaded by
Neha AgrawalCopyright:
Available Formats
Supporting document of how to choose empirical antibiotics in ICU video lecture
Dr. Ankur Gupta, Intensivist, Video link: https://youtu.be/xoWKR_suFq0
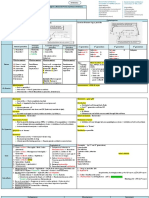
Common antibiotics classification
Cell wall Protein synthesis DNA replication
Beta-lactam antibiotics Rifamycins Sulfa drugs
• Penicillins Aminoglycosides Quinolones
• Cephalosporins Macrolides Metronidazole
• Carbapenems Tetracylines/Glycylcyclines
• Monobactam Chloramphenicol
Glycopeptides Clindamycin
Daptomycin Linezolid
Colistin/Polymyxin-B Nitrofurantoin
Class /mechanism Generic names G+ G- An. At. Remarks
Abx that target cell envelope
Beta lactam abx
Penicillins Atypical bugs not affected as they do not have cell wall.
1. Natural Pencillins Pencillin G Streptococci
Penicllin V ! ! ! 🗴
2. Antistaphlylococcal Nafcillin Bulky side chains prevent
Penicillins Oxacillin binding by beta lacatamases.
Dicloxacillin ! 🗴 🗴 🗴 Used for S. aureus and S.
epidermidies
NOT MRSA And MRSE
3. Amino penicillins Ampicillin Amnio grp in side chain ,
Amoxicillin
! ! ! 🗴 increases hydrophlicity , helps
penetrates through porins Gm-ve
bact.
4. Aminopenicillins / Ampicillin – Very broad spectrum
beta-lactamase sulbactum Except C.difficle
inhibitors Amoxicillin- 🗸 ! 🗸 🗴
combinations clavulanate
5. Extended spectrum
penicillins
Piperacellin
Ticaracillin
! ! ! 🗴 Side chain allows greater
penetration into gram-ve bact.
6. Extended spectrum Piperacellin – 🗸 🗸 🗸 🗴 Very broad spectrum
penicillins / beta- tazobactum Except C.difficle
lactamase inhibitors Ticarcillin-
combinations clavulanate
Cephalosporins Gram –ve activity increases with each generation except 5th gen.
1. First Generation Cefazolin
Cefadroxil
! 🗴 🗴 🗴 Staphyloccoci NOT MRSA And MRSE
and streptococcoi
2. Second Generation Cefotetan*
Cefoxitin*
! ! ! 🗴 More bugs
potent against gram –ve
(*cephamycins) Cephamycins have moderate
Cefuroxime anaerobic activity
3. Third generation Cefotaxime
Ceftazidime
! 🗸 🗴 🗴 Enhanced ve bugs.
activity against gram-
Ceftriaxone Resistance common, should be
Cefoparazone used in combination. (Amp-C
For more info and queries, logon to icu.in/forums
ESBICM – Educational Society of Bedside Intensive Care Medicine
Supporting document of how to choose empirical antibiotics in ICU video lecture
Dr. Ankur Gupta, Intensivist, Video link: https://youtu.be/xoWKR_suFq0
beta-lactamase)
Only ceftazidime active against
P. aeruginosa at the cost of
antisphyloccoal activity.
Ceftriaxone long half-life.
4. Fourth Generation Cefepime
! 🗸 🗴 🗴 Enhanced activity against P.
aeruginosa without
compromising gram+ve cocci
activity.
5. Fifth Generation 🗸 🗸 ! 🗴 Active against MRSA and
MRSE
Carbapenems Quite small and have charge characteristics allows to penetrate gm-ve bugs.
Enterococcus faecium and MRSA intrinsically resistant.
🗸 🗸 🗸 🗴
Imipenem-cilastatin Not active against C.difficle
Highest seizure activity.
Meropenum
Doripenem Least seizure risk
Lower rate of resistance to P.
aeruginosa
Ertapenem Once a day dosing
Less active against P.
aeruginosa
Monobactams Aztreonam 🗴 🗸 🗴 🗴 Not nephrotoxic
Only active against gm-ve
Can be used in patients allergic
to pencillins.
