Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GCSE Formula Sheet
GCSE Formula Sheet
Uploaded by
Sara AyaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GCSE Formula Sheet
GCSE Formula Sheet
Uploaded by
Sara AyaCopyright:
Available Formats
www.mymathscloud.
com © MyMathsCloud
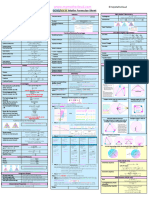
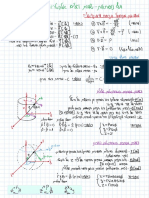
GCSE/iGCSE Maths Formulae Sheet
2D Shapes Compound Measures Right Angled Trigonometry
! Speed speed=
'*)J&+/F Pythagoras !! + # ! = % !
Area of Triangle x base x height J*HF if given hyp⟹subtract, if finding hyp⟹add
" H&))
Density density= "## &'( "##
Area of Parallelogram base x height E"QIHF SOHCAHTOA sin * ° = , c./ *° = , 1!2 *° =
Pressure R"N/F $%# $%# &'(
Area of Rectangle !×# pressure=
&NF&
!
Area of Trapezoid (sum of parallel sides) x height
"
Circumference & Area: % = 2(), + = () "
Circle Exact Trig Values
Length of an arc #
× 2()
$%&
Area of a Sector #
× () "
$%&
Non Right-Angled Trigonometry
3D Shapes
Statistics Sine Rule Finding a side:
&
=
-
=
/
Cuboid Surface area !" = 2%& + 2%( + 2&( RNFSIF+/% )*+, )*+. )*+0
Frequency Density Frequency density = 123 , 123 . 123 0
where x, y , z are side lengths /Q&)) T*'J$ Finding an angle:
&
=
-
=
/
Cuboid Volume ) = %&( Cosine Rule Finding a side: !! = #! + % ! − 2#% cos <
-!6/ !4&!
where x, y , z are side lengths Finding an angle: < = cos 45 = >
!-/
Cylinder Surface Area !" = 2*+ℎ + 2*+ ! Area of Triangle 1
Note: Curved part: 2πrh /&JFD"N% RNFSIF+/% !#/@2A
Pie chart Angle= × 360 2
J"J&Q & - /
Cylinder Volume ) = *+ ! ℎ Sine Rule Finding a side: = =
Cumulative frequency This is a running total of the frequencies )*+, )*+. )*+0
Cone Surface Area !" = *+1 + *+ ! Box Plot Finding an angle:
&
=
-
=
/
)*+, )*+. )*+0
Note: Curved part: *+1, 1 is slant length
1 Circle Theorems
Cone Volume ) = *+ ! ℎ
3 Angle at the centre is double the angle at the circumference
Sphere Surface Area !" = 4*+ !
Note: Hemisphere 3*+ !
Sphere Volume 4
5 = *+ < Fractions/Decimals/Percentages
3
!
Note: Hemisphere= *+ < Simplifying Fractions Step 1: Find a factor of both numbers i.e. a
<
) =Area of cross section x height number that fits in both the numerator AND
Prism Volume
5 denominator
Pyramid Volume ) = × 789: 8+:8 × ℎ Angles subtended in the same Angle in a semicircle is a right
< Step 2: Say how many times for each
segment by a chord are equal angle
Indices Step 3: Check whether you can do steps 1
Multiplication , ' × , ( = , ')( and 2 again.
&
(, ' )( = , '( Fraction Of Amount of amount
-
(%, ' / ( )+ = % + , '+ / (+ Step 1: Divide amount by b
Division ,' Step 2: Multiply answer found by 8
, ' ÷ , ( = ( = , ',( Improper to Mixed Step 1: Divide the numerator by the
,
Negative Powers 1 denominator.
, ,- = - Step 2: Write down the whole number a A tangent meets a radius at BC° Opposite angles of a cyclic
,
. ,- . - Step 3: Put the remainder in the numerator. quadrilateral add to DEC°
Fractions /#
2 3 = # and 2 3 = #
.#
/ . / / The new denominator remains the same as
- - that of the original improper fraction.
Fractional Powers 40 = 5 √47
$
Mixed to Improper Step 1: Multiply the whole number by the
Percentages fraction’s denominator
One amount as a % of 8 as a percentage of 7 Step 2: Add that to the numerator
8 Step 3: Then write the result on the top of
the other amount × 100
(wants answer as a %) 7 the original denominator
Look for the words as a percent of Watch out: All points need to be
=2>>?9?3@?
