Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Per Dev Reviewer
Per Dev Reviewer
Uploaded by
Ishie De Guzman0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views5 pagesThis document provides an overview of adolescent development from physical, cognitive, social, and emotional perspectives. It discusses the following key points:
1. Physical changes occur rapidly during adolescence as youth mature into adulthood. This includes growth spurts and sexual maturation.
2. Cognitive development involves enhanced critical thinking skills and abstract reasoning abilities. Adolescents work to develop their identity and independence.
3. Social and emotional development intertwine as adolescents establish relationships with peers and manage more mature emotions. They face challenges adjusting to new social dynamics and responsibilities.
4. Mental health during this period requires awareness of potential warning signs for disorders like changes in mood, eating/sleeping problems, or withdrawal from
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of adolescent development from physical, cognitive, social, and emotional perspectives. It discusses the following key points:
1. Physical changes occur rapidly during adolescence as youth mature into adulthood. This includes growth spurts and sexual maturation.
2. Cognitive development involves enhanced critical thinking skills and abstract reasoning abilities. Adolescents work to develop their identity and independence.
3. Social and emotional development intertwine as adolescents establish relationships with peers and manage more mature emotions. They face challenges adjusting to new social dynamics and responsibilities.
4. Mental health during this period requires awareness of potential warning signs for disorders like changes in mood, eating/sleeping problems, or withdrawal from
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views5 pagesPer Dev Reviewer
Per Dev Reviewer
Uploaded by
Ishie De GuzmanThis document provides an overview of adolescent development from physical, cognitive, social, and emotional perspectives. It discusses the following key points:
1. Physical changes occur rapidly during adolescence as youth mature into adulthood. This includes growth spurts and sexual maturation.
2. Cognitive development involves enhanced critical thinking skills and abstract reasoning abilities. Adolescents work to develop their identity and independence.
3. Social and emotional development intertwine as adolescents establish relationships with peers and manage more mature emotions. They face challenges adjusting to new social dynamics and responsibilities.
4. Mental health during this period requires awareness of potential warning signs for disorders like changes in mood, eating/sleeping problems, or withdrawal from
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
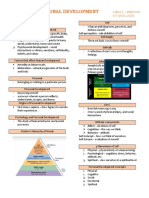
Chapter 1: Knowing The Self Chapter 2:
Concept of Self Psychology refers to the science of mental
- Your developmental stage is called processes and behaviors.
adolescence.
1. Early Adolescence 12-14 Physiological Development
years old - Refers to the physical changes that
2. Middle Adolescence 15-17 occur in the body.
years old
3. Late Adolescence 18-21 Early Adolescence
years old Girls (12-14 years old)
- Experiencing rapid physical changes - Breast Develop
until their full completion in late - Pubic Hair
adolescence - Hair Under the Arms
- Showing ability to comprehend - Menstruation starts as early as 10
abstract concepts in mathematics late as 16 years old
- Questioning old values without fear - Hips become more defined and
- Moving gradually toward a more curved
mature sense of identity - Void becomes firmer and fuller
The Johari Window Boy (12-14 years old)
1. Open self - known by you and others - Testicles enlarge
2. Blind Self - only known by others - Penis enlarges one year after
3. Hidden Self - only known by you testicles
4. Unknown Self - unknown to you and - Appearance of Pubic hair at 13.5
others years old
- Nocturnal emission may happen at
Unique self 14 years old
A. Characteristics - Hair under arms and on face grows
a. Refers to the unique features - Voice becomes firmer and fuller
or qualities typically - Acne starts appearing at 15 years
describing you as an old
adolescent - Adam's apple become visible
B. Habits
a. This is the first special and Middle (15-17 years old) to Late
unique tendencies, activities Adolescence (18-21 years old)
or practices that you find - Physiological changes become more
yourself having difficulty to let stable. You have become more
go or give up’ profound with a sense of acceptance
C. Experiences and comfort.
a. Refers to significant
experiences that contribute Cognitive Development
to the unique self. - Refers to your capacity to think and
reason.
Social Development + Emotional Chapter 5 : Aspects of Personal
Development Development
- Both of these are intertwined during
middle and late adolescence. Stress - state of mental or emotional strain
or tension resulting from adverse or very
Spiritual Development demanding circumstances.
