Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views11.nervous System
11.nervous System
Uploaded by
Leena HassaninThe document discusses the structure and function of the human neural system. It describes that the neural system consists of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system. Within the central nervous system, the brain is made up of the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. Neurons are the basic functional units and transmit signals through electrical and chemical synapses. The process of nerve impulse generation, conduction, and transmission between neurons is also explained.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Ebook Principles of Neural Science Sixth Edition Eric R Kandel Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesEbook Principles of Neural Science Sixth Edition Eric R Kandel Online PDF All Chapterkendall.fox383100% (8)
- Essentials of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing 7th Edition Townsend Test BankDocument15 pagesEssentials of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing 7th Edition Townsend Test Bankkimberlymorriscntsoqmyjw100% (6)
- June 17 26 s001 PDFDocument9 pagesJune 17 26 s001 PDFBetul RojeabNo ratings yet
- Biology - Brain (Neural Communication)Document6 pagesBiology - Brain (Neural Communication)Teacă Mădălina ElenaNo ratings yet
- Marcus Jacobson (Auth.) - Foundations of Neuroscience (1993)Document394 pagesMarcus Jacobson (Auth.) - Foundations of Neuroscience (1993)patata100% (1)
- Full Sentence OutlineDocument7 pagesFull Sentence Outlineapi-384035981No ratings yet
- CH 4 - CoordinationDocument23 pagesCH 4 - CoordinationnawarakanNo ratings yet
- 10 Neural Control N Coordination-Notes Blog (Full Permission)Document5 pages10 Neural Control N Coordination-Notes Blog (Full Permission)fariha khanNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument86 pagesGen BioPaul MagbagoNo ratings yet
- Intro Animal Physiology Ch-2.1Document97 pagesIntro Animal Physiology Ch-2.1Jojo MendozaNo ratings yet
- Neural Control and Coordination - Shobhit NirwanDocument13 pagesNeural Control and Coordination - Shobhit Nirwanmfx79qh7wbNo ratings yet
- Neural Control and Coordination - Shobhit NirwanDocument14 pagesNeural Control and Coordination - Shobhit NirwanSWASTIKA MALONo ratings yet
- Nureal Control and CoordinationDocument16 pagesNureal Control and CoordinationthushyanthNo ratings yet
- NeurophysiologyDocument31 pagesNeurophysiologyChezkah Nicole MirandaNo ratings yet
- Histology 9Document8 pagesHistology 9amirhsheikhiNo ratings yet
- Neural Control and CoordinationDocument8 pagesNeural Control and CoordinationAman Singh RaoNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From SUPERCOPDocument6 pagesMaterial Downloaded From SUPERCOPfast-track for n2021No ratings yet
- TR Cyvp 93 I 1 R1 H 034 Rat 0Document5 pagesTR Cyvp 93 I 1 R1 H 034 Rat 0aadeshthite476No ratings yet
- PHC 513 Flipped Class QuestionDocument17 pagesPHC 513 Flipped Class QuestionALISYA SOPHIA MOHAMMAD ABU SHAHID CHRISNo ratings yet
- Points To Remember: Neural Control and CoordinationDocument107 pagesPoints To Remember: Neural Control and CoordinationRagheNo ratings yet
- Biology F4 Review Summary NoteDocument117 pagesBiology F4 Review Summary NoteSocdal AbdiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The NerveDocument18 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The NervejudssalangsangNo ratings yet
- Bio Chap 21 NotesDocument9 pagesBio Chap 21 NotesYogesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Nervous System LectureDocument234 pagesNervous System Lecturealyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Notes - Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesNotes - Nervous Systemdarkadain100% (1)
- Le Neuron Structure: Reflexes: Sensory Nuerons: Trasmit Info From Sensors That DetectDocument5 pagesLe Neuron Structure: Reflexes: Sensory Nuerons: Trasmit Info From Sensors That DetectYiboNo ratings yet
