Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cefuroxime
Cefuroxime
Uploaded by
Marjorie Erag0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageThis document summarizes information about the drug cefuroxime, including its classification as a second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic used to treat various bacterial infections. It lists the drug's indications, contraindications, mechanisms of action, potential adverse reactions and side effects, dosage and administration routes, and important nursing considerations when using this drug.
Original Description:
Drug study
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes information about the drug cefuroxime, including its classification as a second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic used to treat various bacterial infections. It lists the drug's indications, contraindications, mechanisms of action, potential adverse reactions and side effects, dosage and administration routes, and important nursing considerations when using this drug.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageCefuroxime
Cefuroxime
Uploaded by
Marjorie EragThis document summarizes information about the drug cefuroxime, including its classification as a second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic used to treat various bacterial infections. It lists the drug's indications, contraindications, mechanisms of action, potential adverse reactions and side effects, dosage and administration routes, and important nursing considerations when using this drug.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
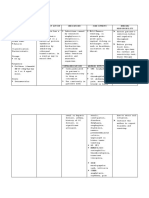
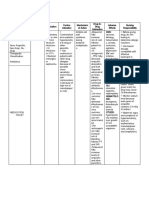
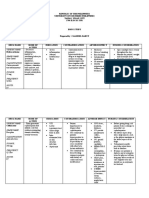
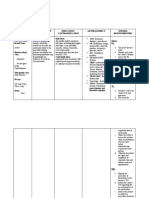
DRUG STUDY
cefuroxime
Name of Drug
CLASSIFICATION INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION MECHANISM OF ADVERSE REACTION ROUTE/DOSAGE NURSING
ACTION & SIDE EFFECT INTERVENTION
Therapeutic: ➢ Serious lower ➢ Contraindicated in patients ➢ Inhibits cell-wall CV: phlebitis, ➢ Infusion: 750-mg, ➢ Tell patient to take
Antibiotics respiratory tract hypersensitive to drug or other synthesis, thrombophlebitis. GI: 1.5-g vials, infusion drug as prescribed,
infection, UTI, skin or cephalosporins. even if feeling better.
skin-structure ➢ Use cautiously in patients promoting osmotic diarrhea, pseudomembranous packs, and ADD- ➢ Advise patient who
Pharmacologic: infections, bone or joint hypersensitive to penicillin instability; usually colitis, nausea, anorexia, Vantage vials has difficulty
Second-generation infection, septicemia, because of possibility of cross- bactericidal. vomiting. Hematologic: ➢ Injection: 750 mg, swallowing tablets to
cephalosporins meningitis, and sensitivity with other beta-lactam hemolytic anemia, 1.5 g ask prescriber for the
gonorrhea antibiotics. suspension.
➢ Perioperative ➢ According to the CDC, oral
thrombocytopenia, transient ➢ PO: 125 mg, 250 ➢ Tell parent to shake
Brand name: prophylaxis cephalosporins aren't neutropenia, eosinophilia. mg,u 500 mg suspension well
Zinacef ➢ Mild to moderate acute recommended to treat gonococcal Skin: maculopapular and before measuring
bacterial exacerbations infections. erythematous rashes, dose. Suspension
References: of chronic bronchitis ➢ According to clinical practice urticaria, pain, induration, may be stored at
➢ Acute bacterial guidelines, cefotaxime or room temperature or
maxillary sinusitis ceftriaxone should be used to treat sterile abscesses, temperature refrigerated, but must
➢ Pharyngitis and childhood bacterial meningitis elevation, tissue sloughing at be discarded after 10
tonsillitis and pneumococcal and IM injection site. Other: days.
➢ Otitis media meningococcal meningitis caused anaphylaxis, hypersensitivity ➢ Instruct caregiver to
➢ Uncomplicated skin and by penicillin-resistant strains and give oral suspension
skin-structure infection Haemophilus influenzae type b
reactions, serum sickness. with food.
