Professional Documents
Culture Documents
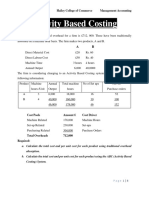
ABC and Standard Costing Problem
ABC and Standard Costing Problem
Uploaded by
MARC OLIVER CASTANEDAOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ABC and Standard Costing Problem
ABC and Standard Costing Problem
Uploaded by
MARC OLIVER CASTANEDACopyright:
Available Formats
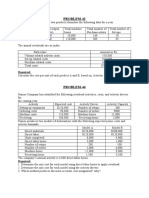
PRACTICAL ACCOUNTING PROBLEMS II
Activity-Based Costing
The budgeted manufacturing overhead costs of Zomboss Company for 2010 are as follows:
Type of Cost Cost Amount
Electric Power P 1,000,000
Work Cells 6,000,000
Materials Handling 2,000,000
Quality Control Inspections 2,000,000
Product Runs (machine setups) 500,000
Total Budgeted Overhead Costs P 11,500,000
For the last five years, the cost accounting department has been charging overhead
production costs based on machine hours. The estimated budgeted capacity for 2006 is
2,000,000 machine hours.
The president of Zomboss Company recently attended a seminar on activity-based costing.
He now believes that ABC results in more reliable cost data cost data that, in turn, will give
the company an edge in pricing over its competitors. At the president’s request, the
production manager provided the following data regarding expected 2006 activity for the cost
drivers of the preceding budgeted overhead costs.
Type of Cost Activity Drivers
Electric Power 200,000 kilowatt hours
Work Cells 1,200,000 square feet
Materials Handling 500,000 material moves
Quality Control Inspections 400,000 inspections
Product Runs (machine setups) 50,000 product runs
The Vice President of Marketing received an offer to sell 5,000 doors to a local construction
company. The VP asked the head of the cost accounting to prepare cost estimates for
producing the 5,000 doors. The head of cost accounting accumulated the following data
concerning production of 5,000 doors:
Direct material cost P 200,000
Direct labor cost P 400,000
Machine hours 10,000
Direct labor hours 20,000
Electric power-kilowatt hours 2,000
Work cells-square feet 12,000
Number of material handling moves 120
Number of quality control inspections 60
Number of product runs (setups) 30
Requirements:
1. What is the predetermined overhead rate if the traditional measure of machine hours
is used?
2. What is the manufacturing cost per door as presently accounted for?
3. What is the manufacturing cost per door under the proposed ABC method?
Prepared by: Marc Oliver B. Castañeda, CPA, MSBA Page 1
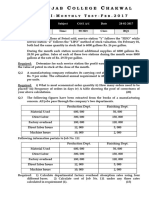
PRACTICAL ACCOUNTING PROBLEMS II
Standard Costing
Zombross Co. manufactures screen doors with the following standard quantity and cost
information per door:
Aluminum 4 sheets at P2 P 8
Copper 3 sheets at P5 15
Direct labor 7 hours at P7 49
Variable overhead 6 machine hours at P3 18
Fixed overhead 5 machine hours at P2 10
Overhead rates were based on normal monthly capacity 5,000 machine hours.