+ 8@P − Fractions Need a common denominator (the smallest on the circumference!
Percentage gain/loss × 100 number that that both the numerator and
A92B237C Alternate segment theorem: The Tangents which meet at a point
(wants answer as a %) Look for the words percentage denominator fit into) angle between a tangent and a are equal in length
gain/loss/increase/decrease × Fractions Don’t need common denominator. side of a triangle is equal to the
Find percentage of an % Can cancel diagonally or vertically, not opposite angle
× 8=>?@A horizontally.
amount 100
Given % of an amount, D*EF+ &H"I+J ÷ Fractions Don’t need common denominator.
%
“Keep change flip”
find the full amount &''
Decimal to Fraction Write over 10,100,1000 etc depending on
Increasing/decreasing amountB1 ± D
%
5LL how many places after the decimal and
by a % + if increase simplify.
− if decrease Decimal to Percent Multiply by 100 For two intersecting chords, the products of their diagonals are equal
Reverse percentage ,H"I+J
Fraction to Decimal Write as an equivalent fraction over !# = %F !(! + #) = %(% + F)
%
5±&''
10,100,1000 etc and then easy to divide by
+ if increase
this number
− if decrease
OR
Look for the words originally, at the
Use short division if can’t write as an
beginning, before…
equivalent fraction
Pyramid Method For Percentages: Fraction to Percent Turn into a decimal and then just a decimal Extra helpful fact to remember
to percent question i.e. multiply decimal
found by 100
Percent to Decimal Divide by 100
Percent to Fraction Write over 100 and simplify
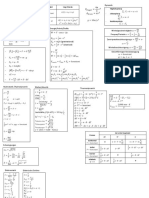
Geometry
Simple Interest % Straight Line Equation • Slope intercept & = =% + O
amount + Bamount × × timeD
(interest on initial
5LL
% • General 8% + 7& + P = 0
Interest: = amount × × time (get rid of fractions and move all on one Functions
amount) 5LL
Note: Make sure t and % are same unit side to get into this form) Inverse Replace !(#) with %, swap # & %, solve for %
of time Methods to find & = =% + O
J Composite !((#) means plug ((#) into !(#)
Compound Interest FV = PVB1 + D
N straight line equation Step 1: Find gradient =
!
(interest added also 5LL • Given a graph – pick any 2 points on the Transformations a=vertical stretch sf ), b=horizontal stretch sf "
FV=future value, PV=present value N*)F )!(*# + ,) + - c=translation c units x direction, d=translation d
earns interest) A=times, += interest rate graph and use “anything in a bracket affects
NI+ units in y direction
• Told parallel to another line⟹ same # and does the opposite” !(−#)=reflcn in %, axis − !(#)=reflcn in # axis
Quadratics
slope Series (iGCSE only)
Quadratic Function: %=
4-±O-(4P&/
,8 ≠0 • Told perpendicular to another line Arithmetic sequence: IJK term:
Solutions to !&
⟹”flip fraction and change the sign u3 = a + (n − 1)d
891 + ;9 + < = = (slopes multiply to make −1) sum of n terms
!
Completing The Square 8 B% ±
-
D +O−
-(
•
% 4%
Given 2 points. Use formula ( & n 2
S3 = [2a + (n − 1)d] = (! + P)
891 ± ;9 + < = = !& P& ;(4;& 2 2
-(
Step 2: Find & intercept O where ! =first term, d= common diff,
Max/Min Value O− • Given a graph – where the line crosses P=last term
P&
Congruent Shapes the & intercept Geometric sequence: u3 = ar 345
7(549") 7(9"45)
SSS Three sides of each triangle equal • Plug point in and solve for c (make sure S3 =
549
=
945
,r≠1
SAS Two sides and included angle equal this is correct point-line passes through). where ! =first term, r= common ratio
Straight Line Gradient &!4 &5
AAS Two angles and corresponding side == Differentiation (iGCSE only)
%!4 %5
equal Rule * + ⟹ 2* +45
Distance between 2 T(%!4 %5 )! + (&!4 &5 )! Remember: Constants go to 0
RHS Contains right angle and hypotenuse
points (WU , XU ), (WV , XV ) Turning/Stationary Points '%
and another side equal Solve =0
Coordinates of midpt of B
;&);( %&)%(
, D (Max/Min) ';
Direct/Indirect Proportion (WU , XU ), (WV , XV ) ! !