➢ Uncomplicated UTI meningitis. ➢ Instruct patient to
➢ Uncomplicated ➢ Use cautiously in patients with notify prescriber
gonorrhea history of colitis and in those with about rash, loose
➢ Early Lyme disease renal insufficiency. stools, diarrhea, or
➢ Impe tigo evidence of
superinfection.
➢ Advise patient
receiving drug IV to
report discomfort at
IV insertion site.
You might also like
- NFDN 2008 Self Assessment Assignment 2Document10 pagesNFDN 2008 Self Assessment Assignment 2api-276773856No ratings yet
- Pharmacology Case Study2.11.14Document3 pagesPharmacology Case Study2.11.14NickCiardielloNo ratings yet
- Clinical ReflectionDocument3 pagesClinical ReflectionNaomi MasudaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Essentials of Pharmacology For Health Professions 7th Edition by WoodrowDocument9 pagesTest Bank For Essentials of Pharmacology For Health Professions 7th Edition by WoodrowcandyblueNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Nursing DepartmentDocument1 pageDrug Study: Nursing Departmentgiselle chloeNo ratings yet
- CEFUROXIMEDocument2 pagesCEFUROXIMEMelvz BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyPau-pau BasiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudySwag MasterNo ratings yet
- Gabato - Drug Study 1-3Document6 pagesGabato - Drug Study 1-3Denise GabatoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Clindamycin)Document1 pageDrug Study (Clindamycin)roseonabreeze100% (7)
- Drug Study of Generation Antibiotics Mohamedzein, Nura Mohamedzein, SalwaDocument8 pagesDrug Study of Generation Antibiotics Mohamedzein, Nura Mohamedzein, SalwaNone BbNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Axetil (IV)Document2 pagesCefuroxime Axetil (IV)STORAGE FILENo ratings yet
- Name Mode of Action Indications Contraindications Adverse Effects Health Teaching Generic Name: Classifications: CNS: Chills, FatigueDocument2 pagesName Mode of Action Indications Contraindications Adverse Effects Health Teaching Generic Name: Classifications: CNS: Chills, FatigueAngelica OlivarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of CiprofloxacinDocument3 pagesDrug Study of CiprofloxacinZyra MendozaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AmpicillinDocument6 pagesDrug Study AmpicillinDgjj Compuiter100% (1)
- Drug Study - AmoxicillinDocument2 pagesDrug Study - AmoxicillinVANESSA PAULA ALGADORNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug AlgeDocument1 pageName of Drug Algealgerich_delacuestaNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Axetil (Oral)Document2 pagesCefuroxime Axetil (Oral)STORAGE FILENo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument1 pageCefuroximehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesRae DaWn VaLesNo ratings yet
- Cefoxitin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesCefoxitin Drug StudyBea Dela Cena100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyRoland YusteNo ratings yet
- 3) Pharmacologic Management: Sound AlikeDocument7 pages3) Pharmacologic Management: Sound AlikeValerie LeddaNo ratings yet
- Cefixime: Suprax Class and CategoryDocument3 pagesCefixime: Suprax Class and CategoryArianne Joy SalvadorNo ratings yet
- CeferoximeDocument1 pageCeferoximeGwen Stefanie Lagrimas ValloyasNo ratings yet
- MC - Drug Study Dela Rosa, Angeline FDocument7 pagesMC - Drug Study Dela Rosa, Angeline FventimiglionNo ratings yet
- Sample Drug Study CefuroximeDocument1 pageSample Drug Study CefuroximeHoorise NShineNo ratings yet
- Medication Management in OBDocument5 pagesMedication Management in OBLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Azithromycin, Ceftriaxone, MetropololDocument7 pagesAzithromycin, Ceftriaxone, Metropolollei_odanNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion Case PresentationDocument16 pagesPleural Effusion Case PresentationDhindee OmahoyNo ratings yet