- LIFS1902 Nervous System Revision NotesDocument6 pagesLIFS1902 Nervous System Revision NotesmystudylifechloeNo ratings yet
- 10 Neuro PDFDocument16 pages10 Neuro PDFKamoKamoNo ratings yet
- Neural Control N Coordination-NotesDocument5 pagesNeural Control N Coordination-Notessudeep27krNo ratings yet
- Neural Contraol & Coordinaton - SNDocument7 pagesNeural Contraol & Coordinaton - SNPushpa DhruvNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Points To RememberDocument6 pagesChapter 22 Points To RememberSaksham YadavNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 21 Neural Control and Coordination NotesDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 21 Neural Control and Coordination NotesShivalgiri Goswami0% (1)
- Structure of The Nervous System: Lesson 1Document41 pagesStructure of The Nervous System: Lesson 1Samuel ThangarajanNo ratings yet
- CAPE Nervous Coordination NotesDocument24 pagesCAPE Nervous Coordination NotesSharina GeraldNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue-06.11-2wlDocument57 pagesNervous Tissue-06.11-2wlapi-19641337No ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch21 Neural Control and Coordination PDFDocument3 pages11 Biology Notes ch21 Neural Control and Coordination PDFRamachandranPerumal100% (1)
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Document11 pagesStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Ayush KumarNo ratings yet
- Neural CoordinationDocument7 pagesNeural CoordinationTushar SinghNo ratings yet
- Neurons NervousDocument10 pagesNeurons NervousAldi RegarNo ratings yet
- Psy121 - Psychobiological Determinants of BehaviourDocument42 pagesPsy121 - Psychobiological Determinants of BehaviourLarry UdehNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 9 NERVOUS CONTROL My Notes 1Document11 pagesTOPIC 9 NERVOUS CONTROL My Notes 1shealtielchigariso06No ratings yet
- Unit 8 Learning Guide Name: Brandon Au-Young: InstructionsDocument25 pagesUnit 8 Learning Guide Name: Brandon Au-Young: InstructionsBrandonNo ratings yet
- Ch08 Nervous SystemDocument62 pagesCh08 Nervous SystemDanna Loize Noble LazaroNo ratings yet
- Nerve and Its Function PDFDocument26 pagesNerve and Its Function PDFJose albert MauanayNo ratings yet
- Structure of The NeuronDocument7 pagesStructure of The NeuronSmitaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesNervous SystemYUAN FRANCIS SINGCULANNo ratings yet
- A12. Nervous SystemDocument184 pagesA12. Nervous SystemAbdurahman TainyNo ratings yet
- BN Week1 Neurons 08-22-19Document59 pagesBN Week1 Neurons 08-22-19marissaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System & Nerve ImpulsesDocument21 pagesThe Nervous System & Nerve ImpulsesPrabhathNo ratings yet
- Neural Control and CoordinationDocument6 pagesNeural Control and CoordinationRonaldNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System & Nerve ImpulsesDocument22 pagesThe Nervous System & Nerve Impulsestas xoNo ratings yet
- Neurons and Neuroglia - PPTX 2nd LecDocument23 pagesNeurons and Neuroglia - PPTX 2nd Leczaraali2405No ratings yet
- Biology 30 Student Notes Nervous ReproductionDocument53 pagesBiology 30 Student Notes Nervous ReproductionDennis Limosnero MayorNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Grade 10 - Science HANDOUT No.2 On Neurons, Reflex, Reflex Arc & Brain General Information About The Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesSecond Quarter Grade 10 - Science HANDOUT No.2 On Neurons, Reflex, Reflex Arc & Brain General Information About The Nervous SystemMartin ReaporNo ratings yet
- Physiology Handouts (Topic 16-26)Document35 pagesPhysiology Handouts (Topic 16-26)bc200411046No ratings yet
- Physio CH-2Document24 pagesPhysio CH-2aliraza67570No ratings yet
- NeurophysicsDocument8 pagesNeurophysicsMakavana SahilNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Mitochondria "Organelles"Document6 pagesCell Membrane Mitochondria "Organelles"Ashraf MobyNo ratings yet
- 1 Hist Sept 13 ReadingNerve - Tissue2020Document26 pages1 Hist Sept 13 ReadingNerve - Tissue2020n-gorNo ratings yet
