Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Network Security
Network Security
Uploaded by
Subash .S0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesNetwork security involves protecting a company's infrastructure from threats by preventing unauthorized access and damage. There are various types of network security like access control, antivirus software, firewalls, and intrusion prevention systems. Network security provides benefits such as protecting client data, reducing losses from incidents, and maintaining organizational reputation. Standards help create policies to avoid risks, identify threats, and respond to incidents across the security program. Wireless security similarly focuses on preventing unauthorized access to wireless networks and their devices. There are different wireless encryption protocols including WEP, WPA, WPA2, and the newest WPA3, with each iteration providing stronger security than the last.
Original Description:
Network Security
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNetwork security involves protecting a company's infrastructure from threats by preventing unauthorized access and damage. There are various types of network security like access control, antivirus software, firewalls, and intrusion prevention systems. Network security provides benefits such as protecting client data, reducing losses from incidents, and maintaining organizational reputation. Standards help create policies to avoid risks, identify threats, and respond to incidents across the security program. Wireless security similarly focuses on preventing unauthorized access to wireless networks and their devices. There are different wireless encryption protocols including WEP, WPA, WPA2, and the newest WPA3, with each iteration providing stronger security than the last.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesNetwork Security
Network Security
Uploaded by
Subash .SNetwork security involves protecting a company's infrastructure from threats by preventing unauthorized access and damage. There are various types of network security like access control, antivirus software, firewalls, and intrusion prevention systems. Network security provides benefits such as protecting client data, reducing losses from incidents, and maintaining organizational reputation. Standards help create policies to avoid risks, identify threats, and respond to incidents across the security program. Wireless security similarly focuses on preventing unauthorized access to wireless networks and their devices. There are different wireless encryption protocols including WEP, WPA, WPA2, and the newest WPA3, with each iteration providing stronger security than the last.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Network Security
Definition:
Network security is a set of technologies that protects the
usability and integrity of a company's infrastructure by
preventing the entry or proliferation within a network of a wide
variety of potential threats.
Types of Network Security:
The few types of network securities are discussed below:
Access Control
Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software
Cloud Security
Email Security
Firewalls
Application Security
Intrusion Prevention System(IPS)
Benefits of Network Security:
Network Security has several benefits, some of which are
mentioned below:
1. Network Security helps in protecting clients’ information and
data which ensures reliable access and helps in protecting the
data from cyber threats.
2. Network Security protects the organization from heavy losses
that may have occurred from data loss or any security
incident.
3. It overall protects the reputation of the organization as it
protects the data and confidential items.
Architecture and Standards:
The standards help create mechanisms by which the policies are
enacted in order to avoid risks, identify threats, and take action in
the event of an incident.
These policies and standards apply to different areas of the
security program that stretch out across the entire organization.
Wireless Security:
Wireless security is the prevention of unauthorized access or
damage to computers or data using wireless networks, which
include Wi-Fi networks. The term may also refer to the protection of
the wireless network itself from adversaries seeking to damage the
confidentiality, integrity, or availability of the network.
Types of Wireless Security:
Wireless security encryption is mainly divided into four main types:
Wired Equivalent Privacy Protocol (WEP)
Wi-Fi Protected Access Protocol (WPA)
Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 Protocol (WPA2)
Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 Protocol (WPA3)
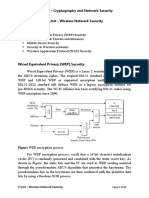
1. WEP Protocol : Wired Equivalent Privacy Protocol abbreviated as
WEP, was initially originated in the 1999 and is considered the standard
for wireless security encryption. It is less found in today’s modern world
because of the risk of security it is associated with directly/ indirectly.
WEP is not considered stable and Wi-Fi discontinued its use in 2004
because it is easy to exploit this level of security.
Example: Security added in the LAN connections to protect from
unauthenticated users trying to breach privacy.
2. WPA Protocol: WEP was succeeded by Wi-Fi Protected Access
Protocol abbreviated as WAP which offers more security and safety.
WPA has a 128-bit dynamic key called Temporary Key Integrity Protocol
(TKIP) that’s hard to break and makes it unique. One noticeable
disadvantage of WPA was that since it was made for WEP-enabled
devices, so the core components were majorly the same for WPA and
WEP.
3. WPA 2 Protocol : Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 Protocol abbreviated as
WPA2 came next and was better than the previous encryption types.