During November, the company produced only 800 doors and the following costs were
incurred in October:
Materials
Aluminum 3,400 sheets purchased and used at P2.20
Copper 2,500 sheets purchased and used at P4.20
Labor
Direct labor 5,250 hours at P8.00
Overhead
Variable overhead P11,800 (based on 4,250 machine hours)
Fixed overhead P9,500 (based on 4,250 machine hours)
Requirements:
1. Material Price Variance for each material
2. Material Quantity Variance for each material
3. Total Material Variance for each material
4. Labor Rate variance
5. Labor Efficiency variance
6. Total Labor Variance
7. Overhead Spending Variance
8. Overhead Efficiency Variance
9. Total Overhead Variance
10. Fixed Overhead Spending Variance
11. Prepare Journal entries
Prepared by: Marc Oliver B. Castañeda, CPA, MSBA Page 2
You might also like
- Midterm Quiz 2 - Problem and Answer KeyDocument6 pagesMidterm Quiz 2 - Problem and Answer KeyRynette Flores100% (1)
- Problem Solving Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument6 pagesProblem Solving Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisFranklin Galope100% (5)
- Strongholds of HeritageDocument9 pagesStrongholds of Heritageusman zafarNo ratings yet
- Absorption & Marginal CostingDocument17 pagesAbsorption & Marginal CostingAhmed Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- P2 09Document8 pagesP2 09Mark Levi CorpuzNo ratings yet
- She's Yours For The TakingDocument281 pagesShe's Yours For The TakingMichel Aus Lönneberga75% (8)
- Barcelona S Natural WonderDocument2 pagesBarcelona S Natural WonderDavid CortésNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Optimum Design Chasis of Three Wheel Auto Rickshaw Passenger VehicleDocument16 pagesAnalysis and Optimum Design Chasis of Three Wheel Auto Rickshaw Passenger VehiclenahomNo ratings yet
- Activity Based CostingDocument6 pagesActivity Based CostingAngel Alejo AcobaNo ratings yet
- Asian Academy For Excellence Foundation, Inc.: Practical Accounting 2-Cost CPA Review O2017Document6 pagesAsian Academy For Excellence Foundation, Inc.: Practical Accounting 2-Cost CPA Review O2017didi chenNo ratings yet
- ADDITIONAL PROBLEMS Variable and Absorption and ABCDocument2 pagesADDITIONAL PROBLEMS Variable and Absorption and ABCkaizen shinichiNo ratings yet
- AFAR Set BDocument11 pagesAFAR Set BRence Gonzales0% (2)
- Cost Accounting and ControlDocument8 pagesCost Accounting and ControlJevbszen RemiendoNo ratings yet
- Activity Based Costing HCCDocument8 pagesActivity Based Costing HCCIhsan danishNo ratings yet
- ABC AssignmentDocument3 pagesABC AssignmentSunil ThapaNo ratings yet
- ABC Costing Assignment Problems 209Document3 pagesABC Costing Assignment Problems 209DenNo ratings yet
- Unit4 ActivityDocument11 pagesUnit4 ActivityJasper John NacuaNo ratings yet
- Activity Based Costing ExerciseDocument5 pagesActivity Based Costing Exercisejudeaharmony.wamildaNo ratings yet
- MAS Final RequirementDocument19 pagesMAS Final RequirementDonna Zandueta-TumalaNo ratings yet
- Activity Based CostingDocument5 pagesActivity Based CostingMAZLIZA AZUANA ABDULLAHNo ratings yet
- Costs Concepts and ClassificationDocument14 pagesCosts Concepts and Classificationsheng100% (1)
- Name: Score: Prof. Mark Lester T. Balasa, Cpa, Mba Date:: Standard CostingDocument3 pagesName: Score: Prof. Mark Lester T. Balasa, Cpa, Mba Date:: Standard CostingCherrylane EdicaNo ratings yet
- Problem in Activity Based CostingDocument3 pagesProblem in Activity Based CostingLee Thomas Arvey FernandoNo ratings yet
- Activity Based CostingproblemsDocument6 pagesActivity Based CostingproblemsDebarpan HaldarNo ratings yet
- Hand-Out 4 - ABC and Support Cost AllocationDocument2 pagesHand-Out 4 - ABC and Support Cost AllocationJerric CristobalNo ratings yet
- HACC428 Tutorial QuestionsDocument36 pagesHACC428 Tutorial QuestionstapiwanashejakaNo ratings yet
- Cost Chap 6 ContinuationDocument7 pagesCost Chap 6 ContinuationPeter Paul DeiparineNo ratings yet
