Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 006
How Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 006
Uploaded by
Raj0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageThe document discusses methods for pricing options. It presents three methods: 1) partial replication using long and short call positions, 2) using an implied risk neutral distribution, and 3) Black-Scholes formula pricing. It then provides an example of using partial replication to price a digital option by taking long and short positions on calls with different strikes and maturities, arriving at price bounds of 0.435 and 0.34 for the option.
Original Description:
Original Title
478425791-How-much-is-a-smile-worth-in-an-exotic-world-of-equities_006
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses methods for pricing options. It presents three methods: 1) partial replication using long and short call positions, 2) using an implied risk neutral distribution, and 3) Black-Scholes formula pricing. It then provides an example of using partial replication to price a digital option by taking long and short positions on calls with different strikes and maturities, arriving at price bounds of 0.435 and 0.34 for the option.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageHow Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 006
How Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 006
Uploaded by
RajThe document discusses methods for pricing options. It presents three methods: 1) partial replication using long and short call positions, 2) using an implied risk neutral distribution, and 3) Black-Scholes formula pricing. It then provides an example of using partial replication to price a digital option by taking long and short positions on calls with different strikes and maturities, arriving at price bounds of 0.435 and 0.34 for the option.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
low and shall be further used.
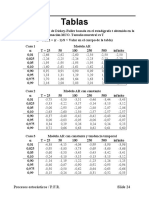
Table 2: Strikes (vertical) and lifetimes (horizontal)
K \TTM 1M 3M 6M 1Y 2Y 3Y
80 40.91% 30.77% 25.02% 25.68% 28.28% 28.23%
85 45.74% 29.52% 28.60% 27.15% 28.29% 27.87%
90 35.54% 23.46% 26.24% 29.48% 29.19% 27.18%
95 22.07% 27.49% 26.39% 27.11% 28.36% 27.89%
100 27.36% 26.19% 29.19% 27.69% 28.44% 29.12%
105 25.95% 27.41% 27.80% 28.59% 28.57% 28.93%
110 28.56% 24.22% 27.21% 28.49% 28.11% 27.92%
115 29.11% 26.06% 28.95% 26.72% 26.95% 26.99%
120 25.69% 27.08% 29.65% 25.91% 24.61% 25.62%
3.3 Q1: Pricing and its methodologies
We can find an approximate price through (at least )three methods:
M1. By partial replication.
M2. By using implied risk neutral distribution of ST from property 2.0.1
M3. Through B & S formula pricing.
Instrument A:
M1: Partial replication could entail:
A long/short position on calls with strikes K1 = 95, K2 = 100, maturities =
1 year and exposures w1 = 51 , w2 = − 15 .
The resulting cost would then be 15 · (c(95; 1) − c(100; 1)) = 0.435
Another approximate (sub)replication could be:
A long/short position on calls with strikes K1 = 100, K2 = 100, maturities =
1 year and exposures w1 = 15 , w2 = − 51 (1/5 of the notional). The cost is 0.34.
We have therefore provided bounds for the real value of the digital op-
tion.
You might also like
- ISYE 2028 Chapter 8 SolutionsDocument41 pagesISYE 2028 Chapter 8 SolutionsWillie Seo100% (2)
- Orc Wing ModelDocument5 pagesOrc Wing ModelRajNo ratings yet
- 1 Vibration Analysis Using MATLABDocument26 pages1 Vibration Analysis Using MATLABreachspk100% (1)
- Example For NumericalDocument9 pagesExample For Numericaltekalign yerangoNo ratings yet
- Simple Linear Regression (Solutions To Exercises)Document28 pagesSimple Linear Regression (Solutions To Exercises)blu runner1No ratings yet
- CH 08Document41 pagesCH 08Saied Aly SalamahNo ratings yet
- Transmutation Table NewDocument1 pageTransmutation Table Newlheanz0% (1)
- Kunci Soal LatihanDocument7 pagesKunci Soal LatihanAgus SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Kunci Soal LatihanDocument7 pagesKunci Soal LatihanAgus SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Quiz 08 - Questions & SolutionsDocument3 pagesQuiz 08 - Questions & SolutionsthuctranduynguyenNo ratings yet
- Latihan 3 Linear RegressionDocument3 pagesLatihan 3 Linear RegressionilhamNo ratings yet
- Data Klimatologi Stasiun W Undulako Bulan Januari Februari Maret April MeiDocument1 pageData Klimatologi Stasiun W Undulako Bulan Januari Februari Maret April MeiannisaNo ratings yet