Glycopeptides Very large molecule, active against gm+ bugs only.
Poorly absorbed orally; must be given IV only.
🗸 🗴 ! 🗴
Vancomycin MRSA
Active against C.difficle (orally)
Hearing loss, red man syndrome
, neutropenia
Teicoplanin MRSA
Thrombocytopenia
Lipopeptide Daptomycin 🗸 🗴 ! 🗴 MRSA, VRE, Pencillin resistant
streptococci
Causes reversible myopathy
Poor activity in lungs( should
not be used to treat pneumonia)
Polymyxin grp. Colistin 🗴 🗸 🗴 🗴 Positively charged, causes cell
lysis.
Nephrotoxic
Polymyxin-B 🗴 🗸 🗴 🗴 Active drug and relatively renal
safe.
Abx that that block protein
production
Rifamycins Potent inducers of cytochrome-P-450 system
! 🗴 🗴 🗴
Rifampin Used is TB.
For more info and queries, logon to icu.in/forums
ESBICM – Educational Society of Bedside Intensive Care Medicine
Supporting document of how to choose empirical antibiotics in ICU video lecture
Dr. Ankur Gupta, Intensivist, Video link: https://youtu.be/xoWKR_suFq0
Most potent inducer of
cytochrome-P-450 system
Orange discolouration of tears,
urine and other body fluids.
Rifabutin Less potent inducer of
cytochrome-P-450 system
Can be used as an alternative to
rifampin in HIV patients .
Rifapentine Long half life , once a week
dose in TB.
Rifaximin Treatment of travellers’
diarrhoea.
Aminoglycosides Positively charged , quite large (but smaller than glycopeptides). Easily penetrate
gm-ve bugs. Works poorly in anaerobic conditions and acidic environment (like
abcesses). Resistance is not always class-wise. Can be used in low doses with
beta-lactams for synergistic doses. Nephrotoxic and ototoxic.
! 🗸 🗴 🗴
Streptomycin TB
Gentamicin Both gm+ve and gm-ve
Tobramycin Lacks activity against
enterococci.
Amikacin Can be used if resistant against
gentamicin and tobramycin.
Lacks activity against
enterococci
Macrolides Resistance to one macrolide grp usually implies to resistance to all members.
Thrombophlebitis and QT prolongation. Inhibitor of cytochrome-P-450 system.
Blurred vision.
! ! 🗴 !
Erythromycin Less useful for respiratory
infections as lacks activity
against H.influenzae
Clarithromycin
Azithromycin Taken up in tissues and released
over subsequent days.
Tetracyclilnes and Not to be given to children and pregnant women. Phototoxicity.
Glycylcyclines
🗴 ! ! 🗸
Tetracycline
Doxycycline Long half life
Minocycline MRSA
Blue black hyper-pigmentaion
of skin and mucus membranes.
Tigecycline 🗸 🗸 🗸 🗸 Very broad spectrum, MRSA,
VRE, Acinetobactor spp.
Anaerobic activity less than
carbapenems and pipercillins.
Not active against P.aeruginosa
and Proteus spp.
Chloramphenicol ! ! 🗸 🗸 Bone marrow suppression
For more info and queries, logon to icu.in/forums
ESBICM – Educational Society of Bedside Intensive Care Medicine
Supporting document of how to choose empirical antibiotics in ICU video lecture
Dr. Ankur Gupta, Intensivist, Video link: https://youtu.be/xoWKR_suFq0
Clindamycin
! 🗴 ! 🗴 Causes Clostridium difficile
colitis.
Active against community
acquired MRSA
Linezolid 🗸 🗴 🗴 🗴 Gram-ve bugs intrinsically
resistant.
Completely synthetic drug.
Should not be used with MAO
inhibitors (causes serotonin
syndrome). Pancytopenia.
Metabolic acidosis.
