Professional Documents
Culture Documents
States Were Selected For Each: Arthur M. (Art) Dowell, III, PE Process Improvement Institute
States Were Selected For Each: Arthur M. (Art) Dowell, III, PE Process Improvement Institute
Uploaded by
Jinyoung ChoiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
States Were Selected For Each: Arthur M. (Art) Dowell, III, PE Process Improvement Institute
States Were Selected For Each: Arthur M. (Art) Dowell, III, PE Process Improvement Institute
Uploaded by
Jinyoung ChoiCopyright:
Available Formats
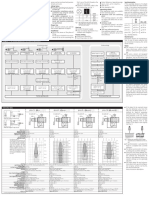
What Is the Real Risk Reduction for 3 Sensors Using the Mid-Value for
Control and 2oo3 Voting for Safety?
Arthur M. (Art) Dowell, III, PE
Process Improvement Institute
What happens to the risk when two good States were selected for each Recommendations
ideas are combined? degradation path • If the SIF trips on the 2oo3 sensors, the BPCS control loop
shall be automatically placed in manual and the output
• Median (or mid-value) • 2oo3 voting for safety • 3 sensors working – dark blue to the valve shall be set to 0. Required to avoid a “race”
Select for 3 control sensors sensors condition in which the control loop sees a 0 PV and
• 1 sensor failed, drift (dangerous detected or dangerous
Median Select SIF Solenoid Valves attempts to open the control valve.
or Mid-Value Select 2oo3 Voting undetected), bad PV (detected) – light blue – control &
• The loops for each of the three sensors shall be powered
Instr. Air
Instr. Air
Supply
SIF are still functional
by the SIF logic solver.
Input Logic Output
Input CPU Output Cards Solver Cards
Supply
• Unavailability states with 2 or 3 sensors failed. – light red
Cards Cards
I/P
S-12 • There are other schemes to share process variables
Vent Vent • Tripped states – light green between the SIF and the BPCS but analysis of their failure
Positioner
modes is beyond the scope of this paper.
SA SB SC
1 2 3
• Provision should be made for the BPCS to calculate the
BPCS Sensors BPCS Valve
SIF Sensors SIF Valve A SIF Valve B
Transitions between states mean value correctly when the sensors are in a degraded
• Based on failure rates (and number of sensors that have state
not yet failed) and repair rate. • 1 sensor with bad PV (detected)
Advantages of each independent • Sensor failure rate, λ = 1.67E-2/year • 1 sensor drifted (detected)
configuration • DD Drift, δδ = 0.8* λ = 1.34E-2/yr.
• DU Drift, δυ = 0.1* λ = 1.67E-3/yr. • It is critical that detected failures be repaired within 72
• Median (or mid-value) • 2oo3 voting for safety hours.
• Bad PV, βπω = 0.1* λ = 1.67E-3/yr.
Select for 3 control sensors sensors • Future work: include more explanation for human factors
• Repair rate, µ = 121.67/yr.
• Reduced trips from • Reduced spurious trips (72 hr. MTTR) that introduce errors during testing [4].
transmitters that drift or that • Lower PFD than 1oo1 • Proof Test Interval = 1 year
have bad PV voting
BPCS Loops are Red; SIF Loops are Blue
Markov Model References
1. IEC 61511-1:2016+AMD1:2017 CSV, Consolidated version: Functional safety -
Control & SIF are independent! (Required by Safety instrumented systems for the process industry sector - Part 1: Framework,
definitions, system, hardware and application programming requirements,
[1, 2]) International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), 2010, Geneva, Switzerland.
2. ANSI/ISA-61511-1-2018 / IEC 61511-1:2016+AMD1:2017 CSV, Functional Safety –
Median Select 2oo3 Voting Safety Instrumented Systems for the Process Industry Sector – Part 1: Framework,
SIF Solenoid Valves definitions, system, hardware and application programming requirements (IEC
or Mid-Value Select Input Logic Output
Cards Solver Cards 61511-1:2016+AMD1:2017 CSV, IDT), International Society of Automation,
Instr. Air Instr. Air Research Triangle Park, North Carolina.