- Exer 2 (Overhead) QDocument2 pagesExer 2 (Overhead) QFerl ElardoNo ratings yet
- CA 07 - Standard CostingDocument3 pagesCA 07 - Standard CostingJoshua UmaliNo ratings yet
- WDocument9 pagesWSamantha CabugonNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 QuestionsDocument4 pagesTutorial 4 QuestionsSunay PNo ratings yet
- Answer Key For Strategic Cost Management MC QuestionsDocument18 pagesAnswer Key For Strategic Cost Management MC QuestionsDalia DelrosarioNo ratings yet
- Matarial & FOH Half Feb 2017Document1 pageMatarial & FOH Half Feb 2017farukhmairaNo ratings yet
- Standard CostingDocument3 pagesStandard CostingElijah MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Answer Key For Strategic Cost Management - CompressDocument19 pagesAnswer Key For Strategic Cost Management - CompressMikee RizonNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting ExercisesDocument1 pageCost Accounting ExercisesRaniel PamatmatNo ratings yet
- Kuis Paralel AML - UTSDocument4 pagesKuis Paralel AML - UTSGrace EsterMNo ratings yet
- JOB ORDER COSTING-Production LossesDocument7 pagesJOB ORDER COSTING-Production LossesJude TadiosNo ratings yet
- Standard CostingDocument3 pagesStandard CostingSergio, JesharelleNo ratings yet
- Cost Acctg Lecture Inventory Management ABCDocument5 pagesCost Acctg Lecture Inventory Management ABCMikay Gabion0% (1)
- Revision Week 1. Questions. Question 1. Cost of Goods Manufactured, Cost of Goods Sold, Income Statement. (A)Document5 pagesRevision Week 1. Questions. Question 1. Cost of Goods Manufactured, Cost of Goods Sold, Income Statement. (A)Sujib BarmanNo ratings yet
- ABC Quiz ProblemsDocument6 pagesABC Quiz Problemslou-924No ratings yet
- Problem-42: RequiredDocument7 pagesProblem-42: RequiredRADHIKA V HNo ratings yet
- Job Costing Home Work Question 1Document3 pagesJob Costing Home Work Question 1Simbai JowaNo ratings yet
- Activity Based Costing-ExerciseDocument4 pagesActivity Based Costing-ExerciseKevin James Sedurifa OledanNo ratings yet
- Planning, Control and Performance Management: Time Allowed 3 Hours ALL FOUR Questions Are Compulsory and MUST Be AnsweredDocument5 pagesPlanning, Control and Performance Management: Time Allowed 3 Hours ALL FOUR Questions Are Compulsory and MUST Be Answeredapi-19836745No ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document2 pagesQuiz 1rosalesdelacruz816No ratings yet
- QUIZ - Cost1.atest PaperDocument3 pagesQUIZ - Cost1.atest PaperArnold Ramos ChuidianNo ratings yet
- Factory OverheadDocument2 pagesFactory OverheadKeanna Denise GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Job Order Costing Spoilage Defective - StudentDocument4 pagesJob Order Costing Spoilage Defective - StudentVince Christian PadernalNo ratings yet
- Activity in Activity Based Cost AccountingDocument4 pagesActivity in Activity Based Cost AccountingLucy HeartfiliaNo ratings yet
- Ho Abc0abmDocument5 pagesHo Abc0abmAngel Alejo AcobaNo ratings yet
- Handout 1 Cost ManagementDocument9 pagesHandout 1 Cost ManagementPatricia AtienzaNo ratings yet
- 602 Assignment 1Document8 pages602 Assignment 1Irina ShamaievaNo ratings yet
- Bos 45818 P 3Document25 pagesBos 45818 P 3Sourav ChamoliNo ratings yet
- CAC Quiz No. 3 PDFDocument14 pagesCAC Quiz No. 3 PDFEdi wow WowNo ratings yet
- Test 3Document2 pagesTest 3Kim LimosneroNo ratings yet
- Afar Job Order Costing Spoilage DefectiveDocument4 pagesAfar Job Order Costing Spoilage DefectiveKaye Angelie UsogNo ratings yet
- T5 - Activity-Based Costing - Open Book TeamDocument3 pagesT5 - Activity-Based Costing - Open Book TeamSujib BarmanNo ratings yet
- BAC1624 - Tutorial 1Document4 pagesBAC1624 - Tutorial 1Amiee Laa PulokNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 ABC System For StudentsDocument14 pagesChapter 5 ABC System For StudentsNour Al Kaddah100% (1)
- Additive Manufacturing and Strategic Technologies in Advanced CeramicsFrom EverandAdditive Manufacturing and Strategic Technologies in Advanced CeramicsKiyoshi ShimamuraNo ratings yet