- Biology and Psychology 15065G PP 3Document59 pagesBiology and Psychology 15065G PP 3SalahideenNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Structure and Functions of The CellsDocument12 pagesUnit 2 - Structure and Functions of The CellssindhusivasailamNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solution of Neural Coordination and Control Class 11Document17 pagesNcert Solution of Neural Coordination and Control Class 11Ayush DuttaNo ratings yet
- Biology 3201: Unit 1 - Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Section 1 - Nervous System "The Neuron"Document22 pagesBiology 3201: Unit 1 - Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Section 1 - Nervous System "The Neuron"Harshil PatelNo ratings yet
- Somatosensory Teachers Manual: for Somatosensory Science FactsFrom EverandSomatosensory Teachers Manual: for Somatosensory Science FactsNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Ebersole and Hess Gerontological Nursing and Healthy Aging 2nd Canadian Edition by TouhyDocument7 pagesTest Bank For Ebersole and Hess Gerontological Nursing and Healthy Aging 2nd Canadian Edition by Touhyjohnflorescdjrfwqxzs100% (32)
- Reflex Arc LabDocument2 pagesReflex Arc Labapi-377433445No ratings yet
- Psychology An Exploration Canadian 1st Edition Ciccarelli Solutions ManualDocument21 pagesPsychology An Exploration Canadian 1st Edition Ciccarelli Solutions Manualdictumhuronianhsor100% (33)
- 6 - 5 - Nerves 2023Document45 pages6 - 5 - Nerves 2023Eudmarly GEDEONNo ratings yet
- (English) The Nervous System, Part 3 - Synapses! - Crash Course A&P #10 (DownSub - Com)Document8 pages(English) The Nervous System, Part 3 - Synapses! - Crash Course A&P #10 (DownSub - Com)bank townNo ratings yet
- Smola PDFDocument271 pagesSmola PDFsri1991nivasNo ratings yet
- Santiago Ramón y Cajal en La NeuroscienciaDocument11 pagesSantiago Ramón y Cajal en La NeuroscienciaAmy Medina VelazquezNo ratings yet
- Neural Control and Co OrdinationDocument16 pagesNeural Control and Co OrdinationDARSHAN KUMAR TNo ratings yet
- Wk2 Paper InfoDocument5 pagesWk2 Paper InfokellyNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience Science of TheDocument60 pagesNeuroscience Science of TheALA Meditation - Relaxing MusicNo ratings yet
- Thanksgiving Day SermonDocument13 pagesThanksgiving Day Sermoncarolyn6302No ratings yet
- Lifespan Development Canadian 5th Edition Boyd Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesLifespan Development Canadian 5th Edition Boyd Solutions Manual 1justinfleminggfcqziaonr100% (33)
- Dopamine Receptor Subtypes, Physiology and Pharmacology - New Ligands and Concepts in SchizophreniaDocument17 pagesDopamine Receptor Subtypes, Physiology and Pharmacology - New Ligands and Concepts in SchizophreniaolivukovicNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan IN Grade 10 Science Nerve Cell: Mariano Ponce National High SchoolDocument11 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan IN Grade 10 Science Nerve Cell: Mariano Ponce National High SchoolAdrian DionisioNo ratings yet
- Essence of Memory: Progress in Brain ResearchDocument430 pagesEssence of Memory: Progress in Brain ResearchH4K3R BCD8421No ratings yet
- Extra Class This Sat: Time: 9am-12pm Venue: CG04 PurposeDocument35 pagesExtra Class This Sat: Time: 9am-12pm Venue: CG04 Purposelengers poworNo ratings yet
- Full Chapter Neuroscience in The 21St Century From Basic To Clinical 2Nd Edition Donald W Pfaff PDFDocument53 pagesFull Chapter Neuroscience in The 21St Century From Basic To Clinical 2Nd Edition Donald W Pfaff PDFjonathan.davis372100% (8)
- BIO 2311 Lab Test 4 Study Guide Fall 2020Document1 pageBIO 2311 Lab Test 4 Study Guide Fall 2020Annabell CheungNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitters and ReceptorsDocument8 pagesNeurotransmitters and ReceptorsmahambaqaiNo ratings yet
- Physiology Brain Bloc 16Document80 pagesPhysiology Brain Bloc 16iqiqiqiqiqNo ratings yet