Nitrofurantoin ! ! 🗴 🗴 Only for cystitis
Accumulates in urine.
Abx that target DNA
replication.
Sulpha drugs ! ! 🗴 🗴
Trimethoprim- Steven Johnson syndrome
Sulfamethoxazole
Dapsone For leprosy
Quniolones Causes cartilage abnormalities, Achilles tendon rupture. QT prolongation.
! 🗸 ! 🗸
Ciprofloxacin Most potent of quinolones
against gram –ve organisms
including Psuedomonas
aeruginosa.
Weak against gram+ve ones.
Levofloxacin Active against grm+ve and –ve
ones. But less against
Psuedomonas aeruginosa.
Ofloxacin Less potent than levofloxacin.
Moxifloxacin More active against S.
Gemifloxacin pneuomanie (including pencillin
resistant strains).
Some activity against anaerobes.
Metronidazole 🗴 🗴 🗸 🗴 Very small molecule and diffuse
very fast. Disulfiram like
reaction.
For more info and queries, logon to icu.in/forums
ESBICM – Educational Society of Bedside Intensive Care Medicine
Supporting document of how to choose empirical antibiotics in ICU video lecture
Dr. Ankur Gupta, Intensivist, Video link: https://youtu.be/xoWKR_suFq0
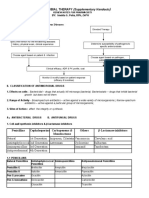
Gram +ve bacteria Gram –ve bacteria Atypical bacteria
Staphylococci1 Enterobacteriaceae2 Legionella
Pneumococci Pseudomonas Chlamydia
Other Streptococci Neisseria Mycoplasma
Enterococci H. Influenzae Brucella
Listeria monocytogenes Campylobacter jejuni3 Rickettsia
B. anthracis Helicobactor pylori3
Acinetobactor
Anaerobic bacteria Spirochetes Mycobacteria
Clostridia4 Treponema pallidum M. tuberculosis
Bacteroides Borrelia burgdorferi M. avium complex
Leptospira interrogans M. leprae
1. S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. viridians
2. E.coli, Klebsiella, Proteus spp., Salmonella enterica, Shigella spp.,
3. V. cholera
4. C. perfringens, C. botulinum, C. tetani , C. difficlie
Summary of common bacteria
Bacteria Remarks
Gram positive
Staphylococcus Resistant to heat and drying. Persist on fomites for longer time.
aureus Skin and soft tissue infections, TSS, pneumonia, endocarditis,
osteomyelitis, bacteraemia . Produces lots of toxins.
Staphylococcus Infections involving foreign objects (catheters, valves, joints).
epidermedies
Pneumococci Boldly and forcefully attack the human body. Human are carriers.
CAP, sinusitis , meningitis, otitis media.
S. pyogenes Pharyngitis, skin and soft tissue infections, TSS.
S. agalactiae Colonolize female genital tract . sepsis and meningitis in neonates.
S. viridans Colonise the human GI and urogenital tract. Infective endocarditis and
abscesses.
Enterococci Fickle residents of human GI tract. Intraabodominal infections, uti,
For more info and queries, logon to icu.in/forums
ESBICM – Educational Society of Bedside Intensive Care Medicine
Supporting document of how to choose empirical antibiotics in ICU video lecture
Dr. Ankur Gupta, Intensivist, Video link: https://youtu.be/xoWKR_suFq0
wound infections,endocarditis , bacteremia,
Highly resistant to drugs (bacterocidil drugs are bacteriostatic against
it) . E. faecium more resistant than E. faecalis.
Listeria (bacillus) Widespread in soil and fecal flora of many animals. gasteroenteritis in
healthy subjects and meningitis in immunocompromised people.
Bacillus anthracis Spore forming bacillus. Inhalational, cutaneous, GI anthrax. (central
black eschar. ) hemorraghic mediastinal adenopathy, bloody pleural
effusions, bacteraemia)
Gram negative
Enterobacteriaceae Most of inhabiting the human GI tract. Opportunistic pathogens.