- 77th Conference on Glass Problems: A Collection of Papers Presented at the 77th Conference on Glass Problems, Greater Columbus Convention Center, Columbus, OH, November 7-9, 2016From Everand77th Conference on Glass Problems: A Collection of Papers Presented at the 77th Conference on Glass Problems, Greater Columbus Convention Center, Columbus, OH, November 7-9, 2016S. K. SundaramNo ratings yet
- ApachetaDocument17 pagesApachetaJesús MazaNo ratings yet
- Steel Bar:: Basically Mild Steel BarsDocument7 pagesSteel Bar:: Basically Mild Steel BarsEdu PlatformNo ratings yet
- ABB KR Dry Type Transformer CatalogDocument16 pagesABB KR Dry Type Transformer CatalogGia Minh ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Green Areas in Urban Landscape of Lucknow: Need For Holistic Intervention With Respect To River GomtiDocument10 pagesTransformation of Green Areas in Urban Landscape of Lucknow: Need For Holistic Intervention With Respect To River GomtiASHUTOSH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Measurement LabDocument4 pagesMeasurement LabHenessa GumiranNo ratings yet
- Electrode Consumption PDFDocument1 pageElectrode Consumption PDFharold_bhieNo ratings yet
- Air-Main Charging Systems: DHS 4.0 Series Compact Assistants That Make A Big DifferenceDocument12 pagesAir-Main Charging Systems: DHS 4.0 Series Compact Assistants That Make A Big DifferenceandreaNo ratings yet
- EschatologyDocument6 pagesEschatologycorne.g.zaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7,8 Water PollutionDocument13 pagesLecture 7,8 Water PollutionParva PatelNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of The Lymphatic System: Melody A. SwartzDocument18 pagesThe Physiology of The Lymphatic System: Melody A. SwartzFeña Peña GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Paik I Expose The Music EN HHDocument4 pagesPaik I Expose The Music EN HHHanna B. HöllingNo ratings yet
- Biologic Width - The No Encroachment Zone: I J D ADocument8 pagesBiologic Width - The No Encroachment Zone: I J D AJinny ShawNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.1 2 Unpacking The Self The Physical Self Sexual Self.Document81 pagesLesson 2.1 2 Unpacking The Self The Physical Self Sexual Self.Jonel Maristela100% (1)
- Fortune Is Unpredictable and MutableDocument4 pagesFortune Is Unpredictable and MutablenucleaNo ratings yet
- Res#2018-697 PROVINCIAL ORDINANCE NO. 2018-177 - Responsible Pet Ownership Ordinance of 2018Document6 pagesRes#2018-697 PROVINCIAL ORDINANCE NO. 2018-177 - Responsible Pet Ownership Ordinance of 2018Imarie Pinuela100% (1)
- Thermal Decomposition of Calcium Carbonate PDFDocument3 pagesThermal Decomposition of Calcium Carbonate PDFSriArthiNo ratings yet
- CCTV PoleDocument180 pagesCCTV PoleAnonymous zMWvcTNo ratings yet
- 121 Hu SC90Document8 pages121 Hu SC90rocks tusharNo ratings yet
- Cleaner Production Leather ProductionDocument20 pagesCleaner Production Leather ProductionThắngNguyễnVănNo ratings yet
- Revised Neurophysiology of Pain QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesRevised Neurophysiology of Pain QuestionnaireivanNo ratings yet
- Hatz Diesel B Series BrochureDocument8 pagesHatz Diesel B Series BrochureColdbloodedbikerNo ratings yet
- The Excitement and Celebratory Spirit That Diwali Brings Is Unmatchable. Celebrating Eco Friendly Diwali With Friends and Family Has Its Own CharmDocument2 pagesThe Excitement and Celebratory Spirit That Diwali Brings Is Unmatchable. Celebrating Eco Friendly Diwali With Friends and Family Has Its Own CharmShreyansh TiwariNo ratings yet
- GemologyDocument7 pagesGemologyManish MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Air Force Catalog 21-209, Volume 2afcat21-209v2Document43 pagesAir Force Catalog 21-209, Volume 2afcat21-209v2jmkoh78No ratings yet
- UV Technology For DisinfectionDocument95 pagesUV Technology For DisinfectionMINEC YARACUYNo ratings yet
- Adinkra Are Symbols From Ghana ThatDocument9 pagesAdinkra Are Symbols From Ghana ThatAlison_VicarNo ratings yet