- Tulip Series English GuideDocument11 pagesTulip Series English GuideUrwah hassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Study GuideDocument4 pagesChapter 7 Study GuidejbradeeNo ratings yet
- 2023 Patanietal NatureReviewsNeurologyDocument15 pages2023 Patanietal NatureReviewsNeurologyFrancineide FreitasNo ratings yet
- Quantum Coherence in Microtubules: A Neural Basis For. Emergent Consciousness?Document28 pagesQuantum Coherence in Microtubules: A Neural Basis For. Emergent Consciousness?anon_496879006No ratings yet
- Ronald John Recio, M.A., Rpsy, Emdrprac. Mbpss Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila Puso MoDocument22 pagesRonald John Recio, M.A., Rpsy, Emdrprac. Mbpss Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila Puso MoChunelle Maria Victoria EspanolNo ratings yet
11.nervous System
11.nervous System
Uploaded by
Leena Hassanin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views14 pagesThe document discusses the structure and function of the human neural system. It describes that the neural system consists of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system. Within the central nervous system, the brain is made up of the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. Neurons are the basic functional units and transmit signals through electrical and chemical synapses. The process of nerve impulse generation, conduction, and transmission between neurons is also explained.
Original Description:
Original Title
11.NERVOUS SYSTEM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the structure and function of the human neural system. It describes that the neural system consists of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system. Within the central nervous system, the brain is made up of the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. Neurons are the basic functional units and transmit signals through electrical and chemical synapses. The process of nerve impulse generation, conduction, and transmission between neurons is also explained.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views14 pages11.nervous System
11.nervous System
Uploaded by
Leena HassaninThe document discusses the structure and function of the human neural system. It describes that the neural system consists of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system. Within the central nervous system, the brain is made up of the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. Neurons are the basic functional units and transmit signals through electrical and chemical synapses. The process of nerve impulse generation, conduction, and transmission between neurons is also explained.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 14
Content Owned by Eduscope International FZ LL, DHCC, Dubai.
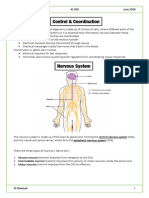
Co-ordination is the process by which 2 or more
organs interact and complement functions of each
other.
Cells of the neural system Neurons.
Human Neural System
Central neural system Peripheral Neural system
Brain Spinal Cord Somatic Autonomic
(CNSskeletal muscles) (CNSsmooth
muscles)
Content Owned by Eduscope International FZ LL, DHCC, Dubai.
A neuron has 3 parts: Cell body, dendrites
and axon.
Cell body has cytoplasm and granules called
Nissl’s granules.
Dendrites are fibres that branch repeatedly
from cell body to tranmit impulses.
Axon is a long fibre which is branched at the
end. It ends in bulb-like structures called
synaptic knobs.
Synaptic knobs have synaptic vesicles which
have chemicals called neurotransmitters.
Content Owned by Eduscope International FZ LL, DHCC, Dubai.
Neurons are of 2 types:
Myelinated: They are covered by Schwann cells
Non-myelinated: They aren’t covered by
Schwann cells.
Nodes of Ranvier: The gaps between the Myelin
sheath.
Content Owned by Eduscope International FZ LL, DHCC, Dubai.
A nerve impulse is a signal sent by the
neurons.
There are 3 things done by a neuron for a
nerve impulse:
Generation
Conduction through same neuron
Transmission to another neuron
Content Owned by Eduscope International FZ LL, DHCC, Dubai.