- During adolescence, spiritual
awakening happens and Stressor - chemical or biological agent,
adolescents become aware of the environmental condition, external stimulus
existence of the divine, share their that causes stress to an organism.
spiritual experiences with peers and
find a way to put faith into practice. 1. External Stressor
a. Changes in temperature
Chapter 3: Development Stages in Middle i. Heat or cold
and Late Adolescents b. Stressful environment
i. Classroom Conditions
- Refers to tasks that arise during ii. Abusive Relaitonship
certain periods in your life 2. Internal Stressor
a. Physical Ailments
Adjust to new physical changes i. Infection
Adjust to new intellectual abilities ii. Inflammation
Adjust to higher cognitive demands in iii. Psychological
school problems
Adjust to higher demands for verbal 1. Worrying
communication skills 2. Overthinking
Develop a personal sense of identity
Establish Vocational Goals Chapter 6 : The Powers of the Mind
Establish Emotional and Physical
Independence from parents The Human Brain is a highly essential and
Develop Stable peer relationships powerful part of the Human body. It is one of
Manage sexuality the largest and most complex organs of the
Adopt a personal value system body.
Chapter 4 Brain is the processing center of different
signals and information, communicating
Challenges of Middle and Late Adolescents over a trillion connections through
synapses.
Sexual Relationship
Peer Adjustment Basic Parts Include the ff:
Intellectual Maturation 1. Brainstem
Vocational Choice a. Conists of the medula.
Emotional maturity Controls breathing, digestion,
heart rate and other
autonomic processes.
2. Cerebellum - Looking for personal meaning
a. Has an important role for - Giving sensory input
motor control. It is also - Joining group studies
involved in language,
emotional functions, end Organized, sequential, planned and details
processing of procedural - Following directions
memories - Doing repetitive detailed homework
3. Cerebrum problems
a. Forebrain, make up 75 - Managing time and schedules
percent of the brain volume
and 85 percent by weight Interpersonal, Feeling-based, kinesthetic,
Emotional
Ned Herrmann - Looking at the big picture
- Is known as the “Father od Brain - Taking initiative
dominance Technology” - Simulations
- He developed the theory of brain - Visual Aids
dominance where people develop a - Brainstorming
dominant mode of thinking
preferences.
The Right Brain The Left Brain
The Whole Brain Model
- States that the brain is divided into The right side of the The left side of the
four metaphoric quadrants. This also brain is best at the brain is considered
refers your preferred modes of expressive and to be adept at tasks
thinking, learning and working creative tasks that involve logic,
language and
analytical thinking
The right and the left-brain theory
- According to the theory of right brain Recognizing Faces Language
or left-brain dominance, each side of Expressing Logic
the brain has its designated function, Emotions Critical Thinking
and each person has his/her own Music Numbers
Reading Emotions Reasoning
preference as the which side is
Colors
mostly used. Images
Intuition
Logical, Analytical, fact-based Quanitative Creativity
- Collecting data
- listening to informational lectures Chapter 7 : Mental health and well-being in
- reading textbooks middle and late adolescence
- Judging ideas based on facts,
criteria The following are considered possible
- Logical reasoning warning signs for mental disorders
- Frequent expression of anger and
Holistic, intuitive, Integrating, Synthesizing worry
- Listening to and sharing ideas - Difficulty in sleeping and eating
- Inability to enjoy pleasurable tired, difficulty in
activities concentrating, mind going
- Isolation and avoiding social blank, irritability, muscular
interactions tension and difficulty falling
- Extended feeling of grief after a loss asleep or stay asleep
or death of a loved one together with unsatisfying
- Obession with exerccising, ddieting sleep.
or binge-eating D. Social Anxiety Disorder
- Seek to hurt other people or destroy - Refers to persistent fear of
property socializing with unfamiliar
- High or low energy situations or people with fear
- Engaging in smoking, drinking and to act in ways that may be
prohibited drugs embarrassing and humiliating
- Difficulty in controlling emotions E. Panic Disorder
- Thougts of suicide - Surge of fear or intense
- Self harm discomfort reaching its peak
- Hearing voices within minutes.