(bacilli) Nosocomial infections .
E.coli Gasteroenteritis , meningitis (neonates)
Klebsiella CAP. HCA infections , UTI, HAP, bacterimia, wound infections, intra-
abdominal infections.
Proteus spp.
Pseudomonas Opportunistic pathogens. Normal inhabitant soil, water, plant, animals.
(bacilli) HAP, wound infections, uti. Very fast develops resistance.
Always should use 2 abx from 2 different groups .
Nessiria (diplococci)
N. meningitis
N. gonorrhoeae Genitourinary tract and skin and soft tissue infections.
Campylobacter Gasteroenteritis (colonoise wild and domestic animals ) . infection
through contaminated food and water.
H. plyori Peptic ulcer disease
H. influenza Cap, meningitis, sinusitis , otitis media, conjcuctivitis, septic arthritis.
(pleomorphic) Droplet infection
Acinetobacter (rod Wound infections, pneumonia , bacteremia
shaped and coco- Soil organaisms (trauma patient)
bacilli)
Anaerobic
Clostridia (positive)
C. tetani
C. botulinum
C. perfringens
C. difficle
Bacteroides Oral cavity, gi tract, vagina.
PID, pulmonary infections, periodontal, intra-abdominal abscesses.
Atypical bacteria
Chlamydia Obligate intracellular bug,
CAP , eye infections. STD
Mycoplamsa Smallest living organism , pneumonia .
Legionella Inhabit natural and man made water.
Pneumonia with altered sensorium and hyponatremia . also liver and
renal involvement.
Brucella (cocco- Transmitted through animals. Milk and milk products (cheese).
bacilli) Prolonged fever.
Rickettsia gram Obligate intracellular organism.
negative Arthropod borne infections, rash and eschar.
Spirochetes
Treponema pallidum STD
Borrelia burgodoferi Lymes disease (cardiac disease, meningitis, arthritis, rash)
Leptospira Urine of domestic and wild animals . hepatitis, renal disease,
For more info and queries, logon to icu.in/forums
ESBICM – Educational Society of Bedside Intensive Care Medicine
Supporting document of how to choose empirical antibiotics in ICU video lecture
Dr. Ankur Gupta, Intensivist, Video link: https://youtu.be/xoWKR_suFq0
meningitis. Febrile illness.
Mycobacteria
M. tuberculosis
M. avium complex
M. leprae
For more info and queries, logon to icu.in/forums
ESBICM – Educational Society of Bedside Intensive Care Medicine
You might also like
- Adult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookFrom EverandAdult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Antibacterial Drugs SummaryDocument13 pagesAntibacterial Drugs SummaryNeo Ramagaga100% (1)
- AntibioticsDocument8 pagesAntibioticsmohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial SDocument37 pagesAntibacterial Ssanish tiwariNo ratings yet
- Cell Wall Synthesis InhibitorsDocument57 pagesCell Wall Synthesis InhibitorsNica MendozaNo ratings yet
- 1 Generation: Cefalexin Cefradin Cefadroxil Cefachlor Yes Yes Yes Yes YesDocument67 pages1 Generation: Cefalexin Cefradin Cefadroxil Cefachlor Yes Yes Yes Yes YesadystiNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument4 pagesAntibioticsTan Geok Eng100% (1)
- Group I: Penicillin G (Benzylpenicillin), Penicillin V (Phenoxymethylpenicillin)Document16 pagesGroup I: Penicillin G (Benzylpenicillin), Penicillin V (Phenoxymethylpenicillin)jhk451No ratings yet
- Classification of Antibiotics For PrintingDocument4 pagesClassification of Antibiotics For PrintingMuthu Kumar100% (2)
- Antibiotic Classification Mechanism - Sheet1Document2 pagesAntibiotic Classification Mechanism - Sheet1api-329501044No ratings yet
