Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter - 1 Reproduction in Organism
Chapter - 1 Reproduction in Organism
Uploaded by
Dr.MonikaShekhawatOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter - 1 Reproduction in Organism
Chapter - 1 Reproduction in Organism
Uploaded by
Dr.MonikaShekhawatCopyright:
Available Formats
BEST BIOLOGY
CLASSSES
BIOLOGY
Chapter 1: Reproduction In Organisms
Email - bestbiologyclasses.kota@gmail.com , Contact No.- 8302714003
REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
01 BEST BIOLOGY
CLASSSES
Reproduction In Organisms
Life Span: The period which begins from birth and ends with the natural death of
an organism is known as its life span.
Reproduction
Reproduction is a biological process wherein younger ones produced are identical
to their parents. This phenomenon is significant in the continuity of the species,
generation after generations. Typically, reproduction is observed in all living
organisms from single-celled entities such as amoeba to multicellular entities of
the most advanced forms, such as human beings. Reproduction is carried out in
two modes, depending upon the participation of one or both parents.
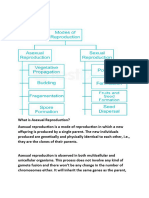
Types of Reproduction:
Based on whether there is one or two organisms taking part in the process of
reproduction.
• Asexual Reproduction
• Sexual Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction: When the offspring is produced by single parents with or
without the involvement of gamete formation, the reproduction is called asexual
reproduction.
Sexual Reproduction: When two parents (opposite sex) participates in
reproduction process and also involves the fusion of male and female gametes, it is
called sexual reproduction.
Mode of Asexual Reproduction:
Email - bestbiologyclasses.kota@gmail.com , Contact No.- 8302714003 (1)
REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
01 BEST BIOLOGY
CLASSSES
• Usually followed by organisms with relatively simpler organizations.
• Offsprings produced by single parent.
• With/ without involvement of gamete formation.
• Clones: Offsprings produced are genetically and morphologically similar to
each other and to the parent, i.e. they are clones.
• In Protista and Monera, the parent cells divides into two to give rise to new
individuals. Thus, in these organisms cell division is the mode of
reproduction itself.
• Binary fission in this method of asexual reproduction, a cell divides into two
halves and rapidly grows into an adult. Ex. amoeba, paramecium.
• Budding small buds are produced that remain attached initially with parents
and get separated on maturation. Ex. Yeast.
• Fungi and simple plants like algae reproduce through special reproductive
structures like zoospores (motile structure), conidia (penicillium), buds
(hydra) and gemmules (sponges).
• In plants, vegetative reproduction occurs by vegetative propagules like
runner, rhizome, sucker, tuber, offset and bulb.
• Asexual reproduction is the most common method of reproduction in
organisms having simpler body like in algae and fungi but during
unfavourable condition they shift to sexual reproduction.
Vegetative Propagation:
It is a type of process in which new plants are obtained without the production of
sexual structures i.e., seeds or spores. It involves the propagation of plants through
different types of vegetative parts such as the rhizome, sucker, tuber, bulb, etc. In
this, a fusion of the male and the female gamete does not take place and requires
Email - bestbiologyclasses.kota@gmail.com , Contact No.- 8302714003 (2)
REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
01 BEST BIOLOGY
CLASSSES
only one parent. This is grouped into natural and artificial.
Vegetative Propagules:
• Runner- oxalis
• Sucker- Mint and Chrysanthemum
• Tuber- potato
• Offset- water hyacinth, pistia
• Bulb- onion, garlic
• Rhizome- ginger
• Bulbil- agave
• Leaf buds- Bryophyllum
Artificial Methods: In this type of method, only a small part of the plant organ is
utilized for obtaining a new complete plant. Amongst them, the most common
methods which are used are cutting, layering, and grafting.
Cutting: In cutting, a small piece of root is cut and when planted in moist soil, it will
lead to the artificial inducement and development of adventitious roots. For
example, in lemon.
In Rose, sugarcane, hibiscus, and chrysanthemum plants are developed by cuttings
that involve stem pieces with the presence of nodes. The small cuttings are
planted in moist soil to develop new plants. Underground parts of the stem leading
to the development of adventitious roots, whereas buds develop and sprout on
the aerial parts of stems. The new plants are in a common language known as
cutting. Later, these cuttings are transplanted in different prepared places.
Layering: This method is used for growing rose, lemon, grape, hibiscus, and
jasmine. The lower branches of these plants are bent a little bit and covered with
soil in such a way that the tip of the branch protrudes from the ground and the
middle part of the plant is inside the soil. It will then develop adventurous roots
from this buried area of the stem of the plant, at that time this branch is cut off
and separated from the mother plant, whereby a new plant is obtained.