Proving whether Use knowledge of shape of graph
/ is … proportional to , Circles (% − 8)! + (& − 7)! = + ! Max/Min +* ! happy face min
2 centre (8, 7), radius +
Directly: / = ?, , Inversely: / = −* ! sad face max
. <
+* max on left, min on right
<
−* min on left, max on right
You might also like
- Winalc: Plasser TheurerDocument35 pagesWinalc: Plasser TheurerSuciu Florin100% (5)
- Digital SAT - Math TextbookDocument42 pagesDigital SAT - Math Textbookzain nawaz100% (3)
- Approximate Method For Plug Nozzle DesignDocument2 pagesApproximate Method For Plug Nozzle DesignRou MàissàNo ratings yet
- Januaru 2015 Math ADocument20 pagesJanuaru 2015 Math AShibraj DebNo ratings yet
- GCSE Formula SheetDocument1 pageGCSE Formula SheetShahzeb AliNo ratings yet
- GCSE Formula SheetDocument1 pageGCSE Formula SheetSonia ClaraNo ratings yet
- GCSE Formula SheetDocument1 pageGCSE Formula Sheetaadilmiah2019No ratings yet
- AP Calculus AB Formula SheetDocument1 pageAP Calculus AB Formula SheetArad zeinaliNo ratings yet
- A Level Formula SheetDocument1 pageA Level Formula SheetstudierNo ratings yet
- Deflection of Beams NotesDocument21 pagesDeflection of Beams Notes周暐凱No ratings yet
- Ch.10 Trignometric IdentitiesDocument1 pageCh.10 Trignometric IdentitiesMira SafadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document1 pageChapter 10halharbi0568No ratings yet
- Recalling Trigonometry: Property of STIDocument3 pagesRecalling Trigonometry: Property of STIKetaks MooNo ratings yet
- Föreläsning 8Document1 pageFöreläsning 8tokNo ratings yet
- Formelnblatt@110123Document3 pagesFormelnblatt@110123Lara CastroNo ratings yet
- IB Applications and Interpretation Formula SheetDocument1 pageIB Applications and Interpretation Formula SheetsachinNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Rules Chart - 230407 - 124119Document2 pagesDifferentiation Rules Chart - 230407 - 124119Sara AyaNo ratings yet
- IB Analysis and Approaches Formula SheetDocument1 pageIB Analysis and Approaches Formula SheetpaulaNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Information and Formulas: Operator Precedence Fprintf SPECIFIERDocument3 pagesMATLAB Information and Formulas: Operator Precedence Fprintf SPECIFIEROmar El MasryNo ratings yet
- Mat 441Document12 pagesMat 441nadia athiraNo ratings yet
- E Honors PreCalculus Textbook EWH 1Document404 pagesE Honors PreCalculus Textbook EWH 1Joshua BentataNo ratings yet
- Ce Document Est Mis À Disposition Selon Les Termes de La Licence Creative Commons "Attribution - Partage Dans Les Mêmes Conditions 4.0 International". HTTPS://WWW - Immae.eu/coursDocument10 pagesCe Document Est Mis À Disposition Selon Les Termes de La Licence Creative Commons "Attribution - Partage Dans Les Mêmes Conditions 4.0 International". HTTPS://WWW - Immae.eu/coursEnidroun OutNo ratings yet
- Project FlowchartDocument1 pageProject FlowchartShakibNo ratings yet
- Lecture PPT SlidesDocument4 pagesLecture PPT Slidesapi-459173295No ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document4 pagesLecture 1yifan zengNo ratings yet
- Algebra II 4Document1 pageAlgebra II 4Miyu TakahashiNo ratings yet
- Maths Tool Till 9 JuneDocument148 pagesMaths Tool Till 9 JuneSCAREDexeNo ratings yet
- NotebookDocument3 pagesNotebookQ TAI TSZ WINGNo ratings yet
- CTCDocument49 pagesCTCdatbaclieuNo ratings yet
- Gradient, Divergence and Curl PDFDocument9 pagesGradient, Divergence and Curl PDFAnonymous HH11bOW0I0100% (1)