Input CPU Output Supply Supply
Cards Cards 3. CCPS, Layer of Protection Analysis, Simplified Process Risk Assessment, American
I/P Institute of Chemical Engineers, New York, New York, 2001.
Vent Vent 4. ISA-TR84.00.02-2015, Safety Integrity Level Verification of Safety Instrumented
Functions, Annex E, Markov Analysis. International Society of Automation,
Positioner Research Triangle Park, North Carolina.
1 2 3 SA SB SC 5. “SIL-3, SIL-2, and Unicorns (There Is a High Probability Your SIL 2 and SIL 3 SIFs Have
No Better Performance Than SIL 1)”, A.M. (Art) Dowell, III, W. Bridges, M. Massello,
and H.W. (Hal) Thomas, 15th Global Congress on Process Safety, New Orleans,
BPCS Sensors SIF Sensors BPCS Control Valve SIF Valve A SIF Valve B LA, AIChE, March 31-April 3, 2019
Acronym Definition
1oo1 1 out of 1 voting
Sensors shared between SIF and BPCS 2oo3 2 out of 3 voting
BPCS Basic Process Control System
βπω Bad PV failure rate
Signals CPU Central Processing Unit (or Controller Card)
from SIF DD Dangerous Detected
Sensors to
BPCS (hard
Input Logic Output
Cards Solver Cards
DU Dangerous Detected
BPCS
Glossary
wired)
SIF δδ Drift dangerous detected failure rate
CPU Output
Drift dangerous undetected failure rate
Input
Cards Cards
2oo3 Voting δυ
I/P Current to pneumatic transducer
λ Failure rate, per year
Median Select
or Mid-Value Select mA Milliampere
MTTR Mean Time To detect and Repair, years. 1/MTTR = µ
A B C µ repair rate, per year
SIF Sensors & PFD Probability of Failure on Demand
BPCS Sensors O = unavailability state Pm = Mean probability of a state PV Process Variable
Mean unavailability states (PFD) = 5.6E-4 Mean availability states = 9.99E-1 SIF Safety Instrumented Function
SIL Safety Integrity Level
How to Estimate Relative Risk of Sensors
Shared?
• Fault Tree Analysis could be used, but it is difficult to model
Conclusions Calculations done by
failure modes and failure sequences in time.
• Markov models can handle different failure modes and
•For 2oo3 sensor voting, the Probability of Failure • The Markov Model Module in Reliability
Workbench 13.0.2.0 provided by
failure sequences in time. on Demand (PFD) is 5.62E-4. This is a reasonable Isograph LTD.
• A Markov model was used [3].
• For simplicity, the model was limited to the sensors value for the sensor part of an SIF.
configuration.
•For median select or mid-value select for control
ART DOWELL, III Principal Process Safety Engineer
sensors, the expression PFD = λT/2 is solved for λ. adowell@piii.com
For a 1 year test interval, the failure rate, λ, for the Art has a BA and BS in Chemical Engineering and has more than 50 years of process safety
experience, including 42 years at Rohm & Haas; now The Dow Chemical Company. Art has
control sensors is 1.12E-3/yr, an order of published more than 50 papers, many on PHA, LOPA, and SIS implementation.
PII has helped more than a hundred companies implement process safety since 2003. This
includes leading hundreds of PHAs for both new projects and existing plants and training
magnitude lower than the single sensor failure more than 4000 PHA leaders and scribes. PII staff has performed more than 1000 LOPA and
more than 1000 SIL Verification.
rate of 1.67E-2/yr.