Grafting: Grafting is carried out on plants that are having difficulty in forming roots
or that generally have a weak root system. This method involves joining two plants
of the same or different species, this is achieved by connecting the tissues of the
two plants directly to The. When brought into contact, the meristematic tissue of
both plants divides and multiplies, and finally the cells of each plant fuse.
The rooted plant is called the stem plant. The plant that is grafted onto it is called
the sprout. A plant is selected as the "scion" that has superior and desirable
properties. The stock is generally strong, robust, and resilient, mango, apple, pear,
citrus, guava, lychee, and many other fruit plants are obtained and kept in this
Email - bestbiologyclasses.kota@gmail.com , Contact No.- 8302714003 (3)
REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
01 BEST BIOLOGY
CLASSSES
way. The graft can be of several types, namely, bud graft, lateral graft, and tongue
graft, wedge graft, and crown graft, depending on the methods of joining the two
parts.
Significance of Vegetative Reproduction:
• Vegetative reproduction is an ideal method of reproduction in plants in
which we want to preserve parental characteristics.
• It is best for plants that are less efficient sexually, small seeds, long seed
dormancy, poor seed viability, etc. They can also be easily multiplied by this
method.
• Vegetative propagation is useful for obtaining disease-free plants.
• By using grafting, the desired characters can be brought together from two
varieties.
Water Hyacinth (Terror of Bengal)
• One of the most invasive weeds.
• Grows wherever there is standing water.
• Drains oxygen from water- leads to death of fishes.
• Introduced in India because of its pretty flowers & shape of leaves.
• Vegetative propagation occurs at a phenomenal rate.
Sexual Reproduction:
• Involves formation of male and female gamete by two individuals of the
opposite sex.
• Offspring produced by fusion of male and female gametes not identical to
each other or to the parents.
• All sexually reproducing organisms share a similar pattern of reproduction.
• In sexual reproduction, fusion of male and female gametes results in
offspring that are not identical to parents.
Different Phases in Sexual Reproduction:
Juvenile phase: It is the period of growth after birth in an individual organism,
and before it meets reproductive maturity.
Reproductive phase: It is the time when a human organism sexually reproduces.
Email - bestbiologyclasses.kota@gmail.com , Contact No.- 8302714003 (4)
REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
01 BEST BIOLOGY
CLASSSES
Senescent phase: It is the end of reproductive phase. Old age ultimately leads to
death
Events in Sexual Reproduction: Pre-fertilization, Fertilization, Post-fertilization
Pre-fertilization: all the events prior to fusion of gametes are included in it. It
includes gametogenesis and gamete transfer.
Gametogenesis: Is the process of formation of male and female gametes.
Gametes are haploid cells which may be similar or dissimilar in structure. In algae,
When both gametes are similar in structure called homogametes (isogametes). In
higher organism that reproduces sexually, two morphologically distinct gametes
are formed called heterogametes, male gametes are called antherozoid or sperm
and female gametes are called ovum or egg.
Isogametes Heterogametes:
In fungi and plants, homothallic and monoecious terms are used to denote the
bisexual condition and heterothallic and dioecious are used for unisexual
condition. In flowering plants, the unisexual male flower is staminate, i.e., bearing
stamens, while the female is pistillate or bearing pistils.
In animals, species which possess both male and female reproductive organs in
same individual are called bisexual or hermaphrodites (earthworm, sponges,
tapeworm etc.) and both having either male or female reproductive organs are
called unisexual (cockroach, human).
Gametes are always haploid( having half set of chromosome ), although organisms
may be haploid and diploid. Diploid organisms form gametes by meiotic division.
The organisms belonging to algae, fungi, and bryophytes have haploid plant body
and pteridophytes, gymnosperms, angiosperms and most of animals are diploid
(having double set of chromosome)
In diploid organisms, gamete mother cell (meiocyte) undergoes meiosis in which
one set of chromosome is present in gametes.
Gamete Transfer:
In majority of organisms, male gametes are motile and females gametes are non-
motile, except in fungi and algae in which both gametes are motile. In simple
plants like algae, fungi, bryophytes and pteridophytes water is the medium
through which male and female gametes moves. The number of male gametes are
much more than number of female gametes as most of male gametes fail to reach
the female gametes.
In higher plants pollen grains are carrier of male gametes and ovule has eggs.
Email - bestbiologyclasses.kota@gmail.com , Contact No.- 8302714003 (5)
REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
01 BEST BIOLOGY
CLASSSES
Pollen grains must be transferred from anther to stigma to facilitate fertilization.
Pollination: The transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma is called
pollination. Pollination may be self (anther to stigma of same flower) or cross
(anther to stigma of different flower).