When neuron is at rest, the membrane of
axon is more permeable to K+ ions and
impermeable to Na+ ions and –vely charged
proteins.
So, inside the axon, there is more K+ and low
Na+
Outside the axon, there is low K+ and high
Na+.
This ionic gradient is maintained by the Na-K
pump. For every 2 K+ ions inside cell, it
pumps 3 Na+ outside cell.
Content Owned by Eduscope International FZ LL, DHCC, Dubai.
Outer surface of axon is +ve and inner
surface is –ve charge.
The electrical potential difference across
resting plasma membrane is called resting
membrane potential.
Content Owned by Eduscope International FZ LL, DHCC, Dubai.
When a signal is sent at a site (A) on the
resting membrane, that site becomes
permeable to Na+.
A lot of Na+ comes inside neuron at that
point.
Polarity is reversed at that point, outer
surface is –ve and inner surface is +ve.
This is called depolarisation.
The potential difference across membrane at
this point is called action potential/nerve
impulse.
Content Owned by Eduscope International FZ LL, DHCC, Dubai.
At the site next to A (B), membrane has +ve
charge outside and –ve charge inside.
Current flows from +ve to –ve.
Current flows inside from A-B.
Current flows outside from B-A to complete
circuit.
Site A returns to being impermeable to Na+
and permeable to K+. This is called
repolarization.
This process continues throughout the
neuron.
Content Owned by Eduscope International FZ LL, DHCC, Dubai.
Nerve impulse is transmitted from one
neuron to another through junctions called
synapses.
A synapse includes membrane of 1st neuron,
membrane of 2nd neuron and a gap in
between.
There are 2 types of synapses:
Electrical synapse
Chemical synapse
Content Owned by Eduscope International FZ LL, DHCC, Dubai.
The 2 neurons are very close to each other.
Electric current can flow easily from one
neuron to another.
Transmission of impulse is just like
conduction of impulse along the axon.
It is fast
It is rare in our system
Content Owned by Eduscope International FZ LL, DHCC, Dubai.
2 neurons are separated by a space called
synaptic cleft.
Chemicals called neurotransmitters are there in
the synaptic vesicles of neurons.
When the impulse reaches the end of 1st axon,
the synaptic vesicles in the synaptic knobs start
moving towards the membrane and fuse with it.
It will release neurotransmitters into synaptic
cleft.
The neurotransmitters will bind to receptors on
the membrane of 2nd neuron and transfer
impulse to it.
Content Owned by Eduscope International FZ LL, DHCC, Dubai.
Brain is covered by cranial meninges.
Brain has 3 parts:
Forebrain:
Cerebrum: Largest part of brain. (Grey matter)
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Midbrain:
Hindbrain:
Pons (respiratory
centre)
Cerebellum
Medulla
Content Owned by Eduscope International FZ LL, DHCC, Dubai.
Involuntary response is produced without
thinking, produced by CNS
Reflex arc: Pathway for the signal to travel
Content Owned by Eduscope International FZ LL, DHCC, Dubai.