You might also like
- Model CC-D: Instruction ManualDocument172 pagesModel CC-D: Instruction ManualBruce Adorno100% (2)
- Vibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisFrom EverandVibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- J9A Manual English 1766 Adndm 2589Document138 pagesJ9A Manual English 1766 Adndm 2589static_fluxNo ratings yet
- Basic Two Stroke Tuning by Eric Gorr (I Think)Document7 pagesBasic Two Stroke Tuning by Eric Gorr (I Think)Dr DNo ratings yet
- Cat 500kva GensetDocument613 pagesCat 500kva GensetGanapati Hegde100% (2)
- Trx4841a and Trx4851a Intellivue TransceiversDocument40 pagesTrx4841a and Trx4851a Intellivue TransceiverspaskNo ratings yet
- Fault Tracing: FMI 3: Checking The Sensor CircuitDocument1 pageFault Tracing: FMI 3: Checking The Sensor Circuituser1No ratings yet
- GE LOGIC P9-P7 BASIC USER MANUAL 5791623-100 Rev.3 Vol.2 PDFDocument486 pagesGE LOGIC P9-P7 BASIC USER MANUAL 5791623-100 Rev.3 Vol.2 PDFmohamed elborlsyNo ratings yet
- Pundit Lab Operating Instructions English HighDocument32 pagesPundit Lab Operating Instructions English HighRhyza Jullianne RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Alaris GW - OxpsDocument77 pagesAlaris GW - OxpsEdgar DauzonNo ratings yet
- 2023 PS MOR EHS Dashboard Report - Oct-23Document15 pages2023 PS MOR EHS Dashboard Report - Oct-23vinay kumarNo ratings yet
- Manual de Aplicaciones NemioDocument454 pagesManual de Aplicaciones NemioJorge SanchezNo ratings yet
- Elmos High Voltage Direct Drive Ultrasonic Sensor Ic E52433 IsDocument2 pagesElmos High Voltage Direct Drive Ultrasonic Sensor Ic E52433 IsЕвгений ИвановNo ratings yet
- OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS. MODEL SP-5A 13 Range Analog MultimeterDocument12 pagesOPERATING INSTRUCTIONS. MODEL SP-5A 13 Range Analog Multimetercharles blairNo ratings yet
- IntellichargeforexitsDocument2 pagesIntellichargeforexitsregist81No ratings yet
- Ba Eng Lpc+xxxcfiDocument3 pagesBa Eng Lpc+xxxcfipecf VOLTESTNo ratings yet
- Knick PH Transmitter ManualDocument6 pagesKnick PH Transmitter ManualViktor SalánkiNo ratings yet
- Ba Eng Ews-Xxxm18Document2 pagesBa Eng Ews-Xxxm18pecf VOLTESTNo ratings yet
- How To Use The 3300 XL Shaft Micrometer Kit SetupDocument2 pagesHow To Use The 3300 XL Shaft Micrometer Kit SetupLinh LyNo ratings yet
- Art Evo Service M503-E342Document30 pagesArt Evo Service M503-E342Shahmir ShahidNo ratings yet
- HASSAN InstrumentationDocument12 pagesHASSAN InstrumentationGodlisten NyariNo ratings yet
- Ludlum Model 3 Operation Manual - Feb2013Document42 pagesLudlum Model 3 Operation Manual - Feb2013Bil MinarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Monitoring and ControlDocument45 pagesChapter 3 Monitoring and ControlabiyyaNo ratings yet
- Ba Eng Nano-XxcfDocument2 pagesBa Eng Nano-Xxcfpecf VOLTESTNo ratings yet
- User Guia TDR2000-2Document135 pagesUser Guia TDR2000-2Casttell PaulNo ratings yet
- DWDM Optical Power DebuggingDocument17 pagesDWDM Optical Power DebuggingJuancarlos ArrietaNo ratings yet
- Piramid xl2Document17 pagesPiramid xl2vico2711No ratings yet
- HtutdcDocument5 pagesHtutdcKhả Phúc 2No ratings yet
- Service Relay 87BDocument35 pagesService Relay 87BNguyễn Phúc ThưởngNo ratings yet
- Belt Tension Checking Tool Use1Document14 pagesBelt Tension Checking Tool Use1JohnnoNo ratings yet
- 02-Relay Operating PrinciplesDocument36 pages02-Relay Operating Principlesfdsfs2131No ratings yet
- As 104811 Ix-Series-Pcsoft SG 96M15144 GB WW 1059-2Document36 pagesAs 104811 Ix-Series-Pcsoft SG 96M15144 GB WW 1059-2carlos lopez hernandezNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual Section 3 390821Document10 pagesOperation Manual Section 3 390821PiratadelNorteNo ratings yet