Pollen grains germinate on stigma to produce pollen tube that delivers the male
gametes near the ovule.
Fertilization: The fusion of male and female gamete is called fertilization or
syngamy. It results in the formation of diploid zygote.
Parthenogenesis: The process of development of new organisms without
fertilization of female gametes is called parthenogenesis. For example honey bee,
rotifers, and lizards.
There are two types of fertilization:
i. External Fertilization: Syngamy occurs outside the body of the organism
Large numbers of gametes are released in the surrounding medium.
Example: Bony fishes and Amphibians.
ii. Internal Fertilization: Syngamy occurs inside the body of the organism
Numbers of ova produced are less, but large numbers of male gametes are
released and they travel towards the ovum. Example: Birds and Mammals.
Post Fertilization Events: events in the sexual reproduction after formation of
zygote.
Zygote is the vital link that ensures continuity of species between organisms of one
generation and the next. Every sexually reproducing organism, including human
beings, begin life as a single cell–the zygote.
In the organisms, having external fertilization, zygote is formed in external medium
(water) and those having internal fertilization zygote is formed inside the body of
female.
In algae and fungi, zygote develops a thick wall resistant to desiccation and
damage. This germinates after a period of rest.
In the organisms having haplontic life cycle, zygote divides to form haploid spores
that germinate to form haploid individual.
Embryogenesis: the process of development of embryo from the zygote. During
this, zygote undergoes mitotic division and cell differentiation. Cell division
increase the number and cell differentiation help information of new group of cells
and organs.
Email - bestbiologyclasses.kota@gmail.com , Contact No.- 8302714003 (6)
REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
01 BEST BIOLOGY
CLASSSES
There are two types of animals:
Oviparous: Development of zygote takes place outside the body of organisms and
lay fertilized of unfertilized eggs. Example: Reptiles and birds.
Viviparous: Development of zygote takes place inside the body of organisms and
produces young ones. Example: Human, dog, horse etc.
Pericarp: In flowering plants, zygote is formed inside the ovule. After fertilization,
sepals, petals and stamens of flower fall off. The zygote develops into embryo and
ovules into seeds. The ovary develops into fruits which develop a thick wall called
pericarp, protective in function.
In animals:
By Copulation: e.g., Reptiles, Birds and Mammals.
By External medium: e.g., Fishes and Amphibians.
Sporulation: During unfavourable conditions organisms like Amoeba surrounded
by resistant coat (three layered—hard covering) or cyst. This is called encystation.
Within cyst a number of spores are formed. On returning favourable conditions,
the cyst burst and spores are liberated and gradually grows in adults. This process
is known as sporulation (multiple fission).
Fragmentation: It is a type of asexual reproduction where an organism splits into
fragments. Their fragments develops into fully grown individual. e.g. spirogyra,
fungi and some annelids.
Regeneration: It is a process of renewal, restoration and growth. It can occur at
the level of the cell, tissue and organ. It is common in Hydra, Planaria and
echinoderms
• In human, liver has power of regeneration, if it is partially damaged.
• During danger a lizard discard a part of its tail which can regenerate later.
Email - bestbiologyclasses.kota@gmail.com , Contact No.- 8302714003 (7)
REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
01 BEST BIOLOGY
CLASSSES
Email - bestbiologyclasses.kota@gmail.com , Contact No.- 8302714003 (8)
REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
01 BEST BIOLOGY
CLASSSES
Important Questions
➢ Multiple Choice Questions:
1. A few statements describing certain features of reproduction are given below:
(i) Gametic fusion takes place
(ii) Transfer of genetic material takes place
(iii) Reduction division takes place
(iv) Progeny have some resemblance with parents
Select the options that are true for both asexual and sexual reproduction from the options
given below:
(a) i and iii
(b) ii and iii
(c) ii and iv
(d) i and iii
2. The term ‘clone’ cannot be applied to offspring formed by sexual reproduction because:
(a) Offspring do not possess exact copies of parental DNA.
(b) DNA of only one parent is copied and passed on to the offspring.
(c) Offspring are formed at different times
(d) DNA of parent and DNA of offspring are completely different.
3. Amoeba and Yeast reproduce asexually by fission and budding respectively, because they
are:
(a) Microscopic organisms
(b) Heterotrophic organisms
(c) Unicellular organisms
(d) Uninucleate organisms.
4. A few statements with regard to sexual reproduction are given below:
(i) Sexual reproduction does not always require two individuals.
(ii) Sexual reproduction generally involves gametic fusion.
(iii) Meiosis never occurs during sexual reproduction
(iv) External fertilisation is a rule during sexual reproduction.