- Idea that one’s midn is controlled F. Schizophrenia
best by someone else - Related to “gross deficits in
reality testing” This can mean
A. ADHD or attention that to properly detect what is
deficit-hyperactivity Disorder real and not reals, can
a. Persistent inattention and or manifest delusion,
hyper-activity impulsivity that hallucinations, disorganized
disrupts normal functioning speech, disorganized or
or development and whose catatonic behavior
symptoms present G. Depression
themselves. - Refers to feeling of sadness
b. Has a direct negative impact that lingers for weeks or
on social, academic and longer, accompanied by a
occupational functioning feeling of worthlessness or
B. Bipolar Disorder hopelessness.
a. A serious mental illness, they H. Eating Disorder
go through an unusual mood - Commonly used as a
changes and extremes of lifestyle-related disorder.
emotions such as happy, - Considered more serious
highly energetic phased since it may cause severe
called maniac episode. disturbance to an
C. Generalized Anxiety Disorder adolescent’s eating and can
a. Reers t excessive anxiety lead to fatal illness.
and working with difficult to - Such as anorexia nervosa,
control oneself. bulimia nervosa and binge
b. Also associated with eating
restlessness, being easily I. Personality Disorder
- An adolescent who has a Vulnerability
personality disorder may 1. Biological Vulnerability
display behavior that - Includes being affected base
markedly deviates from the on some physical illness like
expectations of the culture of asthma or heart disease
the individual who exhibits it. 2. Early experiences
J. Conduct Disorder - In life it includes intense
- Refers to disruptive emotions; experience such
behaviors such as as parents; separation
aggression o people and
animals
K. Substance-related Disorders
- Conditions that have
something to do with
problematic pathological se
of alcohol and illegal drugs
L. Internet adiction
- Refers to excessive use of
the internet which impair
daily life
What are the tracers and threats to
psychological well-being?
1. Family is knows as basic unit of
society. It is currently benign
challenged in relation to rearing
adolescence
2. Community and neighborhood
- Could also affect your
well-being, they could
influence your choices and
interest.
3. School-related factors
- Can contribute to or threaten
your health and well-being.
Good factors such as you
joining academic and non
academic activities
4. Socioeconomic Status
- May give rise to multiple
personality disorders in the
instability of the home
environment
You might also like
- English SbaDocument16 pagesEnglish SbaSatyanand Loutan100% (3)
- Lesson Plan - Mood Disorders - Bipolar DisordersDocument5 pagesLesson Plan - Mood Disorders - Bipolar DisordersBhawna Pandhu100% (2)
- PD Reviewer 1st QuarterDocument5 pagesPD Reviewer 1st Quarterandrian diazNo ratings yet
- SOCSCI1 ReviewerDocument6 pagesSOCSCI1 ReviewerCHRISTIAN KAYE UMALINo ratings yet
- Textual Summary Lessons 1 6Document6 pagesTextual Summary Lessons 1 6Mai RuizNo ratings yet
- PERDEVDocument7 pagesPERDEVanglnparungaoNo ratings yet
- ReviewerforperdevDocument3 pagesReviewerforperdevaltheamagbitang04No ratings yet
- Reviewer in Personal Development For ExaminationDocument2 pagesReviewer in Personal Development For ExaminationMalvin NapaoNo ratings yet
- PDF 20221212 142450 0000Document12 pagesPDF 20221212 142450 0000NicoleNo ratings yet
- Personal DevelopmentDocument7 pagesPersonal DevelopmentRenz PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Perdev ReviewerDocument9 pagesPerdev Reviewerchewie ble100% (1)
- Personal DevelopmentDocument9 pagesPersonal DevelopmentMarxinne PajarinNo ratings yet
- PerDevt ReviewerDocument2 pagesPerDevt ReviewerhydeNo ratings yet
- Perdev Q3Document5 pagesPerdev Q3Sam VillegasNo ratings yet
- Personal Development ReviewerDocument5 pagesPersonal Development ReviewerAdrian AranoNo ratings yet
- Ot102 Finals NotesDocument24 pagesOt102 Finals NotesFrancesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Knowing Oneself: Components of AttitudeDocument12 pagesLesson 1: Knowing Oneself: Components of AttitudeChristine Joie FernandezNo ratings yet
- Personal Development ReviewerDocument4 pagesPersonal Development ReviewerWensil FaithNo ratings yet