- Machine Conditioning Monitoring SystemDocument49 pagesMachine Conditioning Monitoring SystemSanthosh V SamudramNo ratings yet
- EnerLyzer Live Handout ENUDocument4 pagesEnerLyzer Live Handout ENUtom.grebertNo ratings yet
- Operational and Maintenance Manual Ips System: Rev.00: Al Mazroui Medical & Chemical SuppliesDocument23 pagesOperational and Maintenance Manual Ips System: Rev.00: Al Mazroui Medical & Chemical SuppliesanfalapNo ratings yet
- Ba Eng Pico+xxxtf FDocument3 pagesBa Eng Pico+xxxtf Fpecf VOLTESTNo ratings yet
- Digital Selection Guide - 3Document46 pagesDigital Selection Guide - 3Akash YadavNo ratings yet
- V&T 2900CUV Service Manual (New Board) 2010513Document9 pagesV&T 2900CUV Service Manual (New Board) 2010513nelubaiNo ratings yet
- 2 PO - SM2201 - E01 - 1 GPON Routine MaintanceDocument28 pages2 PO - SM2201 - E01 - 1 GPON Routine MaintanceErnestoLopezGonzalezNo ratings yet
- C2020 Installation & Operation Guide Rev.01Document12 pagesC2020 Installation & Operation Guide Rev.01Dave PotterNo ratings yet
- TI375FENDocument28 pagesTI375FENDenisNo ratings yet
- Getting Started With Intuition-E v3.0Document17 pagesGetting Started With Intuition-E v3.0Beceanu CristianNo ratings yet
- Operating Instructions Multipulse de en FR It PT Es ZH Ja Ru Im0084414Document38 pagesOperating Instructions Multipulse de en FR It PT Es ZH Ja Ru Im0084414Andre RomanoNo ratings yet
- Probe Tack Tester: MODEL PT-1000 Operating InstructionsDocument17 pagesProbe Tack Tester: MODEL PT-1000 Operating InstructionsSarah LinvilleNo ratings yet
- T200A Single Phase Universal Test SetDocument8 pagesT200A Single Phase Universal Test SetpiticelNo ratings yet
- 35 Fault FindingsDocument32 pages35 Fault FindingsKARTHIK S SNo ratings yet
- BeneView T1 - Quick Guide - (EN) - v4.0Document12 pagesBeneView T1 - Quick Guide - (EN) - v4.0anhhp8xNo ratings yet
- Installation Troubleshooting: Fault Tracing InfoDocument9 pagesInstallation Troubleshooting: Fault Tracing InfoHassan Mody TotaNo ratings yet
- Digital Ripple & Noise Meter: No Hesitation On ReadingDocument4 pagesDigital Ripple & Noise Meter: No Hesitation On Readingรุ่งทิวา ทวีทรัพย์No ratings yet
- Time Domain Reflectometer Megger TDR2000Document161 pagesTime Domain Reflectometer Megger TDR2000shashi bhushan singhNo ratings yet
- Preliminary: Idle Validation Switch Circuit - TestDocument2 pagesPreliminary: Idle Validation Switch Circuit - TestJose Cruz Martinez MedinaNo ratings yet
- 2016-06 Online Monitoring Softsensor PerformanceDocument6 pages2016-06 Online Monitoring Softsensor PerformancejmpbarrosNo ratings yet
- Sti Wiring Sys PDFDocument148 pagesSti Wiring Sys PDFEdwinNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet - MI 5 Interface UnitDocument2 pagesData Sheet - MI 5 Interface UnitleonNo ratings yet
- S&T UNIT I INTRODUCTION Part A (2mark)Document3 pagesS&T UNIT I INTRODUCTION Part A (2mark)senthilkumar100% (1)
- 030 2076 00RevA Eng Elance DownloadDocument4 pages030 2076 00RevA Eng Elance DownloadKaranNo ratings yet
- FT-2500 Advanced Tachometer: Operation ManualDocument12 pagesFT-2500 Advanced Tachometer: Operation ManualMD Shahidul HoqueNo ratings yet
- Corometrics 170 Monitor - Service Manual (120-248)Document129 pagesCorometrics 170 Monitor - Service Manual (120-248)Igor78No ratings yet
- Lecture10 InstrumentationDocument21 pagesLecture10 InstrumentationbobNo ratings yet