You might also like
- Ebook Principles of Neural Science Sixth Edition Eric R Kandel Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesEbook Principles of Neural Science Sixth Edition Eric R Kandel Online PDF All Chapterkendall.fox383100% (8)
- Essentials of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing 7th Edition Townsend Test BankDocument15 pagesEssentials of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing 7th Edition Townsend Test Bankkimberlymorriscntsoqmyjw100% (6)
- June 17 26 s001 PDFDocument9 pagesJune 17 26 s001 PDFBetul RojeabNo ratings yet
- Biology - Brain (Neural Communication)Document6 pagesBiology - Brain (Neural Communication)Teacă Mădălina ElenaNo ratings yet
- Marcus Jacobson (Auth.) - Foundations of Neuroscience (1993)Document394 pagesMarcus Jacobson (Auth.) - Foundations of Neuroscience (1993)patata100% (1)
- Full Sentence OutlineDocument7 pagesFull Sentence Outlineapi-384035981No ratings yet
- CH 4 - CoordinationDocument23 pagesCH 4 - CoordinationnawarakanNo ratings yet
- 10 Neural Control N Coordination-Notes Blog (Full Permission)Document5 pages10 Neural Control N Coordination-Notes Blog (Full Permission)fariha khanNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument86 pagesGen BioPaul MagbagoNo ratings yet
- Intro Animal Physiology Ch-2.1Document97 pagesIntro Animal Physiology Ch-2.1Jojo MendozaNo ratings yet
- Neural Control and Coordination - Shobhit NirwanDocument13 pagesNeural Control and Coordination - Shobhit Nirwanmfx79qh7wbNo ratings yet
- Neural Control and Coordination - Shobhit NirwanDocument14 pagesNeural Control and Coordination - Shobhit NirwanSWASTIKA MALONo ratings yet
- Nureal Control and CoordinationDocument16 pagesNureal Control and CoordinationthushyanthNo ratings yet
- NeurophysiologyDocument31 pagesNeurophysiologyChezkah Nicole MirandaNo ratings yet
- Histology 9Document8 pagesHistology 9amirhsheikhiNo ratings yet
- Neural Control and CoordinationDocument8 pagesNeural Control and CoordinationAman Singh RaoNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From SUPERCOPDocument6 pagesMaterial Downloaded From SUPERCOPfast-track for n2021No ratings yet
- TR Cyvp 93 I 1 R1 H 034 Rat 0Document5 pagesTR Cyvp 93 I 1 R1 H 034 Rat 0aadeshthite476No ratings yet
- PHC 513 Flipped Class QuestionDocument17 pagesPHC 513 Flipped Class QuestionALISYA SOPHIA MOHAMMAD ABU SHAHID CHRISNo ratings yet
- Points To Remember: Neural Control and CoordinationDocument107 pagesPoints To Remember: Neural Control and CoordinationRagheNo ratings yet
- Biology F4 Review Summary NoteDocument117 pagesBiology F4 Review Summary NoteSocdal AbdiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The NerveDocument18 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The NervejudssalangsangNo ratings yet
- Bio Chap 21 NotesDocument9 pagesBio Chap 21 NotesYogesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Nervous System LectureDocument234 pagesNervous System Lecturealyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Notes - Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesNotes - Nervous Systemdarkadain100% (1)
- Le Neuron Structure: Reflexes: Sensory Nuerons: Trasmit Info From Sensors That DetectDocument5 pagesLe Neuron Structure: Reflexes: Sensory Nuerons: Trasmit Info From Sensors That DetectYiboNo ratings yet
- LIFS1902 Nervous System Revision NotesDocument6 pagesLIFS1902 Nervous System Revision NotesmystudylifechloeNo ratings yet
- 10 Neuro PDFDocument16 pages10 Neuro PDFKamoKamoNo ratings yet
- Neural Control N Coordination-NotesDocument5 pagesNeural Control N Coordination-Notessudeep27krNo ratings yet
- Neural Contraol & Coordinaton - SNDocument7 pagesNeural Contraol & Coordinaton - SNPushpa DhruvNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Points To RememberDocument6 pagesChapter 22 Points To RememberSaksham YadavNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 21 Neural Control and Coordination NotesDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 21 Neural Control and Coordination NotesShivalgiri Goswami0% (1)