- Assignment 4Document16 pagesAssignment 4Whoam INo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Forced and Damped Oscillations PDFDocument3 pagesLecture 7 Forced and Damped Oscillations PDFSahaj ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Matematicas Empresariales Temario Apuntes Temas 1 5Document77 pagesMatematicas Empresariales Temario Apuntes Temas 1 5JermenNo ratings yet
- תרגיל בית 10Document4 pagesתרגיל בית 10ofek kolaNo ratings yet
- AerationDocument6 pagesAerationAshmeet MahanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Functions 12Document97 pagesAdvanced Functions 12Rishab AnandNo ratings yet
- Solraxrolda: Paramefic BDocument6 pagesSolraxrolda: Paramefic Bgwpyv8w7xyNo ratings yet
- GCSE Foundation Maths Formula SheetDocument2 pagesGCSE Foundation Maths Formula Sheetjaimo3000No ratings yet
- Exercise 5Document19 pagesExercise 5Benjamin KjelbyNo ratings yet
- 02Document10 pages02gracehangi930No ratings yet
- f4 ch7 Exponential Function 1Document13 pagesf4 ch7 Exponential Function 1api-517118868No ratings yet
- Nota Akhir SPMDocument6 pagesNota Akhir SPMWan FadhNo ratings yet
- The PN Junction Parameters: Depletion Region ( )Document10 pagesThe PN Junction Parameters: Depletion Region ( )Eren CetinNo ratings yet
- Dzexams 3am Mathematiques 334343Document3 pagesDzexams 3am Mathematiques 334343bennacer.mansourNo ratings yet
- Double Angle Identities Worksheet With Graphysc CalculatorDocument4 pagesDouble Angle Identities Worksheet With Graphysc CalculatorErin PhillipsNo ratings yet
- Quantum Field TheoryDocument4 pagesQuantum Field Theoryyeminoo1335No ratings yet
- MathsDocument3 pagesMathsKaushalya PeoplezzNo ratings yet
- Mechanics M1 9709 Revision SheetDocument12 pagesMechanics M1 9709 Revision SheetaminahNo ratings yet
- 26 Nisan AnalysisDocument11 pages26 Nisan AnalysisaklNo ratings yet
- Lecture23 FilledinDocument3 pagesLecture23 FilledinyonathanNo ratings yet
- Sanetst Quadratic Equation Mathematics For Jee and Cbse Math Book Book 12 NodrmDocument82 pagesSanetst Quadratic Equation Mathematics For Jee and Cbse Math Book Book 12 NodrmAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Notes - Alto Clef: D4 To D5: Name: - DateDocument1 pageNotes - Alto Clef: D4 To D5: Name: - DateGreta KlemenzNo ratings yet
- Fórmulas 2º Série MatemáticaDocument2 pagesFórmulas 2º Série MatemáticaLetíciaNo ratings yet
- Plane and Solid Geometry Formulas: Prepared By: RtfverterraDocument2 pagesPlane and Solid Geometry Formulas: Prepared By: RtfverterraAdonis EscartinNo ratings yet
- v4.0.0 Cheatsheet: Pruning Text Summary Parameter BasicsDocument1 pagev4.0.0 Cheatsheet: Pruning Text Summary Parameter BasicsfcgarciaNo ratings yet
- Aalborg Universitet: Wasilewski, J. Wiechowski, Wojciech Tomasz Bak, Claus LethDocument8 pagesAalborg Universitet: Wasilewski, J. Wiechowski, Wojciech Tomasz Bak, Claus LethAwan Uji KrismantoNo ratings yet
- Geometria Anual - Uni Sem07 Congruencia de TriángulosDocument5 pagesGeometria Anual - Uni Sem07 Congruencia de TriángulosJOSUE EDMUNDO BENDEZU AGUILARNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of CurrentDocument12 pagesMagnetic Effects of CurrentCHINMAY UPADHYAYA X-DNo ratings yet
- 。CalculusDocument1 page。Calculus2121anjalisNo ratings yet
- דף נוסחאות דוריןDocument18 pagesדף נוסחאות דוריןyotam27No ratings yet
- Globalization: A Threat to Cultural Diversity in Southern Ethiopia?From EverandGlobalization: A Threat to Cultural Diversity in Southern Ethiopia?No ratings yet