- Benchmark 24 03 03 12 58 01Document3 pagesBenchmark 24 03 03 12 58 01Joao PedroNo ratings yet
- Exp.2 Gay Lussac's LawDocument6 pagesExp.2 Gay Lussac's LawBilal LiaqatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Radiography Arithmatic of ExposureDocument27 pagesChapter 7 Radiography Arithmatic of ExposureHrishikesanNo ratings yet
- Technical Information SCS UP (-XT) (-US) - V2.22Document55 pagesTechnical Information SCS UP (-XT) (-US) - V2.22Muzamil FaizNo ratings yet
- Ie208 QuestionsDocument8 pagesIe208 QuestionsEren GüngörNo ratings yet
- Forecasting Level Time SeriesDocument36 pagesForecasting Level Time SeriesManuel Alejandro Sanabria AmayaNo ratings yet
- Tablas: Procesos Estocásticos / P.F.R. Slide 24Document1 pageTablas: Procesos Estocásticos / P.F.R. Slide 24jorgec74No ratings yet
- Stat 2032 2014 Final SolutionsDocument12 pagesStat 2032 2014 Final SolutionsJasonNo ratings yet
- Solutions Chapter 8Document8 pagesSolutions Chapter 8rabxcv-3100% (1)
- Critical Values For The Dickey-Fuller Unit Root T-Test StatisticsDocument1 pageCritical Values For The Dickey-Fuller Unit Root T-Test Statisticswjimenez1938No ratings yet
- CRE99Document31 pagesCRE99wissalriyaniNo ratings yet
- Distribucion de Frecuencia Del PesoDocument12 pagesDistribucion de Frecuencia Del PesoDANIELNo ratings yet
- Numbers Error Error 2 Estimate 70Document6 pagesNumbers Error Error 2 Estimate 70ammarNo ratings yet
- Gage Repeatability and Reproducibility Data Collection SheetDocument12 pagesGage Repeatability and Reproducibility Data Collection SheetkkdilliNo ratings yet
- Initial FeDocument131 pagesInitial FeMiguel SaezNo ratings yet
- Practical BIT-2Document7 pagesPractical BIT-2sudikshya.shakya2004No ratings yet
- Final Physics IADocument14 pagesFinal Physics IAjonathan_coleman_933% (3)
- Probability and StatisticDocument24 pagesProbability and StatisticChe RryNo ratings yet
- TITLE: Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR) ObjectiveDocument25 pagesTITLE: Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR) ObjectivealijadoonNo ratings yet
- Interest Rate Risk: Maturity Model The Price-Market Yield Relationship: A Single InstrumentDocument24 pagesInterest Rate Risk: Maturity Model The Price-Market Yield Relationship: A Single InstrumentMad_of_booksNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document4 pagesCH 5Maulik ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Douglus Chap 8Document41 pagesDouglus Chap 8Al Farabi0% (1)
- Project CalculusDocument17 pagesProject CalculusNabil IkhwanNo ratings yet
- Gauss SeidelDocument10 pagesGauss SeidelSulaiman AhlakenNo ratings yet
- Critical Analysis Of: Multiple Regression ModelDocument12 pagesCritical Analysis Of: Multiple Regression Modelsanket patilNo ratings yet
- HO4 EstimationDocument9 pagesHO4 EstimationMirza Naveed BaigNo ratings yet
- GSM Performance Report - 100 999 MallDocument7 pagesGSM Performance Report - 100 999 MallBenjamin MedinaNo ratings yet
- LampiranDocument9 pagesLampiranIzza MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Finance in A Nutshell Javier Estrada FT Prentice Hall, 2005: Answer Key To Challenge SectionsDocument63 pagesFinance in A Nutshell Javier Estrada FT Prentice Hall, 2005: Answer Key To Challenge Sectionssanucwa6932No ratings yet
- Doe How To Transform Data With Unequal VariancesDocument5 pagesDoe How To Transform Data With Unequal VarianceshankermonkerNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 9-Lectures Dr. SAEEDDocument90 pagesChapter - 9-Lectures Dr. SAEEDفيصل القرشيNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis Central TendencyDocument3 pagesData Analysis Central TendencyBucad, Jimwell Dave EraNo ratings yet
- LP Prcatical 2 Jupyter NotebookDocument5 pagesLP Prcatical 2 Jupyter Notebookxifavo8319No ratings yet
- 2.0 MaccaptieleDocument1 page2.0 MaccaptieleRamazan TosunNo ratings yet
- Radar Lab 1Document8 pagesRadar Lab 1hamasahmad46No ratings yet
- Stats BusinessDocument10 pagesStats BusinessJehan solutionsNo ratings yet
- Ops Assignment 2Document4 pagesOps Assignment 2Indraseenayya ChilakalaNo ratings yet
- Price Forecasting of High Value Commercial Crops (HVCC) For The GMA-HVCC ProgrammeDocument30 pagesPrice Forecasting of High Value Commercial Crops (HVCC) For The GMA-HVCC ProgrammeUPLB Office of the Vice Chancellor for Research and ExtensionNo ratings yet