Here, Temporary Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) was replaced by Counter
Mode Cipher Block Chaining Message (CCMP). It is one of the most
used security encryption types. In 2006, WPA2 was declared to be
used in all wi-fi devices for wireless security encryption. WPA2 offers
Advanced Encryption Standards (AES). However, the major
disadvantage of WPA2 is that if the security key reached the hands of
the hacker then the entire network is vulnerable to attack.
4. WPA3 Protocol: WPA3 or Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 (WPA3)
Protocol is the newest security encryption that’s gaining popularity.
WPA3 offers high protection and prevents unauthorized access.
Unauthenticated and unauthorized individuals can’t breach this level of
security. WPA3 is the most desired for public networks as it performs
automatic encryption.
You might also like
- Catalogue-Mitutoyo-2022 Final Ok PDFDocument638 pagesCatalogue-Mitutoyo-2022 Final Ok PDFHuỳnh Quốc DũngNo ratings yet
- 4 - 2D Design HelpsheetsDocument2 pages4 - 2D Design HelpsheetsSascha ALVARES100% (2)
- Unit-V Network Access Control and Cloud Security: PDF Transport Level SecurityDocument14 pagesUnit-V Network Access Control and Cloud Security: PDF Transport Level SecurityayushNo ratings yet
- WirelessDocument5 pagesWirelesskalab haileNo ratings yet
- Report On Network SecurityDocument8 pagesReport On Network SecurityfarahilyasNo ratings yet
- Network Security: Presented By: Dr. Munam Ali ShahDocument25 pagesNetwork Security: Presented By: Dr. Munam Ali ShahNadeem ShoukatNo ratings yet
- Wifi SecurityDocument17 pagesWifi Securityviniskykumar100% (2)
- Wi Fi Hacking PDFDocument26 pagesWi Fi Hacking PDFShahinur IslamNo ratings yet
- Physical Layer Encryption 802.1X User Authentication VPN SecurityDocument18 pagesPhysical Layer Encryption 802.1X User Authentication VPN SecurityAbin AndrewsNo ratings yet
- Wireless Network SecurityDocument4 pagesWireless Network SecurityZam ZamNo ratings yet
- CSS10-1ST Quarter - Week 5Document21 pagesCSS10-1ST Quarter - Week 5George Mar Bien AriolaNo ratings yet
- (IJCST-V4I2P61) :akshika Aneja, Garima SodhiDocument4 pages(IJCST-V4I2P61) :akshika Aneja, Garima SodhiEighthSenseGroupNo ratings yet
- Network Security-Research PaperDocument5 pagesNetwork Security-Research PaperAbhi ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Eminar On Omputer Etwork SecurityDocument17 pagesEminar On Omputer Etwork SecuritySubhasmita PatelNo ratings yet
- Scrutinizing The Current Wi-Fi Security Protocol (Wpa2-Psk) To Improve Its SecurityDocument22 pagesScrutinizing The Current Wi-Fi Security Protocol (Wpa2-Psk) To Improve Its SecurityInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Lesson 04 - Wireless LAN SecurityDocument86 pagesLesson 04 - Wireless LAN SecurityZ OureelNo ratings yet
- Itwd Unit 3Document6 pagesItwd Unit 3ayushsingh96510No ratings yet
- Unit - 2: Infrastructure of Network Security: StructureDocument44 pagesUnit - 2: Infrastructure of Network Security: StructureSreeprada VNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Network SecurityDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Network Securityamtu.ms53No ratings yet
- Objective 13Document7 pagesObjective 13Emmanuel ChichesterNo ratings yet
- V Unit - Wireless Network SecurityDocument22 pagesV Unit - Wireless Network SecurityBRINDHA C it2018No ratings yet
- Synopsis 1Document6 pagesSynopsis 1URVI BALEKUNDRINo ratings yet
- Network Security: Presented By: Dr. Munam Ali ShahDocument31 pagesNetwork Security: Presented By: Dr. Munam Ali ShahNadeem ShoukatNo ratings yet
- (Wi-Fi Protected Access - 3) : "Future of Wireless Security"Document18 pages(Wi-Fi Protected Access - 3) : "Future of Wireless Security"pradeep100% (1)
- Wireless Network Security Vulnerabilities Threats and CountermeasuresDocument6 pagesWireless Network Security Vulnerabilities Threats and CountermeasuresMaria BatoolNo ratings yet