- Session 2 - Antibiotic GeneralDocument14 pagesSession 2 - Antibiotic GeneralrekabmariamNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial: Topics: 1. Cell Wall Synthesis InhibitorDocument26 pagesAntibacterial: Topics: 1. Cell Wall Synthesis InhibitorMusfira YaseenNo ratings yet
- Iii. Antibacterial DrugsDocument6 pagesIii. Antibacterial DrugskhaileenafaeNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic 1-Terminology: 1. Inhibition of Cell Wall SynthesisDocument12 pagesAntibiotic 1-Terminology: 1. Inhibition of Cell Wall SynthesismidoNo ratings yet
- CASE 37 Otitis Media 010320103456Document10 pagesCASE 37 Otitis Media 010320103456Alemuddin AbdulezizNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial AgentsDocument44 pagesAntibacterial Agentsbelindasithole965No ratings yet
- Cephalosporins Quick ReviewDocument19 pagesCephalosporins Quick ReviewErinson Custodio PlasenciaNo ratings yet
- FINALS - Module 6Document29 pagesFINALS - Module 6Thereza CahigNo ratings yet
- Cell Wall Inhibitors (2t)Document3 pagesCell Wall Inhibitors (2t)Vivian VillaNo ratings yet
- Description of AntibacterialDocument102 pagesDescription of AntibacterialChristopher SongoroNo ratings yet
- Katzung Pharmacology Semester 5 TablesDocument29 pagesKatzung Pharmacology Semester 5 TablesfatimaNo ratings yet
- Drugs / Antibiotik: AntimicrobialDocument23 pagesDrugs / Antibiotik: AntimicrobialSania NadianisaNo ratings yet
- Cell Wall Inhibitors - Cephalosporins Others 2Document32 pagesCell Wall Inhibitors - Cephalosporins Others 2Yosra AkashNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics ListDocument14 pagesAntibiotics ListBrenda LiawNo ratings yet
- PharmacyDocument16 pagesPharmacyJow RamosNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action of Penicillin & CephalosporinDocument7 pagesMechanism of Action of Penicillin & CephalosporinshahabahmadNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Drugs Lec 3 Cephalosporins Learning ObjectivesDocument2 pagesAntimicrobial Drugs Lec 3 Cephalosporins Learning ObjectivesNashat SaadiNo ratings yet
- Common GI PathogensDocument12 pagesCommon GI Pathogenshokifoh169No ratings yet
- Notebook PDFDocument4 pagesNotebook PDFCJMALNo ratings yet
- Beta-Lactam Antibiotics & Other Cell Wall Synthesis InhibitorsDocument29 pagesBeta-Lactam Antibiotics & Other Cell Wall Synthesis InhibitorsRen PastelNo ratings yet
- Beta Lactam AntibioticsDocument28 pagesBeta Lactam AntibioticsHassan.shehri100% (11)
- 2.inhibitors of Cell Wall SynthesisDocument20 pages2.inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesisalihyderabro166No ratings yet
- Cephalosporins GenerationDocument7 pagesCephalosporins GenerationSam SmileyNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: Penicillium-Terrestrial Mold Cephalosporium - Marine Mold Bacillus - Bacteria Streptomyces - BacteriaDocument9 pagesAntibiotics: Penicillium-Terrestrial Mold Cephalosporium - Marine Mold Bacillus - Bacteria Streptomyces - BacteriavexicaNo ratings yet
- Daftar Antibiotik Dan Kerjanya YudistraDocument13 pagesDaftar Antibiotik Dan Kerjanya YudistraYudistra R ShafarlyNo ratings yet
- 4 IGP Basics of Antimicrobial TherapyDocument11 pages4 IGP Basics of Antimicrobial TherapyTin NatividadNo ratings yet
- First Aid PharmDocument52 pagesFirst Aid PharmJason ClemonsNo ratings yet