- Patent Health Monitoring System 1Document19 pagesPatent Health Monitoring System 1imtiaj.amadershomoyNo ratings yet
- Towards The Application of Safety Integrity Level For Improving Process SafetyDocument6 pagesTowards The Application of Safety Integrity Level For Improving Process SafetyJinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- Attachment 01Document104 pagesAttachment 01Jinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- Escape Route Improvement by Specialized Escape and Evacuation Simulation For Oil and Gas FacilityDocument6 pagesEscape Route Improvement by Specialized Escape and Evacuation Simulation For Oil and Gas FacilityJinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- POSTER Four Gaps in PSM Rev FDocument1 pagePOSTER Four Gaps in PSM Rev FJinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- Functional Safety Management SystemDocument18 pagesFunctional Safety Management SystemJinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- Making Sure IEs and IPLs Are Included in Management Systems - Rev CDocument24 pagesMaking Sure IEs and IPLs Are Included in Management Systems - Rev CJinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- TextbookDocument294 pagesTextbookJinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- WebtocDocument7 pagesWebtocJinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- 4 Gaps in PSM - R1 - GCPS 2019Document24 pages4 Gaps in PSM - R1 - GCPS 2019Jinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- FMDS0700Document21 pagesFMDS0700Jinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- 19th Gcps Online Grid v16 4Document11 pages19th Gcps Online Grid v16 4Jinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- 2 Chapter 7-1 - 7-4 PDFDocument51 pages2 Chapter 7-1 - 7-4 PDFJinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- 17th - Gcps - Dowell - Is Your SIF Trying To Do Too Much FinalDocument7 pages17th - Gcps - Dowell - Is Your SIF Trying To Do Too Much FinalJinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- Gains From Getting Near Misses Reported: William Bridges Process Improvement Institute, Inc. Tennessee, USADocument25 pagesGains From Getting Near Misses Reported: William Bridges Process Improvement Institute, Inc. Tennessee, USAJinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- Di 2021 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1802 022064Document11 pagesDi 2021 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1802 022064Jinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- Dowell - Art - PII - Generator - 16th - Gcps - Paper - PPSS - Paper - Final 2020-08-04Document9 pagesDowell - Art - PII - Generator - 16th - Gcps - Paper - PPSS - Paper - Final 2020-08-04Jinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- Process Safety Competency - Effective Approaches To Creating and Judging Competency On Process SafetyDocument18 pagesProcess Safety Competency - Effective Approaches To Creating and Judging Competency On Process SafetyJinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- Fiabilit Nouveau Composant 1996Document9 pagesFiabilit Nouveau Composant 1996Jinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- Llbrarv Loan: C E N T R A L Research Library Document CollectionDocument38 pagesLlbrarv Loan: C E N T R A L Research Library Document CollectionJinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- Lopa in Action: Making Sure Initiating Events (Ies) and Independent Protection Layers (Ipls) Are Included in Integrated Management SystemsDocument16 pagesLopa in Action: Making Sure Initiating Events (Ies) and Independent Protection Layers (Ipls) Are Included in Integrated Management SystemsJinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- Ipl Rules: Independent Capable Maintained AuditedDocument1 pageIpl Rules: Independent Capable Maintained AuditedJinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- Definitions: Maximum Out-of-Service Time (MOST)Document1 pageDefinitions: Maximum Out-of-Service Time (MOST)Jinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- Here and Here+ - MANUALDocument3 pagesHere and Here+ - MANUALFazrulNo ratings yet