Choose the correct statements from the options below:
(a) i and iv
(b) i and ii
(c) ii and iii
Email - bestbiologyclasses.kota@gmail.com , Contact No.- 8302714003 (9)
REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
01 BEST BIOLOGY
CLASSSES
(d) i and iv
5. A multicellular, filamentous alga exhibits a type of sexual life cycle in which the meiotic
division occurs after the formation of zygote. The adult filament of this alga has
(a) Haploid vegetative cells and diploid gametangia
(b) Diploid vegetative cells and diploid gametangia
(c) Diploid vegetative cells and haploid gametangia
(d) Haploid vegetative cells and haploid gametangia.
6. The male gametes of rice plant have 12 chromosomes in their nucleus. The chromosome
number in the female gamete, zygote and the cells of the seedling will be respectively
(a) 12, 24, 12
(b) 24, 12, 12
(c) 12, 24, 24
(d) 24, 12, 24
7. Given below are a few statements related to external fertilisation. Choose the correct
statements.
(i) The male and female gametes are formed and released simultaneously.
(ii) Only a few gametes are released into the medium.
(iii) Water is the medium in a majority of organisms exhibiting external fertilisation.
(iv) Offspring formed as a result of external fertilisation have better chance of survival
than those formed inside an organism.
(a) iii and iv
(b) i and iii
(c) ii and iv
(d) i and iv
8. The statements given below describe certain features that are observed in the pistil of
flowers.
(i) Pistil may have many carpels
(ii) Each carpel may have more than one ovule
(iii) Each carpel has only one ovule
(iv) Pistil has only one carprel
Choose the statements that are true from the options below:
(a) i and ii
(b) i and iii
(c) ii and iv
(d) iii and iv
Email - bestbiologyclasses.kota@gmail.com , Contact No.- 8302714003 (10)
REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
01 BEST BIOLOGY
CLASSSES
9. Which of the following situations correctly describe the similarity between an angiosperm
egg and a human egg?
(i) Eggs of both are formed only once in a lifetime
(ii) Both the angiosperm egg and human egg are stationary
(iii) Both the angiosperm egg and human egg are motile.
(iv) Syngamy in both results in the formation of zygote
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) ii and iv
(b) iv only
(c) iii and iv
(d) i and iv
10.Appearance of vegetative propagules from the nodes of plants such as surgarcane and
ginger is mainly because:
(a) Nodes are shorter than internodes
(b) Nodes have meristematic cells
(c) Nodes are located near the soil
(d) Nodes have non-photosynthetic cells
11.Which of the following statements supports the view that elaborate sexual reproductive
process appeared much later in the organic evolution?
(i) Lower groups of organisms have simpler body design
(ii) Asexual reproduction is common in lower groups
(iii) Asexual reproduction is common in higher groups of organisms
(iv) There is high incidence of sexual reproduction in angiosperms and vertebrates.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) i and ii
(b) i and iii
(c) ii and iv
(d) ii and iii
12.Offspring formed by sexual reproduction exhibit more variations than those formed by
asexual reproduction because:
(a) Sexual reproduction is a lengthy process
(b) Gametes of parents have qualitatively different genetic composition
(c) Genetic material comes from parents of two different species
(d) Greater amount of DNA is involved in sexual reproduction.
13.Choose the correct statement from amongst the following:
Email - bestbiologyclasses.kota@gmail.com , Contact No.- 8302714003 (11)
REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
01 BEST BIOLOGY
CLASSSES
(a) Dioecious (hermaphrodite) organisms are seen only in animals
(b) Dioecious organisms are seen only in plants
(c) Dioecious organisms are seen in both plants and animals
(d) Dioecious organisms are seen only in vertebrates.
14.There is no natural death in single celled organisms like Amoeba and bacteria because:
(a) They cannot reproduce sexually
(b) They reproduce by binary fission
(c) Parental body is distributed among the offspring
(d) They are microscopic.
15.There are various types of reproduction. The type of reproduction adopted by an organism
depends on:
(a) The habitat and morphology of the organism
(b) Morphology of the organism
(c) Morphology and physiology of the organisms
(d) The organism’s habitat, physiology and genetic makeup
➢ Very Short Question:
1. Offsprings produced by asexual reproduction are referred to as clones. Why?
2. Name the most invasive aquatic plant weed which is called as Terror of Bengal.
3. How does Zygote usually differ from Zoospore in terms of ploidy?
4. Mention the main difference between the offspring produced by asexual reproduction and
progeny produced by sexual reproduction.