- First Aid Pharm PDFDocument52 pagesFirst Aid Pharm PDFRayan OlivaNo ratings yet
- CephalosporinDocument34 pagesCephalosporinliamhenry9449No ratings yet
- 2.2.4 - Cell Wall Inhibitors - Cephalosporines 2010-Oct 2014Document25 pages2.2.4 - Cell Wall Inhibitors - Cephalosporines 2010-Oct 2014tresorstephane669No ratings yet
- Ncm106pharma EndtermDocument17 pagesNcm106pharma EndtermKM PanganibanNo ratings yet
- 1a Antiinfective DrugsDocument4 pages1a Antiinfective DrugsMaria Donabella OngueNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Classification and MechanismsDocument43 pagesAntibiotic Classification and Mechanismsyoza_kidNo ratings yet
- Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors: Dr. Mohammed Al-KhawlaniDocument16 pagesCell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors: Dr. Mohammed Al-Khawlaniخالد الشرعبيNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics of ChoiceDocument6 pagesAntibiotics of ChoiceTunas AndriantoNo ratings yet
- CephalosporinsDocument21 pagesCephalosporinsMoha Bin Ladiif75% (4)
- L16 ANTIBIOTICS - IN - ORAL - MAXILLOFACIAL - SURGERY Copy 2Document19 pagesL16 ANTIBIOTICS - IN - ORAL - MAXILLOFACIAL - SURGERY Copy 2Ju JuNo ratings yet
- 6 - Antibacterial-Cell Wall Synthesis InhibitorsDocument29 pages6 - Antibacterial-Cell Wall Synthesis InhibitorsDr. SaniaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - pphm203 Unit 2Document113 pagesPharmacology - pphm203 Unit 2Ãqûã FîggâNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy NotesDocument9 pagesChemotherapy Notesnileshkumarhjoshi942No ratings yet
- Antibacterials For Respiratory Tract Infections: Cecilia C. Maramba-Lazarte, MD, MscidDocument29 pagesAntibacterials For Respiratory Tract Infections: Cecilia C. Maramba-Lazarte, MD, MscidCecile Maramba-LazarteNo ratings yet
- CefalosporinasDocument12 pagesCefalosporinasVALENTINA ZAMBRANO ROMERONo ratings yet
- Antibiotics in EndodonticsDocument74 pagesAntibiotics in EndodonticsdrishyaNo ratings yet
- Beta Lactam AntibioticsDocument15 pagesBeta Lactam AntibioticsNiharika ModiNo ratings yet
- Penicillins 1Document30 pagesPenicillins 1John PaulNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial DR Mostafa Alfishawy AntibioticDocument64 pagesAntibacterial DR Mostafa Alfishawy Antibioticramzi MohamedNo ratings yet
- Antibiotik Beta Laktam: Apt. Ika Mustikaningtias, M.SCDocument26 pagesAntibiotik Beta Laktam: Apt. Ika Mustikaningtias, M.SCdita novia maharaniNo ratings yet
- 11 CephalosporinsDocument74 pages11 Cephalosporinsblue sapphireNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic SummaryDocument4 pagesAntibiotic Summaryshazia100% (1)
- Small Molecular Immunomodifiers of Microbial Origin: Fundamental and Clinical Studies of BestatinFrom EverandSmall Molecular Immunomodifiers of Microbial Origin: Fundamental and Clinical Studies of BestatinHamao UmezawaNo ratings yet
- Reuma EnglezaDocument137 pagesReuma EnglezaAd AdrianaNo ratings yet
- Adcon Group 14Document34 pagesAdcon Group 14TMC PGI GENER MICKONo ratings yet
- 1-Gastroenteritis and DehydrationDocument29 pages1-Gastroenteritis and Dehydrationabdalmajeed alshammaryNo ratings yet
- Dorval 2009Document9 pagesDorval 2009frcubidesNo ratings yet
- Henoch - Schonlein Purpura (HSP) : - It Is The Most Common Cause of Non-Thrombocytopenic Purpura in ChildrenDocument23 pagesHenoch - Schonlein Purpura (HSP) : - It Is The Most Common Cause of Non-Thrombocytopenic Purpura in ChildrenLaith DmourNo ratings yet