- Structure of The Nervous System: Lesson 1Document41 pagesStructure of The Nervous System: Lesson 1Samuel ThangarajanNo ratings yet
- CAPE Nervous Coordination NotesDocument24 pagesCAPE Nervous Coordination NotesSharina GeraldNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue-06.11-2wlDocument57 pagesNervous Tissue-06.11-2wlapi-19641337No ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch21 Neural Control and Coordination PDFDocument3 pages11 Biology Notes ch21 Neural Control and Coordination PDFRamachandranPerumal100% (1)
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Document11 pagesStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Ayush KumarNo ratings yet
- Neural CoordinationDocument7 pagesNeural CoordinationTushar SinghNo ratings yet
- Neurons NervousDocument10 pagesNeurons NervousAldi RegarNo ratings yet
- Psy121 - Psychobiological Determinants of BehaviourDocument42 pagesPsy121 - Psychobiological Determinants of BehaviourLarry UdehNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 9 NERVOUS CONTROL My Notes 1Document11 pagesTOPIC 9 NERVOUS CONTROL My Notes 1shealtielchigariso06No ratings yet
- Unit 8 Learning Guide Name: Brandon Au-Young: InstructionsDocument25 pagesUnit 8 Learning Guide Name: Brandon Au-Young: InstructionsBrandonNo ratings yet
- Ch08 Nervous SystemDocument62 pagesCh08 Nervous SystemDanna Loize Noble LazaroNo ratings yet
- Nerve and Its Function PDFDocument26 pagesNerve and Its Function PDFJose albert MauanayNo ratings yet
- Structure of The NeuronDocument7 pagesStructure of The NeuronSmitaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesNervous SystemYUAN FRANCIS SINGCULANNo ratings yet
- A12. Nervous SystemDocument184 pagesA12. Nervous SystemAbdurahman TainyNo ratings yet
- BN Week1 Neurons 08-22-19Document59 pagesBN Week1 Neurons 08-22-19marissaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System & Nerve ImpulsesDocument21 pagesThe Nervous System & Nerve ImpulsesPrabhathNo ratings yet
- Neural Control and CoordinationDocument6 pagesNeural Control and CoordinationRonaldNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System & Nerve ImpulsesDocument22 pagesThe Nervous System & Nerve Impulsestas xoNo ratings yet
- Neurons and Neuroglia - PPTX 2nd LecDocument23 pagesNeurons and Neuroglia - PPTX 2nd Leczaraali2405No ratings yet
- Biology 30 Student Notes Nervous ReproductionDocument53 pagesBiology 30 Student Notes Nervous ReproductionDennis Limosnero MayorNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Grade 10 - Science HANDOUT No.2 On Neurons, Reflex, Reflex Arc & Brain General Information About The Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesSecond Quarter Grade 10 - Science HANDOUT No.2 On Neurons, Reflex, Reflex Arc & Brain General Information About The Nervous SystemMartin ReaporNo ratings yet
- Physiology Handouts (Topic 16-26)Document35 pagesPhysiology Handouts (Topic 16-26)bc200411046No ratings yet
- Physio CH-2Document24 pagesPhysio CH-2aliraza67570No ratings yet
- NeurophysicsDocument8 pagesNeurophysicsMakavana SahilNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Mitochondria "Organelles"Document6 pagesCell Membrane Mitochondria "Organelles"Ashraf MobyNo ratings yet
- 1 Hist Sept 13 ReadingNerve - Tissue2020Document26 pages1 Hist Sept 13 ReadingNerve - Tissue2020n-gorNo ratings yet
- Biology and Psychology 15065G PP 3Document59 pagesBiology and Psychology 15065G PP 3SalahideenNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Structure and Functions of The CellsDocument12 pagesUnit 2 - Structure and Functions of The CellssindhusivasailamNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solution of Neural Coordination and Control Class 11Document17 pagesNcert Solution of Neural Coordination and Control Class 11Ayush DuttaNo ratings yet
- Biology 3201: Unit 1 - Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Section 1 - Nervous System "The Neuron"Document22 pagesBiology 3201: Unit 1 - Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Section 1 - Nervous System "The Neuron"Harshil PatelNo ratings yet