- Metanalisis Con RDocument8 pagesMetanalisis Con RHéctor W Moreno QNo ratings yet
- Abstract - A PID Controller Can Be Used To Control Level, Temperature, Flow, Pressure, andDocument7 pagesAbstract - A PID Controller Can Be Used To Control Level, Temperature, Flow, Pressure, andMuhammad AdiwirawanNo ratings yet
- Exercise-No.-3 (ZANORIA, STEPHANIE)Document4 pagesExercise-No.-3 (ZANORIA, STEPHANIE)stephanie zanoriaNo ratings yet
- hw8 f08Document2 pageshw8 f08Lucia AntoniusNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument27 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyAlvin DeliroNo ratings yet
- Applied Corporate Finance A Users Manual 2nd Edition Damodaran Solutions ManualDocument31 pagesApplied Corporate Finance A Users Manual 2nd Edition Damodaran Solutions Manualthioxenegripe.55vd100% (30)
- Computer Simulation 1 Group 2Document19 pagesComputer Simulation 1 Group 2Kevin WilliamNo ratings yet
- Paper2 Scheme Physics Form4 SBP 2007 Mid YearDocument7 pagesPaper2 Scheme Physics Form4 SBP 2007 Mid YearruslawatiNo ratings yet
- MTH 2500 hwk4Document6 pagesMTH 2500 hwk4Jonathan BubbIes NeumanNo ratings yet
- 7.2 DCC - MEP Works TrackingDocument6 pages7.2 DCC - MEP Works TrackingMohammed ShakeelNo ratings yet
- Opengamma Local Vol - 004Document1 pageOpengamma Local Vol - 004RajNo ratings yet
- Opengamma Local Vol - 008Document1 pageOpengamma Local Vol - 008RajNo ratings yet
- Opengamma Local Vol - 006Document1 pageOpengamma Local Vol - 006RajNo ratings yet
- Opengamma Local Vol - 001Document1 pageOpengamma Local Vol - 001RajNo ratings yet
- How Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 014Document1 pageHow Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 014RajNo ratings yet
- Opengamma Local Vol - 003Document1 pageOpengamma Local Vol - 003RajNo ratings yet
- How Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 016Document1 pageHow Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 016RajNo ratings yet
- Opengamma Local Vol - 005Document1 pageOpengamma Local Vol - 005RajNo ratings yet
- How Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 015Document1 pageHow Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 015RajNo ratings yet
- How Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 017Document1 pageHow Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 017RajNo ratings yet
- How Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 011Document1 pageHow Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 011RajNo ratings yet
- 5.3 References: 2K S (K/S,T) ∂σ ∂ (K/S) ∂ σ ∂ (K/S)Document1 page5.3 References: 2K S (K/S,T) ∂σ ∂ (K/S) ∂ σ ∂ (K/S)RajNo ratings yet
- How Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 012Document1 pageHow Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 012RajNo ratings yet
- How Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 013Document1 pageHow Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 013RajNo ratings yet
- How Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 002Document1 pageHow Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 002RajNo ratings yet
- How Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 005Document1 pageHow Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 005RajNo ratings yet
- How Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 004Document1 pageHow Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 004RajNo ratings yet
- How Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 003Document1 pageHow Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 003RajNo ratings yet
- How Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 001Document1 pageHow Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 001RajNo ratings yet
- How Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 007Document1 pageHow Much Is A Smile Worth in An Exotic World of Equities - 007RajNo ratings yet
- MAFS5030 hw2Document3 pagesMAFS5030 hw2RajNo ratings yet
- MAFS5030 hw3 004Document1 pageMAFS5030 hw3 004RajNo ratings yet
- MAFS5030 hw3 003Document1 pageMAFS5030 hw3 003RajNo ratings yet
- Non SalaryDocument1 pageNon SalaryRajNo ratings yet
- MAFS5030 hw1Document4 pagesMAFS5030 hw1RajNo ratings yet
- MAFS5030 hw3 002Document1 pageMAFS5030 hw3 002RajNo ratings yet
- MAFS5030 hw3Document4 pagesMAFS5030 hw3RajNo ratings yet
- FINA556 hw1Document3 pagesFINA556 hw1RajNo ratings yet
- PRMKARERA1251446PR200526003419Document18 pagesPRMKARERA1251446PR200526003419RajNo ratings yet