5. Which characteristic property of Bryophyllum is exploited by gardeners and farmers?
6. What represents the life span of an organism?
7. Which individuals can be termed as clones?
8. How do the following organisms reproduce: Paramoecium and Penicillium?
9. State the function of a vegetative propagule.
10. How will you grow a banana and a ginger plant?
➢ Short Questions:
1. Higher organism have resorted to sexual reproduction inspite of its complexity. Why?
2. Tapeworms posses both male and female reproductive organs. What is the name given to
such organism? Give two more examples of such organisms.
3. Study the relationship between first two words and suggest a suitable word for fourth
place.
Email - bestbiologyclasses.kota@gmail.com , Contact No.- 8302714003 (12)
REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
01 BEST BIOLOGY
CLASSSES
(a) Male flower: Stamens :: Female Flower : ………………………..
(b) Birds: oviparous :: Primates : ………………………..
(c) Chlamydomonas : Zoospores :: Penicilium : ………………………..
(d) Ginger: Rhizome :: Agave : ………………………..
4. Bryophytes and Pteridophytes produce a large number of male gametes but relatively very
few female gametes. Why?
5. Enlist the significance of reproduction.
6. Why do hilly areas of Kerela, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu transform into blue stretches that
attracts many tourists?
7. Define ‘oestrus’ and ‘menstrual’ cycles.
8. What regulates the reproduction processes and the associated behavioural expressions in
organisms?
➢ Long Questions:
1. Explain the process of budding in yeast.
2. Describe the importance of vegetative propagation.
3. Describe the post-fertilisation changes in a flower.
➢ Assertion & Reason Questions:
1. For two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason. Select
the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
a. Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b. Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of
assertion.
c. Assertion is true, but reason is false.
d. Both assertion and reason are false.
Assertion: Asexual reproduction involves formation of clones of an organism.
Reason: Clones are morphologically and genetically similar individuals.
2. For two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason. Select
the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
a. Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b. Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of
assertion.
c. Assertion is true, but reason is false.
d. Both assertion and reason are false.
Assertion: Several seed bearing plants propagate vegetatively.
Email - bestbiologyclasses.kota@gmail.com , Contact No.- 8302714003 (13)
REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
01 BEST BIOLOGY
CLASSSES
Reason: Sweet potatoes undergo vegetative propagation by means of root tubers.
✓ Answer Key-
➢ Multiple Choice Answers:
1. (c) ii and iv
2. (a) Offspring do not possess exact copies of parental DNA.
3. (c) Unicellular organisms
4. (b) i and ii
5. (d) Haploid vegetative cells and haploid gametangia.
6. (c) 12, 24, 24
7. (b) i and iii
8. (a) i and ii
9. (b) iv only
10. (b) Nodes have meristematic cells
11. (c) ii and iv
12. (b) Gametes of parents have qualitatively different genetic composition
13. (c) Dioecious organisms are seen in both plants and animals
14. (c) Parental body is distributed among the offspring
15. (d) The organism’s habitat, physiology and genetic makeup
➢ Very Short Answers:
1. Because offsprings produced by Asexual reproduction is morphologically and genetically
identical to parent.
2. Water hyacinth (Eicchornia)
3. Zygote diploid, zoospore haploid.
4. Offspring produced by asexual reproduction are genetically similar while progeny
produced by sexual reproduction exhibit genetic variation.
5. Adventitious bud arising from margin of the leaf.
6. The period from the birth to the natural death of an organism represents its life span.
7. The individuals who are morphologically and genetically identical are called clones.
8. a) Paramoecium reproduces by the process of binary fission.
b) Penicillium reproduces with the help of asexual structures called conidia.
Email - bestbiologyclasses.kota@gmail.com , Contact No.- 8302714003 (14)
REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
01 BEST BIOLOGY
CLASSSES
9. The vegetative propagules are the asexual vegetative structures of the plant that are
capable of giving rise to a new plant.
10. The rhizomes of a banana and a ginger are used to propagate new plantlets.
➢ Short Answer:
1. Because of variations, gene pool, Vigour and Vitality and Parental care.
2. Hermaphrodite; Examples : Earthworm, Leech.
3. (a) Carpel (b) Viviparous
(c) Conidia (d) Bulbil
4. Because male gemete need medium (water) to reach egg/female gamete.A large number of
the male gametes fail to reach the female gamete.
5. Significance of reproduction includes:
• Propagation of species.
• Sustenance of life on this planet.
• Variation introduced during reproduction plays a role in evolution of new species.
6. Strobilanthus kunthiana which flowers only once in every 12 years flowered in 2006 that
resulted into transformation of the hilly tracks of Kerela, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu into
blue stretches.
7. Non- Primates like cows, sheep etc. show certain cyclic changes during reproduction called
oestrus cycle while Primates like apes, humans the cycle is referred to as menstrual cycle.
8. Interaction between hormones and certain environmental factors regulate the reproductive
processes and the associated behavioural expressions of organisms.