- JizupiwalaDocument4 pagesJizupiwalaSilki ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Wirless HackingDocument58 pagesWirless HackingTumwine Kahweza ProsperNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networks - Network SecurityDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Networks - Network SecurityFaical BitamNo ratings yet
- IEEE Paper Review On Wireless Security and LoopholesDocument4 pagesIEEE Paper Review On Wireless Security and LoopholesMahesh SainiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Network SecurityDocument7 pagesAssignment 3 Network Securitykainat KhalidNo ratings yet
- Sumit Paper - Securing Wireless Network Using Penetration Testing and Counter MeasuresDocument7 pagesSumit Paper - Securing Wireless Network Using Penetration Testing and Counter Measuressumit meshramNo ratings yet
- Network Firewall Technologies: 1. Security Threats From Connecting To The InternetDocument19 pagesNetwork Firewall Technologies: 1. Security Threats From Connecting To The Internetvikash rediffNo ratings yet
- Wired and Wireless SecurityDocument14 pagesWired and Wireless SecuritySandesh ShresthaNo ratings yet
- The Weakness of Wireless NetworksDocument7 pagesThe Weakness of Wireless NetworksAndysah Putra Utama Siahaan100% (2)
- A Review On Network SecurityDocument4 pagesA Review On Network SecuritylujainmohammedNo ratings yet
- Wireless Security TechniquesDocument18 pagesWireless Security TechniquesAndiebou SalamedaNo ratings yet
- Security IssuesDocument9 pagesSecurity IssuesYogesh DeoNo ratings yet
- CSC-308 M3 StudentsDocument18 pagesCSC-308 M3 Studentsjonnel talañaNo ratings yet
- REPORTDocument3 pagesREPORTDominique EijansantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Network SecurityDocument40 pagesChapter One Network SecurityOfficial AminhoNo ratings yet
- Wireless LAN Security: Addressing Challenges, Attacks and SolutionsDocument6 pagesWireless LAN Security: Addressing Challenges, Attacks and SolutionsseventhsensegroupNo ratings yet
- Wireless Security: Merged DiscussDocument55 pagesWireless Security: Merged DiscussRamaguru Radhakrishnan100% (2)
- Wireless Security DraftDocument6 pagesWireless Security Draftdjumbo8No ratings yet
- Implementation of A Security Protocol For Bluetooth and Wi-FiDocument17 pagesImplementation of A Security Protocol For Bluetooth and Wi-FiAIRCC - IJNSANo ratings yet
- Security FinalDocument13 pagesSecurity Finalyoussifmadbouly5No ratings yet
- Network Security - A Layered Approach: H. I. M. T. Greater Noida, D. N. College, Hisar, G. P. HisarDocument4 pagesNetwork Security - A Layered Approach: H. I. M. T. Greater Noida, D. N. College, Hisar, G. P. Hisarsrs0507No ratings yet
- WLAN SecurityDocument20 pagesWLAN SecurityPankia Mer AmunNo ratings yet
- WWW - Oeclib.in: Odisha Electronics Control LibraryDocument24 pagesWWW - Oeclib.in: Odisha Electronics Control Librarymuneebrahat100% (1)
- Network SecuurityDocument25 pagesNetwork SecuurityDebopriyo SarkarNo ratings yet
- 06 Designand Implementationofa Network Security Modelfor Cooperative NetworkDocument12 pages06 Designand Implementationofa Network Security Modelfor Cooperative NetworkMicrowork BitcoinNo ratings yet
- Exploring Vulnerabilities in Enterprise Wireless Networks (EWPT)Document2 pagesExploring Vulnerabilities in Enterprise Wireless Networks (EWPT)thelastsamuraiisbackNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of A Network Security Model For Cooperative Network PDFDocument11 pagesDesign and Implementation of A Network Security Model For Cooperative Network PDFyassin alkulaiNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of A Network Security Model For Cooperative Network PDFDocument11 pagesDesign and Implementation of A Network Security Model For Cooperative Network PDFSpad ParnianNo ratings yet
- How To Hack Wifi (Wireless) Network: Topics Covered in This TutorialDocument7 pagesHow To Hack Wifi (Wireless) Network: Topics Covered in This Tutorialjaveeed0401No ratings yet
- A Comparitive Analysis of WirelessDocument7 pagesA Comparitive Analysis of WirelessijansjournalNo ratings yet
- Network Security (M.fazeel)Document18 pagesNetwork Security (M.fazeel)amazingthings2743No ratings yet