- Somatosensory Teachers Manual: for Somatosensory Science FactsFrom EverandSomatosensory Teachers Manual: for Somatosensory Science FactsNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Ebersole and Hess Gerontological Nursing and Healthy Aging 2nd Canadian Edition by TouhyDocument7 pagesTest Bank For Ebersole and Hess Gerontological Nursing and Healthy Aging 2nd Canadian Edition by Touhyjohnflorescdjrfwqxzs100% (32)
- Reflex Arc LabDocument2 pagesReflex Arc Labapi-377433445No ratings yet
- Psychology An Exploration Canadian 1st Edition Ciccarelli Solutions ManualDocument21 pagesPsychology An Exploration Canadian 1st Edition Ciccarelli Solutions Manualdictumhuronianhsor100% (33)
- 6 - 5 - Nerves 2023Document45 pages6 - 5 - Nerves 2023Eudmarly GEDEONNo ratings yet
- (English) The Nervous System, Part 3 - Synapses! - Crash Course A&P #10 (DownSub - Com)Document8 pages(English) The Nervous System, Part 3 - Synapses! - Crash Course A&P #10 (DownSub - Com)bank townNo ratings yet
- Smola PDFDocument271 pagesSmola PDFsri1991nivasNo ratings yet
- Santiago Ramón y Cajal en La NeuroscienciaDocument11 pagesSantiago Ramón y Cajal en La NeuroscienciaAmy Medina VelazquezNo ratings yet
- Neural Control and Co OrdinationDocument16 pagesNeural Control and Co OrdinationDARSHAN KUMAR TNo ratings yet
- Wk2 Paper InfoDocument5 pagesWk2 Paper InfokellyNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience Science of TheDocument60 pagesNeuroscience Science of TheALA Meditation - Relaxing MusicNo ratings yet
- Thanksgiving Day SermonDocument13 pagesThanksgiving Day Sermoncarolyn6302No ratings yet
- Lifespan Development Canadian 5th Edition Boyd Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesLifespan Development Canadian 5th Edition Boyd Solutions Manual 1justinfleminggfcqziaonr100% (33)
- Dopamine Receptor Subtypes, Physiology and Pharmacology - New Ligands and Concepts in SchizophreniaDocument17 pagesDopamine Receptor Subtypes, Physiology and Pharmacology - New Ligands and Concepts in SchizophreniaolivukovicNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan IN Grade 10 Science Nerve Cell: Mariano Ponce National High SchoolDocument11 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan IN Grade 10 Science Nerve Cell: Mariano Ponce National High SchoolAdrian DionisioNo ratings yet
- Essence of Memory: Progress in Brain ResearchDocument430 pagesEssence of Memory: Progress in Brain ResearchH4K3R BCD8421No ratings yet
- Extra Class This Sat: Time: 9am-12pm Venue: CG04 PurposeDocument35 pagesExtra Class This Sat: Time: 9am-12pm Venue: CG04 Purposelengers poworNo ratings yet
- Full Chapter Neuroscience in The 21St Century From Basic To Clinical 2Nd Edition Donald W Pfaff PDFDocument53 pagesFull Chapter Neuroscience in The 21St Century From Basic To Clinical 2Nd Edition Donald W Pfaff PDFjonathan.davis372100% (8)
- BIO 2311 Lab Test 4 Study Guide Fall 2020Document1 pageBIO 2311 Lab Test 4 Study Guide Fall 2020Annabell CheungNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitters and ReceptorsDocument8 pagesNeurotransmitters and ReceptorsmahambaqaiNo ratings yet
- Physiology Brain Bloc 16Document80 pagesPhysiology Brain Bloc 16iqiqiqiqiqNo ratings yet
- Tulip Series English GuideDocument11 pagesTulip Series English GuideUrwah hassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Study GuideDocument4 pagesChapter 7 Study GuidejbradeeNo ratings yet
- 2023 Patanietal NatureReviewsNeurologyDocument15 pages2023 Patanietal NatureReviewsNeurologyFrancineide FreitasNo ratings yet
- Quantum Coherence in Microtubules: A Neural Basis For. Emergent Consciousness?Document28 pagesQuantum Coherence in Microtubules: A Neural Basis For. Emergent Consciousness?anon_496879006No ratings yet
- Ronald John Recio, M.A., Rpsy, Emdrprac. Mbpss Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila Puso MoDocument22 pagesRonald John Recio, M.A., Rpsy, Emdrprac. Mbpss Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila Puso MoChunelle Maria Victoria EspanolNo ratings yet