- Case Pres Drug StudyDocument3 pagesCase Pres Drug StudyMark Teofilo Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mode of Action Indication Contraindication Drug Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mode of Action Indication Contraindication Drug Effects Nursing ConsiderationsRoxanne Memeg MartinNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument14 pagesDischarge PlanAsniah Hadjiadatu AbdullahNo ratings yet
- (Duty MDH (Ward) Drug StudyDocument7 pages(Duty MDH (Ward) Drug StudyMikaella R. AcenaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FormDocument2 pagesDrug Study FormJessa Mae PagoboNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyJessica Pacris MaramagNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CEFAZOLINDocument6 pagesDrug Study CEFAZOLINAicelle Love Sampat LapenaNo ratings yet
- I. Drug Study: AllopurinolDocument1 pageI. Drug Study: Allopurinolkimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-ClindamycinDocument3 pagesDrug Study-ClindamycinDUMANGENG ELLAINE D.100% (1)
- Drug Study NicoleDocument6 pagesDrug Study NicoleFrancheska Nicole Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Dosage/ Frequency /route Mechanism of Action Indication Contra-Indication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesDrug Classification Dosage/ Frequency /route Mechanism of Action Indication Contra-Indication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesLouisse Angeli AbucejoNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument2 pagesCefuroximeAnreezahy GnoihcNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CefuroximeDocument1 pageDrug Study CefuroximeDUMANGENG ELLAINE D.No ratings yet
- Drug Study Cefuroxime CelecoxibDocument3 pagesDrug Study Cefuroxime CelecoxibRem remNo ratings yet
- Cefu, Metro, KetoDocument4 pagesCefu, Metro, KetoSethlyn_Gomez_5337No ratings yet
- 5.2.2 Drug Therapeutic RecordDocument2 pages5.2.2 Drug Therapeutic Recordjoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PediaDocument3 pagesDrug Study PediaDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines University of Northern Philippines Tamag, Vigan City 2700 Ilocos SurDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines University of Northern Philippines Tamag, Vigan City 2700 Ilocos SurMariam Yiani Aspiras RacelesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ICUDocument3 pagesDrug Study ICURolina ParagasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: AmoxicillinDocument3 pagesDrug Study: AmoxicillinKrzia TehNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Therapeutic Actions Indications Adverse Effect Indication Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesDrug Name Therapeutic Actions Indications Adverse Effect Indication Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesJoshua Davantes100% (1)
- JM Drug Study CaseDocument4 pagesJM Drug Study CaseMilky Lescano LargozaNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy - Delivery RoomDocument12 pagesDrugstudy - Delivery RoomAUBREY MARIE . GUERRERONo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ko BFF Pa-Print Pls Thanks Much Mwa!Document3 pagesDrug Study Ko BFF Pa-Print Pls Thanks Much Mwa!shasheeeeyNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument2 pagesCefuroximeJon Corpuz AggasidNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RLEDocument5 pagesDrug Study RLEGenierose YantoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RLEDocument8 pagesDrug Study RLEGenierose YantoNo ratings yet
- GentamicinDocument1 pageGentamicinreinaNo ratings yet
- ... Drug Study...Document2 pages... Drug Study...Chona FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Nursing DepartmentDocument1 pageDrug Study: Nursing Departmentgiselle chloeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyBea Marie A. ValdezNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone SodiumDocument2 pagesCeftriaxone SodiumSTORAGE FILENo ratings yet