➢ Long Answer:
1. Budding in yeast. It is a common type of vegetative reproduction. In a medium which is
abundantly supplied with sugar, yeast cytoplasm forms a bud-like outgrowth. The growth
soon enlarges and a part of the nucleus protrudes into the bud and breaks off. The bud
then begins to grow and then separates from the mother cell. Often it will itself form a
bud before it breaks away, and straight or branched chains are produced.
Email - bestbiologyclasses.kota@gmail.com , Contact No.- 8302714003 (15)
REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
01 BEST BIOLOGY
CLASSSES
Thus, as a result, branched or unbranched chains of cells called pseudo my cilium are
produced. The cells are loosely held together. Sooner or later they become independent.
2. Merits of vegetative propagation:
i. Plants produced by vegetative propagation are genetically similar and constitute a
uniform population called a clone.
ii. Plants with reduced power of sexual reproduction, long dormant period of seed, poor
viability, etc. are multiplied by vegetative methods.
iii. Some fruit trees like banana and pineapple do not produce viable seeds. So these are
propagated by only vegetative methods.
iv. It is a more rapid and easier method of propagation.
v. Good characters are preserved by vegetative propagation.
vi. Some plants such as doob grass (Cynodon dactylon) which produce only a small
quantity of seed are mostly propagated by vegetative propagation.
vii. Grafting helps in getting an economically important plant having useful characteristics
of two different individuals in a short time.
3. Post-fertilisation changes in a flower.
Email - bestbiologyclasses.kota@gmail.com , Contact No.- 8302714003 (16)
REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
01 BEST BIOLOGY
CLASSSES
➢ Assertion and Reason Answers:
1) b) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Explanation:
The reproduction is known as asexual reproduction, when an offspring is produced by a single
parent without the involvement of gamete formation. As a result, the offspring that are
produced are not only similar to one another but are also exact copies of their parent. Such a
group of morphologically and genetically similar individuals are called clones.
2) b) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Explanation:
Formation of new plants by means of vegetative units as tubers, buds, rhizomes is called
vegetative propagation. It is useful for producing large number of offsprings within a short
time and for preserving qualities such as disease resistance. In sweet potato, root tubers take
part in vegetative propagation.
Email - bestbiologyclasses.kota@gmail.com , Contact No.- 8302714003 (17)
You might also like
- Asexual ReproductionDocument13 pagesAsexual Reproductionkritishaa8100No ratings yet
- Class 12-Biology (CHSE &CBSE) Chapter-01: Reproduction in OrganismsDocument6 pagesClass 12-Biology (CHSE &CBSE) Chapter-01: Reproduction in OrganismsAbhipsa dash nikyNo ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction 1Document92 pagesAsexual Reproduction 1Zerica JohnNo ratings yet
- Science 7 UNIT 6 & 7 Study GuideDocument21 pagesScience 7 UNIT 6 & 7 Study GuideMae RicañaNo ratings yet
- NEET Biology Reproduction NotesDocument8 pagesNEET Biology Reproduction NotesShubham Aggarwal0% (1)
- Army Public School Gopalpur: Class-Xii Science Subject - Biology Chapter-1 Reproduction in Organisms NotesDocument5 pagesArmy Public School Gopalpur: Class-Xii Science Subject - Biology Chapter-1 Reproduction in Organisms NotesAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Class X Chapter 8 How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument55 pagesClass X Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproducesmithastanphen mesNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Spectrum SquareDocument15 pagesReproduction Spectrum SquareAgastya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction - Types, Advantages, Disadvantages, ExamplesDocument6 pagesAsexual Reproduction - Types, Advantages, Disadvantages, ExamplesAsadNo ratings yet
- OrganogenesisDocument65 pagesOrganogenesisNavodit GoelNo ratings yet
- Asexual Repro NotesDocument23 pagesAsexual Repro NotesMs ZoyaNo ratings yet
- Asexual Rep and Sex RepDocument35 pagesAsexual Rep and Sex RepJen NyNo ratings yet