- Topic 2. Network SecurityDocument5 pagesTopic 2. Network SecurityRosetephanie ZalunNo ratings yet
- IJCER (WWW - Ijceronline.com) International Journal of Computational Engineering ResearchDocument5 pagesIJCER (WWW - Ijceronline.com) International Journal of Computational Engineering ResearchInternational Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)No ratings yet
- Network Security Consists of The Provisions Made in An UnderlyingDocument26 pagesNetwork Security Consists of The Provisions Made in An UnderlyingChirag ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Data Security Book 1: Proper Guide to Data Security in Communication Networks. Cryptography and Data Security in PracticeFrom EverandCryptography and Data Security Book 1: Proper Guide to Data Security in Communication Networks. Cryptography and Data Security in PracticeNo ratings yet
- Franchezka Pegollo BSBM M 3-1 Toshiba Corporation Corporate InformationDocument4 pagesFranchezka Pegollo BSBM M 3-1 Toshiba Corporation Corporate InformationFranchezka PegolloNo ratings yet
- CIT212Document255 pagesCIT212CharlesNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuit Design and Analysis For Space ApplicationsDocument8 pagesElectronic Circuit Design and Analysis For Space ApplicationsH SMNo ratings yet
- Tybca 15 MarksDocument30 pagesTybca 15 Marksapi-446272000No ratings yet
- Bsbops601 - Week 4Document13 pagesBsbops601 - Week 4Natti NonglekNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 PII MACHINE LEARNINGDocument43 pagesUnit 6 PII MACHINE LEARNINGSakshi ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- BRM 2021 - 22 Outline Sec A B C eDocument8 pagesBRM 2021 - 22 Outline Sec A B C eEkalavya ChaudhuriNo ratings yet
- HMMT 24Document71 pagesHMMT 24nov428571No ratings yet
- Value-Based Strategy For Industrial Products: John L. Forbis and T. MehtaDocument19 pagesValue-Based Strategy For Industrial Products: John L. Forbis and T. MehtaHarshali ShreyaNo ratings yet
- PGL - Online 101.1 DraftDocument4 pagesPGL - Online 101.1 DraftZaeni AhmadNo ratings yet
- Zee 5 AccountsDocument5 pagesZee 5 AccountsM U J E E B MujeebNo ratings yet
- Sovannary Bunchan: Curriculum Vita EDocument3 pagesSovannary Bunchan: Curriculum Vita Eសម្បត្តិ សិទ្ធិការ្យ សុខោទ័យNo ratings yet
- Discussion Forum 1.4 - Marketing Management - DDocument2 pagesDiscussion Forum 1.4 - Marketing Management - DAhmed Wael Ali .No ratings yet
- Avijit Sood: BackgroundDocument7 pagesAvijit Sood: BackgroundAshwani kumarNo ratings yet
- Irfp 462Document7 pagesIrfp 462scribderougNo ratings yet
- Tensores Van GorpDocument17 pagesTensores Van GorpsalematadorNo ratings yet
- Pseudowire Concepts and Troubleshooting PDFDocument10 pagesPseudowire Concepts and Troubleshooting PDFEze Alexander IkNo ratings yet
- Weaknesses in The Key Scheduling Algorithm of RC4Document24 pagesWeaknesses in The Key Scheduling Algorithm of RC4Sigifredo Segundo Thomas CampoNo ratings yet
- Institute WorkFromHomeActivityDocument78 pagesInstitute WorkFromHomeActivitydkkmaa5No ratings yet
- Concept NoteDocument9 pagesConcept NoteJustus CyrilNo ratings yet
- Monster Power - HTS3500 Manual PDFDocument42 pagesMonster Power - HTS3500 Manual PDFJose MondragonNo ratings yet
- MP1200 CatalogueDocument8 pagesMP1200 Cataloguejuly.ph29No ratings yet
- Method Statement Ceiling RemovalDocument7 pagesMethod Statement Ceiling RemovalSimpol MathNo ratings yet
- Aspid On KubDocument11 pagesAspid On KubMarcus Wolf100% (1)
- Flammable Vapor Ignition Initiated by HoDocument12 pagesFlammable Vapor Ignition Initiated by HoNurettin TERZİOĞLUNo ratings yet
- Lab On A Chip: CommunicationDocument14 pagesLab On A Chip: CommunicationDispensasi unipasbyNo ratings yet
- Competition Hits Deutsche Telekom: Firms and Markets Mini-CaseDocument4 pagesCompetition Hits Deutsche Telekom: Firms and Markets Mini-CasemarkNo ratings yet
- Briggs & Stratton LLC - Briggs & Stratton Power Guide 2024Document65 pagesBriggs & Stratton LLC - Briggs & Stratton Power Guide 2024Benoît MARTINNo ratings yet