- The Perfect Neutropenic Diet Cookbook; The Complete Nutrition Guide To Reinstating Overall Health For General Wellness With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesFrom EverandThe Perfect Neutropenic Diet Cookbook; The Complete Nutrition Guide To Reinstating Overall Health For General Wellness With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesNo ratings yet
- HbA1c Lab Leaflet 0509Document2 pagesHbA1c Lab Leaflet 0509ppeterarmstrongNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0213911121001989 MainDocument3 pages1 s2.0 S0213911121001989 MainVinna LestaryNo ratings yet
- Nur330-Virtual Practicum Covid-19 in SchoolsDocument21 pagesNur330-Virtual Practicum Covid-19 in Schoolsapi-559074394No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Claytons Basic Pharmacology For Nurses 18th Edition by WillihnganzDocument4 pagesTest Bank For Claytons Basic Pharmacology For Nurses 18th Edition by WillihnganzJohn Molon100% (37)
- Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis GuidelinesDocument4 pagesStress Ulcer Prophylaxis GuidelinesAzi Rifki NasutionNo ratings yet
- Insurance PlansDocument2 pagesInsurance PlansDeeksha AgrawalNo ratings yet
- T SoliumDocument17 pagesT SoliumKanchan LalwaniNo ratings yet
- Contact Tracers:: Roles and Referrals at The Barangay LevelDocument10 pagesContact Tracers:: Roles and Referrals at The Barangay LevelMae Rabadon BermudezNo ratings yet
- Antara Provider LeafletDocument2 pagesAntara Provider Leafletganapa247No ratings yet
- The Monoplane Occlusion For Complete Dentures: T H e SP Herical TheoryDocument7 pagesThe Monoplane Occlusion For Complete Dentures: T H e SP Herical TheorySahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Peer Assessment Rating (Par) Index: ReliabilityDocument5 pagesPeer Assessment Rating (Par) Index: ReliabilityLaween AbdulkhaliqNo ratings yet
- Prophylactic Cervical Cerclage (Modified Shirodkar Operation) For Twin and Triplet Pregnancies After Fertility TreatmentDocument8 pagesProphylactic Cervical Cerclage (Modified Shirodkar Operation) For Twin and Triplet Pregnancies After Fertility TreatmentAiraNo ratings yet
- Breast and Nipple ConditionsDocument23 pagesBreast and Nipple ConditionsdaveNo ratings yet
- Canada Resume FormatDocument1 pageCanada Resume FormatPatrick Andrew PanizalesNo ratings yet
- Maternal & Child Health Nursing - Care of The Childbearing & Childrearing FamilyDocument292 pagesMaternal & Child Health Nursing - Care of The Childbearing & Childrearing FamilyFlorence GuerraNo ratings yet
- Hazard Report Form-Checklist 4 - Covid-19 - 16252 - Rebeca RaducuDocument3 pagesHazard Report Form-Checklist 4 - Covid-19 - 16252 - Rebeca RaducuRebeca RaducuNo ratings yet
- VAERS Summary 09242021Document12 pagesVAERS Summary 09242021rehankedhenNo ratings yet
- Problem Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Plan Intervention Evaluation Subjective Short Term IndependentDocument1 pageProblem Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Plan Intervention Evaluation Subjective Short Term IndependentkyawNo ratings yet
- Patient Information Leaflet Management of Cancer PainDocument2 pagesPatient Information Leaflet Management of Cancer PainNana Nurliana NoorNo ratings yet
- Hospital Diagnostic Center Management SystemDocument23 pagesHospital Diagnostic Center Management SystemBani Amel RanaNo ratings yet
- PerkeniDocument2 pagesPerkeniDwi Edhityasrini PNo ratings yet
- Awareness Towards Heart DiseaseDocument7 pagesAwareness Towards Heart DiseaseAlok MishraNo ratings yet
- Breastcrawl PDFDocument41 pagesBreastcrawl PDFRyan AndarestaNo ratings yet
- HIRA For Patient Safety Check Risk - FinalDocument10 pagesHIRA For Patient Safety Check Risk - FinalMelvin DsouzaNo ratings yet
- FCP Network ListDocument150 pagesFCP Network Listoscpramod2695No ratings yet
- Glycemic Targets: American Diabetes AssociationDocument8 pagesGlycemic Targets: American Diabetes AssociationHelenaNo ratings yet