- Divided States: Strategic Divisions in EU-Russia RelationsFrom EverandDivided States: Strategic Divisions in EU-Russia RelationsNo ratings yet
- Prisms and Cylinders 2Document1 pagePrisms and Cylinders 2api-172469602No ratings yet
- Integral CalculusDocument4 pagesIntegral CalculusJoevhin Patrice BambicoNo ratings yet
- ADM SPM Formulae KBSMDocument4 pagesADM SPM Formulae KBSMJason LeeNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Math Lesson 19: Verbal Phrases and Mathematical Phrases Learning GuideDocument5 pagesGrade 7 Math Lesson 19: Verbal Phrases and Mathematical Phrases Learning GuideMelanie Laraño-Baruiz VillameraNo ratings yet
- 2015 Basic - Math - Handbook For Water Plant OperatorsDocument155 pages2015 Basic - Math - Handbook For Water Plant OperatorsPedro CabanNo ratings yet
- Area of Composite Shapes: Learning CompetenciesDocument14 pagesArea of Composite Shapes: Learning CompetenciesROSE AMOR M. LACAYNo ratings yet
- DSE 15 CirclesDocument4 pagesDSE 15 CirclesWaSx3lyNo ratings yet
- HEC-RAS MapperUsersManualDocument149 pagesHEC-RAS MapperUsersManualFaizal RohmatNo ratings yet
- C 4 MathsDocument5 pagesC 4 Mathspriya kurienNo ratings yet
- Outlook Kelapa SawitDocument5 pagesOutlook Kelapa SawitEtty PasewangNo ratings yet
- Write Only The Letter Which Corresponds Choose The Correct Answer Un The Space Provided To Each Question On The Separate Answer SheetDocument6 pagesWrite Only The Letter Which Corresponds Choose The Correct Answer Un The Space Provided To Each Question On The Separate Answer SheetAYUUB TAHIRNo ratings yet
- Class 10 ICSE PROJECTS (SESSION 2020-2021) : Rehmat Singh)Document19 pagesClass 10 ICSE PROJECTS (SESSION 2020-2021) : Rehmat Singh)AnanyaNo ratings yet
- Paper4 Mock QPDocument17 pagesPaper4 Mock QPEric PlaneNo ratings yet
- Area and PerimeterDocument10 pagesArea and Perimeterd.gupta0807No ratings yet
- FS6 Lesson 6 - Traversing & Area Computation - RevDocument36 pagesFS6 Lesson 6 - Traversing & Area Computation - RevJames harvyNo ratings yet
- Revision List With Links HigherDocument5 pagesRevision List With Links HigherBen StocksNo ratings yet
- Poster CalculoDocument1 pagePoster CalculoGabriel OñateNo ratings yet
- Chain SurveyDocument43 pagesChain SurveySiva Raman85% (13)
- Creative Technology 8 Last Quarter ProjectDocument4 pagesCreative Technology 8 Last Quarter ProjectArnea Joy TajoneraNo ratings yet
- 4pm1 01r Que 20230113Document28 pages4pm1 01r Que 20230113riyanavoraNo ratings yet
- 2023 Practice Paper 2 Higher (Calculator) PDFDocument17 pages2023 Practice Paper 2 Higher (Calculator) PDFBivvyNo ratings yet
- Intermediate IVMO Sample 1Document11 pagesIntermediate IVMO Sample 1jericoNo ratings yet
- Areas of Plane Regions Using Definite IntegralsDocument16 pagesAreas of Plane Regions Using Definite Integralsjennie100% (1)
- Determining The Inclusion Content of Steel: Standard Test Methods ForDocument19 pagesDetermining The Inclusion Content of Steel: Standard Test Methods ForSaid MohamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 StudyguidesDocument14 pagesChapter 1 StudyguidesAnonymous O7NI8R3gFANo ratings yet
- 2014 MTAP 5 ReviewerDocument6 pages2014 MTAP 5 ReviewerRodel AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Plane Figures Mfe 2 2021 2022Document70 pagesPlane Figures Mfe 2 2021 2022Aaliyah Jean BelenNo ratings yet
- ASCE 7 10 Wind Load ExampleDocument19 pagesASCE 7 10 Wind Load ExampleRajib BiswasNo ratings yet