- Perdev - NotesDocument12 pagesPerdev - Notespretzel.bergantinosNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Developing The Whole Person AdolescenceDocument4 pagesModule 2: Developing The Whole Person AdolescenceAndrea ElcanoNo ratings yet
- Psychoanalytic TheoryDocument9 pagesPsychoanalytic TheoryHeliosNo ratings yet
- PER DEV Reviewer Q1Document6 pagesPER DEV Reviewer Q1lun3l1ght18No ratings yet
- PERDEV-reviewer (Lesson 1-11)Document8 pagesPERDEV-reviewer (Lesson 1-11)Rainzel Faith P. CASTILLONo ratings yet
- UTS D. Until LastDocument10 pagesUTS D. Until LastROWENA VILLAMINNo ratings yet
- Personal Development Reviewer w1 9Document4 pagesPersonal Development Reviewer w1 9lanonjonalynNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Developing The Whole PersonDocument91 pagesModule 2 - Developing The Whole PersonArchi Archi100% (2)
- Uts NotesDocument12 pagesUts NotesScyrah Allana RiegoNo ratings yet
- Beliefs: Knowing Yourself Means Understanding Your StrengthsDocument8 pagesBeliefs: Knowing Yourself Means Understanding Your StrengthsKathy suNo ratings yet
- Per Dev ReviewerDocument2 pagesPer Dev ReviewerAQUA JUICENo ratings yet
- Holistic 19 Development: Chapter 1: Knowing Oneself Chapter 2: Developing The Whole PersonDocument4 pagesHolistic 19 Development: Chapter 1: Knowing Oneself Chapter 2: Developing The Whole PersonEunice C. LoyolaNo ratings yet
- Perdev Module2Document10 pagesPerdev Module2tallerrayallen4No ratings yet
- LM03 Human DevelopmentDocument11 pagesLM03 Human DevelopmentElena MoralesNo ratings yet
- PERDEV Handout - M2 & M4 (Developing The Whole Person & Challenges)Document2 pagesPERDEV Handout - M2 & M4 (Developing The Whole Person & Challenges)Ella MirandaNo ratings yet
- S11PD Prelims ReviewerDocument23 pagesS11PD Prelims ReviewerChristine FerrerNo ratings yet
- Prefinal - GEC 1 - Understanding The SelfDocument3 pagesPrefinal - GEC 1 - Understanding The SelfKatherine RaferNo ratings yet
- Perdev NotesDocument2 pagesPerdev Notesacademic pusposesNo ratings yet
- PERDEV ReviewerDocument4 pagesPERDEV ReviewerKathleen Joyce ParangatNo ratings yet
- ITP ReviewerDocument9 pagesITP ReviewerRegine PalconanNo ratings yet
- Gen 002 Reviewer SAS 8Document3 pagesGen 002 Reviewer SAS 8KaartianeNo ratings yet
- Personal Development ReviewerDocument6 pagesPersonal Development ReviewerJocelyn RosalNo ratings yet
- Local Media2246351459788256841Document4 pagesLocal Media2246351459788256841Reyster AfricaNo ratings yet
- Perdev-Reviewer (1) - 091445Document12 pagesPerdev-Reviewer (1) - 091445graceleen.ssilangNo ratings yet
- PerdevDocument6 pagesPerdevJøhn Anrol ParochaNo ratings yet
- Perdev 00Document2 pagesPerdev 00Nasser GementizaNo ratings yet
- Perdev Midterm ReviewerDocument8 pagesPerdev Midterm ReviewerNathaniel BudayNo ratings yet
- Developmental PsychologyDocument6 pagesDevelopmental PsychologySean RicoNo ratings yet
- PerDev Worksheet 5Document4 pagesPerDev Worksheet 5Princess Edelyn Mae PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Personality Development NSTPDocument34 pagesPersonality Development NSTPMc HarrisNo ratings yet
- Topic 1: Introduction To Human DevelopmentDocument9 pagesTopic 1: Introduction To Human DevelopmentDOLL LINANo ratings yet
- Developing The Whole Person: Holistic DevelopmentDocument34 pagesDeveloping The Whole Person: Holistic DevelopmentasdasdasdNo ratings yet
- Week2 Module2 PerdevDocument27 pagesWeek2 Module2 PerdevJamaica C. AquinoNo ratings yet
- Developing The Whole Person Holistic Development I. Physiological Development II. Cognitive DevelopmentDocument2 pagesDeveloping The Whole Person Holistic Development I. Physiological Development II. Cognitive DevelopmentAstxilNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7: The Power of The Mind: The Whole Brain Theory: Prepared By: Ms. Jessa Mae C. MallillinDocument10 pagesCHAPTER 7: The Power of The Mind: The Whole Brain Theory: Prepared By: Ms. Jessa Mae C. MallillinMigaeaNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter PERDEV ReviewerDocument8 pages1st Quarter PERDEV ReviewerMarigel BuenaNo ratings yet
- Normality, Mental Health, Life Cycle TheoryDocument2 pagesNormality, Mental Health, Life Cycle TheoryKo HakuNo ratings yet