- 3 1 Reproduction and DvelopmentDocument39 pages3 1 Reproduction and DvelopmentMarcStep De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Reproduction of Living Organisms Asexual and Sexual ReproductionDocument36 pagesReproduction of Living Organisms Asexual and Sexual Reproductionstephenalfa7No ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument2 pagesAsexual ReproductionShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- CH 1 ReproductionDocument9 pagesCH 1 ReproductionSandesh RNo ratings yet
- Biology REVISION - SCIENCE (YT)Document47 pagesBiology REVISION - SCIENCE (YT)jyotiNo ratings yet
- Major Difference Between Sexual and Asexual ReproductionDocument6 pagesMajor Difference Between Sexual and Asexual ReproductionAsadNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument4 pagesReproduction in Plantsnell jaesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01-Reproduction in Organisms STD XiiDocument27 pagesChapter 01-Reproduction in Organisms STD XiiAbcNo ratings yet
- Organ Culture and Organogenesis - 2021 - 2Document76 pagesOrgan Culture and Organogenesis - 2021 - 2Asri Mawaddah CharunnisaNo ratings yet
- Module 1ADocument26 pagesModule 1AChristine LacanariaNo ratings yet
- AsexuAL ReproductionDocument21 pagesAsexuAL Reproductionkiller_xd09No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Plant ReproductionDocument50 pagesChapter 5 Plant ReproductionRina Abigail CarterNo ratings yet
- Share Reproduction 1Document56 pagesShare Reproduction 1Balbir KaurNo ratings yet
- S4 Bio (Reproduction) NOTESDocument27 pagesS4 Bio (Reproduction) NOTESatuhairemartha62No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document24 pagesChapter 1reilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Sexual and Asexual ReproductionDocument12 pagesSexual and Asexual ReproductionrosalynNo ratings yet
- Asexual V Sexual ReproductionDocument16 pagesAsexual V Sexual ReproductionFi SonnetNo ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction: Name:-Siddhesh Taraate STD: - 10 Venus Sub: - BiologyDocument16 pagesAsexual Reproduction: Name:-Siddhesh Taraate STD: - 10 Venus Sub: - BiologysidNo ratings yet
- NomanDocument5 pagesNomannomanansari54813No ratings yet
- Genbio2 q2 Mod1.1 Reproduction-And-DevelopmentDocument9 pagesGenbio2 q2 Mod1.1 Reproduction-And-DevelopmentHazel AbitriaNo ratings yet
- Genbio2 Week 2 2Document44 pagesGenbio2 Week 2 2kimberlyfritzzunigaNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument8 pagesHow Do Organisms ReproducesushantNo ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction - GR 8Document23 pagesAsexual Reproduction - GR 8AmmuNo ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction - GR 8Document23 pagesAsexual Reproduction - GR 8AmmuNo ratings yet
- To Reviewgen BioDocument19 pagesTo Reviewgen Bioguia.mareeseNo ratings yet
- 8-How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument35 pages8-How Do Organisms ReproduceTECHNICAL CHASKANo ratings yet
- BIO 101 Lesson 1-3Document14 pagesBIO 101 Lesson 1-3chibuikeokafor302No ratings yet
- Lesson 9 - Reproduction IntroductionDocument4 pagesLesson 9 - Reproduction IntroductionlemoniteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - How Do Organisms Reproduce?Document6 pagesChapter 8 - How Do Organisms Reproduce?RiddhimaNo ratings yet
- (Biology II) : de Mesa, Lance Christian M. Espiritu, Abram Paul C. Ignacio, Marinelle V. Napa, Hannah Grace PDocument125 pages(Biology II) : de Mesa, Lance Christian M. Espiritu, Abram Paul C. Ignacio, Marinelle V. Napa, Hannah Grace PDavis ShamolmolNo ratings yet
- Types of Reproductive System 2Document15 pagesTypes of Reproductive System 2cristin ungabNo ratings yet
- AsexualDocument4 pagesAsexualAR JAY FRANCONo ratings yet
- Reproduction in OrganismsDocument21 pagesReproduction in Organismskaziba stephenNo ratings yet
- ASEXUAL AND SEXUALREPRODUCTIO ExtDocument4 pagesASEXUAL AND SEXUALREPRODUCTIO ExtMakanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- General Biology II: Compare and Contrast: Reproduction in Plants and AnimalsDocument31 pagesGeneral Biology II: Compare and Contrast: Reproduction in Plants and AnimalsJoanna LapuzNo ratings yet
- Ready Reckoner BiologyDocument19 pagesReady Reckoner BiologyMrigank MitraNo ratings yet
- Summary of All Topics and DiscussionDocument55 pagesSummary of All Topics and Discussionjason balmasNo ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument17 pagesPlant Reproductionshaim xd.No ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIONDocument9 pagesREPRODUCTIONshashwatdwivedi9000No ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document33 pagesGeneral Biology 2Treshia Jazmin EguinNo ratings yet
- Plant BiotechnologyDocument62 pagesPlant Biotechnologyabdurrafihasan2023No ratings yet