- Haemotology Notes Haemotology Notes: Medicine (University of Glasgow) Medicine (University of Glasgow)Document20 pagesHaemotology Notes Haemotology Notes: Medicine (University of Glasgow) Medicine (University of Glasgow)shravaniNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer Clinical DiagnosisDocument13 pagesAlzheimer Clinical DiagnosisClarissa Castro RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation On Head InjuryDocument28 pagesCase Presentation On Head Injuryarchana verma86% (7)
- Surgery 5 - Questions v1Document50 pagesSurgery 5 - Questions v1Humzala BashamNo ratings yet
- 2022 - Efficacy and Safety of Intramuscular Administration of Tixagevimab-Cilgavimab For Early Outpatient Treatment of COVID-19 (TACKLE)Document12 pages2022 - Efficacy and Safety of Intramuscular Administration of Tixagevimab-Cilgavimab For Early Outpatient Treatment of COVID-19 (TACKLE)rodrigo sacchiNo ratings yet
- FA MEDICINUS 35 (2) - Agustus 2022 - Ejournal - 220831 - 164113Document85 pagesFA MEDICINUS 35 (2) - Agustus 2022 - Ejournal - 220831 - 164113Tulus Java Rimbunan S.No ratings yet
- Shared Psychotic Disorder A Case Study Submitted byDocument27 pagesShared Psychotic Disorder A Case Study Submitted byChin Lee100% (1)
- Warning Signs by James For English For Health I by JamesDocument43 pagesWarning Signs by James For English For Health I by JamesDami OrtizNo ratings yet
- нструкция импловит.enDocument28 pagesнструкция импловит.enFrère HorNo ratings yet
- Global Health Estimates 2019 Summary Tables: Deaths by Cause, Age and Sex, by World Bank Income Group, 2000-2019Document42 pagesGlobal Health Estimates 2019 Summary Tables: Deaths by Cause, Age and Sex, by World Bank Income Group, 2000-2019DanielaNo ratings yet
- Nejmcpc 1208152Document10 pagesNejmcpc 1208152FrinkooFrinkoBNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic Pulmonary EdemaDocument30 pagesCardiogenic Pulmonary EdemaVale BravoNo ratings yet
- Heart RhythmDocument68 pagesHeart RhythmMwanja MosesNo ratings yet
- The Role of The Qi Mechanism in The Treatment of Knotty DiseasesDocument6 pagesThe Role of The Qi Mechanism in The Treatment of Knotty DiseasesInfohogg100% (2)
- Pmlsp1 - Routine Lab TestsDocument3 pagesPmlsp1 - Routine Lab TestsJm AshiiNo ratings yet
- CM UVC Certificate BacteriaDocument23 pagesCM UVC Certificate BacteriaFateh SinghNo ratings yet
- Patient Education Sheet: GI TipsDocument1 pagePatient Education Sheet: GI Tipsvasarhely imolaNo ratings yet
- Tuesdays With Morrie. (Reaction Paper)Document3 pagesTuesdays With Morrie. (Reaction Paper)Nyaaaw100% (1)
- Module 3 - Gen Bio 1 - MidtermDocument7 pagesModule 3 - Gen Bio 1 - MidtermAngel Cuacko GacmatanNo ratings yet
- UrolithiasisDocument4 pagesUrolithiasisمصطفى سهيلNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacology of Antibiotics - PMCDocument19 pagesClinical Pharmacology of Antibiotics - PMCJosette LeyvaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology For Oral RecitDocument16 pagesPharmacology For Oral RecitAngel DiangNo ratings yet
- Data Pasien Konsulan NeuroDocument1 pageData Pasien Konsulan NeuroDewi backup IslamiNo ratings yet
- Surgery Question From AbeideDocument44 pagesSurgery Question From Abeide69xXALModr3EMXx69 McAnusNo ratings yet
- The Brain Regeneration GuideDocument43 pagesThe Brain Regeneration GuideCara CulerNo ratings yet