- CORE 11 12 Personal Development q0 CLAS2 Week2 Developing The Whole Person 2 RHEA ANN NAVILLADocument13 pagesCORE 11 12 Personal Development q0 CLAS2 Week2 Developing The Whole Person 2 RHEA ANN NAVILLAelementalgamer276No ratings yet
- PsychologyDocument30 pagesPsychologyAndrei DonaireNo ratings yet
- PSTHEDocument4 pagesPSTHEZaira CalingasanNo ratings yet
- PERDEV Chapter 78 HandoutsDocument3 pagesPERDEV Chapter 78 HandoutsDanielle Rose JalagatNo ratings yet
- G11 - Personal Development - 1st Sem - Midterm NotesDocument9 pagesG11 - Personal Development - 1st Sem - Midterm NotesaglubatjohngrayNo ratings yet
- Perdev Q2 ReviewerDocument3 pagesPerdev Q2 Revieweranastacio.althea.nievaNo ratings yet
- Compulsive-Sexual-Behavior-Disorder-In-Obsessive-Compulsive-Disorder-Prevalence-And-Associated-Comorbidity - Content File PDFDocument8 pagesCompulsive-Sexual-Behavior-Disorder-In-Obsessive-Compulsive-Disorder-Prevalence-And-Associated-Comorbidity - Content File PDFAlexandra SadkowskaNo ratings yet
- AbPsy Phase1Document7 pagesAbPsy Phase1Belle PelNo ratings yet
- Global Assessment of FunctioningDocument1 pageGlobal Assessment of FunctioningKen Carter100% (2)
- Biological Basis of Psychological DisordersDocument18 pagesBiological Basis of Psychological DisordersAkanksha katkarNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan ContentDocument9 pagesUnit Plan ContentS KANIMOZHINo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument28 pagesThesisKolong JembatanNo ratings yet
- IMAGINE+Caregiver+Program SSA+Document59 pagesIMAGINE+Caregiver+Program SSA+Nikola VeleskiNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Criteria For Borderline Personality Disorder (DSM IV, 1994)Document2 pagesDiagnostic Criteria For Borderline Personality Disorder (DSM IV, 1994)Theo KhouryNo ratings yet
- Mutant Superpowers ZineDocument79 pagesMutant Superpowers ZineBecky DaleNo ratings yet
- Narcissistic Personality DisorderDocument9 pagesNarcissistic Personality DisorderJoeNo ratings yet
- Brain CalipersDocument13 pagesBrain CalipersNadz RlanNo ratings yet
- Multiple Personalities, The SearchDocument3 pagesMultiple Personalities, The SearchLordgelyn Diane ViernesNo ratings yet
- Written Report On Mental Health PDFDocument7 pagesWritten Report On Mental Health PDFLovelene ChrizzeNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia: National Institute of Mental HealthDocument8 pagesSchizophrenia: National Institute of Mental HealthCristian ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Abnormal Psychology 7th Edition PDF ScribdDocument41 pagesInstant Download Ebook PDF Abnormal Psychology 7th Edition PDF Scribdvictor.lewis791100% (41)
- Headache: Differential Diagnosis of HeadacheDocument139 pagesHeadache: Differential Diagnosis of Headachemero1983No ratings yet
- Module 7 - Mental HealthDocument28 pagesModule 7 - Mental HealthEdithaNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry Ii - Personality Traits and Defenses in The Medically Ill - 3.01Document2 pagesPsychiatry Ii - Personality Traits and Defenses in The Medically Ill - 3.01Ravi Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument3 pages1 PDFM VNo ratings yet
- Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders FinalDocument16 pagesObsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders Finalnatashamarie.relampagosNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Concept Map For Jack BellDocument1 pageWeek 3 Concept Map For Jack BelldessyrichNo ratings yet
- Schizotypal Personality DisorderDocument5 pagesSchizotypal Personality DisorderJoel LenamingNo ratings yet
- Project On GothicDocument14 pagesProject On GothicMazana ÁngelNo ratings yet
- Rupal Arora - Diagnostic Criteria For Neuropychological DisordersDocument21 pagesRupal Arora - Diagnostic Criteria For Neuropychological Disordersrupal aroraNo ratings yet
- Aripiprazole Drug InfoDocument3 pagesAripiprazole Drug InfoAshish KarnNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia (F20) : Crisis Paper Presentation Provider 3Document47 pagesSchizophrenia (F20) : Crisis Paper Presentation Provider 3سهى الغامديNo ratings yet
- Toxicity: System of A DownDocument6 pagesToxicity: System of A DownKelson Daniel RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Mental Health ProgramDocument4 pagesMental Health ProgramMADULI, Marlone G.100% (1)