- Explants: Irisan Organ Tanaman Yang Telah Disteril Yang Digunakan Sebagai Bahan Tanam Awal Dalam Kultur in VitroDocument48 pagesExplants: Irisan Organ Tanaman Yang Telah Disteril Yang Digunakan Sebagai Bahan Tanam Awal Dalam Kultur in VitroGerii PitaNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Term 3 Notes 2024Document18 pagesYear 10 Term 3 Notes 2024raghavmathur639No ratings yet
- OneShot - How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument84 pagesOneShot - How Do Organisms ReproduceMuskan GoyalNo ratings yet
- Biology HSC Notes:: Sexual AsexualDocument26 pagesBiology HSC Notes:: Sexual AsexualGeorge EskandarNo ratings yet
- Reproduction AND Development: (In Plants and Animals)Document29 pagesReproduction AND Development: (In Plants and Animals)Samarra LouisseNo ratings yet
- Open Folder DownloadsDocument6 pagesOpen Folder DownloadsAarush GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Plant and Fungal Diversity: Chapter ObjectivesDocument15 pagesThe Evolution of Plant and Fungal Diversity: Chapter Objectivesirene9tan9ailianNo ratings yet
- 2019toefl-2019 10 12Document16 pages2019toefl-2019 10 12limmmm1919No ratings yet
- Study Guide AnswersDocument3 pagesStudy Guide AnswersmisterbrownerNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Chapter 13 Meiosis, Mel Bio 17, Mel Bio 16Document32 pagesAP Bio Chapter 13 Meiosis, Mel Bio 17, Mel Bio 16EUNAH LimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Active Reading GuideDocument5 pagesChapter 10 Active Reading GuidedorothyNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument4 pagesPlant Kingdomkumarm78No ratings yet
- Meiosis and The Sexual Life Cycle Reviewer NotesDocument23 pagesMeiosis and The Sexual Life Cycle Reviewer NotesJestoni BigaelNo ratings yet
- Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology: BiologyDocument41 pagesAngiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology: BiologySem GacomsNo ratings yet
- Pteridophyte: Dryopteris (Aspidium)Document10 pagesPteridophyte: Dryopteris (Aspidium)ManashNo ratings yet
- TO Medical ParasitologyDocument65 pagesTO Medical ParasitologyMengistu MalkeNo ratings yet
- 06 ChlorophytaDocument56 pages06 ChlorophytayvonneNo ratings yet
- Obelia: Habitat, Structure and DiagramDocument24 pagesObelia: Habitat, Structure and DiagramSunil BundelaNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument13 pagesMeiosistaylorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13:meiosis and Sexual Life CyclesDocument7 pagesChapter 13:meiosis and Sexual Life Cycleskuitang100% (1)
- Foundation DesignDocument27 pagesFoundation DesignSushilkumar Magade50% (2)
- Common Plants Animals: Project Study OFDocument17 pagesCommon Plants Animals: Project Study OFGöùräv ÇhäkräbørtýNo ratings yet
- Test Series For NEET-2020 - TestNo.1 - Answer and SolutionsDocument11 pagesTest Series For NEET-2020 - TestNo.1 - Answer and SolutionsAmitesh TejaswiNo ratings yet
- Txt.05 - Std'11 - Biology - Exemplar ProblemsDocument170 pagesTxt.05 - Std'11 - Biology - Exemplar ProblemsAmruta BhalkarNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom NotesDocument25 pagesPlant Kingdom NotesV 4UNo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Campbell Biology in Focus 2nd Edition Urry Test Bank Full ChapterDocument44 pagesInstant Download PDF Campbell Biology in Focus 2nd Edition Urry Test Bank Full Chapterpaayawyukwai100% (7)
- CH 22 Introduction To Plants - Google SearchDocument1 pageCH 22 Introduction To Plants - Google Searchz82tynq64yNo ratings yet
- Algae General CharctersticsDocument16 pagesAlgae General CharctersticsSahil Azam100% (2)
- Asexual and Sexual ReproductionDocument12 pagesAsexual and Sexual ReproductionPrecious MapehNo ratings yet
- DU Botany 2014Document14 pagesDU Botany 2014Siddhartha ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Ch11 Test File-The Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument43 pagesCh11 Test File-The Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDollar'sCornerNo ratings yet
- Added Topics (NEET 2024) - Book by Dr. Anand ManiDocument58 pagesAdded Topics (NEET 2024) - Book by Dr. Anand ManiShriansh BaroniaNo ratings yet
- Aakash Botany Study Package 4 SolutionssssDocument120 pagesAakash Botany Study Package 4 SolutionssssRishika PaulNo ratings yet
- Riccia: .Genus: Riccia:-Thallus Usually RosetteDocument9 pagesRiccia: .Genus: Riccia:-Thallus Usually RosetteAditya NarvekarNo ratings yet
- Unlock SGCh28Document15 pagesUnlock SGCh28SilaxNo ratings yet