- Fmea 39 PDF FreeDocument5 pagesFmea 39 PDF Freeahya azizahNo ratings yet
- Test Case and Use CasesDocument19 pagesTest Case and Use Casesapi-3732800No ratings yet
- Railway Reservation SysytemDocument63 pagesRailway Reservation SysytemParag Waghmare0% (1)
- Metrics To Power DevOpsDocument38 pagesMetrics To Power DevOpseto laho100% (1)
- PPT For Seminar On W EngineDocument19 pagesPPT For Seminar On W Engineasif shaikhNo ratings yet
- OWASP Application Security Verification Standard 4.0-Vn-V1Document80 pagesOWASP Application Security Verification Standard 4.0-Vn-V1Nguyên ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Report Builder EditionsDocument1 pageReport Builder EditionsjosefinoeNo ratings yet
- I&C Inspection and Test Plan - NWC Dhurma Pump Station, Pp11, Pp12, Pp13Document16 pagesI&C Inspection and Test Plan - NWC Dhurma Pump Station, Pp11, Pp12, Pp13Mohd Sami UddinNo ratings yet
- BSGDocument14 pagesBSGsri_sriNo ratings yet
- LogDocument74 pagesLogQhayiya NjomeniNo ratings yet
- Technical Information For PERFECTA PREMIUM LineDocument9 pagesTechnical Information For PERFECTA PREMIUM LineDevraj KulasekarNo ratings yet
- CarnacDocument2 pagesCarnacNeymat GurbanovNo ratings yet
- CSC404 Chapter2 Part1Document27 pagesCSC404 Chapter2 Part1Nurain Syamimi NadiaNo ratings yet
- L1 CV4 Web 2019 - (Blue-Book) PDFDocument36 pagesL1 CV4 Web 2019 - (Blue-Book) PDFRCesar Ag100% (1)
- Computer Science: DebuggingDocument8 pagesComputer Science: Debuggingrahul kumar jhaNo ratings yet
- Definition of Technical TermsDocument17 pagesDefinition of Technical TermsAyush HazarikaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Software EngineeringDocument142 pagesIntroduction To Software EngineeringJaro Alexander AguilarNo ratings yet
- M1 ABCDE-Android IntroductionDocument66 pagesM1 ABCDE-Android IntroductionAlroy AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Amna Mazhar Quiz 2 ITCDocument4 pagesAmna Mazhar Quiz 2 ITCAmna MazharNo ratings yet
- Ghezzi, C., Jazayeri, M. y Mandrioli, D. (2002) - Fundamentals of Software Engineering.Document626 pagesGhezzi, C., Jazayeri, M. y Mandrioli, D. (2002) - Fundamentals of Software Engineering.Sebastian CubidesNo ratings yet
- Requirement and Specifications: Chapter - 3Document17 pagesRequirement and Specifications: Chapter - 3Chandrashekhar KuriNo ratings yet
- Car Rental SystemDocument24 pagesCar Rental SystemMalaika WaseemNo ratings yet
- Nutanix Tech Notes System ReliabilityDocument4 pagesNutanix Tech Notes System ReliabilityRochdi BouzaienNo ratings yet
- ISTQB Foundation Sample Question Paper No 13 To 15Document19 pagesISTQB Foundation Sample Question Paper No 13 To 15sumit3344No ratings yet
- Selenium With Java Course ContentDocument26 pagesSelenium With Java Course Contentpraveen murugesanNo ratings yet
- Shagufta Sheikh Resume-1Document3 pagesShagufta Sheikh Resume-1Santosh GanganeNo ratings yet
- 2.3.1.2 Packet Tracer - Sensors and The PT MicrocontrollerDocument4 pages2.3.1.2 Packet Tracer - Sensors and The PT Microcontrollernaif arroishedNo ratings yet